Africa’s Slide Toward Disaster August 2, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Dictatorship, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights Watch on Human Rights Violations Against Oromo People by TPLF Ethiopia, Tyranny, UK Aid Should Respect Rights, US-Africa Summit, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny
add a comment
Africa’s Slide Toward Disaster
By HELEN EPSTEIN, The New York Times, Opinion page, AUG. 1, 2014
A specter is haunting Africa — the specter of impunity. Many countries the United States considers allies are in the grip of corrupt, repressive tyrants; others are mired in endless conflict. As Washington prepares to host the first-ever U.S.-Africa Leaders Summit next week, American policy makers must acknowledge their contributions to this dismal situation. By lavishing billions of dollars in military and development aid on African states while failing to promote justice, democracy and the rule of law, American policies have fostered a culture of abuse and rebellion. This must change before the continent is so steeped in blood that there’s no way back.
The summit seeks to highlight Africa’s development successes and promote trade and investment on a continent rich in oil and natural resources. Justice and the rule of law aren’t on the agenda. But they should be, unless American C.E.O.s want to see their investments evaporate.
Read interesting comments @ http://ayyaantuu.com/africa/africas-slide-toward-disaster/#respond
Ethiopia: UK Aid Should Respect Rights July 14, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in African Poor, Aid to Africa, Amane Badhaso, Dictatorship, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights Watch on Human Rights Violations Against Oromo People by TPLF Ethiopia, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Ogaden, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, UK Aid Should Respect Rights.Tags: African Studies, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, UK Aid Should Respect Rights
add a comment
A UK High Court ruling allowing judicial review of the UK aid agency’s compliance with its own human rights policies in Ethiopia is an important step toward greater accountability in development assistance.
Ethiopia: UK Aid Should Respect Rights
By Human Rights Watch, 14th July 2014
(London) – A UK High Court ruling allowing judicial review of the UK aid agency’s compliance with its own human rights policies in Ethiopia is an important step toward greater accountability in development assistance.
In its decision of July 14, 2014, the High Court ruled that allegations that the UK Department for International Development (DFID) did not adequately assess evidence of human rights violations in Ethiopia deserve a full judicial review.
“The UK high court ruling is just a first step, but it should be a wake-up call for the government and other donors that they need rigorous monitoring to make sure their development programs are upholding their commitments to human rights,” said Leslie Lefkow, deputy Africa director. “UK development aid to Ethiopia can help reduce poverty, but serious rights abuses should never be ignored.”
The case involves Mr. O (not his real name), a farmer from Gambella in western Ethiopia, who alleges that DFID violated its own human rights policy by failing to properly investigate and respond to human rights violations linked to an Ethiopian government resettlement program known as “villagization.” Mr. O is now a refugee in a neighboring country.
Human Rights Watch has documented serious human rights violations in connection with the first year of the villagization program in Gambella in 2011 and in other regions of Ethiopia in recent years.
A January 2012 Human Rights Watch report based on more than 100 interviews with Gambella residents, including site visits to 16 villages, concluded that villagization had been marked by forced displacement, arbitrary detentions, mistreatment, and inadequate consultation, and that villagers had not been compensated for their losses in the relocation process.
People resettled in new villages often found the land infertile and frequently had to clear the land and build their own huts under military supervision. Services they had been promised, such as schools, clinics, and water pumps, were not in place when they arrived. In many cases villagers had to abandon their crops, and pledges of food aid in the new villages never materialized.
The UK, along with the World Bank and other donors, fund a nationwide development program in Ethiopia called the Promotion of Basic Services program (PBS). The program started after the UK and other donors cut direct budget support to Ethiopia after the country’s controversial 2005 elections.
The PBS program is intended to improve access to education, health care, and other services by providing block grants to regional governments. Donors do not directly fund the villagization program, but through PBS, donors pay a portion of the salaries of government officials who are carrying out the villagization policy.
The UK development agency’s monitoring systems and its response to these serious allegations of abuse have been inadequate and complacent, Human Rights Watch said. While the agency and other donors to the Promotion of Basic Services program have visited Gambella and conducted assessments, villagers told Human Rights Watch that government officials sometimes visited communities in Gambella in advance of donor visits to warn them not to voice complaints over villagization, or threatened them after the visits. The result has been that local people were reluctant to speak out for fear of reprisals.
The UK development agency has apparently made little or no effort to interview villagers from Gambella who have fled the abuses and are now refugees in neighboring countries, where they can speak about their experiences in a more secure environment. The Ethiopian government’s increasing repression of independent media and human rights reporting, and denials of any serious human rights violations, have had a profoundly chilling effect on freedom of speech among rural villagers.
“The UK is providing more than £300 million a year in aid to Ethiopia while the country’s human rights record is steadily deteriorating,” Lefkow said. “If DFID is serious about supporting rights-respecting development, it needs to overhaul its monitoring processes and use its influence and the UK’s to press for an end to serious rights abuses in the villagization program – and elsewhere.” Read @http://www.hrw.org/news/2014/07/14/ethiopia-uk-aid-should-respect-rights
Ethiopia & poverty: Ethiopia Ranks the second poorest country in the world and Africa, Oxford University study reveals June 24, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Free development vs authoritarian model, Gambella, No to land grabs in Oromia, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Poverty, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The extents and dimensions of poverty in Ethiopia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


Ethiopia & the extents of its poverty
(OPHI) –The Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), published by Oxford University reveals that Ethiopia ranks the second poorest country in the world and Africa, just ahead of Niger. The study is based on analysis of acute poverty in 108 developing countries around the world. Despite making progress at reducing the percentage of destitute people, Ethiopia is still home to more than 76 million poor people (out of total population of 87 million). 87.3% of Ethiopians are classified as MPI poor, while 58.1% are considered destitute. Oxford University says poverty is not just about a lack of money. It’s also about not having enough food, education, healthcare and shelter, and some poor are much worse off than others.
A person is identified as multidimensionally poor (or ‘MPI poor’) if they are deprived in at least one third of the weighted MPI indicators. The destitute are deprived in at least one-third of the same weighted indicators, The Global MPI uses 10 indicators to measure poverty in three dimensions: education, health and living standards. 
In rural Ethiopia 96.3% are poor while in the urban area the percentage of poverty is 46.4%.
The 10 Poorest Countries in the World:
1. Niger
2. Ethiopia
3. Mali
4. Burkina Faso
5. Burundi
6. Somalia
7. Central African Republic
8. Liberia
9. Guinea
10. Sierra Leone
According to Dr. Sabina Alkire — director of the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative, the U.N. Millennium Development Goals – which set targets regarding poverty, hunger, malnutrition, health and other issues – expire at the end of next year. Thus, MPI could help in the creation of a replacement for the MDGs that gives a complete picture of poverty. “We need a replacement that keeps our eyes really focused on human poverty and the pain and suffering that it entails, but also brings in the environment. And our suggestion is really simple. That along side the $1.25 a day measure – or some extreme income poverty measure – that we bring into view these people who are multidimensionally poor. And that we can do so with a measure of destitution and a measure of multidimensional poverty and maybe even a measure of vulnerability that would be more appropriate for middle and high income countries.”

OPHI Country Briefing 2014: Ethiopia
http://www.dataforall.org/dashboard/ophi/index.php/
http://www.dataforall.org/dashboard/ophi/index.php/mpi/country_briefings
see Alkire, Conconi and Seth (2014), available at: http://www.ophi.org.uk/multidimensional-poverty-index/.
Ethiopia:
MPI Value 0.564
Percentage of Population:
MPI Poor 87.3%
MPI Poor and Destitute 58.1%
$1.25/day Poor 30.65%
Human Development Index (HDI) 0.396
Inequality (Gini Index) 0.336
Income level Low income
Gross National Income (GNI) per capita 380
Survey: DHS Year: 2011A person is identified as multidimensionally poor (or ‘MPI poor’) if they are deprived in at least one third of the weighted indicators shown above; in other words, the cutoff for poverty (k) is 33.33%.
The proportion of the population that is multidimensionally poor is the incidence of poverty, or headcount ratio (H). The average proportion of indicators in which poor people are deprived is described as the intensity of their poverty (A). The MPI is calculated by multiplying the incidence of poverty by the average intensity of poverty across the poor (MPI = H x A); as a result, it reflects both the share of people in poverty and the degree to which they are deprived.
64.6%
Percentage of Poor People (H)(k = 33.3%)
Average Intensity Across the Poor (A)
58.1%
Inequality Among the MPI PoorVulnerable toPoverty(k = 20%-33.3%)
In SeverePoverty(k = 50%)See more @ Oxford and Human Development Initiative (2014). “Ethiopia Country Briefing”, Multidimensional Poverty Index Data Bank. OPHI, University of Oxford. Available at /.
http://www.ophi.org.uk/multidimensional-poverty-index/mpi-country-briefings
More reference to famine in Ethiopia:
In the last two or three decades, there has been a revolution in thinking about the
explanations of famines. The entitlement’s approach by Amartya Sen brought the issue
of food accessibility to the forefront of the academic debate on famine. Sen noted that,
often enough, there is enough food available in the country during famines but all
people do not have the means to access it. More specifically, famines are explained by
entitlement failures, which in turn can be understood in terms of endowments,
production possibilities, and exchange conditions among others (Sen, 1981).
Ethiopia is a good case in point where, for instance, food was moving out of Wollo
when the people in the region were affected by the 1972-3 famine (Sen, 1981), and even
today some regions in Ethiopia produce surplus, while people in other regions face
famine threats. There are of course infrastructural problems in the country to link the
surplus producing regions to the food-deficit ones. However, the question goes beyond
this simplistic level, as some people simply do not have enough entitlements to have a
share of the food available in the country, a situation which can be described as a case
of direct entitlement failures (Tully 2003: 60)7. Or else, peasants do not find the right
price for their surplus, as in the 2002 Bumper Harvest which ended up in an 80 per cent
price drop, which illustrated a failure in peasants’ exchange entitlements. Alternatively,
the most irrigated land of the country in the Awash River basin, for instance, is used
primarily for cash crop production to be exported to the western world (even when there
is drought) leading the vulnerability of various pastoralist groups to turn into famine or
underpinned by what is known as a crisis in endowments and production possibilities.
In short, while drought and population pressure can partly explain famine threats in
Ethiopia, the entitlements approach provides an explanation from an important but less
visible angle. By shifting the attention from absence of food to lack of financial access
to food, the approach points in the direction of policy failures. That only some classes in
society are affected by famine clearly indicates that policy failures are central to the
understanding of famine. http://portal.svt.ntnu.no/sites/ices16/Proceedings/Volume%203/Alexander%20Attilio%20Vadala%20-%20Understanding%20Famine%20in%20Ethiopia.pdf
How not to make a master plan June 24, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Amane Badhaso, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Dictatorship, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinne is Oromia's land, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Finfinnee n Kan Oromoo ti, Free development vs authoritarian model, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, Human Rights, Human Rights Watch on Human Rights Violations Against Oromo People by TPLF Ethiopia, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Jen & Josh (Ijoollee Amboo), Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Language and Development, Nimoona Xilahuun Imaanaa, Nimoonaa Tilahun, No to land grabs in Oromia, No to the Addis Ababa Master Plan, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Ogaden, OMN, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia wide Oromo Universtiy students Protested Addis Ababa Expansion Master Plan, Oromians Protests, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo and the call for justice and freedom, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Protests, Oromo Protests in Ambo, Oromo students movement, Oromo students protests, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromo University students and their national demands, Poverty, Say no to the expansions of Addis Ababa, Sidama, State of Oromia, Stop evicting Oromo people from Cities, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The extents and dimensions of poverty in Ethiopia, The Mass Massacre & Imprisonment of ORA Orphans, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: African Studies, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Tyranny, World Bank
add a comment
‘The master plan is the master killer.’- #OromoProtests
HOW NOT TO MAKE A MASTER PLAN
What went wrong, where and when?
The grand plan that was warmly welcomed by ONRS senior officials failed to attract the same reception from the lower and mid-level political leadership of the Special Zone as well as local governments within the zone. Most of them were skeptical and some viewed it as an effort to annex the Special Zone of Oromia into Addis Abeba. There were few incidents where Oromia regional state officials refused to cooperate with the Project Office in making information necessary for the planning process easily accessible.
The Project Office, too, has done little to establish trust among the Special Zone and ONRS mid and lower level officials. Trust between the two had reached rock-bottom when the Project Office developed what it said was a spatial plan without involving mayors of the municipalities as well as other officials in the metropolitan area and relevant regional and Special Zone officials. In June 2013 the Project Office unveiled a readymade draft metropolitan plan in Adama town, 100km east of Addis Abeba and the capital of the ONRS, that determined, among others, the locations of waste treatment, landfill sites, industrial zones, and transportation corridors. Once again the draft metropolitan plan was welcomed by the top Oromia regional state leadership; but it left the rank and file officials disgruntled. Most of them considered it (perhaps rightly) as a violation of their autonomy. However, since the top leadership has given the grand plan its blessings the Project Office went ahead with it. Things went vividly out of control during a meeting between officials of the Oromia regional state and the Addis Abeba city administration representatives held in Adama town on March 26 and April 12-13.The questions raised in these meetings revealed that the Project Office has failed to build trust on the motive of the Master Plan let alone actively involve the ONRS officials in the planning process.
How not to make a Master Plan
What happened with the preparation of this master plan was an approach that gave strategic planning and political inclusiveness a zero chance. Five fundamental problems highlight the plan.
First, this master planning approach viewed planning as a mere technocratic process and the planner as the chief architect of the spatial area that comes up with a readymade blueprint that everyone is expected to accept.
Strategic spatial planning is as much of a political process as it is professional; it requires the active involvement of political leadership, major urban or regional actors-including the private sector, community organizations and civil society groups. In addition, the planner’s role should mainly be as a facilitator and a negotiator among the diverse actors who have conflicting (and competing) interests.
There was groundbreaking effort to shift urban planning culture to a more strategic and inclusive approach in the 2002-12 City Development Plan of Addis Abeba. In the two year planning process, for example, over 150 workshops and consultative meetings with a wide range of stakeholders, including a city exhibition and public forum, were organized. That is something the current master plan project lacked; it has organized not more than nine consultative workshops.
A grand plan such as this need to be owned as much by politicians and their constituency as by professional urban planners. The only way to do this is if the authorities and the public were involved actively in the planning process. Nevertheless, the Project Office single-handedly decided where to locate the waste treatment, the land fill site or the industrial zone with no formal consent from the respective local government officials who are supposedly the elected representatives of the constituencies in the areas affected by the plan. It was a planning process that gave way to the infamous planning syndrome known as Not in My Backyard (NIMBY). When a planner decides to put a waste treatment in one district, the least s/he needs to do is negotiate with the respective district authorities on how to mitigate the negative externalities. With the new master plan, nothing of this happened, compromising the constitutionally guaranteed autonomy of the Oromia regional state and the Special Zone to make decisions that affect their constituency.
Second, it failed to secure the legitimacy for joint planning. The reason for the suspicion by many low and middle level officials of the ONRS is twofold. The first one is metropolitan planning in Ethiopia is unheard of and Addis Abeba’s administrative boundary has been expanding for the last century, in which the latest one has more than doubled its jurisdiction in 1994. It is, therefore, totally understandable if ONRS officials and concerned citizens fear the encroachment of the Special Zone by the capital city. The second reason is the project office kept most of the process secrete.
Third, amalgamation of municipalities into one gargantuan metropolitan government has lost credence since the late 1980s and new forms of metropolitan cooperation are promoted in lieu of annexation. However, the project office failed in clarifying its intention and mobilizing support from the Oromia region officials and other stakeholders due to its closed door planning process.
Fourth, and the major limitation of the process is the composition of the planning office. As it was mentioned above the project office was initially commissioned by AACA to prepare a city development plan for Addis Abeba. The same planning team was tasked to develop a metropolitan plan with the exception of the recruitment of a handful of former Oromia Urban Planning Institute staff. Less than 10 planners from close to 80 technical staff of the project office cannot ensure Oromia’s interest, the largest and most populous region of the country, in the metropolitan plan. The majorities of the planning team members are born in Addis Abeba or have lived in the city for long or were former staff members of the Addis Abeba city administration, which makes them perfect candidates for sentimental compromise against the interests of the Oromia region.
And finally, the top leadership of ONRS welcomed the draft metropolitan plan regardless of opposition from their subordinates as well as the wider public. The stubbornness of the ruling party, which is seen in other policy arena, was also visible in this planning process. The government, rather than accommodating the reservation of various individuals and groups on the plan or on its motive, chose to label those who complained against the plan as working for the so-called obscure “anti-peace agents”. This was the major reason that led to the widespread protest in many Universities and several towns in Oromia, which claimed the lives of eleven people by the account of the government (other sources put the death as high as 49) and resulted in countless property damages. (Please see A new master plan:Complicated-turned-deadly).
he way out
Many people may believe it may be already too late. But there are things one can do to reverse courses. The first step is to establish a taskforce, which comprises ONRS officials, Special Zone officials, Mayors of the eight municipalities of the Special zone together with the Regional Urban Planning Institute planners or commissioned consultants, to review the draft metropolitan and suggest recommendations that ensure Oromia’s interest. This taskforce in turn needs to consult with the civil society, the private sector, opposition party members, residents of the Special zone, University students and other concerned bodies in its reviewing process. The second and perhaps the most important one, is clarifying the provisions of Art. 49(5) of the country’s constitution by a federal proclamation before signing the metropolitan plan into a law; the metropolitan plan need to be used as an instrument to materialize the constitutional provision of the country. Third, and most sensitive, should be bringing before justice those who ordered the killings of the students who were protesting against the plan as well as those who executed the orders.
#OromoProtests in Perspective, By Ayantu Tibeso* June 8, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Amane Badhaso, Ambo, Colonizing Structure, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Finfinnee n Kan Oromoo ti, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromian Voices, Oromians Protests, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo and the call for justice and freedom, Oromo Diaspora, Oromo Nation, Oromo Protests, Oromo Protests in Ambo, Oromo students movement, Oromo students protests, Say no to the expansions of Addis Ababa, State of Oromia, Stop evicting Oromo people from Cities, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Media and #OromoProtests, Oromo, Oromo people
add a comment
The brutal crackdown on the Oromo people is not new. The Ethiopian state itself has been predicated upon the expropriation of Oromo lands and held together through violent assimilationist policies, the destruction of the identity of conquered and resistant people, and economic and political exploitation of groups who are not represented in government. With each changing regime state power has been retained in the hands of minority rulers and the Oromos, who are the largest group living on the richest land, have remained the main targets of Ethiopian state repression, terrorism and discrimination. Over the last two decades alone multiple human rights organizations have released reports documenting the extent of extrajudicial killings, mass imprisonment, and torture on a massive scale, mutilations and disappearances. For instance, as of May 2012, the Oromia Support Group reported 4,407 extra-judicial killings and 992 disappearances of civilians perceived to support the political and even social groups opposing the current regime. Most of these have been Oromo people.
The crisis in Ethiopia is a major international story of mass protest, wholesale dispossession of millions of peasants, and state-sponsored violence. Yet it has gone almost completely ignored in the international media.
There are a number of reasons the story hasn’t grabbed attention around the world—the situation’s complexity, the tight control of information by Ethiopian authorities, and western journalists’ unfamiliarity with Ethiopia’s tense ethnic politics, to name just a few. But the bigger issue has to do with Western media bias.
As long as this bias remains salient, the deaths of hundreds, possibly thousands, will continue to go unreported and unrecognized, and the cause for which so many have sacrificed will remain hidden. -Ayantu Tibeso
Since April 25th, thousands of high school and university students across Ethiopia’s largest region, Oromia, have turned out in peaceful protest against a government land grab that stands to displace millions of indigenous peoples from their ancestral

Image via Twin Cities Daily Planet
lands. Even though the country’s constitution theoretically allows for peaceful demonstrations, the student protesters, along with local populations in many cities and towns, have faced a ruthless crackdown from Ethiopian Special Forces, known as the Agazi Commandos. These forces have used excessive violence by indiscriminately shooting into crowds in an attempt to quash the protests. Children as young as eleven years old have been killed, according to statement issued by Amnesty International on May 13, and reports of fatal injuries, torture, imprisonment, disappearances and killings have been coming out of Ethiopia since then.
The Ethiopian government has evicted millions of indigenous peoples from their homelands at gunpoint under the pretext of “development” since it took power. In and around the capital of the country, Addis Ababa, over 200,000 of these residents have been removed from their lands without proper compensation since 2005. The newly-announced Integrated Development Master Plan for Addis Ababa (known simply as the “Master Plan”) seeks to legalize past land grab activities and to consolidate larger areas of territory displacing native peoples from their land. The Master Plan will expand the territory of Addis Ababa city administration to about 25 times its current size and is expected to forcefully remove another four to five million Oromo peasants from their lands within the coming years.
The current Ethiopian government came to power in 1991. It is a government dominated mainly by elites from a single ethnic group, the Tigray, which constitute approximately six percent of the peoples within Ethiopian boundaries. The Oromo, who are targeted by this Master Plan, make up between 40-50 percent of the population. The Ethiopian Agazi special Commando force is almost entirely Tigrayan. The government relies on this ethnic army to stamp out the Oromo protests.
The current crisis cannot be understood apart from the ethnic dynamics at play in the policy of the Master Plan and in its response. In the Ethiopian political, social and economic system, ethnicity and language are the two most important factors which influence policy preferences and choices of different sectors or communities in Ethiopia. It is also along these two dimensions that the Ethiopian state has been structured since the current regime came to power. In recognition of these factors, a formal system of Ethnic Federalism has been instituted and written into law as the centerpiece of the Constitution of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Oromia, where most Oromos reside, is legally recognized as one of the nine members of the Ethiopian Federation.
In practice, however, all the key government positions and institutions are controlled by elites—directly and indirectly—that come from the Tigrayan ethnic group. Key positions in security sectors, including the military, are exclusively under the control of Tigrayan rulers. It is this group of elites that have aggressively pursued policies that have drawn on the military might to remove Oromo peasants involuntarily from their homeland over the last decade or more. The new Master Plan for Addis Ababa should be seen in this context, as the protestors well understand. The Master Plan is one more chapter in implementing a disastrous policy that has already displaced thousands of the native peasants, and now officially aims to displace millions more. This is the policy against which Oromo students have gone out to protest. In keeping with their former legacy of sheer brutality, the Tigrayan ethnic armed force, the Agazi, responded to peaceful gatherings with a rain of bullets.
The brutal crackdown on the Oromo people is not new. The Ethiopian state itself has been predicated upon the expropriation of Oromo lands and held together through violent assimilationist policies, the destruction of the identity of conquered and resistant people, and economic and political exploitation of groups who are not represented in government. With each changing regime state power has been retained in the hands of minority rulers and the Oromos, who are the largest group living on the richest land, have remained the main targets of Ethiopian state repression, terrorism and discrimination. Over the last two decades alone multiple human rights organizations have released reports documenting the extent of extrajudicial killings, mass imprisonment, and torture on a massive scale, mutilations and disappearances. For instance, as of May 2012, the Oromia Support Group reported 4,407 extra-judicial killings and 992 disappearances of civilians perceived to support the political and even social groups opposing the current regime. Most of these have been Oromo people.
It is within this context that the current violent response to Oromo protests should be understood and appreciated. Like it has always been, kidnappings and/or extrajudicial killings, arbitrary arrests and disappearances continue in different parts of Oromia Regional State. Those being imprisoned face an imminent danger of death, torture or disappearance. Yet despite the fact that the situation is quickly deteriorating, it is going largely unreported in the international media. The Ethiopian government is notorious for keeping very tight control over all local and international media in the country. Information is not easily attainable. Independent journalism and human rights monitoring are securitized and criminalized. Major restrictions remain on exchange of information, as the government is known to block almost all websites it regards as forums capable of providing information about the atrocities committed by its security agents. These include all independent websites that are situated both in and outside of Ethiopian territories. Given these circumstances, it has not been possible to determine the exact number of victims of the recent retaliation against Oromo protesters. But thanks to social media and mobile technology, a view of the scale of the crisis is emerging.
Some human rights organizations have managed to get limited information and offer an insight regarding what is taking place as the protests continue. For instance, according to the above-mentioned statement released by Amnesty International, hundreds of those arrested during the protests have been held at different detention centers, including at unauthorized places such as police and military training camps. Detention in these places is almost always arbitrary, with prisoners spending months and years without being formally charged or taken to a courtroom. As the Amnesty International report notes, “military camps in Oromia have regularly been used to detain thousands of actual or perceived government opponents.” These detainees are not allowed access to lawyers or relatives, usually throughout the duration of their detention. In many instances, relatives do not know where their loved ones have been taken upon arrest. Human rights organizations, including Amnesty International have received reports of torture on a massive scale at these unofficial holding places.
In addition to Amnesty International, other human rights organizations have also released statements of concern that recent detainees face imminent risk of torture and abuse, if not death. Human Rights Watch reported that security forces beat and shot at peaceful Oromo protesters in many towns in Oromia Regional State, among others, Ambo, Nekemte, Gimbi and Jimma. The Human Rights League of Horn of Africa has also issued a report citing torture and disappearances in places where student protesters are being held in Naqamte, East Wollega zone. In one instance alone, fifty detainees were taken away by security forces in Naqamte. Their whereabouts remain unknown.
The crisis in Ethiopia is a major international story of mass protest, wholesale dispossession of millions of peasants, and state-sponsored violence. Yet it has gone almost completely ignored in the international media. To be sure, the story has attracted fleeting attention from English-language outlets like the BBC and the Guardian, while Al-Jazeera has curated what little information trickles out of the country from social media users on the ground. But sustained analysis of the causes and context of the government’s plan, the protests in response and the violent government crackdown have been hard to come by.
There are a number of reasons the story hasn’t grabbed attention around the world—the situation’s complexity, the tight control of information by Ethiopian authorities, and western journalists’ unfamiliarity with Ethiopia’s tense ethnic politics, to name just a few. But the bigger issue has to do with Western media bias. Over the years, a considerable amount of attention has rightly been given to bloggers and journalists whose individual rights have been violated by the Ethiopian government. This is not surprising. It is easy to sympathize with those trying to practice their freedom of expression or tell a difficult story in the face of authoritarianism. The repression of media in a given country is an easier account to give, and it is a simpler story to process. The miseries and violence of the other repression—that against the voiceless masses—cannot afford to be get lost in the shuffle, as the situation in Oromia makes clear. As long as this bias remains salient, the deaths of hundreds, possibly thousands, will continue to go unreported and unrecognized, and the cause for which so many have sacrificed will remain hidden.
*Ayantu Tibeso is a researcher and communications consultant based in North America. She can be reached at atibeso@gmail.com or on twitter @diasporiclife.
Read more @ http://warscapes.com/opinion/oromoprotests-perspective#sthash.FmxKbAdj.fqpFJ2bA.dpu
COVERING OROMO ISSUES: ETHIOPIA’S BESIEGED PRESS, INSTITUTIONAL BIAS AND THE #OROMOPROTESTS June 4, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Amane Badhaso, Ambo, Finfinne is Oromia's land, Finfinnee, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Finfinnee n Kan Oromoo ti, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, No to land grabs in Oromia, No to the Addis Ababa Master Plan, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Oromia Satelite Radio and TV Channels, Oromia wide Oromo Universtiy students Protested Addis Ababa Expansion Master Plan, Oromian Voices, Oromians Protests, Oromo and the call for justice and freedom, Oromo Diaspora, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Protests, Oromo Protests in Ambo, Oromo students protests, State of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: Addis Ababa Master Plan, Ambo, Economic and Social Freedom, Free Media, Free Press, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Media and #OromoProtests, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromo Students Protests
add a comment
The local coverage of the protests offer a best case study to look at Ethiopian media’s inherent, institutional bias toward Oromo stories. Given the foregoing discussion on Ethiopia’s challenging media environment, the dangers of balanced coverage are not contested. The government’s choke-hold on the media and fear of repercussions have discouraged journalists from visiting the scenes of protests and accurately reporting on the events. Ethiopia’s independent press is saturated in Finfinne, and many simply don’t have credible regional sources, especially in Oromia, who can feed them with the news of the protests. Besides, media institutions and some journalists consider approaching the protesters or contacting the victims’ families almost existential.
There is also an ideological bias toward “ethnic” based activism. In part this explains the reluctance among many journalists to visit some of the 15 towns included in the master plan and interview local residents and farmers. However, speaking to government officials and opposition politicians about the master plan, the protests and violent crackdown could have been done with minimum effort.
A closer look at reports by six web-based publications and three international correspondents reveals much not only about Ethiopia’s handcuffed press but also the deficiency of the so-called independent press itself. It took almost a month for most local outlets to offer basic, even if lopsided coverage on the cause of the protest and the causalities. Even considering the grim media environment, there were many missing links in those reports.
Others completely disregarded the matter and kept to their business as usual. For example, Addis Fortune, a weekly English newspaper with 10,000 monthly circulations, devoted only one singlesentence to the protests its May 11 report about the master plan.
Awramba Times republished a video and text from EthioFirst blog. To his credit, the EthioFirst reporter went to the scene of protests in Ambo town. The online only publication provided coverage supported with text and videos of what it said were destroyed properties. It also interviewed residents of Ambo, students of the Ambo University and chief of the university all denouncing the destruction of property. The report’s focus on the damage caused to properties as opposed to the loss of lives and arrests of hundreds gives us a reason for pause. Besides, the reporter made no attempt to speak with protesters, victims or their families.
Others recycled government statements and news releases from opposition political parties. For example, both the English and Amharic editions of The Reporter made its first coverage based on government statements. The English edition of the newspaper tried to balance the story by asserting“independent observers and those who claim to be eyewitnesses say that the death toll and injuries might be higher than what has been officially admitted.”
Sendek Amharic newspaper, which gave its reporting five days after the protests began, referred to a press release from the opposition Oromo Federalist Congress (OFC) and later conducted interviews with the party’s leaders.
Addis Admas, another local Amharic daily, also did its initial coverage using government statement and anonymous sources from Ambo, Robe and Haromaya, where the protests took place. In a subsequent report on May 10, the paper reached out to a farmer residing in Sabata, one of the 15 towns included in the master plan, and offered local grievances over issues of compensation and threat to the farmer’s livelihood. Addis Standard, a local English magazine, also did its “best” by relying on sources from the universities where protests were reported, otherwise largely toeing the line from government statement.
Unfortunately, Finfinne-based foreign correspondents also kept to the official line. The Associated Press carried a police statement, and even went a step further linking the protests to secession andOromo Liberation Front. Bloomberg News also repurposed the government statement, with a passing reference to opposition leaders. Reuters simply ignored the news.
Other newspapers offered sensationalized stories that reflect their bias more than journalistic inclinations. For example, on May 2, Addis Guday wrote, ‘Oromia: Gize Tebikiwu Yeminfeneda Bomboch-Yetameku ye politika bisotoch. Ye tebab bihertenynet tosoch’ roughly translated as ‘ Oromia: a ticking time bomb waiting to explode and a concealed political dissatisfaction. The scar of narrow-minded ethnicity” In all, almost no attempt was made to contact to the protesters or the farmers and residents affected by the master plan. And none of the aforementioned outlets treated the incident as a breaking news item.
Ethiopian journalism is still at its infancy stage. Restrictions against the press and physical harassment of journalist make it impossible to cover issues of public interest. The reliance on government press statement reveals the challenges of obtaining first-hand reports from the scene of the incident. The country’s ethnicized politics confounds the lack of impartial coverage. In a country where there is no single Oromo media outlet and given the jamming of diaspora-based websites, the Oromo are left with no voice so to speak. Dozens of Oromo newspapers and magazines that existed in the 1990s were either banned or forced out of business when Oromo journalists fled the country.
With a varying degree, both private and government media outlets share a common hostility toward Oromo interests. While some of the private media practitioners are in government pockets, others cater to non-Oromo political groups. The rest are far more concerned with making money and they know what their audience wants. “There is little independent media in Oromia to monitor these events, and foreign journalists who have attempted to reach demonstrations have been turned away or detained,” the HRW said. A case in point is the four-hour detention of Bloomberg’s William Davison on May 1, after attempting to report on protests that took place at Addis Ababa University.
In a nutshell, independent, objective journalism has essentially become a crime in Ethiopia. Given the highly restrictive media environment, Ethiopia’s “independent” press continues to teeter on the edge of death and survival. Under the circumstances, a lot of journalists have begrudgingly embraced the “developmental state” storyline. For others, strict self-censorship has become more of a norm. As a result, the professionalism and quality of Ethiopian journalism has been significantly compromised. Still more concerning is the inherent ideological and institutional bias toward coverage of “ethnic” stories, particularly stories about Oromo activism. The role of a journalist is to report on events as objectively and truthfully as possible. Journalists should act as non-participating spectators of events. When reporters become part of a story or offer their opinions, they are expected be transparent and issue a disclosure. These ethical values are rare in Ethiopia. However, if there’s any hope for future of Ethiopian journalism, Addis Ababa-based media houses should start checking their ethnicized and detached coverage of events outside of the capital. -To read the full article, visit OPride, original source @http://www.opride.com/oromsis/news/3756-ethiopia-s-besieged-press-and-the-oromoprotests
Speaking for the voiceless: Amane Badhasso, President of the International Oromo Youth Association (IOYA), Discusses about the Ongoing #OromoProtests in Oromia State on SaharaTV May 18, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Amane Badhaso, Colonizing Structure, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Finfinnee n Kan Oromoo ti, Free development vs authoritarian model, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, Human Rights, Human Rights Watch on Human Rights Violations Against Oromo People by TPLF Ethiopia, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, No to land grabs in Oromia, No to the Addis Ababa Master Plan, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Oromia Support Group, Oromia wide Oromo Universtiy students Protested Addis Ababa Expansion Master Plan, Oromian Voices, Oromians Protests, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Diaspora, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Protests, Oromo Protests in Ambo, Oromo students movement, Oromo students protests, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromo University students and their national demands, Oromummaa, Prof. Muhammad Shamsaddin Megalommatis, Say no to the expansions of Addis Ababa, Self determination, State of Oromia, Stop evicting Oromo people from Cities, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromummaa, Social Sciences, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Related:
IOYA Appeal Letter

Dear Sir, Madam,
We are reaching out to you as the Board of officers of the International Oromo Youth Association (IOYA) whose nation is in turmoil back in Oromia, Ethiopia. Recently, Oromo students have been protesting against the new Addis Ababa “Integrated Master Plan” which aims at incorporating smaller towns surrounding Addis Ababa for the convenience of vacating land for investors by displacing millions of Oromo farmers. As a political move, this will essentially result in the displacement of the indigenous peoples and their families. Oromo farmers will be dispossessed of their land and their survival both economic and cultural terms will be threatened. The Oromos strongly believe that this plan will expose their natural environment to risk, threaten their economic means of livelihood (subsistence farming), and violate their constitutional rights.
The Ethiopian government is executing its political agenda of progressive marginalization of the Oromo people from matters that concern them both in the Addis Ababa city and the wider Oromia region. The master plan is an unconstitutional change of the territorial expansion over which the city administration has a jurisdiction. The government justifies the move in the name of enhancing the development of the city and facilitating economic growth. The justification is merely a tactical move masked for the governments continued abuse of human rights of the Oromo people. While the Oromos understand that Addis Ababa itself is an Oromo city that serves as the capital of the federal government, they also consider this move as an encroachment on the jurisdiction and borders of the state of Oromia.
The protesters peacefully demonstrated against this move. University students and residents have been in opposition to the plan, but their struggle has been met by a brutal repression in the hands of the military police (famously known as the Agazi). It has been reported that shootings, arrests, and imprisonments are becoming rampant. It is also reported that the death toll is increasing by the hour. Recently, sources indicate that over 80 people have been shot dead, others severally injured and thousands arrested. In addition, Oromo students have been protesting peacefully for over three weeks now, despite mass killings and arrests by Ethiopian security forces. University and high school students from more than ten universities have been engaging in the Oromo protests. The peaceful rally has now spread across the whole country and is expected to continue until the Ethiopian government refrains from incorporating over 36 surrounding smaller towns into Addis Ababa. It is stated to be displacing an estimate of 6.6 million people and violating constitutional rights of regional states.
As an organization subscribing to broader democratic engagement of the Oromo youth, we oppose the brutal violence that the Ethiopian government is meting out on innocent, unarmed young students who are peacefully protesting. As leaders of the Oromo community, we support and stand in solidarity with Oromo protests in Ethiopia. The human rights violations being carried out by the Ethiopian government against innocent students are unacceptable. Continuous assaults, tortures, and killings of innocent civilians must be stopped. We urge you to join us in denouncing these inhumane and cruel activities carried out by the Ethiopian government. We believe it is imperative that the international community raise its voice and take action to stop the ongoing atrocities that are wreaking havoc to families and communities in the Oromia region.
We urgently request that such actions be taken in an attempt to pressure the Ethiopian government to stop terrorizing and killing peaceful protesters:
- The US government and other International organizations should condemn the Ethiopian government’s brutal action taken on unarmed innocent civilians. Furthermore, we demand over 30,000 innocent protesters to be released from prisons, as they will be subjected to torture and ill treatment.
- The Ethiopian People’s Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) is currently terrorizing its own electorates/nation. Under the law of R2P in the UN constitution, the international community is obliged to protect a nation that is being terrorized by its own government and EPRDF should be taken accountable.
- We demand Ethiopia to be expelled from any regional and international cooperation including and not limited to AU and UN for its previous and current human rights violations. The International community should stop providing support in the name of AID and development to Ethiopia as it is violating the fundamental and basic needs of its nation.
- The Ethiopian government should be stopped on immediate effect; its forceful displacement of the indigenous peoples across Ethiopia is unjust and unconstitutional. We ask the United States, European Union, and the United Nations to stand in solidarity with peaceful student protesters who are condemning such injustice.
- The onus is on the international community to act in favor of the innocent and civilian populace that is seeking its fundamental right. Punitive actions towards this government should be taken for cracking down on freedom of expression and other democratic rights being expressed by its citizens.
We believe it is in the interest of our common humanity to take responsibility, to pay attention to this problem, to witness the plight of the voiceless victims, and to raise concerns to the Ethiopian government so it can desist from its brutal acts of repression.
We count on your solidarity to help the Oromo youth be spared from arbitrary arrest, incarceration, and shootings.
Yours Respectfully,
International Oromo Youth Association
http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/ioya-appeal-letter/
Protests, State Violence, and the Manufacture of Dissent in Ethiopia May 6, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, America, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinne is Oromia's land, Finfinnee, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Finfinnee n Kan Oromoo ti, Free development vs authoritarian model, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, Hetosa, Human Rights, Human Rights Watch on Human Rights Violations Against Oromo People by TPLF Ethiopia, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Meroetic Oromo, No to land grabs in Oromia, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia wide Oromo Universtiy students Protested Addis Ababa Expansion Master Plan, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo Culture, Oromo Diaspora, Oromo Protests, Oromo Protests in Ambo, Oromo students protests, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromo University students and their national demands, Oromummaa, Say no to the expansions of Addis Ababa, State of Oromia, Stop evicting Oromo people from Cities, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: African Studies, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, The Tyranny of Experts, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
Two things happened simultaneously on May 1st, both involving the U.S. State Department and its relation to Ethiopia. Thing one was the State Department’s news program, Voice of America, broadcasting its brief account of Ethiopian security forces firing upon student demonstrations the previous day (April 30) at three universities resulting in 17 dead and many wounded. Thing two was the Secretary of State John Kerry in Ethiopia giving a speech full of praise for Ethiopia’s rapid economic development as well as the U.S.-Ethiopia partnership in addressing the violence against civilians in neighboring Sudan and Somalia. Apparently, Kerry was unaware that the day before, just a two-hour’s drive down the road from where he was speaking, America’s supposed partner, the Ethiopian government, had committed acts of violence against its citizens. In fact, thousands of individuals at universities and in cities across the Oromia region of Ethiopia had been protesting for days, and as the journalist Mohammed Ademo’s article for Think Africa pointed out on Tuesday (August 29), what they were protesting was precisely the consequences of the rapid economic development and foreign direct investment that Kerry praised in his speech – the eviction and displacement of tenant farmers and poor people due to the expansion of the capital city Addis Ababa into the Oromia region.
We might observe a contradiction here within the same State Department. While the State Department’s news program laments an event and clearly points to the root cause, the State Department’s secretary appears ignorant of the event and also strangely unable to discern the causes of ethnic unrest across Africa. An Al Jazeera op-ed responding to Kerry’s speech suggests that the United States fails to see the contradiction in its policy that talks about democracy and human rights but in practice emphasizes security for foreign direct investment (as per the State Department’s own report on such investment in Ethiopia published shortly before Kerry’s visit.) Noticeably, two contradictory ideas are coming out of the State Department simultaneously. What do we make of that contradiction?
Before I answer that question, I might add on to this strange state of affairs by pointing out that Kerry did criticize the Ethiopian government for using repressive tactics against its journalists — the famous Zone 9 bloggers — but what strikes me is that at the very moment that Kerry criticizes the state of journalism in Ethiopia, the mainstream American news outlets such as CNN, National Public Radio, and the NY Times have for a long time neglected to give any serious coverage of the issues within Ethiopia and in fact did not report on the student demonstrations. The only American media mention of the recent student demonstrations and deaths is a very brief Associated Press article that appeared the day after Kerry’s speech (May 2) and that article embarrassingly gets its facts wrong about what happened and why. Such poor journalism is increasingly perceived to be the norm of America’s once celebrated media whose many factual inaccuracies and lack of any genuine will to truth arguably contributed to the Iraq War back in 2003. Curiously, the only news organization in America that did its job (the VOA) is the news organization intended to serve communities outside of America. Moreover, the VOA is part of the very same “department” that Kerry heads. The quality of mainstream American media coverage might seem excusable if it weren’t for the fact that BBC covered these tragic events in Ethiopia reasonably well, first on its radio program immediately after the massacre (May 1st) and then more comprehensively on its website the following day.
Two things happened simultaneously on May 1st, both involving the U.S. State Department and its relation to Ethiopia. Thing one was the State Department’s news program, Voice of America, broadcasting its brief account of Ethiopian security forces firing upon student demonstrations the previous day (April 30) at three universities resulting in 17 dead and many wounded. Thing two was the Secretary of State John Kerry in Ethiopia giving a speech full of praise for Ethiopia’s rapid economic development as well as the U.S.-Ethiopia partnership in addressing the violence against civilians in neighboring Sudan and Somalia. Apparently, Kerry was unaware that the day before, just a two-hour’s drive down the road from where he was speaking, America’s supposed partner, the Ethiopian government, had committed acts of violence against its citizens. In fact, thousands of individuals at universities and in cities across the Oromia region of Ethiopia had been protesting for days, and as the journalist…
View original post 1,351 more words
Statement of Oromo Community Organizations in the U.S. and Oromo Studies Association (OSA) to condemn the heinous crimes committed against defenseless and innocent Oromo University students and those who joined their just movements in solidarity May 3, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinne is Oromia's land, Finfinnee, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Free development vs authoritarian model, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, Hetosa, Human Rights, Humanity and Social Civilization, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., No to land grabs in Oromia, No to the Addis Ababa Master Plan, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Satelite Radio and TV Channels, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromia wide Oromo Universtiy students Protested Addis Ababa Expansion Master Plan, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo students movement, Oromo students protests, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromo University students and their national demands, Oromummaa, Say no to the expansions of Addis Ababa, Self determination, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: African Studies, Genocide against the Oromo, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
Ibsa Ijjannoo Waldaa Qorannoo Oromoo fi Waldaalee Hawaasa Oromoo Ameerikaa Kaabaa: Ijjechaa Barattootaa Oromootiif Ummata Oromoo Ilaalchisee | Statement of Oromo Community Organizations in the U.S. and Oromo Studies Association (OSA)
Posted: Caamsaa/May 3, 2014 · Finfinne Tribune | Gadaa.com
————————-
We, Oromo Community Organizations in USA, and OSA jointly prepared this press statement in Afaan Oromoo to condemn the heinous crimes committed against defenseless and innocent Oromo University students and those who joined their just movements in solidarity. We also expressed our readiness to stand in solidarity with the Oromo University Students and the #OromoProtests. We ask the Ethiopian regime to unconditionally release the hundreds of University Students detained by the Federal Security Forces and bring to justice those who ordered the use of live bullets to put down the protest. We ask the Oromo in Diaspora to protest in all major cities where the Oromo live in large numbers and fund raise money to support the victims of the massacre and affected families by covering some of their medical and miscellaneous expenses. We have formed a National committee to coordinate the fund raising activities during rallies and at prayer places (Mosques, Churches). This is a work in progress and seek your support as we go forward. We strongly believed that the regime can only be defeated through concerted and sustained resistance movements which requires our collective material and intellectual resources. The Oromo must be ready to pay the utmost sacrifices the struggle demands to free our nation and heal the broken hearts of its oppressed masses.
————————-
Ibsa Ijjannoo Waldaa Qorannoo Oromoo fi Waldaalee Hawaasa Oromoo Ameerikaa Kaabaa: Ijjechaa Barattootaa Oromootiif Ummata Oromoo Ilaalchisee
Seensa:
Nuuti Waldaleen Hawaasa Oromoo Ameerikaa Kaabaa keessaa tiif Waldaan Qorannoo Oromoo yeroo ammaan kanaa mootummaa abbaa irree Impaayeera Itoophiyaatiin sochii mormii barattoota Yunivarsittii, barattoota mana barumsaa sadarkaa adda addaa fi ummmata Oromoo dhaamsuuf jechaa ijjechaa garaa hammeennaan barattoota irratti raawwatameen lubbuun barataa hedduu dhabamuun haalaan nu gaddisiise jira.
Mootummaan Itoophiyaa mootummaa mirga ummattoota Itoophiyaa hiree ofii ofiin murteeffachuu humnaan ittisee karaa seeraan alaatiin angoo siyaasaa ofii dheerrafachuuf tattafataa jiruudha. Mootummaa Itoophiyaa TPLFn durfamu jalatti waggoottan 23 dabran keessatti ummatii Oromoo hiree siyaasaa biyya isaa irratti wal-qixxummaan murtessuu dhabee, akka bineensa bosonaa mootummaan yeroo fedhutti ijjeessu ta’ee jira. Ummatii Oromoo mirga bilisummaan gurmaa’uu, dhaabbata siyaasa fedhu deeggaru, mirgaa odeeffannoo walabaa midiyaa walabaa irraa argachuu, hiriira nagaa bahuu dhorkamee biyya isaa irratti lammii lammaffaa fi garboota ta’anii jiraachaa jiru. Haallii Sabii Oromoo tiif ummattootii Itoophiyaa biro keessa jiran gonkummaa fudhatama kan hin qabneef jijjiramuu kan qabuudha.
Guyyaa hardhaa Camsaa 2, 2014 walga’ii hatattamaa Waldaaleen Hawaasa Oromoo Ameerikaa Kaabaa tiif Waldaan Qorannoo Oromoo godheen ibsa ijjannoo waloo kana baafne jirra. Ibsii ijjannoo kun deeggarsa hawaasi Oromoo biyya alaa keessa jiru sochii didda gabrummaa fi fincila barattoota Oromoo Yunivarsitii Oromiyaa/biyyoleessa keessa jiraniif qabnu muldhisuudhaaf kan qophaa’eedha.
Ibsa Ijjannoo:
1. Gocha farrummaa ummataa Oromotiif qabu irraa kan ka’e mootummaan Itoophiyaa Ijjechaa seeraan alaa barattoota Oromoo tiif ummata Oromoo hiriira nagaa bahe irratti raawwate cimsinee kan balaaleffannu ta’u keenna ibsina. Ijjeechaa garaa hammeennaan barattoota Oromoo irratti raawwatameef hoggantoota mootummaa abbaa irreetiin ala qaamnii biraa itti gaafatamu akka hin jirre amanna. Ijjechaan bara baraan dhala Oromoo irratti raawwatamu gocha fixiinsa sanyii Oromoo ta’uuti hubbanna. Hoggantootii mootummaan Itoophiyaa TPLFn durfamu Dhiiga ilmaan Oromoo jissuu irraa akka of-qusatan akkeekkachiifna.
2. Maqaa misooma qindomina qabuu fiduuf jechuudhaan tarsiisoo mootummaan abbaa irree lafa Oromoo ummata Oromoo irraa buqqisuudhaan deeggartootaa fi abbaa fedheef kennuuf maqaa “Addis Ababa and Oromiya Special Zone Joint Development Master Plan” jedhuun moggaase raawwii isaaf tattafachaa jiru cimsinee kan balaleeffannu ta’uu ibsina. Karoorrii kun akkuma ummata Oromoo biyya keessa jiruuf dhimmii kun kallatiin ilaalu biratti fudhatama hin qabne, nu Oromoota biyya ambaa jiraannu birattis akka fudhatama hin qabne ibsuu barbaanna. Mootummaan abbaa irree Impaayeera Itoophiyaa qondaaltoota siyaasaa isaa ijjechaa ilmaan Oromoo keessatti kallatiin qooda qaban hatattamaan too’annoo jala oolanii gara seeraati akka dhiihatan akka godhu akkeekachiifna. Galmaa’an gahuu kaayyoo kanatiif dhaabbileen mirga dhala namaatiif falman hudumtuu mootummaa Itoophiyaa irratti akka dhiibbaa godhan gaafanna. Gochaan ummata Oromotiif ummattoota biroo Itoophiyaa Keessa jiran ukkamsuudhaaf mootummaan Itoophiyaan yeroo yerooti fudhatamaa jiru, fixiinsa sanyii namaa akka ta’e hubatamee qaamnii dhimmii Kun ilaalu kan akka International Criminal Court (ICC) qorannoo shakkamtoota yakka kanaa gara seeraati dhiheessuuf barbaachisu amumma akka eegalan gaafanna.
3. Maatii Wareegamtoota ilmaan Oromoo ijjechaa mootummaan TPLFn raawwatameen dhuman hundaaf gadda guddaa nutti nagahame ibsina. Dhiigii ilmaan Oromoo dhiiga bineensa bosonaa akka hin taane hubannee gumaa isaanii deebisuudhaaf qabsoo gaggeeffamu keessatti deeggarsa nurra barbaadamu godhuudhaaf qophii ta’uu keenna ibsina. Gaddii keessan gadda keennaaf gadda ummata Oromoo cufaa. Kanaafuu,gadda keessan isan waliin dhaabbanne isin sabbarsiisuuf qophii ta’uu keenna ibsina. Galatii ilmaan Oromoo qabsoo mirgaa Oromootiif kufanii bilisummaa saba Oromootiif walabummaa Oromiyaa callaa akka ta’e hubbanna.
4. Barattoota hidhaman hundaa haala duree tokko malee akka gad dhiifaman cimsinee gaafanna. Hidhaamtoota Siyaasa mana hidhaa Impaayeera Itoophiyaa keessa jiran maraa akka gad dhiifaman cimsinee gaafanna. Ummatii Oromoo Ameerikaa kaabaa keessa jiraannu qabsoo haqaa Oromoo keessatti ummata Oromoo biyya jiru cinaa jiraachuu keenna yeroon mirkaneessinu ammaan kana jennee amanna.
Qabsa’aan ni kufa, Qabsoon itti fufa!
Tokkummaan Ummata Oromoo haa jabaatu!
Ibsa Waloo Waldaalee Oromoo armaan gadiiti maqaan tarreeffame:
1. Waldaa Qorannoo Oromoo
2. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Chicago
3. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Ohio
4. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Michigan
5. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Nashville fi Memphis, Tennessee
6. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Kentucky
7. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Seattle
8. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo South Dakota
9. Waldaa Manguddoo Oromoo Minnesota
10. Waldaa Hawaasa Oromoo Denver
——————–

Ethiopia’s Villagisation Scheme is a failure April 28, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa Rising, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Ethnic Cleansing, Free development vs authoritarian model, Gambella, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Satelite Radio and TV Channels, Oromia Support Group, Oromian Voices, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Finfinnee, Gambella and Omo Valley, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
The orderly village of Agulodiek in Ethiopia‘s western Gambella region stands in stark contrast to Elay, a settlement 5km west of Gambella town, where collapsed straw huts strewn with cracked clay pots lie among a tangle of bushes.
Agulodiek is a patch of land where families gradually gathered of their own accord, while Elay is part of the Ethiopian government’s contentious “villagisation” scheme that ended last year. The plan in Gambella was to relocate almost the entire rural population of the state over three years. Evidence from districts surrounding Gambella town suggest the policy is failing.
Two years ago people from Agulodiek moved to Elay after officials enticed them with promises of land, livestock, clean water, a corn grinder, education and a health clinic. Instead they found dense vegetation they were unable to cultivate. After one year of selling firewood to survive, they walked back home.
“All the promises were empty,” says Apwodho Omot, an ethnic Anuak, sitting in shade at Agulodiek. There is a donor-funded school at the village whose dirt paths are swept clear of debris, and the government built a hand pump in 2004 that still draws water from a borehole. Apwodho’s community says they harvest corn twice a year from fertile land they have cleared. “We don’t know why the government picked Elay,” she says.
Gambella region’s former president Omod Obang Olum reported last year that 35,000 households had voluntarily moved from a target of 45,000. The official objective had been to cluster scattered households to make public service delivery more efficient. Critics such as Human Rights Watch said the underlying reason was to clear the way for agricultural investors, and that forced evictions overseen by soldiers involved rape and murder. The Ethiopian government refute the allegations.
Last month the London-based law firm Leigh Day & Co began proceedings against the UK Department for International Development (DfID) at the high court after a man from Gambella alleged he suffered abuse when the agency supported the resettlement scheme. Since 2006, DfID and other donors have funded a multibillion-dollar programme in Ethiopia that pays the salaries of key regional government workers such as teachers and nurses through the Protection of Basic Services scheme.
A DfID spokesman said: “We will not comment on ongoing legal action, however, the UK has never funded Ethiopia’s resettlement programmes. Our support to the Protection of Basic Services Programme is only used to provide essential services like healthcare, schooling and clean water.”
Karmi, 10km from Gambella town, is a newly expanded community for those resettled along one of the few tarmac roads. Two teachers scrub clothes in plastic tubs on a sticky afternoon. A herd of goats nibble shrubs as purple and orange lizards edge up tree trunks. There is little activity in the village, which has bare pylons towering over it waiting for high-voltage cables to improve Gambella’s patchy electricity supply.
The teachers work in an impressive school built in 2011 with funds from the UN refugee agency. It has a capacity of 245 students for grades one to five – yet the teachers have only a handful of pupils per class. “This is a new village but the people have left,” says Tigist Megersa.
Kolo Cham grows sorghum and corn near the Baro river, a 30-minute walk from his family home at Karmi. The area saw an influx of about 600 people at the height of villagisation, says Kolo, crouching on a tree stump, surrounded only by a group of children with a puppy. Families left when they got hungry and public services weren’t delivered. “They moved one by one so the government didn’t know the number was decreasing,” he says.
The Anuak at Karmi have reason to fear the authorities, particularly Ethiopia’s military. Several give accounts of beatings and arrests by soldiers as they searched for the perpetrators of a nearby March 2012attack on a bus that killed 19. The insecurity was a key factor in the exodus, according to residents.
As well as the Anuak, who have tended crops near riverbanks in Gambella for more than 200 years, the region is home to cattle-herding Nuer residents, who began migrating from Sudan in the late 19th century. Thousands of settlers from northern Ethiopia also arrived in the 1980s when the highlands suffered a famine. The government blamed the bus attack on Anuak rebels who consider their homeland colonised.
David Pred is the managing director of Inclusive Development International. The charity is representing Gambella residents, who haveaccused the World Bank of violating its own policies by funding the resettlement programme. An involuntary, abusive, poorly planned and inadequately funded scheme was bound to fail, he says. “It requires immense resources, detailed planning and a process that is truly participatory in order for resettlement to lead to positive development outcomes,” he adds.
Most of flood-prone Gambella, one of Ethiopia’s least developed states, is covered with scrub and grasslands. Inhospitable terrain makes it difficult for villagisation to take root in far-flung places such as Akobo, which borders South Sudan. Akobo is one of the three districts selected for resettlement, according to Kok Choul, who represents the district in the regional council.
In 2009, planners earmarked Akobo for four new schools, clinics, vets, flourmills and water schemes, as well as 76km of road. But the community of about 30,000 has seen no change, says 67-year-old Kok, who has 19 children from four wives. “There is no road to Gambella so there is no development,” he says. One well-placed civil servant explains that funds for services across the region were swallowed by items such as daily allowances for government workers.
A senior regional official says the state ran low on funds for resettlement, leading to delivery failures and cost-cutting. For example, substandard corn grinders soon broke and have not been repaired, he says. The government will continue to try to provide planned services in three districts including Akobo this year and next, according to the official.
However, the programme has transformed lives, with some farmers harvesting three times a year, says Ethiopia’s ambassador to the UK, Berhanu Kebede. The government is addressing the “few cases that are not fully successful”, he says. Service provision is ongoing and being monitored and improved upon if required, according to Kebede.
At Elay, Oman Nygwo, a wiry 40-year-old in cut-off jeans, gives a tour of deserted huts and points to a line of mango trees that mark his old home on the banks of the Baro. He is scathing about the implementation of the scheme but remains in Elay as there is less risk of flooding. There was no violence accompanying these resettlements, Oman says, but “there would be problems if the government tried to move us again”.
Read @ original source:http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/apr/22/ethiopia-villagisation-scheme-fails?CMP=twt_gu
Make Ogaden Accessible US House Urges Ethiopia April 24, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa Rising, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Sidama, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: African Studies, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human Rights Violation Against Ogaden people, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Ogaden, Oromia, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
The U.S House of Representatives and the government of United Kingdom plus EU Parliament and United Nations have recently stepped up a campaign to help Somalis from Ogaden region to realize that their voice has been heard by the International Community after decades of virtually silent.
As UK’s government recently released a report indicating allegations of abuses by the Liyu Police or “Special Police”,which London expressed its concerns,United States House of Representatives and EU Parliament have both sent strong messages to Addis Ababa,which was meant to open the Somali religion of Ogaden to the humanitarian agencies and International media to have free access to avoid further humanitarian crisis.
The U.S Congress issued a message which eventually published on Somalilandsun that reads:
The US House of Representatives has asked Ethiopia to Permit Human Rights and Humanitarian Organizations Access to its Somali region of Ogaden. The House informed (d) ETHIOPIA. “That Funds appropriated by this Act that are available for assistance for Ethiopian military and police forces shall not be made available unless the Secretary of State–
(A) certifies to the Committees on Appropriations that the Government of Ethiopia is implementing policies to–
(i) protect judicial independence; freedom of expression, association, assembly, and religion; the right of political opposition parties, civil society organizations, and journalists to operate without harassment or interference; and due process of law; and (ii) permit access to human rights and humanitarian organizations to the Somali region of Ethiopia; and (B) submits a report to the Committees on Appropriations on the types and amounts of United States training and equipment proposed to be provided to the Ethiopian military and police including steps to ensure that such assistance is not provided to military or police personnel or units that have violated human rights, and steps taken by the Government of Ethiopia to investigate and prosecute members of the Ethiopian military and police who have been credibly alleged to have violated such rights.”http://somalilandsun.com/index.php/world/4945-make-ogaden-accessible-us-house-urges-ethiopia–
The EU’s head of International Unit Party Socialist democrat,Anna Gomes,MEP said “Ethiopia is one of the largest humanitarian and development aid receiver yet these donations are used incorrectly and corruptly. Western governmental Organizations and Western Embassies to Addis Ababa ignored the stolen donations and humanitarian aid that are being used as a political tool by the Ethiopian regime, which is contrary to EU rules on the funding”.http://www.tesfanews.net/eu-holds-discussion-on-ethiopian-human-rights-crisis-in-ogaden-and-kality-prison/
Ulvskog, MEP,in her part when she was speaking about the steps needed to be taken in order to stop the human rights abuses that is being committed against Ethiopian and Ogaden civilians, she said that the EU could use sanctions or words against Ethiopia or follow up documents and information like the one provided by Ogadeni whistle-blower, Abdullahi Hussein,who smuggled out one-hundred-hours filmed footage, to show the reality in the ground.
The UK government’s website said last week that there have been many reports of mistreatment associated with the Special police,including torture and executions of villagers accused of supporting the Ogade n National Liberation Front.
“The UK government and the UN have pressed the Ethiopian government to articulate a reform plan for the Special police.The Ethiopian government has agreed this is needed,so we will encourage them to take action”,added the report.https://www.gov.uk/government/case-studies/country-case-study-ethiopia-justice-and-treatment-in-detention
The Rights Groups such as Human Rights Watch,Amnesty International and Genocide Watch have accused of Ethiopia that it has committed war crimes and crimes against humanity in Ogaden region.The ONLF accuses Addis Ababa similar charges of egregious human rights abuses against Somali civilians in the region.
John Holmes, The highest UN Official to visit Somali Region of Ogaden in part of its fact finding mission,since the Ethiopian crackdown (2007) called on a further investigation,a plan to wait its implementation until now.
Somali people of Ogaden Region,who has been deplored the international Community’s inaction and silence,when it comes to human rights violations committed at Ogaden region could now feel that they have been heard as the International Community including U.S,UK,EU and United Nations are ready to take action against those committed war crimes and crimes against humanity yet believe that they can get away with it.
How Long the Sufferings of the Oromo People go on under the Unjust and Tyrannic Rule of Ethiopia? April 22, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Dictatorship, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Oromia Support Group, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Poverty, Self determination, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny.Tags: African Studies, Finfinnee, Genocide against the Oromo, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
The TPLF Ethiopian government is a government controlled by one person, or a small group of people. In this form of government the power rests entirely in the hands of one person or cliques, and can be obtained by force or inheritance.
The dictator(s) may also take away much of its peoples’ freedom. In contemporary usage, dictatorship refers to an autocratic form of absolute rule by leadership unrestricted by law, constitution, or other social and political factors within the state.
In the 20th century and in this early 21st century hereditary dictatorship remained a relatively common phenomenon.
For some scholars, a dictatorship is a form of government that has the power to govern without consent for those who are being governed (similar to authoritarianism, while totalitarianism describes a state that regulates nearly every aspect of public and private behavour of the people. In other words, dictatorship concerns the source of the governing power (where the power comes from) and totalitarianism concerns the scope of the governing power (what is the government).
In this sense, dictatorship (government without people’s consent) is a contrast to democracy (government whose power comes from people) and totalitarianism (government controls every aspect of people’s life) opposes pluralism.
There for, in the case of Ethiopian’s dictatorial system , not only disappearance of exercising democracy, free speech, free election, free mass media and freedom of demonstrations but also the existence of droughts, poverty and hunger through out the ages of Ethiopian empire.
In fact, Ethiopia today is 123 out of 125 worst fed countries in the world. According to a new Oxfam food database “while the Netherlands ranks number one in the world for having the most plentiful, nutritious, healthy and affordable diet, Chad is last on 125th behind Ethiopia and Angola.”
In the presence of democratic right, according to the International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights:
Here, we’ve got all we need: Article 1, paragraphs 1 and 2 (International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which includes the exact same text as the first article) :
- All peoples have the right of self-determination. By virtue of that right they freely determine their political status and freely pursue their economic, social and cultural development.
- All people may, for their own ends, freely dispose of their natural wealth and resources without prejudice to any obligations arising out of international economic cooperation, based upon the principle of mutual benefit, and international law. In no case may a people be deprived of its own means of subsistence.
On the contrary Ethiopia is facing an ecological catastrophe: deforestation, desertification, soil erosion, overgrazing and population explosion .Tens of thousands of Oromo’s who are sick and dying from drinking the polluted waters of Lake Koka, once a pristine lake, located some 50km south of FINFINNE. Like the people who are dying around Lake Koka, the people who live in the Omo River Basin in South-western Ethiopia are facing an environmental disaster that could push them not only to hunger, starvation, dislocation and conflict, but potentially to extinction through habitat destruction. According to International Rivers, a highly respected environmental and human rights organization committed to protecting rivers and defending the rights of communities that depend on them. Furthermore, in 2004 when the then President of Oromia ( now Refugee) agreed to move Caffe Oromia from Finfinne To Adama, Oromo students peacefully demonstrated to oppose the systematic disposition of Finfinne from Oromia. Hundreds of students dismissed from universities, dozens of Metcha Tulema leaders thrown to prison, the Organization which was functional for over 40 years get closed.
In the last 100 years under various regimes of Abyssinians, Oromo farmers and peasants were systematically displaced from the land they lived on for generations. Under TPLF Wayanes regime, oromos in areas around Finfinne have been snatched off their land and left for destitution and forced to work as a daily laborer on their own land or their whereabout is unknown.
Obviously the present project of displacing Oromo’s by Tigrians and amharas is complete, and the next step is the official take over, that is including these areas under Finfinne. When will these expansions stop? Holota? Ambo? Bushoftu? Who is next? We have stopped fighting for ownership of Finfinne since 2004, and they want to take more!
The rights based response to the problem of land and grabbing article 11:
- The States Parties to the present Covenant recognize the right of everyone to an adequate standard of living for himself and his family, including adequate food, clothing and housing, and to the continuous improvement of living conditions. The States Parties will take appropriate steps to ensure the realization of this right, recognizing to this effect the essential importance of international co-operation based on free consent.
- The States Parties to the present Covenant, recognizing the fundamental right of everyone to be free from hunger, shall take, individually and through international co-operation, the measures also including specific programmers, which are needed:
- To improve methods of production, conservation and distribution of food by making full use of technical and scientific knowledge, by disseminating knowledge of the principles of nutrition and by developing or reforming agrarian systems in such a way as to achieve the most efficient development and utilization of natural resources;
- Taking into account the problems of both food-importing and food-exporting countries, to ensure an equitable distribution of world food supplies in relation to need.
In additional, the government has a responsibility to respect his people’s rights!!
The right to life and freedom from torture and degrading treatment. Freedom from slavery and forced labor.
The right to liberty.
The right to a fair trial.
The right not to be punished for something that wasn’t a crime when you did it.
The right to respect for private and family life freedom of thought, conscience and religion, and freedom to express your beliefs freedom of expression freedom of assembly and association.
The right to marry and to start a family.
The right not to be discriminated against the respect of these rights and freedoms.
The right to peaceful enjoyment of your property.
The right to have an education.
The right to participate in free elections.
The right not to be subjected to the death penalty.
Read more @: http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/how-long-injustice-and-suffering-of-the-oromo-people-go-on/
Stop aid to Tyrants: It is time to a new development model April 14, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Finfinnee, Food Production, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Land Grabs in Africa, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Poverty, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“Compare free development in Botswana with authoritarian development in Ethiopia. In Ethiopia in 2010, Human Rights Watch documented how the autocrat Meles Zenawi selectively withheld aid-financed famine relief from everyone except ruling-party members. Meanwhile democratic Botswana, although drought-prone like Ethiopia, has enjoyed decades of success in preventing famine. Government relief directed by local activists goes wherever drought strikes.”- http://time.com/23075/william-easterly-stop-sending-aid-to-dictators/
Traditional foreign aid often props up tyrants more than it helps the poor. It’s time for a new model.
Too much of America’s foreign aid funds what I call authoritarian development. That’s when the international community–experts from the U.N. and other bodies–swoop into third-world countries and offer purely technical assistance to dictatorships like Uganda or Ethiopia on how to solve poverty.
Unfortunately, dictators’ sole motivation is to stay in power. So the development experts may get some roads built, but they are not maintained. Experts may sink boreholes for clean water, but the wells break down. Individuals do not have the political rights to protest disastrous public services, so they never improve. Meanwhile, dictators are left with cash and services to prop themselves up–while punishing their enemies.
But there is another model: free development, in which poor individuals, asserting their political and economic rights, motivate government and private actors to solve their problems or to give them the means to solve their own problems.
Compare free development in Botswana with authoritarian development in Ethiopia. In Ethiopia in 2010, Human Rights Watch documented how the autocrat Meles Zenawi selectively withheld aid-financed famine relief from everyone except ruling-party members. Meanwhile democratic Botswana, although drought-prone like Ethiopia, has enjoyed decades of success in preventing famine. Government relief directed by local activists goes wherever drought strikes.
In the postwar period, countries such as Chile, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan have successfully followed the path of free development–often in spite of international aid, not because of it. While foreign policy concerns have often led America to prop up dictatorial regimes, we need a new rule: no democracy, no aid. If we truly want to help the poor, we can’t accept the dictators’ false bargain: ignore our rights abuses, and meet the material needs of those we oppress. Instead, we must advocate that the poor have the same rights as the rich everywhere, so they can aid themselves.
Easterly is the co-director of New York University’s Development Research Institute and author of The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor.
Read further at original source@
http://time.com/23075/william-easterly-stop-sending-aid-to-dictators/
As protestors from Kiev to Khartoum to Caracas take to the streets against autocracy, a new book from economist William Easterly reminds us that Western aid is too often on the wrong side of the battle for freedom and democracy. In The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor, Easterly slams thedevelopment community for supporting autocrats, not democrats, in the name of helping the world’s poorest. Ignoring human rights abuses and giving aid to oppressive regimes, he maintains, harms those in need and in many ways “un-develops” countries.
The Tyranny of Experts takes on the notion that autocracies deliver stronger economic growth than freer societies. Easterly argues that when economic growth occurs under autocratic regimes, it is more often achieved at the local level in spite of the regime’s efforts. In some instances, growth under autocracies can be attributed to relative increases in freedoms. He points to China as an example of this, attributing the country’s phenomenal growth to its adoption of greater personal and economic freedoms, especially compared to the crippling Maoist policies of the past.
Easterly also rejects the myth that dictators are dependable and that a certain level of oppression should be overlooked for the sake of economic growth and overall prosperity. Most recently, the violence and chaos following the 2011 Arab uprisings has made some nostalgic for the stable, if undemocratic, governments that kept civil unrest in check, allowing for a measure of economic development to take hold. Easterly stresses that instability and tumult in the wake of ousting a dictator is not the fault of an emerging democracy, but instead an understandable result of years of autocratic rule. The answer is not to continue to support autocrats in the name of stability, but rather to start the inevitably messy process of democratization sooner.
Easterly is of course not the first to call attention to the importance of prioritizing rights and freedoms in the development agenda. Scholars from Amartya Sen to more recently, Thomas Carothers and Diane de Gramont, have also advocated for a rights-based approach to development. In Pathways to Freedom: Political and Economic Lessons From Democratic Transitions, my coauthors and I similarly found that economic growth and political freedom go hand-in-hand.
Still, the hard questions remain: how to help those without economic and political freedoms? And when should donors walk away from desperately poor people because their government is undemocratic? Easterly argues that the donor community should draw the line with far more scrutiny than it does today – not just at the obvious cases, such as North Korea, but with other undemocratic countries, such as Ethiopia, where human rights abuses are rampant. He debunks the notion that aid can be “apolitical,” arguing that it is inherently political: giving resources to a government allows it to control and allocate (or withhold) resources as it sees fit. The aid community should focus on ways to help oppressed populations without helping their oppressors. For example, scholarship programs, trade, and other people-to-people exchanges can give opportunities to people in need. At the very least, Easterly argues, development actors should not praise oppressive regimes or congratulate them on economic growth they did not create.
Rather than being seduced by “benevolent dictators,” Easterly urges donors to focus their energy on “freedom loving” governments that need help. The Millennium Challenge Corporation is a step in the right direction but, as Easterly pointed out during the CFR meeting, MCC’s approach is undermined by other U.S. aid agencies, such as USAID, that continue to assist countries even when they don’t meet certain good governance and human rights standards.
Easterly also emphasizes the need for aid organizations to be more transparent about where their money is going. Robert Zoellick made strides in this direction during his tenure as World Bank president. But more recent developments suggest that the Bank still has a way to go in becoming more open and accountable. (Easterly noted that an initial invitation to speak about The Tyranny of Experts at the World Bank was later rescinded for “scheduling reasons.”) http://blogs.cfr.org/development-channel/2014/03/14/helping-the-oppressed-not-the-oppressors/#cid=soc-facebook-at-blogs-helping_the_oppressed_not_the_-031414
No democracy, no aid
http://stream.aljazeera.com/story/201403190105-0023568
March 26, 2014 (The Seattle Times) — SOMEHOW — probably my own fault — I have wound up on Bill Gates’ list of the world’s most misguided economists. Gates singled me out by name in his annual 2014 letter to his foundation as an “aid critic” spreading harmful myths about ineffective aid programs.
I actually admire Gates for his generosity and advocacy for the fight againstglobal poverty through the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation in Seattle. We just disagree about how to end poverty throughout the world.
Gates believes poverty will end by identifying technical solutions. My research shows that the first step is not identifying technical solutions, but ensuring poor people’s rights.
Gates concentrates his foundation’s efforts on finding the right fixes to the problems of the world’s poor, such as bed nets to prevent malarial mosquito bites or drought-tolerant varieties of corn to prevent famine. Along with official aid donors, such as USAID and the World Bank, the foundation works together with local, generally autocratic, governments on these technical solutions.
Last year, Gates cited Ethiopia in a Wall Street Journal guest column as an example, a country where he described the donors and government as setting “clear goals, choosing an approach, measuring results, and then using those measurements to continually refine our approach.”
This approach, Gates said, “helps us to deliver tools and services to everybody who will benefit.” Gates then gives credit for progress to the rulers. When the tragically high death rates of Ethiopian children fell from 2005 to 2010, Gates said this was “in large part thanks to” such a measurement-driven program by Ethiopia’s autocrat Meles Zenawi, who had ruled since 1991. Gates later said Meles’ death in August 2012 was “a great loss for Ethiopia.”
Do autocratic rulers like Meles really deserve the credit?
Gates’ technocratic approach to poverty, combining expert advice and cooperative local rulers, is a view that has appealed for decades to foundations and aid agencies. But if technical solutions to poverty are so straightforward, why had these rulers not already used them?
The technical solutions have been missing for so long in Ethiopia and other poor countries because autocrats are more motivated to stay in power than to fix the problems of poverty. Autocracy itself perpetuates poverty.
Meles violently suppressed demonstrations after rigged elections in 2005. He even manipulated donor-financed famine relief in 2010 to go only to his own ruling party’s supporters. The donors failed to investigate this abuse after its exposure by Human Rights Watch, continuing a long technocratic tradition of silence on poor people’s rights.
Rulers only reliably become benevolent when citizens can force them to be so — when citizens exert their democratic rights.
Our own history in the U.S. shows how we can protest bad government actions and reward good actions with our rights to protest and to vote. We won’t even let New Jersey Gov. Chris Christie get away with a traffic jam on a bridge.
Such democratic rights make technical fixes happen, and produce a far better long-run record onreducing poverty, disease and hunger than autocracies. We saw this first in the now-rich countries, which are often unfairly excluded from the evidence base.
Some developing countries such as Botswana had high economic growth through big increases in democratic rights after independence. Botswana’s democrats prevented famines during droughts, unlike the regular famines during droughts under Ethiopia’s autocrats.
Worldwide, the impressive number of developing countries that have shifted to democracy includes successes such as Brazil, Chile, Ghana, South Korea and Taiwan, as well as former Soviet Bloc countries such as the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovenia.
If the democratic view of development is correct, the lessons for Gates are clear: Don’t give undeserved credit and praise to autocrats. Don’t campaign for more official aid to autocrats. Redirect aid to democrats. If the democratic view is wrong, I do deserve to be on Gates’ list of the world’s most misguided economists.
http://ayyaantuu.com/africa/guest-the-flaw-in-bill-gates-approach-to-ending-global-poverty/
Related findings:
The UK government is providing financial aid to human rights abusers in Ethiopia through funding training paramilitaries, who perpetrate summary killings, rape and torture in the impoverished African country, local media reported.
Through its foreign aid budget, the UK government provides financial support to an Ethiopian government security force known as the “special police” as part of its “peace and development programme”, which would cost up to £15 million in five years, The Guardian reported.
The Department for International Development warned in a leaked document of the “reputational risks” of working with organizations that are “frequently cited in human rights violationallegations”, according to the report.
The Ethiopian government’s counter-insurgency campaign in Ogaden, a troubled region largely populated by ethnic Somalis is being enforced by the 14,000-strong special police.
This is while police forces are repeatedly accused by Human Rights Watch of serious human rights abuses.
Claire Beston, the Amnesty International’s Ethiopia researcher, said it was highly concerning that Britain was planning to work with the paramilitary force.
The Historic Inauguration of Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument and Aannoolee Historical Museum: Siidaa Wareegamtoota Aannolee April 12, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument, Dhaqaba Ebba, Finfinnee, Hetosa, Oromia, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo Identity, Oromummaa, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Self determination, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument, African Studies, Economic and Social Freedom, Governance issues, Hetosa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development
2 comments



The Abyssinian war lord Menelik, also known as African Hitler, cut the right hands and breasts of men and women, respectively, during his conquest of Oromia and the rest of today’s people and lands of Southern Ethiopia in 1880s. During Emperor Hailesellasie and Mengistu Hailemariam’s Dergue time the erection of Aannole memorial monument was not thinkable. The present state of Oromia has spent over a million dollar to build the Aanolee Oromo Martyrs’ memorial monument. Many admirers of the genocidal Menelik have opposed to the erection of memorial center but there is nothing they could do to prevent this inauguration. Aannole observed the largest human gathering on the 6th April 2014 on the event of inauguration of the monument and the historical museum.







The Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument was unveiled in Hetosa, Arsi, Oromiyaa, on April 6, 2014 – also inaugurated was the Aannolee Cultural/Historical Museum. The Monument commemorates the Oromo martyrs whose limbs and breasts were cut off atrociously by the invading Abyssinian/Shoan Amhara army of Menelik II in 1886. Known as the harmaf harka muraa Aannolee, the Menelik’s Abyssinian/Shoan Amhara army mutilated an unknown number of Oromo men’s right hands and Oromo women’s breasts for resisting Abyssinia’s conquest of the Oromo land.
According to the recently published book by Prof. Abbas H. Gnamo, “Conquest and Resistance in the Ethiopian Empire, 1880-1974 – The Case of the Arsi Oromo,” the Aannolee Oromo Martyrdom has “become the symbol of Oromo resistance.”
Prof. Gnamo continues:
“Of all the brutalities committed by the Shoan army and its leaders against the Oromo, the worst was the Anole mutilation known as harmaf harka muraa Anole (the mutilation of hands and breasts at Anole) – a tragedy on which Ethiopian sources are silent …
… Anole is located about 25km north of Asella, an area where most battles took place and where the Arsi inflicted heavy losses on the Shoan army. Anole seemed to have been chosen to avenge Shoan losses and to teach a lesson to the Arsi who still resisted after their shattering defeat at Azule on September 6, 1886. Arsi strong men and women were assembled under the pretext of concluding peace. All the men and women present, whose exact number was unknown perhaps more than thousand people, were mutilated; their right hands and right breasts were cut off. As a further form of humiliation, fear and terror, the mutilated breasts and hands were tied around the necks of the victims who were then sent back home.”
http://gadaa.com/oduu/25205/2014/04/06/in-pictures-the-unveiling-of-the-aannolee-oromo-martyrs-memorial-monument-in-hetosa-oromiyaa/



THE EXPANSION OF THE AMORPHOUS ADDIS ABABA, THE ENDLESS PERSECUTION AND EVICTION OF TULAMA OROMOO April 6, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo Valley, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny.Tags: African Studies, Finfinnee, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
The deliberate expansion of the amorphous city they call “Addis Ababa” is politically created to divide Oromiyaa into east and west sector. It is not a master plan. It is an evil plan mastered to consummate an evil goal.
When we see the history of Abyssinian political philosophy, from which we have a written record, it is entirely based on the philosophy of depriving the Oromos from having any right to homeland. To convert Oromummaa to Amaarummaa and ultimately to Itiyophiyawwinnet has been the policy in action up to this very day.
What happened to those Oromos who were living in Finfinnee for centuries? Particular mention has to be made about those Tulama Oromo groups of Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Aabbuu, Jillee. The answer is very simple: They were mercilessly decimated; their villages burnt down, their pasture and arable lands confiscated and shared among the invading Manzian Nagasii families of whom the Dejazmach Mangasha Seifu and the Ras Birru families were the most notorious ones. Thereafter, the Oromo territory occupied by Matcha-Tulama was officially changed to the expanding Kingdom of Showa, a detached enclave from Gonder, Abyssinia. Finfinnee was given a new colonial name “Addis Ababa”, just like Zimbabwe was changed to Rhodesia, Harare to Salisbury. Under this excruciating condition, the conquered Matcha-Tulama region had to lose its historic significance and had to be involuntarily submitted to the colonial name Showa.
Among the major Oromo descent groups, the Matcha-Tulama group has got one of the largest populations, stretching on vast area of land in central and western Oromia. As we are able to learn from our fathers, Matcha and Tulama are Borana brothers, being Tulama angafa (first born) and Matcha qixisuu (second born son). As common to all Oromo ethno-history, the tradition that governs the social role of “angafa and qixisuu”, which begins right from the immediate family unit, has a deep genealogical meaning and social role in re-invigorating the solidarity of the nation. From the earliest time of which we have a tradition hanging down to us,
- Matcha-Tulama Oromo has had a supreme legislative organ known as Chaffe. The Chaffe legislates laws which will eventually be adopted as Seera Gadaa
They have a senatorial council known as “Yaa’ii Saglan Booranaa”, in which elected individuals from major clans are represented. The function of Yaa’ii Saglan Booranaa is to deliberate on issues pertaining to regional issues, resolve inter-clan disputes and oversees how interests of each clan in the confederacies are represented; how local resources are fairly shared and wisely utilised according to the law.
- These two northern Boorana brothers are historically referred to as Boorana Booroo or Boorana Kaabaa
- Among the known five Oromo Odaas, Odaa Nabee and Odaa Bisil are found in Boorana Booroo
However, beginning from the 13th century onward, the Match-Tulama country (Boorana Booroo), adjacent to Abyssinian border, has begun to be ravaged by a group of individuals whose legendary genealogy connects them to a certain King Solomon of non-African origin. They came and settled at a place they call “Manz”.They organised themselves at this place, and started to attack neighbouring villages of Cushitic Oromo family stock of Laaloo, Geeraa and Mammaa. The attacked villages were gradually incorporated into the expanding Manz, which eventually developed to a military outpost known as Showa in the late 18th century. Hereafter, they declared themselves “Ye Negasi Zer, the root of Showa Amhara Dynasty.
After vanquishing Agaw people’s identity and sovereignty on the northern frontier, the Solomonic Negasi Dynasties of Showa intensified their attacks against the Match-Tulama of Borana and the Karrayyu of Barantu Oromos. In such turbulent situation, the rule of yeNegasi Zer entered nineteenth century era, which ushered the era of the Scramble for Africa by European imperialist powers. From Africa, it was only King Minilik of Showa (1866-1889) who was recognised as a partner and invited to attend the Berlin Imperialist Conference of 1884. In this conference, Minilik was represented by his cousin, Ras Mekonnen Tenagneworq Sahile-Sellasie (1852-1906). After completing their mission, King Minilik and the European imperialist powers made concession on border demarcation. After the border demarcation had been completed, a systematic elimination of his prominent general, Ras Goobanaa Daacci (1819-1889), was meticulously carried out. Minilik was so confident to declare himself Emperor of Ethiopia (1889- 1913).This was the Ethiopia, the first time in the history of the region, that brutally annexed and included Oromo, Sidama, Walaita, Kaficho, Beneshangul, Gambella, and others to the expanding of Abyssinia.
The years 1887-89 were the boiling point for Minilik’s declaration of being “Emperor of Ethiopia, yeItiyophiya Nuguse, nägest. Why?
- Because, it was the time when he exterminated the Gullallee Oromo from the marshy-hot spring and pasture land of Finfinnee and collectivised the place under a new colonial name Addis Ababa.
- Because, it was the time when he built full confidence in himself and built his permanent palace at Dhaqaa Araaraa, a sacred hill, where the evicted Oromos peacefully used to sit together and conduct peaceful deliberation for reconciliation.
- It was the time when he annexed three-fourth of southern peoples’ territories, including the Oromo territory, to the expanding Showan Dynasty and put under the iron-fist of his inderases(viceroys).
- It was the time when he assured un-shivering confidence of being continued to be assisted and advised by his European colonial partners: militarily, diplomatically and technically.
Here is the question: What happened to those Oromos who were living in Finfinnee for centuries? Particular mention has to be made about those Tulama Oromo groups of Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Aabbuu, Jillee. The answer is very simple: They were mercilessly decimated; their villages burnt down, their pasture and arable lands confiscated and shared among the invading Manzian Nagasii families of whom the Dejazmach Mangasha Seifu and the Ras Birru families were the most notorious ones. Thereafter, the Oromo territory occupied by Matcha-Tulama was officially changed to the expanding Kingdom of Showa, a detached enclave from Gonder, Abyssinia. Finfinnee was given a new colonial name “Addis Ababa”, just like Zimbabwe was changed to Rhodesia, Harare to Salisbury. Under this excruciating condition, the conquered Matcha-Tulama region had to lose its historic significance and had to be involuntarily submitted to the colonial name Showa.
In addition to the former derogatory term “Galla”, imposed on the conquered Oromos as a whole, the new regional name of Showa is prefixed to the derogatory term Galla. Hence, “ye Showa Galla” came into force as a collective insulting name in addressing the whole Oromo of Matcha-Tulama. This clearly justifies the vertical segregation policy of the conquerors for easy identification of who is who in the newly colonised territory.
Using various forms of oppressive models, Abyssinian colonial tactics and strategies have been going on violently and, now entered into the first half of the 21st century. Since the second half of the 19thcentury in particular, the oppressive models have been amassing massive firearms from European colonialist partners, enjoying diplomatic immunities and profitable political advises.
In the late 19th century, one European writer commented that, if the Abyssinians had not been armed and advised by global colonial powers of the day, notably France and Britain, late alone to defeat the ferocious Oromo forces, they could not have even dared to encroach upon the limits of Oromo borders. He wrote what he witnessed the real situation of the time as follows:
“Against the Galla [Oromo] Menelik has operated with French technicians, French map-makers, French advice on the management of standing army and more French advice as to building captured provinces with permanent garrison of conscripted colonial troops. The French also armed his troops with firearms, and did much else to organize his campaigns. Menelik was at a work on these adventures as King of Shewa during John’s lifetime; adding to his revenues and conscripting the Oromo were thus conquered by the Amhara for the first time in recorded history during the last thirteen years of the nineteenth Century. Without massive European help the Galla [Oromo] would not have been conquered at all.”
The writer further explained what he personally encountered during the campaign in the following unambiguous language:
“A large expedition was sent as far South in Arsi as frontier of Kambata to return with100, 000 head of Cattle. The king’s army fought against tribes who have no other weapons but a lance, a knife and shield, while the Amahras always have in their army several thousand rifles, pistols and often a couple cannon.—-Captive able-bodied males and the elderly were killed. The Severity of the Zamacha [campaign] was aimed at the eradication of all resistance. Whenever the army surged forward, there was the utmost devastation. Houses were burned, crops destroyed, and people executed:”
When we see the history of Abyssinian political philosophy, from which we have a written record, it is entirely based on the philosophy of depriving the Oromos from having any right to homeland. To convert Oromummaa to Amaarummaa and ultimately to Itiyophiyawwinnet has been the policy in action up to this very day. Even though the policy works on all Oromos indiscriminately, the one which has been exercising on the Oromos of Tulama in Finfinnee and surrounding areas has its own unique feature. Some of the unique features are embedded in the formation of “Addis Ababa” itself; as a seat of colonial headquarters with all its oppressive machineries. To have ample space for the settlers, to build army headquarters, to build churches in the name of numerous Saints of Greek and Hebrew origins, to build residences and offices for foreign embassies and missionaries, to build factories and storage houses the crucial demand is land. To fulfil these crucial demands of the customers, helpless Oromo peasants of the area have to be evicted. They have been under routine eviction and land deprivation since the seizure of Burqaa Finfinnee and the establishment of Ethiopian Imperial capital at this place.
It could be incorrect to think of the current TPLF-Arinnet Tigray regime as a detached entity from the whole system of Abyssinian colonial regimes, when we equate what they need against the survival needs of the peoples they generically conquered as “Galla and Shanqilla”. Though since 1991, the Ethiopian imperial system has been overtaken from the Showan Nagasi Dynasty by their junior Tigrean brethren, the life of the colonised Oromo people has been going down from worse to the worst.
What makes TPLF-Arinnet Tigray different from its predecessors is its total monopolisation of resources of the empire, right from the imperial palace to the bottom village levels, from the centre to the periphery. Arable and pasture lands, plain and forest lands, rivers and mining areas are totally under its predatory control. It is routinely evicting peasants from their plots, their only means of existence. They are selling to Chinese, Indians, European, Turkish, Pakistani, Arabians and other companies at the lowest price. In making this huge business, the most preferable area in the empire is Oromoland; of which the land around Finfinee holds rank first.
This politically architected scheme, in the name of investment and development, is daily evicting Oromo peasants around Finfinnee often with meagre or no compensation at all. As a consequence,
- some of the evicted families are migrating to cities like Finfinnee and are becoming beggars
- Some of them are leaving the country for unknown destination and found being refugees in neighbouring countries like Kenya and Yemen.
- Since most of them who have no any alternative, they remain on the sold land and become daily labourers, earning less than half dollar a day.
- Farm lands that had been producing sufficient grains of various types are now turned to produce non-edible flowers and toxic chemicals that contaminate rivers and lakes.
The incumbent Ethiopian regime of TPLF-Arinnet Tigray, more than any other imperial regimes of the past, is committed to make the Oromo people an “African Gypsy”. At one time the deceased prime minister of the Empire and EPDRF leader, Meles Zenawi, refers to the Oromos, who are numerically majority ethnic group in the Empire, said, “It is easy to make them a minority”. They are practically showing us the evil mission they vowed to accomplish. When they become rich of the richest in the Empire, the Oromo peasants they are daily uprooting are becoming poor of the poorest, being reduced to beggary and often deprived of burial sites after death. This evil work, as indicated above, has given priorities to sweep off “garbage” around Finfinnee and ultimately to encompass three-fourth of the region of “Showa” as a domain of “non-garbage” dwellers.
As vividly explained above, the Oromo of Tulama, since the onset of colonisation, have begun to be collectively addressed as “ye Showa Galla”. Those who resisted the derogatory name, the eviction, and the slavery system have been inhumanly executed or hanged. Their land and livestock have been confiscated and shared among the well-armed conquering power.
When Minilik invaded the Gullalle Oromo in Finfinnee, for instance, they remarkably resisted to the last minute but finally defeated. Those who remained behind the massacre had no other option except to leave for other regions against their choice. In their new homes, they have been even treated as collaborators of the invading “Showans” by their own kinsmen, calling them “Goobanaa”.Those able-bodied Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Abbichuu youths were involuntarily conscripted to the colonial army which is typical to all colonial policies. They were forced to go for further campaign to the south, east and west commanded by Showan fitawuraris and dejazmaches
From time to time, all Abyssinian forces, changing forms of their names, swearing in the name of Ethiopian unity and inviolable sovereignty, have never turned down the initial policy of evicting and persecuting the Oromo from their ancestral araddaa. Araddaa Oromoo is the embryonic stage whereOromummaa has begun to radiate from. Hence, by virtue of its original formation, now and then, it could not be integrated into the enforced Abyssinian policy of Itiyophiyawwinnet .
Since the enforced policy has shown no visible success for the past 130 years, this time, it has taken on to shoulder the last option of “sweeping them off” from around what they call “Addis Ababa” as a priority number one. As a consequence, came into being the destruction of Oromo survival relationship with their ancestors’ plot of land. The desecration of their shrines, sacred rivers, sacred mountains and sacred trees of which the case of Odaa and Burqaa Finfinnee, Dhakaa Araaraa and Caffee Tumaa in the vicinity of Finfinnee are quite enough to mention. TPLF’s long range missile policy of destroying Oromos’ relation to their historic araddaa is not the end. It is just the beginning extrapolated to destroy Biyyoo Oromoo.
At this critical time, any concerned Oromo should not be oblivious of the dreadful situation going on in Oromiyaa right now; in Finfinnee and surrounding areas in particular. The deliberate expansion of the amorphous city they call “Addis Ababa” is politically architected to divide Oromiyaa into east and west sector. It is not a master plan. It is an evil plan mastered to consummate an evil goal.
At this critical time, may we believe in the “No life after death”? Rather, may we are for the life right now? Those who are for the life right now are genuinely expected to show discernible power through tangible solidarity to our victimised families at home. Pursuant to our tradition, we have been nurtured learning the wisdom of “Dubbiin haa bultu”. Now, we should redirect this wisdom to “Dubbiin kun hin bultu”,that we ought to swear by great confidence to move in unison against the inhuman act, endless atrocities and perpetual eviction of our families from their ancestral araddaa. Thereof, could we recall the intrinsic wisdom of our fathers’ saying “Tokko dhuufuun namummaadha, lama dhuufuun harrummaadha?”
Urban centers in Oromia:The integration of indigenous Oromo towns into the Ethiopian colonial structure and the formation of garrison and non-garrison cities and towns April 3, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Colonizing Structure, Finfinnee, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo Valley, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development and Change, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Since urban areas and cities are primarily populated by Ethiopian colonial settlers and their collaborators, they are the ones who have access to the limited public facilities such as schools and hospitals. Oromo urbanites like the rural counter parts have been exposed to massive and absolute poverty and have been denied fundamental human rights and needs that Ron Shiffman (1995, 6-8) calls subsistence, protection, affection, and understanding. Most Oromos in urban and rural areas have low levels of subsistence because they lack adequate income, enough food, and livable homes. they do not have protection from disease because they are denied adequate access to health and
medical services.They do not have protection from political violence because the Ethiopian state engages in massive human rights violations and state terrorism ( Jalata 2000). Oromos have been ruled by successive authoritarian-terrorist regimes which have exploited and impoverished them by expropriating their resources. ….The Oromos have been prevented from developing autonomous institutions, organizations, culture, and language, and have been subordinated to the
institutions and organizations of the Habasha colonial settlers in their own cities, towns, and homeland.
Read more @http://works.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1052&context=asafa_jalata
In Ethiopia 40.2% of population are undernourished and the country is one of the world’s 10 hungriest countries April 2, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Ethnic Cleansing, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: African culture, Developing country, Development, Economic development, Economic growth, Ethiopia, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Hunger, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromiyaa, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
- There are over 870 million people in the world who are hungry right now. I’m not talking about could use a snack before lunch hungry, not even didn’t have time for breakfast hungry, but truly, continually, hungry. Of these 870 million people, it’s been estimated by the World Food Programme that 98% live in developing countries, countries that perversely produce most of the world’s food stocks. So why is this the case?
- In Ethiopia an alarming 40.2% of population are undernourished.The 2011 Horn of Africa drought left 4.5 million people in Ethiopia in need of emergency food assistance. Pastoralist areas in southern and south-eastern Ethiopia were most severely affected by the drought. At the same time, cereal markets experienced a supply shock, and food prices rose substantially, resulting in high food insecurity among poor people. By the beginning of 2012, the overall food security situation had stabilized thanks to the start of the Meher harvest after the June-to-September rains resulting in improved market supply — and to sustained humanitarian assistance. While the number of new arrivals in refugee camps has decreased significantly since the height of the Horn of Africa crisis, Ethiopia still continues to receive refugees from Somalia, Sudan and South Sudan. The Humanitarian Requirements Document issued by the government and humanitarian partners in September 2012 estimates that 3.76 million people require relief food assistance from August to December 2012. The total net emergency food and non-food requirement amounts to US$189,433,303. Ethiopia remains one of the world’s least developed countries, ranked 174 out of 187 in the 2011 UNDP Human Development Index.
Read more @ http://www.globalcitizen.org/Content/Content.aspx?id=d7f0ac9b-e3a3-4233-8103-0348bb35e127
Ethiopia: Farmer gets legal aid from UK to sue Britain for giving aid to the brutal regime of Ethiopia March 30, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa Rising, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Ethnic Cleansing, Hadiya and the Omo Valley, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
An Ethiopian farmer has been given legal aid in the UK to sue Britain – because he claims millions of pounds sent by the UK to his country is supporting a brutal regime that has ruined his life.
He says UK taxpayers’ money – £1.3 billion over the five years of the coalition Government – is funding a despotic one-party state in his country that is forcing thousands of villagers such as him from their land using murder, torture and rape.
The landmark case is highly embarrassing for the Government, which has poured vast amounts of extra cash into foreign aid despite belt-tightening austerity measures at home.
Prime Minister David Cameron claims the donations are a mark of Britain’s compassion.
But the farmer – whose case is set to cost tens of thousands of pounds – argues that huge sums handed to Ethiopia are breaching the Department for International Development’s (DFID) own human rights rules.
He accuses the Government of devastating the lives of some of the world’s poorest people rather than fulfilling promises to help them. The case comes amid growing global concern over Western aid propping up corrupt and repressive regimes.
If the farmer is successful, Ministers might have to review major donations to other nations accused of atrocities, such as Pakistan and Rwanda – and it could open up Britain to compensation claims from around the world.
Ethiopia, a key ally in the West’s war on terror, is the biggest recipient of British aid, despite repeated claims from human rights groups that the cash is used to crush opposition.
DFID was served papers last month by lawyers acting on behalf of ‘Mr O’, a 33-year-old forced to abandon his family and flee to a refugee camp in Kenya after being beaten and tortured for trying to protect his farm.
He is not seeking compensation but to challenge the Government’s approach to aid. His name is being withheld to protect his wife and six children who remain in Ethiopia.
‘My client’s life has been shattered by what has happened,’ said Rosa Curling, the lawyer handling the case. ‘It goes entirely against what our aid purports to stand for.’
Africa Rising: So What? March 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Food Production, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, Genocide, Governance issues, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
This study critically discuses the “Africa rising” story and the sub-narratives it carries, including the rise of the African woman, the rise of the African middle class and the power of innovation. The articles included inform that, in too many cases, it is not the wider population but small segments and interested parties, such as the local political elite and foreign investors, who are benefiting from economic growth and resource wealth. Social cohesion, political freedom and environmental protection carry little importance in the comforting world of impressive growth statistics. The glamorous images of Africa’s prominent women and rising middle class produced and re-produced in the media prevent the less attractive and more complex stories about ordinary people’s daily struggles from being heard.
GDP tells us nothing about health of an economy, let alone its sustainability and the overall impact on GDP is simply a measure of market consumption, which has been improperly adopted to assess economic performance. Rebuilding Libya after the civil war has been a blessing for its GDP. But does that mean that Libya is on an enviable growth path? When there is only one brick left in a country devastated by war or other disasters, then just making another brick means doubling the economy (100 percent growth). Another problem is the reliability of GDP statistics in Africa. Economic growth figures for most African countries are incomplete, thus undermining any generalisation about overall economic performance in the continent. Besides statistical problems, there are important structural reasons why one should be suspicious of the ‘Africa rising’ mantra. Most fast- growing Africa economies are heavily dependent on exports of commodities.
Read the full articles @:
Click to access perspectives_feb_2014_web1.pdf
“About 30% of sub-Saharan Africa’s annual GDP has been moved to secretive tax havens.”
http://www.fairobserver.com/article/africa-illicit-outflow-84931
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Africa’s youth and the self-seeking repressive elites March 15, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Finfinnee, Food Production, Human Rights, International Economics, International Trade, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromummaa, Poverty, Saudi Arabia, Self determination, Slavery, South Sudan, Specialization, State of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Africa's repressive elites, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, State and Development, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
Africa’s youth will protest to remove self-seeking and repressive elites
“Some examples: authoritarian regimes, as in Ethiopia and Rwanda, are consolidating their positions. In Zambia, Angola and Mozambique, the press, civil society organisations and the opposition are under threat for demanding that the proceeds from raw material exports and billion dollar multinational corporate investments should benefit everyone. ….Short-term greed is, once again, depriving the African populations of the right to share in the continent’s immense riches. No-one can predict the future, but what can be said with certainty is that the possibility of a sustainable long-term and fair development that is currently at hand in Africa is being put at risk. The frustration that is fuelled among populations that are hungry and feel ignored by their rulers will bring about increasingly strident and potentially violent protest. In the near future, this will change the political climate, not least in urban areas. Utilising the internet and their mobile phones, Africa’s youth and forgotten people will mobilise and act together to remove self-seeking and repressive elites. But the situation is not hopeless, on the contrary. Civil society is growing stronger in many places in Africa. The internet makes it possible for people to access and disseminate information in an unprecedented way. However, I get really disappointed when I hear all the ingenuous talk about the possibilities to invest and make quick profits in the ‘New Africa’. What is in reality new in the ‘New Africa’? Today, a worker in a Chinese-owned factory in Ethiopia earns one-tenth of the wage of an employee in China. Unless African governments and investors act more responsibly and ensure long-term sustainable construction for people and the environment ‒ which is currently not the case ‒ we must all ask ourselves if we should not use the consumer power we all possess to exert pressure. There are no excuses for letting African populations and their environment once again pay for the global demand for its raw materials and cheap consumer goods.” – Marika Griehsel, journalist, film-maker and lecturer
“Thousands of people are demonstrating on the streets to protest against low salaries, the highcost of living and an insufficient state safety net. A reaction to austerity measures in Greece? Or a follow-up to the Arab Spring? No, these are protests for greater equality in Sub-Saharan Africa, most recently in Burkina Faso. The widening gap between rich and poor is as troubling in Africa as in the rest of the world. In fact, many Africans believe that inequalities are becoming more marked: A tiny minority is getting richer while the lines of poor people grow out the door. The contrast is all the more striking in Africa since the poverty level has been at a consistently high level for decades, despite the continent’s significant average GDP growth. Some take a plane to get treated for hay fever, while others are pushing up daisies because they can’t afford basic malaria treatment.”
– Global Voices: http://globalvoicesonline.org/2014/03/11/reducing-the-gap-between-africas-rich-and-poor/
It is now evident that the African ‘lion economies’ have hardly even begun the economic and democratic transformation that is absolutely necessary for the future of the continent.
The largest movement ever in Africa of people from rural to urban areas is now taking place. Lagos, Nigeria, and Nairobi, Kenya, are among the world’s fastest growing cities.
The frustration that is fuelled among populations that are hungry and feel ignored by their rulers will bring about increasingly strident and potentially violent protest.
Soon, this will change the political climate, not least in urban areas. Utilising the internet and their phones, Africa’s youth and forgotten people will mobilise to remove self-seeking and repressive elites.
This piece was written in Namibia, where I was leading a tour around one of Africa’s more stable nations. There are several signs confirming the World Bank’s reclassification of Namibia as a middle-income country, which in turn means that many aid donors, including Sweden, have ended their bilateral cooperation.
I see newly constructed, subsidised single-family homes accessible for low-income families. I drive on good roads and meet many tourists, although this is off-season. I hear about a growing mining sector, new discoveries of natural gas and oil deposits. I read about irregularities committed by people in power, in a reasonably free press whose editors are not thrown into jail. There is free primary level schooling and almost free health care.
Most people I talk to are optimistic. A better future for a majority of Namibians is being envisaged. This is in all probability the result of the country having a small population ‒ just above 2 million ‒ and a functioning infrastructure despite its large area.
In Namibia, economic growth can hopefully be matched by implementing policies for long-term, sustainable social and economic development that will benefit more than the élite.
But Namibia is an exception. Because it is now evident that the African ‘lion economies’ have hardly even begun the economic and democratic transformation that is absolutely necessary for the future of the continent.
Some examples: authoritarian regimes, as in Ethiopia and Rwanda, are consolidating their positions. In Zambia, Angola and Mozambique, the press, civil society organisations and the opposition are under threat for demanding that the proceeds from raw material exports and billion dollar multinational corporate investments should benefit everyone.
The International Monetary Fund, IMF, predicts continued high growth rates across Africa with an average of over 6 per cent in 2014. That is of course good news for the continent. Perhaps the best, from a macroeconomic viewpoint, since the 1960s, when many of the former colonies became independent. This growth is mainly driven by the raw material needs of China, India and Brazil.
Meanwhile, the largest movement ever in Africa of people from rural to urban areas is now taking place. Lagos, Nigeria, and Nairobi, Kenya, are among the world’s fastest growing cities. But, in contrast with China, where the migrants from the rural areas get employment in the manufacturing industry, the urban migrants in Africa end up in the growing slums of the big cities.
In a few places, notably in Ethiopia, manufacturing is beginning to take off. But the wages in the Chinese-owned factories are even lower than in China, while the corporations pay minimal taxes to the Ethiopian state.
Short-term greed is, once again, depriving the African populations of the right to share in the continent’s immense riches. No-one can predict the future, but what can be said with certainty is that the possibility of a sustainable long-term and fair development that is currently at hand in Africa is being put at risk.
The frustration that is fuelled among populations that are hungry and feel ignored by their rulers will bring about increasingly strident and potentially violent protest. In the near future, this will change the political climate, not least in urban areas. Utilising the internet and their mobile phones, Africa’s youth and forgotten people will mobilise and act together to remove self-seeking and repressive elites.
But the situation is not hopeless, on the contrary. Civil society is growing stronger in many places in Africa. The internet makes it possible for people to access and disseminate information in an unprecedented way. However, I get really disappointed when I hear all the ingenuous talk about the possibilities to invest and make quick profits in the ‘New Africa’.
What is in reality new in the ‘New Africa’?
Today, a worker in a Chinese-owned factory in Ethiopia earns one-tenth of the wage of an employee in China. Unless African governments and investors act more responsibly and ensure long-term sustainable construction for people and the environment ‒ which is currently not the case ‒ we must all ask ourselves if we should not use the consumer power we all possess to exert pressure.
There are no excuses for letting African populations and their environment once again pay for the global demand for its raw materials and cheap consumer goods.
Some examples: authoritarian regimes, as in Ethiopia and Rwanda, are consolidating their positions. In Zambia, Angola and Mozambique, the press, civil society organisations and the opposition are under threat for demanding that the proceeds from raw material exports and billion dollar multinational corporate investments should benefit everyone.
http://naiforum.org/2014/03/africas-youth-will-protest/
The World Bank paints an optimistic picture of African potential, but warns against persistently high inequalities:
Economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) remains strong with growth forecasted to be 4.9% in 2013. Almost a third of countries in the region are growing at 6% and more, and African countries are now routinely among the fastest-growing countries in the world […] [however the report] notes that poverty and inequality remain “unacceptably high and the pace of reduction unacceptably slow.” Almost one out of every two Africans lives in extreme poverty today.
 http://globalvoicesonline.org/2014/03/11/reducing-the-gap-between-africas-rich-and-poor/
http://globalvoicesonline.org/2014/03/11/reducing-the-gap-between-africas-rich-and-poor/
Ethiopia is one of the poorest countries in the world and has the second largest population in Africa: Poverty means the health system is weak March 9, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Human Rights, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“In the early 80′s, Bob Geldof of the band called The Boomtown Rats saw in the news the massive famine engulfing the African country of Ethiopia. He felt guilty because he couldn’t believe that while the Western world was suffering from an abundance of wealth and food, a continent just below them were a people that did not have anything at all. He organized Band Aid, enlisting the help of other stars like Bono, George Michael and Sting, to raise funds for Africa through a song entitled “Do They Know It’s Christmas?” Their counterparts in the United States followed suit, with Michael Jackson and Lionel Richie writing a song called “We are the World.” They then banded together for Live Aid, that added stars like Madonna, Paul McCartney and Elton John in a two-continent concert. Yet, almost three decades after, Africa remains a veritable wasteland. Out of the 20 poorest countries in the world, 17 comes from the continent, including nine out of the top 10. Based on the different countries’ gross domestic product purchasing power parity, here are the 20 poorest countries in the world in 2013.”
‘Ethiopia is one of the poorest countries in the world and has the second largest population in Africa. Poverty means the health system is weak, which means:
The average life expectancy is just 59
Out of every 40 women that go in to labour, one dies
Over a third of children are malnourished
90% of Ethiopians have poor health, a low level of education, and inadequate living conditions
Only 200 doctors are trained per year to serve a country with a population of over 80 million.
Ethiopia has suffered periodic droughts and famines, a long civil conflict in the 20th century, and a border war with Eritrea. This brought millions to the brink of starvation in the 1970s and 1980s.’
http://www.healthpovertyaction.org/where-we-work/africa/ethiopia/
About 29 per cent of the population lives below the national poverty line. Ethiopia ranks 174th out of 187 countries on the United Nations Development Programme’s human development index, and average per capita incomes are less than half the current sub-Saharan average.
Ethiopia has enormous potential for agricultural development. At present only about 25 per cent of its arable land is cultivated, and agriculture is dominated by subsistence rain fed farming, using few inputs and characterized by low productivity. The vast majority of farmers are smallholders. About 12.7 million smallholders produce 95 per cent of agricultural GDP. These farmers are extremely vulnerable to external shocks such as volatile global markets and drought and other natural disasters.
Smallholder farmers form the largest group of poor people in Ethiopia. More than half cultivate plots of 1 hectare or less and struggle to produce enough food to feed their households. A large number of poor households face a prolonged hunger season during the pre-harvest period. Herders, like farmers, are vulnerable to increasingly frequent drought, which can wipe out their livestock and assets and bring on severe poverty.
The persistent lack of rainfall is a major factor in rural poverty. Drought has become more frequent and severe throughout the country over the past decade, and the trend shows signs of worsening. The impact of drought is most severe for vulnerable households living in the pastoral areas of lowlands and the high-density parts of highlands.
In addition to their vulnerability to climatic conditions, poor rural people lack basic social and economic infrastructure such as health and education facilities, veterinary services and access to safe drinking water. Among the more specific causes of rural poverty in Ethiopia are:
• An ineffective and inefficient agricultural marketing system;
• Underdeveloped transport and communications networks;
• Underdeveloped production technologies;
• Limited access of rural households to support services;
• Environmental degradation;
• Lack of participation by rural poor people in decisions that affect their livelihoods.
The intensity of poverty varies at the household level in relation to the land’s size, quality and productivity, climate conditions and production technologies. Households headed by women are particularly vulnerable. Women are much less likely than men to receive an education or health benefits, or to have a voice in decisions affecting their lives. For women, poverty means more infant deaths, undernourished families, lack of education for children and other deprivations.
Ethiopia has an estimated 1.3 million people living with HIV and AIDS. Rural areas have low prevalence rates, but available data suggest that the incidence could increase in these areas. With the support of development partners, the government has embarked on major programmes to combat the spread of HIV and AIDS, and assist poor rural households in coping with the social and economic consequences of living with the disease.- IFAD
http://www.ruralpovertyportal.org/country/home/tags/ethiopia
‘A Unicef report states that in Ethiopia there are at this moment 4.5 million orphans on a population of some 90 million. The 4.5 million means that 5 percent of the total population is an orphan. Orphans are in Ethiopia defined as children under 18 whose both parents died. They died of AIDS, untreated illnesses, hunger, draught and war.’
A Calculation: The ‘Orphan Crisis’ in Ethiopia
Copyright © Oromianeconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.
US Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor 2013 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Ethiopia February 28, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, African Poor, Colonizing Structure, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Ethiopia, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Ethiopia:2013 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices
By US Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor
27 February 2014
- The most significant human rights problems included: restrictions on freedom of expression and association, including through arrests; detention; politically motivated trials; harassment; and intimidation of opposition members and journalists, as well as continued restrictions on print media.
- Other human rights problems included arbitrary killings; allegations of torture, beating, abuse, and mistreatment of detainees by security forces; reports of harsh and, at times, life-threatening prison conditions; arbitrary arrest and detention; detention without charge and lengthy pretrial detention; a weak, overburdened judiciary subject to political influence; infringement on citizens’ privacy rights, including illegal searches; allegations of abuses in the implementation of the government’s “villagization” program; restrictions on academic freedom; restrictions on freedom of assembly, association, and movement; alleged interference in religious affairs; limits on citizens’ ability to change their government; police, administrative, and judicial corruption; violence and societal discrimination against women and abuse of children; female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C); trafficking in persons; societal discrimination against persons with disabilities; clashes between ethnic minorities; discrimination against persons based on their sexual orientation and against persons with HIV/AIDS; limits on worker rights; forced labor; and child labor, including forced child labor.
- Impunity was a problem. The government, with some reported exceptions, usually did not take steps to prosecute or otherwise punish officials who committed abuses other than corruption.
- Members of the security forces reportedly committed killings. On August 8, security forces in Addis Ababa detained more than one thousand Muslims participating in Eid al-Fitr celebrations. Authorities released most of the detainees shortly thereafter, but there were credible allegations some of the detainees died while in detention. There continued to be reports of abuses, including killings, by the Somali Region Special Police.
- A few domestic human rights groups operated, but with significant government restrictions. The government was generally distrustful and wary of domestic human rights groups and international observers. State-controlled media were critical of international human rights groups such as Human Rights Watch.
- The CSO law prohibits charities, societies, and associations (NGOs or CSOs) that receive more than 10 percent of their funding from foreign sources from engaging in activities that advance human and democratic rights or promote equality of nations, nationalities, peoples, genders, and religions; the rights of children and persons with disabilities; conflict resolution or reconciliation; or the efficiency of justice and law enforcement services. The implementation of the law continued to result in the severe curtailment of NGO activities related to human rights. In July 2012 the UN high commissioner for human rights expressed concern that civil society space “has rapidly shrunk” since the CSO law’s enactment.
- The country has more than 80 ethnic groups, of which the Oromo, at approximately 35 percent of the population, is the largest. The federal system drew boundaries roughly along major ethnic group lines. Most political parties remained primarily ethnically based.
- Clashes between ethnic groups during the year resulted in injury and death. In January ethnic clashes broke out at Addis Ababa University reportedly due to anti-Oromo graffiti. The clashes resulted in injury to as many as 20 persons.
- The government, controlled by the ruling EPRDF, restricted media freedom and arrested opposition members. Constituent parties of the EPRDF conferred advantages upon their members; the parties directly owned many businesses and were broadly perceived to award jobs and business contracts to loyal supporters. Several opposition political parties reported difficulty in renting homes or buildings in which to open offices, citing visits by EPRDF members to the landlords to persuade or threaten them not to rent property to these parties. There were reports authorities had terminated the employment of teachers and other government workers if they belonged to opposition political parties.
- According to sources, the ruling party via the Ministry of Education continued to give preference to students loyal to the party in assignments to postgraduate programs. Some university staff members commented that priority for employment after graduation in all fields was given to students who joined the party. Authorities limited teachers’ ability to deviate from official lesson plans. Numerous anecdotal reports suggested non-EPRDF members were more likely to be transferred to undesirable posts and bypassed for promotions. There were unspecified reports of teachers not affiliated with the EPRDF being summarily dismissed for failure to attend unscheduled meetings. There continued to be a lack of transparency in academic staffing decisions, with numerous complaints from individuals in the academic community alleging bias based on party membership, ethnicity, or religion. According to multiple credible sources, teachers and high school students in grade 10 and above were required to attend training on the concepts of revolutionary democracy and EPRDF party ideology.
- The state-owned Ethio Telecom was the only internet service provider in the country. The government restricted access to the internet and blocked several websites, including blogs; opposition websites; and websites of Ginbot 7, the OLF, and the ONLF. The government also temporarily blocked news sites such as al-Jazeera. Websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and Yahoo! were temporarily inaccessible at times. Several news blogs and websites run by opposition diaspora groups were not accessible. These included Addis Neger, Nazret, Ethiopian Review, CyberEthiopia, Quatero Amharic Magazine, Tensae Ethiopia, and the Ethiopian Media Forum. Authorities took steps to block access to Virtual Private Network providers that let users circumvent government screening of internet browsing and e-mail. According to the International Telecommunication Union, approximately 1.5 percent of individuals used the internet in 2012. In March, Citizen Lab, a Canadian research center at the University of Toronto, identified 25 countries, including Ethiopia, that host servers linked to FinFisher surveillance software. According to the report, “FinFisher has gained notoriety because it has been used in targeted attacks against human rights campaigners and opposition activists in countries with questionable human rights records.”
- Estimates by human rights groups and diplomatic missions regarding the number of political prisoners varied. The government did not permit access by international human rights organizations.
- All of the Ethiopian journalists, opposition members, and activists previously convicted and jailed under the antiterrorism proclamation remained in prison.
- On January 8, the Federal Court of Cassation denied journalist Reyot Alemu’s appeal of her conviction on the charge of participating in the promotion or communication of a terrorist act. She was serving a five-year prison sentence.
- On May 2, the Federal Supreme Court upheld the sentences of journalist and blogger Eskinder Nega and vice chairman of the opposition front Medrek Andualem Arage for terrorism and treason. In September 2012 the government announced it asked the Federal High Court to freeze the assets of Eskinder and Andualem while investigating whether their assets were used in conjunction with the commission of the crimes for which they were convicted. The court had not issued a decision by year’s end.
- The Federal Supreme Court upheld the 2012 convictions under the criminal code of Bekele Gerba and Olbana Lelisa, two well-known political opposition figures from the Oromo ethnic group, for conspiracy to overthrow the government and conspiracy to incite unrest. The Supreme Court subsequently determined the Federal High Court did not consider mitigating circumstances and reduced Bekele’s sentence from eight years to three years and seven months. The Supreme Court also reduced Olbana’s sentenced from 13 to 11 years. Courts convicted 69 members of Oromo political opposition parties, charged separately in 2011 under the criminal code with “attacking the political or territorial integrity of the state.”
http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2013/af/220113.htm#
– See more at: http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/humanrightsreport/index.htm?dlid=220113&year=2013#wrapper
Ethiopia is a federal republic. The ruling Ethiopian Peoples’ Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF), a coalition of four ethnically based parties, controls the government. In September 2012, following the death of former Prime Minister Meles Zenawi, parliament elected Hailemariam Desalegn as prime minister. In national parliamentary elections in 2010, the EPRDF and affiliated parties won 545 of 547 seats to remain in power for a fourth consecutive five-year term. Although the relatively few international officials allowed to observe the elections concluded that technical aspects of the vote were handled competently, some also noted that an environment conducive to free and fair elections was not in place prior to the election. Authorities generally maintained control over the security forces, although Somali Region Special Police and local militias sometimes acted independently. Security forces committed human rights abuses.
The most significant human rights problems included: restrictions on freedom of expression and association, including through arrests; detention; politically motivated trials; harassment; and intimidation of opposition members and journalists, as well as continued restrictions on print media. On August 8, during Eid al-Fitr celebrations, security forces temporarily detained more than one thousand persons in Addis Ababa. The government continued restrictions on activities of civil society and nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) imposed by the Charities and Societies Proclamation (the CSO law).
Other human rights problems included arbitrary killings; allegations of torture, beating, abuse, and mistreatment of detainees by security forces; reports of harsh and, at times, life-threatening prison conditions; arbitrary arrest and detention; detention without charge and lengthy pretrial detention; a weak, overburdened judiciary subject to political influence; infringement on citizens’ privacy rights, including illegal searches; allegations of abuses in the implementation of the government’s “villagization” program; restrictions on academic freedom; restrictions on freedom of assembly, association, and movement; alleged interference in religious affairs; limits on citizens’ ability to change their government; police, administrative, and judicial corruption; violence and societal discrimination against women and abuse of children; female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C); trafficking in persons; societal discrimination against persons with disabilities; clashes between ethnic minorities; discrimination against persons based on their sexual orientation and against persons with HIV/AIDS; limits on worker rights; forced labor; and child labor, including forced child labor.
Impunity was a problem. The government, with some reported exceptions, usually did not take steps to prosecute or otherwise punish officials who committed abuses other than corruption.
Factions of the Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF), an ethnically based, violent, and fragmented separatist group operating in the Somali Region, were responsible for abuses.
SECTION 1. RESPECT FOR THE INTEGRITY OF THE PERSON, INCLUDING FREEDOM FROM:
a. Arbitrary or Unlawful Deprivation of Life
Members of the security forces reportedly committed killings.
On August 8, security forces in Addis Ababa detained more than one thousand Muslims participating in Eid al-Fitr celebrations. Authorities released most of the detainees shortly thereafter, but there were credible allegations some of the detainees died while in detention.
There continued to be reports of abuses, including killings, by the Somali Region Special Police.
Scattered fighting continued between government forces – primarily regional government-backed militias – and elements of the ONLF. Clashes between ethnic groups resulted in injury and death.
b. Disappearance
There were several reported cases of disappearances of civilians after clashes between security forces and rebel groups.
Security forces detained at least 12 residents of Alamata town in the northern Tigray Region in January following protests against government plans to demolish illegal housing units. The whereabouts of the detainees remained unknown at year’s end.
c. Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment
The constitution and law prohibit such practices; however, there were reports security officials tortured and otherwise abused detainees.
Authorities reportedly tortured Solomon Kebede, a columnist with Muslim Affairs magazine (see section 2.a.).
Sources widely believed police investigators often used physical abuse to extract confessions in Maekelawi, the central police investigation headquarters in Addis Ababa. Human Rights Watch reported abuses, including torture, occurred at Maekelawi. In an October report the NGO described beatings, stress positions, the hanging of detainees by their wrists from the ceiling, prolonged handcuffing, the pouring of water over detainees, verbal threats, and solitary confinement at the facility. Authorities continued to restrict access by diplomats and NGOs to Maekelawi.
In 2010 the UN Committee Against Torture reported it was “deeply concerned” about “numerous, ongoing, and consistent allegations” concerning “the routine use of torture” by police, prison officers, and other members of the security forces – including the military – against political dissidents and opposition party members, students, alleged terrorists, and alleged supporters of violent separatist groups like the ONLF and the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF). The committee reported that such acts frequently occurred with the participation of, at the instigation of, or with the consent of commanding officers in police stations, detention centers, federal prisons, military bases, and unofficial or secret places of detention. Some reports of such abuses continued during the year.
Prison and Detention Center Conditions
Prison and pretrial detention center conditions remained harsh and, in some cases, life threatening. There were numerous reports that authorities beat prisoners. Medical attention following beatings reportedly was insufficient in some cases.
Physical Conditions: As of September 2012 there were 70,000-80,000 persons in prison, of whom approximately 2,500 were women and nearly 600 were children incarcerated with their mothers. Authorities sometimes incarcerated juveniles with adults and sometimes incarcerated small children with their mothers. Male and female prisoners generally were separated.
Severe overcrowding was common, especially in prison sleeping quarters. The government provided approximately eight birr ($0.42) per prisoner per day for food, water, and health care. Many prisoners supplemented this amount with daily food deliveries from family members or by purchasing food from local vendors, although there were unspecified reports officials prevented some prisoners from receiving supplemental food from their families. Medical care was unreliable in federal prisons and almost nonexistent in regional prisons. Prisoners had limited access to potable water, as did many in the country. Also water shortages caused unhygienic conditions, and most prisons lacked appropriate sanitary facilities. Many prisoners had serious health problems in detention but received little treatment. Information released by the Ministry of Health in 2012 reportedly stated that nearly 62 percent of inmates in various jails across the country suffered from mental health problems as a result of solitary confinement, overcrowding, and lack of adequate health care facilities and services.
The country had six federal and 120 regional prisons. The Ethiopian NGO Justice For All-Prison Fellowship Ethiopia (JFA-PFE) ran model prisons in Adama and Mekele, with significantly better conditions than those found in other prisons. There also were many unofficial detention centers throughout the country, including in Dedessa, Bir Sheleko, Tolay, Hormat, Blate, Tatek, Jijiga, Holeta, and Senkele. Most were located at military camps.
Pretrial detention often occurred in police station detention facilities, where the conditions varied widely. Reports regarding pretrial detention in police stations indicated poor hygiene and police abuse of detainees.
Administration: It was difficult to determine if recordkeeping was adequate due to the lack of transparency regarding incarceration. Authorities did not employ alternative sentencing for nonviolent offenders. Prisons did not have ombudspersons to respond to complaints. Legal aid clinics existed in some prisons for the benefit of prisoners. Authorities allowed the submission by detainees of complaints to judicial authorities without censorship. Courts sometimes declined to hear such complaints. The Ethiopian Human Rights Commission (EHRC) and the Federal Police Commission sometimes investigated allegations of abuse, although there were reports that detainees’ discussions with them were not done in private, which could limit their ability to speak freely.
Authorities generally permitted prisoners to have visitors, although some police stations did not allow pretrial detainees access to visitors (including family members and legal counsel). In some cases authorities restricted family visits to prisoners to a few per year. Family members of prisoners charged with terrorist activity alleged instances of blocked access to the prisoners. There were also reports authorities denied those charged with terrorist activity visits with their lawyers, or with representatives of the political parties to which they belonged. In June prison authorities temporarily granted full visitation privileges to imprisoned journalist/blogger Eskinder Nega; previously, Eskinder was been permitted visits by a select group of individuals. Prison officials limited the number of individuals permitted to visit journalist Reyot Alemu.
Prisoners generally were permitted religious observance, but this varied by prison, and even by section within a prison, at the discretion of prison management. There were some allegations that while in custody authorities denied detainees adequate locations in which to pray. Prisoners were permitted to voice complaints about prison conditions or treatment to the presiding judge during their trials.
Independent Monitoring: During the year the International Committee of the Red Cross visited regional prisons throughout the country.
Regional authorities allowed government and NGO representatives to meet regularly with prisoners without third parties present. The government-established EHRC, which is funded by parliament and subject to parliamentary review, monitored federal and regional detention centers and interviewed prison officials and prisoners in response to allegations of widespread human rights abuses. The JFA-PFE was granted access to various prison and detention facilities.
Improvements: The government and prison authorities generally cooperated with efforts of the JFA-PFE to improve prison conditions. Reports indicated prison conditions, including the treatment of prisoners, improved upon the completion of a local legal aid clinic, although specific data was not available.
d. Arbitrary Arrest or Detention
Although the constitution and law prohibit arbitrary arrest and detention, the government often ignored these provisions. There were multiple reports of arbitrary arrest and detention by police and security forces throughout the country.
Civilians, international NGOs, and other aid organizations operating in the Somali Region reported government security forces, local militias, and the ONLF committed abuses such as arbitrary arrest.
ROLE OF THE POLICE AND SECURITY APPARATUS
The Federal Police reports to the Ministry of Federal Affairs, which is subject to parliamentary oversight. The oversight was loose. Each of the country’s nine regions has a state or special police force that reports to the regional civilian authorities. Local militias operated across the country in loose coordination with regional and federal police and the military, with the degree of coordination varying by region. In many cases these militias functioned as extensions of local EPRDF political bosses.
Security forces were effective, but impunity remained a serious problem. The mechanisms used to investigate abuses by the federal police were not known. There continued to be reports of abuse, including killings, by the Somali Region Special Police. The government rarely publicly disclosed the results of investigations into abuses by local security forces, such as arbitrary detention and beatings of civilians.
The government continued its efforts to provide human rights training for police and army recruits. The EHRC trained more than 100 police officers and prison officials during the year and in 2012 on basic human rights concepts and prisoner treatment. The government continued to accept assistance from the JFA-PFE and the EHRC to improve and professionalize its human rights training and curriculum by including more material on the constitution and international human rights treaties and conventions.
ARREST PROCEDURES AND TREATMENT OF DETAINEES
Although the constitution and law require that detainees be brought to court and charged within 48 hours of arrest, authorities did not always respect this requirement. With court approval, persons suspected of serious offenses may be detained for 14 days without being charged and for additional 14-day periods if an investigation continues. Under the antiterrorism proclamation, police may request to hold persons without charge for 28-day periods, up to a maximum of four months, while an investigation is conducted. The law prohibits detention in any facility other than an official detention center; however, local militias and other formal and informal law enforcement entities used dozens of unofficial local detention centers.
A functioning bail system was in place. Bail was not available for persons charged with murder, treason, and corruption. In most cases authorities set bail between 500 and 10,000 birr ($26 and $530), which most citizens could not afford. The government provided public defenders for detainees unable to afford private legal counsel, but only when their cases went to court. While detainees were in pretrial detention, authorities sometimes allowed them little or no contact with legal counsel, did not provide full information on their health status, and did not provide for family visits.
Arbitrary Arrest: Authorities regularly detained persons without warrants.
On May 24, in the western state of Benishangul-Gumuz, local police detained Muluken Tesfaw, a journalist for the Ethio-Mihdar newspaper, who was investigating allegations that local officials unlawfully evicted ethnic Amhara residents from their homes. The journalist reportedly was not carrying his press credentials. On May 31, authorities released Muluken without charge.
Pretrial Detention: Some detainees reported being held for several years without being charged and without trial. Information on the percentage of detainee population in pretrial detention and the average length of time held was not available. Trial delays were most often caused by lengthy legal procedures, the large numbers of detainees, judicial inefficiency, and staffing shortages.
Amnesty: On September 11, in keeping with a long-standing tradition of issuing pardons at the Ethiopian new year, the federal government pardoned 498 prisoners. Regional governments also pardoned persons during the year. For example, the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People’s Region (SNNPR) regional government pardoned 1,984 prisoners, the Oromia regional government pardoned 2,604 prisoners, and the Amhara regional government pardoned 2,084 prisoners.
e. Denial of Fair Public Trial
The law provides for an independent judiciary. Although the civil courts operated with a large degree of independence, the criminal courts remained weak, overburdened, and subject to political influence. The constitution recognizes both religious and traditional or customary courts.
TRIAL PROCEDURES
By law accused persons have the right to a fair public trial by a court of law within a “reasonable time,” a presumption of innocence, the right to be represented by legal counsel of their choice, and the right to appeal. The law provides defendants the right against self-incrimination. The law gives defendants the right to present witnesses and evidence in their defense, cross-examine prosecution witnesses, and access government-held evidence. The government did not always allow defendants the right of access to evidence it held. The court system does not use jury trials. Judicial inefficiency and lack of qualified staff often resulted in serious delays in trial proceedings and made the application of the law unpredictable. The government continued to train lower court judges and prosecutors and made effective judicial administration the primary focus of this training. Defendants were often unaware of the specific charges against them until the commencement of the trial; this also caused defense attorneys to be unprepared to provide an adequate defense.
The Public Defender’s Office provided legal counsel to indigent defendants, although its scope and quality of service remained limited due to the shortage of attorneys. Numerous free legal aid clinics around the country, based primarily at universities, provided advice to clients. In certain areas of the country the law allows volunteers, such as law students and professors, to represent clients in court on a pro bono basis.
On January 22, citing national security concerns, the Federal High Court closed the trial of 28 Muslims identified with July 2012 protests and one Muslim accused of accepting funds illegally from a foreign embassy. On December 12, the Federal High Court dismissed charges against 10 of the defendants and reduced charges against 18 others. Although the Federal High Court also closed the trial of 28 additional Muslims the government alleged to have links to al-Qaida and al-Shabaab, the court reopened the trial to the public on October 29. Both trials continued at year’s end.
Many citizens residing in rural areas generally had little access to formal judicial systems and relied on traditional mechanisms of resolving conflict. By law all parties to a dispute must agree to use a traditional or religious court before such a court may hear a case, and either party may appeal to a regular court at any time. Sharia (Islamic law) courts may hear religious and family cases involving Muslims. Sharia courts received some funding from the government and adjudicated the majority of cases in the Somali and Afar regions, which are predominantly Muslim. In addition other traditional systems of justice, such as councils of elders, continued to function. Some women stated they lacked access to free and fair hearings in the traditional justice system because they were excluded by custom from participation in councils of elders and because there was strong gender discrimination in rural areas.
POLITICAL PRISONERS AND DETAINEES
Estimates by human rights groups and diplomatic missions regarding the number of political prisoners varied. The government did not permit access by international human rights organizations.
All of the Ethiopian journalists, opposition members, and activists previously convicted and jailed under the antiterrorism proclamation remained in prison.
On January 8, the Federal Court of Cassation denied journalist Reyot Alemu’s appeal of her conviction on the charge of participating in the promotion or communication of a terrorist act. She was serving a five-year prison sentence.
On May 2, the Federal Supreme Court upheld the sentences of journalist and blogger Eskinder Nega and vice chairman of the opposition front Medrek Andualem Arage for terrorism and treason. In September 2012 the government announced it asked the Federal High Court to freeze the assets of Eskinder and Andualem while investigating whether their assets were used in conjunction with the commission of the crimes for which they were convicted. The court had not issued a decision by year’s end.
The Federal Supreme Court upheld the 2012 convictions under the criminal code of Bekele Gerba and Olbana Lelisa, two well-known political opposition figures from the Oromo ethnic group, for conspiracy to overthrow the government and conspiracy to incite unrest. The Supreme Court subsequently determined the Federal High Court did not consider mitigating circumstances and reduced Bekele’s sentence from eight years to three years and seven months. The Supreme Court also reduced Olbana’s sentenced from 13 to 11 years. Courts convicted 69 members of Oromo political opposition parties, charged separately in 2011 under the criminal code with “attacking the political or territorial integrity of the state.”
CIVIL JUDICIAL PROCEDURES AND REMEDIES
The law provides citizens the right to appeal human rights violations in civil court. No such cases were filed during the year.
f. Arbitrary Interference with Privacy, Family, Home, or Correspondence
The law requires authorities to obtain judicial warrants to search private property; police often ignored the law, and there were no records of courts excluding evidence found without warrants.
There were periodic reports throughout the year police carried out nighttime raids of Muslims’ homes in Addis Ababa to collect evidence against persons they alleged to be terrorists. The government claimed the police had warrants.
Opposition political party leaders reported suspicions of telephone tapping and other electronic eavesdropping, and alleged government agents attempted to lure them into illegal acts by calling and pretending to be representatives of groups – designated by the country’s parliament as terrorist organizations – interested in making financial donations.
The government reportedly used a widespread system of paid informants to report on the activities of particular individuals. During the year opposition members reported ruling party operatives and militia members made intimidating and unwelcome visits to their homes and offices.
Security forces continued to detain family members of persons sought for questioning by the government. There were reports unemployed youths who were not affiliated with the ruling coalition sometimes had trouble receiving the “support letters” from their kebeles (neighborhoods or wards) necessary to get jobs.
The national government and regional governments continued to put in place “villagization” plans in the Afar, Benishangul-Gumuz, Gambella, SNNPR, and Somali regions. These plans involved the relocation by regional governments of scattered rural populations from arid or semiarid lands vulnerable to recurring droughts into designated clusters. The stated purposes of villagization were to improve the provision of government services (i.e., health care, education, and clean water), protect vulnerable communities from natural disasters and attacks, and change environmentally destructive patterns of shifting cultivation. Some observers stated the purpose was to enable the large-scale leasing of land for commercial agriculture. The government described the villagization program as strictly voluntary.
International donors reported that assessments from more than 16 visits to villagization sites since 2011 did not corroborate allegations of systematic human rights violations in this program. They did find problems such as delays in establishing promised infrastructure from rushed program implementation. Communities and individual families appeared to have agreed to move based on assurances from authorities of food aid, services, and land, although in some instances communities moved before adequate basic services and shelter were in place in the new locations. International human rights organizations, however, continued to express concern regarding the villagization process. A report by the Oakland Institute in February stated that the military forcibly relocated communities and committed human rights violations in the Omo Valley. A report by the Oakland Institute in July asserted that, during a January 2012 assessment in the Lower Omo Valley, donor representatives heard testimony from community members regarding human rights violations.
SECTION 2. RESPECT FOR CIVIL LIBERTIES, INCLUDING:
a. Freedom of Speech and Press
The constitution and law provide for freedom of speech and press; however, authorities arrested, detained, and prosecuted journalists and other persons whom they perceived as critical of the government.
Freedom of Speech: Authorities arrested and harassed persons for criticizing the government. The government attempted to impede criticism through various forms of intimidation, including detention of journalists and opposition activists and monitoring and interference in the activities of political opposition groups. Some persons feared authorities would retaliate against them for discussing security force abuses.
Press Freedoms: The government continued to take actions to close independent newspapers. Regulators revoked the operating licenses of Addis Times magazine and Li-Elina newspaper in February and March, respectively, after independent editor Temesgen Dessalegn acquired them. The remaining 14 newspapers had a combined weekly circulation in Addis Ababa of more than 140,000. Most newspapers were printed on a weekly or biweekly basis, with the exception of the state-owned Amharic and English dailies.
The government controlled the only television station that broadcast nationally, which, along with radio, was the primary source of news for much of the population. Four private FM radio stations broadcast in the capital city, one private radio station broadcast in the northern Tigray Region, and at least 16 community radio stations broadcast in the regions. State-run Ethiopian Radio had the largest reach in the country, followed by Fana Radio, which was affiliated with the ruling party.
Government-controlled media closely reflected the views of the government and the ruling EPRDF. The government periodically jammed foreign broadcasts. The law prohibits political and religious organizations and foreigners from owning broadcast stations.
Violence and Harassment: The government continued to arrest, harass, and prosecute journalists. This included the prosecution of three persons associated with the defunct Muslim Affairs magazine under the antiterrorism proclamation.
On January 17, authorities arrested Solomon Kebede, columnist and managing editor of Muslim Affairs. They charged him along with 27 other Muslims in April under the antiterrorism proclamation.
The case against Temesgen Dessalegn, editor in chief of the defunct Feteh newspaper, continued. Charges against him included inciting and agitating the country’s youth to engage in violence, defamation of the government, and destabilizing the public by spreading false reports. Mastewal Berhanu, former publisher and managing director of Feteh, reportedly left the country due to government harassment.
Censorship or Content Restrictions: Government harassment caused journalists to avoid reporting on sensitive topics. Many private newspapers reported informal editorial control by the government through article placement requests and calls from government officials concerning articles perceived as critical of the government. Private sector and government journalists routinely practiced self-censorship.
Libel Laws/National Security: The government used the antiterrorism proclamation to suppress criticism. Journalists feared covering five groups designated by parliament in 2011 as terrorist organizations (Ginbot 7, the ONLF, the OLF, al-Qaida, and al-Shabaab), citing ambiguity on whether reporting on these groups might be punishable under the law. Several journalists, both local and foreign correspondents, reported an increase in self-censorship.
The government used libel laws during the year to suppress criticism.
On May 15, police in Addis Ababa questioned Ferew Abebe, editor in chief of the Sendek newspaper, about 2012 articles that alleged the widow of former prime minister Meles Zenawi refused to vacate the prime minister’s official residence after the death of her husband. Police requested that Ferew reveal his sources to them and would not disclose who initiated the libel claim against Ferew. Ferew posted bail and was released; authorities did not file formal charges by year’s end.
INTERNET FREEDOM
The state-owned Ethio Telecom was the only internet service provider in the country. The government restricted access to the internet and blocked several websites, including blogs; opposition websites; and websites of Ginbot 7, the OLF, and the ONLF. The government also temporarily blocked news sites such as al-Jazeera. Websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and Yahoo! were temporarily inaccessible at times. Several news blogs and websites run by opposition diaspora groups were not accessible. These included Addis Neger, Nazret, Ethiopian Review, CyberEthiopia, Quatero Amharic Magazine, Tensae Ethiopia, and the Ethiopian Media Forum. Authorities took steps to block access to Virtual Private Network providers that let users circumvent government screening of internet browsing and e-mail. According to the International Telecommunication Union, approximately 1.5 percent of individuals used the internet in 2012.
In March, Citizen Lab, a Canadian research center at the University of Toronto, identified 25 countries, including Ethiopia, that host servers linked to FinFisher surveillance software. According to the report, “FinFisher has gained notoriety because it has been used in targeted attacks against human rights campaigners and opposition activists in countries with questionable human rights records.” A “FinSpy” campaign in the country allegedly “used pictures of Ginbot 7, an Ethiopian opposition group, as bait to infect users.”
In March police arrested university student Manyazewal Eshetu, for posting allegations of government corruption on Facebook. Authorities later released Manyazewal without charge.
ACADEMIC FREEDOM AND CULTURAL EVENTS
The government restricted academic freedom, including through decisions on student enrollment, teachers’ appointments, and the curriculum. Authorities frequently restricted speech, expression, and assembly on university and high school campuses.
According to sources, the ruling party via the Ministry of Education continued to give preference to students loyal to the party in assignments to postgraduate programs. Some university staff members commented that priority for employment after graduation in all fields was given to students who joined the party.
Authorities limited teachers’ ability to deviate from official lesson plans. Numerous anecdotal reports suggested non-EPRDF members were more likely to be transferred to undesirable posts and bypassed for promotions. There were unspecified reports of teachers not affiliated with the EPRDF being summarily dismissed for failure to attend unscheduled meetings. There continued to be a lack of transparency in academic staffing decisions, with numerous complaints from individuals in the academic community alleging bias based on party membership, ethnicity, or religion.
According to multiple credible sources, teachers and high school students in grade 10 and above were required to attend training on the concepts of revolutionary democracy and EPRDF party ideology.
A Ministry of Education directive prohibits private universities from offering degree programs in law and teacher education. The directive also requires public universities to align their curriculum offerings with the ministry’s policy of a 70-to-30 ratio between science and social science academic programs. As a result the number of students studying social sciences and the humanities at public institutions continued to decrease, and private universities focused heavily on the social sciences.
b. Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Association
FREEDOM OF ASSEMBLY
The constitution and law provide for freedom of assembly; however, the government did not respect this right. Organizers of large public meetings or demonstrations must notify the government 48 hours in advance and obtain a permit. Authorities may not refuse to grant a permit but may require that the event be held at a different time or place for reasons of public safety or freedom of movement. If authorities determine an event should be held at another time or place, the law requires that organizers be notified in writing within 12 hours of the time of submission of their request.
The government denied some requests by the Semayawi (Blue) Party and Medrek, the largest opposition coalition, to hold protests in Addis Ababa, although the government officially permitted a June 2 Semayawi Party demonstration. The march was widely reported as the first mass outpouring of discontent permitted by the government since protests in 2005. The government subsequently allowed additional protests to take place in Addis Ababa and several other cities, although organizers in most cases alleged government interference, and authorities required several of the protests to move to different dates or locations from those the organizers requested. Protest organizers alleged the government’s claims of needing to move the protests based on public safety concerns were not credible.
Local government officials, almost all of whom were affiliated with the EPRDF, controlled access to municipal halls, and there were many complaints from opposition parties that local officials denied or otherwise obstructed the scheduling of opposition parties’ use of halls for lawful political rallies. There were numerous credible reports that owners of hotels and other large facilities cited unspecified internal rules forbidding political parties from utilizing their space for gatherings.
Regional governments, including the Addis Ababa regional administration, were reluctant to grant permits or provide security for large meetings.
The government arrested persons in relation to opposition demonstrations. This included a March 17 protest and a planned August 31 protest by the Semayawi Party. Authorities also arrested Unity for Democracy and Justice Party members before and after a July 17 protest.
On August 31, security forces raided the headquarters of the Semayawi Party to prevent a demonstration planned for the following day. Authorities reportedly temporarily detained 60 to 90 persons and beat some of them. The demonstration would have coincided with a mass public rally promoting interfaith tolerance organized by the government.
Beginning in late 2011 and continuing throughout the year, some members of the Muslim community held peaceful protests following Friday prayers at several of Addis Ababa’s largest mosques, the Aweliya Islamic Center in Addis Ababa, and at other locations throughout the country. Most demonstrations occurred without incident, although police met some with arrests and alleged use of unnecessary force. For example, on August 8, security forces in Addis Ababa detained more than one thousand Muslims participating in Eid al-Fitr celebrations.
FREEDOM OF ASSOCIATION
Although the law provides for freedom of association and the right to engage in unrestricted peaceful political activity, the government limited this right.
A report of the UN Special Rapporteur on the Rights to Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Association stated, “The enforcement of these [the CSO law] provisions has a devastating impact on individuals’ ability to form and operate associations effectively.”
The CSO law bans anonymous donations to NGOs. All potential donors were therefore aware their names would be public knowledge. The same was true concerning all donations made to political parties.
International NGOs seeking to operate in the country had to submit an application via Ethiopian embassies abroad, which was then submitted by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to the Charities and Societies Agency.
c. Freedom of Religion
See the Department of State’s International Religious Freedom Report at http://www.state.gov/j/drl/irf/rpt/.
d. Freedom of Movement, Internally Displaced Persons, Protection of Refugees, and Stateless Persons
Although the law provides for freedom of internal movement, foreign travel, emigration, and repatriation, the government restricted some of these rights.
The government cooperated with the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and other humanitarian organizations in providing protection and assistance to internally displaced persons (IDPs), refugees, returning refugees, asylum seekers, stateless persons, and other persons of concern; however, at times authorities, armed groups and the situation of insecurity limited the ability of humanitarian organizations to operate.
According to the UN, humanitarian organizations reported 36 incidents that impeded humanitarian work in the first six months of the year compared with 34 during the same period in 2012; 32 of these cases were in the Somali Region. The incidents included violence and hostility against humanitarian personnel, theft of assets, interference with the implementation of humanitarian programs, and restrictions on importation of personnel and goods into the country for humanitarian work. This data referred broadly to humanitarian work and were not limited to activities focusing on IDPs or refugees.
Although the Somali regional government granted several organizations access to Nogob (formerly Fik) to start humanitarian operations, access to areas in the Somali Region remained challenging due to continuing clashes between government forces and the ONLF, as well as reports of al-Shabaab elements operating in and around Somali refugee camps in Dolo Ado. Cases were noted in which NGOs were denied access to areas of operation despite agreements with regional officials. In numerous cases NGOs deferred travel to program activity sites due to insecurity. On June 13, suspected ONLF gunmen fired on a mobile health and nutrition team supported by the UN Children’s Fund in Korahe zone and seriously injured one person.
In-country Movement: The government continued to relax but did not completely remove restrictions on the movement of persons into and within the Somali Region, continuing to argue the ONLF posed a security threat (see section 2.d., Internally Displaced Persons). Security concerns forced a temporary halt of deliveries of food and medicine in the limited areas affected by fighting.
The government continued a policy that allowed refugees to live outside of a camp. According to the Administration for Returnees and Refugee Affairs (ARRA), which managed the out-of-camp program, 3,412 refugees lived outside of the camps in 2012, compared with 1,294 in 2011. Prior to this policy the government gave such permission primarily to attend higher education institutions, undergo medical treatment, or avoid security threats at the camps.
Foreign Travel: On October 23, the government enacted a temporary ban on citizens travelling to the Middle East for employment. The ban did not affect citizens travelling for investment or business reasons. The government stated it issued the ban to prevent harassment, intimidation, and trauma suffered by those working abroad as domestic employees.
Exile: Several citizens sought political asylum in other countries or remained abroad in self-imposed exile.
INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS (IDPS)
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) estimated the total number of IDPs in the country as of June to be 363,141, an increase of 71,487 from the period January through March. The increase was mostly due to conflict and flooding in the Somali and Gambella regions. Drought also caused displacements during the year.
In January conflict between ethnic Oromos and Somalis over border demarcation and land ownership displaced approximately 55,000 persons from Gursum, Meyu, Kimbi, and Chinaksen districts in Oromia Region. Insecurity resulted in the delay of humanitarian assistance. The impacted population remained displaced at year’s end.
Heavy rainfall in the Somali Region from late March to early April resulted in severe flooding in Faafan, Jerer, Korahe, Nogob, and Shebele zones, destroying homes and displacing thousands. Joint assessments by the United Nations, NGOs, and the government reported the floods affected 500 households in Kebredihar and 5,756 in the Mustahil, Ferfer, and Kelafo districts of Shebelle zone. Flooding from April to June displaced an additional 36,792 individuals in Ferfer, Kelafo, and Mustahil, and 6,657 individuals in the Kebrediar and Dobowein districts of Korahe zone.
During the year drought caused the displacement of more than 22,000 persons in Afar.
According to the IOM, an estimated 80 percent of all IDPs were considered “protracted” IDPs, for whom durable solutions (return to home areas, local integration, and resettlement in other parts of the country) were not possible at the time. This was due to lack of resolution of the conflict, lack of political decision or resources to support local integration, or undesirability of resettlement to other areas of the country.
The government, through the Disaster Risk Management Food Security Sector (DRMFSS) and regional and district administrations, encouraged humanitarian responses to internal displacement and facilitated assessments to determine humanitarian needs. Humanitarian organizations usually provided assistance received by IDPs. For example, both the DRMFSS and the local government helped to coordinate the humanitarian response following conflict between ethnic Somali and Oromo residents of East Hararghe zone, Oromia Region.
PROTECTION OF REFUGEES
Access to Asylum: The law provides for the granting of asylum or refugee status, and the government has established a system for providing protection to refugees.
According to the UNHCR, the country hosted 423,851 refugees as of September. The majority of refugees were from Somalia (242,588), with others coming from Sudan (31,951), South Sudan (67,958), Eritrea (77,083), and other countries particularly Kenya (4,271).
The UNHCR, the ARRA, and humanitarian agencies continued to care for Sudanese arrivals fleeing from conflict in Sudan’s Blue Nile State. The government also extended support to South Sudanese asylum seekers from South Sudan’s Jonglei State; 5,776 of these asylum seekers crossed into the country by July, raising the total of South Sudanese asylum seekers to more than 67,000.
Eritrean asylum seekers continued to arrive in the country. This included a large number of unaccompanied minors. Many Eritreans who arrived in the country regularly departed for secondary migration through Egypt and Sudan to go to Israel, Europe, and other final destinations.
Employment: The government did not grant refugees work permits.
Access to Basic Services: The UNHCR and ARRA, with support from NGOs, provided refugees in camps with basic services such as health, education, water, sanitation, and hygiene. For those outside of camps, there were no reports of discrimination in access to public services.
Durable Solutions: The government granted refugee status to asylum seekers from Eritrea, Somalia, South Sudan, and Sudan. The government welcomed refugees to settle permanently in the country but did not offer a path to citizenship or facilitate integration. It permitted Eritrean refugees to live outside refugee camps provided they sustained themselves financially. The government provided some support for Eritreans who were pursuing higher education. During the first half of the year, approximately 2,600 refugees departed the country for resettlement.
SECTION 3. RESPECT FOR POLITICAL RIGHTS: THE RIGHT OF CITIZENS TO CHANGE THEIR GOVERNMENT
The constitution and law provide citizens the right to change their government peacefully. The ruling party’s electoral advantages limited this right.
Elections and Political Participation
Recent Elections: In August 2012, following the death of Prime Minister Meles Zenawi, the ruling EPRDF elected Hailemariam Desalegn to take Meles’s place as chairman of the party and subsequently nominated him for the post of prime minister. In September 2012 parliament elected Hailemariam as prime minister.
In the 2010 national parliamentary elections, the EPRDF and affiliated parties won 545 of 547 seats to remain in power for a fourth consecutive five-year term. Government restrictions severely limited independent observation of the vote. Although the relatively few international officials allowed to observe the elections concluded technical aspects of the vote were handled competently, some also noted the lack of an environment conducive to free and fair elections prior to election day. Several laws, regulations, and procedures implemented since the 2005 national elections created a clear advantage for the EPRDF throughout the electoral process. There was ample evidence that unfair government tactics, including intimidation of opposition candidates and supporters, influenced the extent of the EPRDF victory. In addition, voter education was limited to information about technical voting procedures and was done only by the National Electoral Board just days before voting began.
The African Union, whose observers arrived one week before the vote, deemed the elections to be free and fair. The EU, some of whose observers arrived a few months before the vote, concluded the elections fell short of international standards for transparency and failed to provide a level playing field for opposition parties. The EU observed a “climate of apprehension and insecurity,” noting that the volume and consistency of complaints of harassment and intimidation by opposition parties was “a matter of concern” and had to be taken into consideration “in the overall assessment of the electoral process.”
The EPRDF’s continued dominance was demonstrated in nationwide elections to local and city council positions held in April. EPRDF-affiliated parties won all but five of 3.6 million seats; 33 opposition parties boycotted the elections.
Political Parties: Political parties were predominantly ethnically based. The government, controlled by the ruling EPRDF, restricted media freedom and arrested opposition members. Constituent parties of the EPRDF conferred advantages upon their members; the parties directly owned many businesses and were broadly perceived to award jobs and business contracts to loyal supporters. Several opposition political parties reported difficulty in renting homes or buildings in which to open offices, citing visits by EPRDF members to the landlords to persuade or threaten them not to rent property to these parties.
There were reports authorities had terminated the employment of teachers and other government workers if they belonged to opposition political parties. According to Oromo opposition groups, the Oromia regional government continued to threaten to dismiss opposition party members, particularly teachers, from their jobs. Government officials alleged that many members of legitimate Oromo opposition political parties were secretly OLF members and more broadly that members of many opposition parties had ties to Ginbot 7. At the university level members of Medrek and its constituent parties were able to teach.
Registered political parties must receive permission from regional governments to open and occupy local offices.
Participation of Women and Minorities: No laws or cultural or traditional practices prevented women or minorities from voting or participating in political life on the same basis as men or nonminority citizens, although women were significantly underrepresented in both elected and appointed positions. The Tigray Regional Council held the highest proportion of women nationwide, at 48.5 percent.
The government’s policy of ethnic federalism led to the creation of individual constituencies to provide for representation of all major ethnic groups in the House of People’s Representatives. There were more than 80 ethnic groups, and small groups lacked representation in the legislature. There were 24 nationality groups in six regional states (Tigray, Amhara, Beneshangul-Gumuz, the SNNPR, Gambella, and Harar) that did not have a sufficient population to qualify for constituency seats based on the 2007 census; however, in the 2010 elections, individuals from these nationality groups competed for 24 special seats in the House of People’s Representatives. Additionally these 24 nationality groups have one seat each in the House of Federation.
Women held three federal government ministerial positions and 152 of 547 seats in the national parliament.
SECTION 4. CORRUPTION AND LACK OF TRANSPARENCY IN GOVERNMENT
The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials. Despite the government’s prosecution of numerous officials for corruption, some officials continued to engage in corrupt practices. Corruption, especially the solicitation of bribes, remained a problem among low-level bureaucrats. Police and judicial corruption also continued to be problems. Some government officials appeared to manipulate the privatization process, and state- and party-owned businesses received preferential access to land leases and credit.
Corruption: The Ministry of Justice has primary responsibility for combating corruption, largely through the Federal Ethics and Anticorruption Commission (FEACC).
During the year the FEACC initiated criminal proceedings against the director general of the Ethiopian Revenues and Customs Authority, his deputy, and as many as 60 other government officials and private business leaders for alleged corrupt practices. Most trials continued at year’s end, although some cases were dropped due to lack of evidence.
Whistleblower Protection: The law provides protection to public and private employees for making internal disclosures or lawful public disclosures of evidence of illegality, such as the solicitation of bribes or other corrupt acts, gross waste or fraud, gross mismanagement, abuse of power, or substantial and specific dangers to public health and safety. The law also specifically bars appointed or elected officials and public servants from making direct or indirect reprisals against whistleblowers.
Financial Disclosure: The law requires all government officials and employees officially register their wealth and personal property. The president and prime minister registered their assets. By the end of 2012, a total of 32,297 federal government officials registered their assets, according to the FEACC. The FEACC held financial disclosure records. According to the law, any person seeking access to these records may do so by making a request in writing, although access to information on family assets may be restricted unless the FEACC deems the disclosure necessary. The law includes financial and criminal sanctions for noncompliance.
Public Access to Information: The law provides for public access to government information, but access was largely restricted. The law includes a sufficiently narrow list of exceptions outlining the grounds for nondisclosure. Responses generally must be made within 30 days of a written request, and fees may not exceed the actual cost of responding to the request. The law includes mechanisms for punishing officials for noncompliance, as well as appeal mechanisms for review of disclosure denials. Information on the number of disclosures or denials during the year was not available.
The government publishes its laws and regulations in the national gazette prior to their taking effect. The Government Communications Affairs Office managed contacts between the government, the press, and the public; the private press reported the government rarely responded to its queries.
SECTION 5. GOVERNMENTAL ATTITUDE REGARDING INTERNATIONAL AND NONGOVERNMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF ALLEGED VIOLATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS
A few domestic human rights groups operated, but with significant government restrictions. The government was generally distrustful and wary of domestic human rights groups and international observers. State-controlled media were critical of international human rights groups such as Human Rights Watch.
The CSO law prohibits charities, societies, and associations (NGOs or CSOs) that receive more than 10 percent of their funding from foreign sources from engaging in activities that advance human and democratic rights or promote equality of nations, nationalities, peoples, genders, and religions; the rights of children and persons with disabilities; conflict resolution or reconciliation; or the efficiency of justice and law enforcement services. The implementation of the law continued to result in the severe curtailment of NGO activities related to human rights. In July 2012 the UN high commissioner for human rights expressed concern that civil society space “has rapidly shrunk” since the CSO law’s enactment.
Some human rights defender organizations continued to register either as local charities, meaning they could not raise more than 10 percent of their funds from foreign donors but could act in the specified areas, or as resident charities, which allowed foreign donations above 10 percent but prohibited activities in those areas.
One of several sets of the law’s implementing regulations, commonly known as the 70/30 rule, caps administrative spending at 30 percent of an organization’s operating budget. The regulations define training of teachers, agricultural and health extension workers, and other government officials as an “administrative” cost, contending the training does not directly affect beneficiaries, thus limiting the number of training programs that can be provided by development assistance partners who prefer to employ train-the-trainer models to reach more persons. The government addressed application of this regulation on a case-by-case basis. A Civil Society Sector Working Group cochaired by the Ministry of Federal Affairs and a representative of the donor community convened periodically to monitor and discuss challenges that arose as the law was implemented.
The government denied most NGOs access to federal prisons, police stations, and political prisoners. The government permitted the JFA-PFE, one of four organizations granted an exemption enabling them to raise unlimited funds from foreign sources and to engage in human rights advocacy, to visit prisoners. The JFA-PFE played a positive role in improving prisoners’ chances for clemency.
Authorities limited the access of human rights organizations, the media, humanitarian agencies, and diplomatic missions to conflict-affected areas, although it eased such restrictions. Humanitarian access in the Somali Region improved in particular. The government lacked a clear policy on NGO access to sensitive areas, leading regional government officials and military officials frequently to refer requests for access to the federal government. Officials required journalists to register before entering conflict regions. There were isolated reports of regional police or local militias blocking NGOs’ access to particular locations on particular days, citing security concerns. Some agencies limited project activities for security reasons.
Some persons feared authorities would retaliate against them if they met with NGOs and foreign government officials who were investigating allegations of abuse.
UN and Other International Bodies: Requests to visit the country from the UN special rapporteur on torture and other cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment remained outstanding.
Government Human Rights Bodies: The EHRC investigated human rights complaints and produced annual and thematic reports. The commission operated 112 legal aid centers in collaboration with 17 universities and two civil society organizations, the Ethiopian Women Lawyers’ Association and the Ethiopian Christian Lawyers Fellowship. The commission also completed the preparatory measures to sign collaborative agreements with two additional universities. The EHRC reported its Addis Ababa headquarters resolved 90 percent of the 952 complaints submitted to it during 2012.
The Office of the Ombudsman has authority to receive and investigate complaints with respect to administrative mismanagement by executive branch offices. From September 2011 to September 2012, the office received 2,094 complaints. Of these, the ombudsman opened investigations into 784, and the office reported it resolved the remaining cases through alternative means. The majority of complaints dealt with social security, labor, housing, and property disputes. The Office of the Ombudsman did not compile nationwide statistics.
SECTION 6. DISCRIMINATION, SOCIETAL ABUSES, AND TRAFFICKING IN PERSONS
The constitution provides all persons equal protection without discrimination based on race, nation, nationality or other social origin, color, gender, language, religion, political or other opinion, property, birth, or status, but the government did not fully promote and protect these rights. The constitution does not address discrimination based on disability, sexual orientation, or gender identity.
Women
Rape and Domestic Violence: The law criminalizes rape and provides for penalties of five to 20 years’ imprisonment, depending on the severity of the case; the law does not expressly address spousal rape. The government did not fully enforce the law, partially due to widespread underreporting. Recent statistics on the number of abusers prosecuted, convicted, or punished were not available. Anecdotal evidence suggested reporting of rapes had increased since the 2004 revision of the criminal code but the justice system was unable to keep up with the number of cases.
Domestic violence, including spousal abuse, was a pervasive social problem.
Although women had recourse to the police and the courts, societal norms and limited infrastructure prevented many women from seeking legal redress, particularly in rural areas. The government prosecuted offenders on a limited scale. Domestic violence is illegal, but government enforcement of laws against rape and domestic violence was inconsistent. Depending on the severity of damage inflicted, legal penalties range from small fines to imprisonment for up to 10 to 15 years.
Domestic violence and rape cases often were delayed significantly and given low priority. In the context of gender-based violence, significant gender gaps in the justice system remained, due to poor documentation and inadequate investigation. “Child friendly” benches hear cases involving violence against children and women. Police officers were required to receive domestic violence training from domestic NGOs and the Ministry of Women, Children, and Youth Affairs. There was a commissioner for women and children’s affairs in the EHRC.
Women and girls experienced gender-based violence, but it was underreported due to cultural acceptance, shame, fear, or a victim’s ignorance of legal protections.
Harmful Traditional Practices: The most prevalent harmful traditional practices were FGM/C, uvula cutting, tonsil scraping and milk tooth extraction, early marriage, and marriage by abduction.
Marriage by abduction is illegal, although it continued in some regions despite the government’s attempts to combat the practice. A 2009 Population Council study of seven regions found that 2.6 percent of married female youth reported their marriage occurred through abduction. The study found the rate to be 12.9 percent in the SNNPR, 4.4 percent in Oromia, 3 percent in Afar, and less than 1percent in Beneshangul Gumuz. The study did not include the Gambella or Somali regions. Forced sexual relationships accompanied most marriages by abduction, and women often experienced physical abuse during the abduction. Abductions led to conflicts among families, communities, and ethnic groups. In cases of marriage by abduction, the perpetrator did not face punishment if the victim agreed to marry the perpetrator.
Female Genital Mutilation/Cutting (FGM/C): FGM/C is illegal, but the government did not actively enforce this prohibition or punish those who practiced it.
Sexual Harassment: Sexual harassment was widespread. The penal code prescribes penalties of 18 to 24 months’ imprisonment, but authorities generally did not enforce harassment laws.
Reproductive Rights: Individuals and couples have the right to decide freely and responsibly the number, spacing, and timing of children and to have the information and means to do so free from discrimination, coercion, and violence. The 2011 Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) indicated a modern contraceptive prevalence of 27 percent nationwide among married women, a twofold increase from the survey done six years earlier. The survey found 25.3 percent of married girls and women ages 15 to 49 had unmet family planning needs. The 2011 DHS indicated the maternal mortality rate was 676 deaths per 100,000 live births as compared with 673 per 100,000 reported in the 2005 DHS. The immediate causes of maternal mortality included excessive bleeding, infection, hypertensive complications, and obstructed labor, with the underlying cause being the prevalence of home births and lack of access to emergency obstetric care. Only 9 percent of women reported delivering in a health facility or with a skilled birth attendant.
Discrimination: Discrimination against women was a problem and was most acute in rural areas, where an estimated 85 percent of the population lived. The law contains discriminatory regulations, such as the recognition of the husband as the legal head of the family and the sole guardian of children more than five years old. Courts generally did not consider domestic violence by itself a justification for granting a divorce. Irrespective of the number of years the marriage existed, the number of children raised, and joint property, the law entitled women to only three months’ financial support if a relationship ended. There was limited legal recognition of common-law marriage. A common-law husband had no obligation to provide financial assistance to his family, and as a result, women and children sometimes faced abandonment. Traditional courts continued to apply customary law in economic and social relationships.
According to the constitution all land belongs to the government. Both men and women have land-use rights, which they may pass on as an inheritance. Land law varies among regions. All federal and regional land laws empower women to access government land. Inheritance laws also enable widowed women to inherit joint property they acquired during marriage.
In urban areas women had fewer employment opportunities than men, and the jobs available did not provide equal pay for equal work. Women’s access to gainful employment, credit, and the opportunity to own or manage a business was further limited by their generally lower level of education and training and by traditional attitudes.
The Ministry of Education reported female participation in undergraduate and postgraduate programs increased to 144,286 during the 2011-12 academic year, compared with 123,706 in 2010-11, continuing the trend of increasing female participation in higher education.
Children
Birth registration: Citizenship is derived from one’s parents. The law requires all children to be registered at birth. Children born in hospitals were registered while most children born outside of hospitals were not. The overwhelming majority of children, particularly in rural areas, were born at home.
Education: As a policy, primary education was universal and tuition-free; however, there were not enough schools to accommodate the country’s youth, particularly in rural areas. The cost of school supplies was prohibitive for many families, and there was no legislation to enforce compulsory primary education. The number of students enrolled in schools expanded faster than trained teachers could be deployed.
Child Abuse: Child abuse was widespread. A 2009 study conducted by the African Child Policy Forum revealed prosecuting offenders for sexual violence against children was difficult due to inconsistent interpretation of laws among legal bodies and the offender’s right to bail, which often resulted in the offender fleeing or coercing the victim or the victim’s family to drop the charges. “Child friendly” benches heard cases involving violence against children and women. During the year the Federal Court of First Instance announced that tribunals hearing cases relating to families and children would keep extended hours to accommodate children’s school schedules. There was a commissioner for women and children’s affairs in the EHRC.
Forced or Early Marriage: The law sets the legal marriage age for girls and boys at 18; however, authorities did not enforce this law uniformly, and rural families sometimes were unaware of this provision. In several regions it was customary for older men to marry young girls, although this traditional practice continued to face greater scrutiny and criticism.
According to the 2011 DHS, the median age of first marriage among women surveyed between the ages of 20 and 49 was 17.1 years. The age of first marriage appeared to be rising. In 2005 the median age of marriage for women surveyed between 20 and 24 was 16.5 years, and while 39 percent of women between 45 and 49 reported being married by age 15, only 8 percent of young women between 15 and 19 years of age reported being or having been married.
In the Amhara and Tigray regions, girls were married routinely as early as age seven. Child marriage was most prevalent in the Amhara Region, where the median first marriage age was 15.1 years, according to the 2011 DHS, compared with 14.7 years in 2005. Regional governments in Amhara and, to a lesser extent, Tigray offered programs to educate young women on problems associated with early marriage.
Harmful Traditional Practices: Societal abuse of young girls continued to be a problem. Harmful practices included FGM/C, early marriage, marriage by abduction, and food and work prohibitions.
The majority of girls in the country have undergone some form of FGM/C, although the results of the 2009 Population Council survey suggested its prevalence had declined. Sixty-six percent of female respondents ages 21 to 24 reported they were subjected to FGM/C compared with 56 percent of those ages 15 to 17. Of the seven regions surveyed, the study found the rates to be highest in Afar (90.3 percent), Oromia (77.4 percent), and the SNNPR (74.6 percent).
FGM/C was much less common in urban areas, where only 15 percent of the population lived. Girls typically experienced clitoridectomies seven days after birth (consisting of an excision of the clitoris, often with partial labial excision) and infibulation (the most extreme and dangerous form of FGM/C) at the onset of puberty. The penal code criminalizes practitioners of clitoridectomy, with imprisonment of at least three months or a fine of at least 500 birr ($26). Infibulation of the genitals is punishable with imprisonment of five to 10 years. No criminal charges have ever been brought for FGM/C. The government discouraged the practice of FGM/C through education in public schools, the Health Extension Program, and broader mass media campaigns.
Sexual Exploitation of Children: The minimum age for consensual sex is 18 years, but authorities did not enforce this law. The law provides for three to 15 years in prison for sexual intercourse with a minor. The law provides for one year in prison and a fine of 10,000 birr ($530) for trafficking in indecent material displaying sexual intercourse by minors. The law prohibits profiting from the prostitution of minors and inducing minors to engage in prostitution; however, commercial sexual exploitation of children continued, particularly in urban areas. Girls as young as age 11 reportedly were recruited to work in brothels. Customers often sought these girls because they believed them to be free of sexually transmitted diseases. Young girls were trafficked from rural to urban areas. They also were exploited as prostitutes in hotels, bars, resort towns, and rural truck stops. Reports indicated family members forced some young girls into prostitution.
Infanticide or Infanticide of Children with Disabilities: Ritual and superstition-based infanticide continued in remote tribal areas, particularly South Omo. Local governments worked to educate communities against the practice.
Displaced Children: According to a 2010 report by the Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs, approximately 150,000 children lived on the streets, of whom 60,000 were in the capital. The ministry’s report stated families’ inability to support children due to parental illness or insufficient household income exacerbated the problem. These children begged, sometimes as part of a gang, or worked in the informal sector.
A 2010 Population Council Young Adult Survey found that 82.3 percent of boys who lived or worked on the streets had been to or had enrolled in school, 26.4 percent had lost one parent, and 47.2 percent had lost both parents. Among these boys, 72 percent worked for pay at some point in their lives. Government and privately run orphanages were unable to handle the number of street children.
Institutionalized Children: There were an estimated 5.4 million orphans in the country, according to a 2010 report by the Central Statistics Authority. The vast majority lived with extended family members. Government orphanages were overcrowded, and conditions were often unsanitary. Due to severe resource constraints, hospitals and orphanages often overlooked or neglected abandoned infants. Institutionalized children did not receive adequate health care.
International Child Abductions: The country is not a party to the 1980 Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction.
Anti-Semitism
The Jewish community numbered approximately 2,000 persons. There were no reports of anti-Semitic acts.
Trafficking in Persons
See the Department of State’s Trafficking in Persons Report at http://www.state.gov/j/tip/.
Persons with Disabilities
The constitution does not mandate equal rights for persons with disabilities. The law prohibits discrimination against persons with physical and mental disabilities in employment and mandates access to buildings. It is illegal for deaf persons to drive.
The law prohibits employment discrimination based on disability. It also makes employers responsible for providing appropriate working or training conditions and materials to persons with disabilities. The law specifically recognizes the additional burden on women with disabilities. The government took limited measures to enforce the law, for example, by assigning interpreters for hearing-impaired civil service employees.
The law mandates building accessibility and accessible toilet facilities for persons with physical disabilities, although specific regulations that define the accessibility standards were not adopted. Buildings and toilet facilities were usually not accessible. Landlords are required to give persons with disabilities preference for ground-floor apartments, and this was respected.
Women with disabilities were more disadvantaged than men with disabilities in education and employment. An Addis Ababa University study from 2008 showed that female students with disabilities were subjected to a heavier burden of domestic work than their male peers. The 2010 Population Council Young Adult Survey found young persons with disabilities were less likely to have ever attended school than young persons without disabilities. The survey indicated girls with disabilities were less likely than boys with disabilities to be in school; 23 percent of girls with disabilities were in school, compared to 48 percent of girls without disabilities and 55 percent of boys without disabilities. Overall, 47.8 percent of young persons with disabilities surveyed reported not going to school due to their disability. Girls with disabilities also were much more likely to suffer physical and sexual abuse than girls without disabilities. Of sexually experienced girls with disabilities, 33 percent reported having experienced forced sex. According to the same survey, some 6 percent of boys with disabilities had been beaten in the three months prior to the survey, compared with 2 percent of boys without disabilities.
There were several schools for hearing and visually impaired persons and several training centers for children and young persons with intellectual disabilities. There was a network of prosthetic and orthopedic centers in five of the nine regional states.
The Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs worked on disability-related problems. The CSO law continued to affect negatively several domestic associations, such as the Ethiopian National Association of the Blind, the Ethiopian National Association of the Deaf, and the Ethiopian National Association of the Physically Handicapped, like other civil society organizations.
National/Racial/Ethnic Minorities
The country has more than 80 ethnic groups, of which the Oromo, at approximately 35 percent of the population, is the largest. The federal system drew boundaries roughly along major ethnic group lines. Most political parties remained primarily ethnically based.
Clashes between ethnic groups during the year resulted in injury and death. In January ethnic clashes broke out at Addis Ababa University reportedly due to anti-Oromo graffiti. The clashes resulted in injury to as many as 20 persons. In February clashes between members of the Afar, Somali, and Oromo ethnic groups in the eastern town of Awash Arba reportedly resulted in the deaths of more than 20 persons.
Authorities in the western region of Benishangul-Gumuz forcibly evicted as many as 8,000 ethnic Amhara residents from their homes; some of those evicted alleged police beat and harassed them because of their ethnicity. The regional president publically stated the evictions were a mistake and called on the evictees to return. Government officials also stated that victims would be compensated for lost property and any injuries sustained. Authorities dismissed several local officials from their government positions because of their alleged involvement in the evictions, and charged some of these officials with criminal offenses.
Societal Abuses, Discrimination, and Acts of Violence Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
Consensual same-sex sexual activity is illegal and punishable by imprisonment under the law. There is no law prohibiting discrimination against lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) individuals. There were some reports of violence against LGBT individuals; reporting was limited due to fear of retribution, discrimination, or stigmatization. There are no hate crime laws or other criminal justice mechanisms to aid in the investigation of abuses against LGBT persons. Persons did not identify themselves as LGBT persons due to severe societal stigma and the illegality of consensual same-sex sexual activity. Activists in the LGBT community stated they were followed and at times feared for their safety. There were periodic detentions of some in the LGBT community, combined with interrogation and alleged physical abuse.
The AIDS Resource Center in Addis Ababa reported the majority of self-identified gay and lesbian callers, most of whom were male, requested assistance in changing their behavior to avoid discrimination. Many gay men reported anxiety, confusion, identity crises, depression, self-ostracism, religious conflict, and suicide attempts.
Other Societal Violence or Discrimination
Societal stigma and discrimination against persons living with or affected by HIV/AIDS continued in the areas of education, employment, and community integration. Persons living with or affected by HIV/AIDS reported difficulty accessing services. Despite the abundance of anecdotal information, there were no statistics on the scale of the problem.
SECTION 7. WORKER RIGHTS
a. Freedom of Association and the Right to Collective Bargaining
The constitution and the law provide workers, except for certain categories of workers primarily in the public sector, with the right to form and join unions, conduct legal strikes, and bargain collectively, although other laws severely restrict or excessively regulate these rights. The law specifically prohibits managerial employees, teachers, health care workers, and civil servants (including judges, prosecutors, and security service workers) from organizing unions. Other workers specifically excluded by law from unionizing include domestic workers and seasonal and part-time agricultural workers.
A minimum of 10 workers is required to form a union. While the law provides all unions with the right to register, the government may refuse to register trade unions that do not meet its registration requirements. The law stipulates a trade union organization may not act in an overtly political manner. The law allows administrative authorities to appeal to the courts to cancel union registration for engaging in prohibited activities, such as political action. While the law prohibits antiunion discrimination by employers and provides for reinstatement for workers fired for union activity, it does not prevent an employer from creating or supporting a workers’ organization for the purpose of controlling it.
Other laws and regulations that explicitly or potentially infringe upon workers’ rights to associate freely and to organize include: the CSO law; Council of Ministers Regulation No. 168/2009 on Charities and Societies to reinforce the CSO law; Proclamation No. 652/2009 on Antiterrorism. During the year the International Labor Organization (ILO) Committee of Experts on the Application of Conventions and Recommendations noted the CSO law gives the government power to interfere in the right of workers to organize, including through the registration, internal administration, and dissolution of organizations, and that the Antiterrorism Proclamation could become a means of punishing the peaceful exercise of freedom of expression and the right to organize.
While the law recognizes the right of collective bargaining, this right was severely restricted. Negotiations aimed at amending or replacing a collective agreement must be completed within three months of its expiration, or the provisions on wages and other benefits cease to apply. Civil servants, including public school teachers, have the right to establish and join professional associations, but are not allowed to negotiate for better wages or working conditions. Furthermore, the arbitration procedures in the public sector are more restrictive than those in the private sector.
Although the constitution and law provide workers with the right to strike to protect their interests, the law contains detailed provisions prescribing excessively complex and time-consuming formalities that make legal strike actions difficult to carry out. The law requires aggrieved workers to attempt reconciliation with employers before striking and includes a lengthy dispute settlement process. These provisions applied equally to an employer’s right to lock workers out. Two-thirds of the workers involved must support a strike for it to occur. If a case has not already been referred to a court or labor relations board, workers retain the right to strike without resorting to either of these options, provided they give at least 10 days’ notice to the other party and the Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs and make efforts at reconciliation.
The law also prohibits strikes by workers who provide essential services, including air transport and urban bus service workers, electric power suppliers, gas station personnel, hospital and pharmacy personnel, firefighters, telecommunications personnel, and urban sanitary workers. The list of essential services exceeds the ILO definition of essential services. The law prohibits retribution against strikers, but also provides for excessive civil or penal sanctions against unions and workers involved in unauthorized strike actions. Unions may be dissolved for carrying out strikes in “essential services.”
The informal labor sector, including domestic workers, is not unionized and is not protected by labor laws. Lack of adequate staffing prevented the government from effectively enforcing applicable laws during the year. Court procedures were subject to lengthy delays and appeals.
Freedom of association and the right to collective bargaining were not respected. Although the government permits unions, the government established and controlled the major trade unions. As it had for more than four years, the government continued to use its authority to refuse to register the National Teachers’ Association (NTA) on the grounds that a national teacher association already existed, and that the NTA’s registration application was not submitted in accordance with the CSO law. According to the Education International report to the ILO in 2011, government security agents subjected members of the NTA to surveillance and harassment, with the goal of intimidating teachers to abandon the NTA and forcing them to give up their long-standing demand for the formation of an independent union. In November 2012 the ILO’s Committee on Freedom of Association expressed its concern with regard to serious violations of the NTA’s trade union rights, including continuous interference in its internal organization that prevented it from functioning normally, as well as interference by way of threats, dismissals, arrest, detention, and mistreatment of NTA members. The committee urged the government to register the NTA without delay; to ensure the CSO law was not applicable to workers’ and employers’ organizations; and to undertake civil service reform to fully protect the right of civil servants to establish and join organizations of their own choosing.
While the government allowed citizens to exercise the right of collective bargaining freely, representatives negotiated wages only at the plant level. It was common for employers to refuse to bargain. Unions in the formal industrial sector made some efforts to enforce labor regulations.
Despite the law prohibiting antiunion discrimination, unions reported employers fired union activists. There were reports most Chinese employers generally did not allow workers to form unions and often transferred or fired union leaders, and intimidated and pressured members to leave unions. Lawsuits alleging unlawful dismissal often take years to resolve because of case backlogs in the courts. Employers found guilty of antiunion discrimination were required to reinstate workers fired for union activities and generally did so. While the law prohibits retribution against strikers, most workers were not convinced the government would enforce this protection. Labor officials reported that, due to high unemployment and long delays in the hearing of labor cases, some workers were afraid to participate in strikes or other labor actions. Antiunion activities occurred but were rarely reported.
b. Prohibition of Forced or Compulsory Labor
The law prohibits most forms of forced or compulsory labor, including by children, but it also permits courts to order forced labor as a punitive measure. The government did not effectively enforce the forced labor prohibition, and forced labor occurred. Both adults and children were forced to engage in street vending, begging, traditional weaving, or agricultural work. Children also worked in forced domestic labor. Situations of debt bondage also occurred in traditional weaving, pottery, cattle herding, and other agricultural activities, mostly in rural areas.
Also see the Department of State’s Trafficking in Persons Report at http://www.state.gov/j/tip/.
c. Prohibition of Child Labor and Minimum Age for Employment
By law the minimum age for wage or salary employment is 14 years. The minimum age provisions, however, only apply to contractual labor and do not apply to self-employed children or children who perform unpaid work. Special provisions cover children between the ages of 14 and 18, including the prohibition of hazardous or night work. The law defines hazardous work as work in factories or involving machinery with moving parts or any work that could jeopardize a child’s health. Prohibited work sectors include passenger transport, electric generation plants, underground work, street cleaning, and many other sectors. The law expressly excludes children under age 16 attending vocational schools from legal protection with regard to the prohibition on young workers performing hazardous work. The law does not permit children between the ages of 14 and 18 to work more than seven hours per day, between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m., on public holidays or rest days, or on overtime.
The government did not effectively enforce these laws. The lack of labor inspectors and controls prevented the government from enforcing the law. The resources for inspections and the implementation of penalties were extremely limited. Despite the introduction of labor inspector training at Gondar University in 2011, insufficient numbers of labor inspectors and inspections resulted in lax enforcement of occupational safety and health measures and in increased numbers of children working in prohibited work sectors, particularly construction. The National Action Plan to Eliminate the Worst Forms of Child Labor was signed at the end of 2012.
While primary education is free, it is not compulsory, and net school enrollment was low, particularly in rural areas. To underscore the importance of attending school, joint NGO and government-led community-based awareness raising activities targeted communities where children were heavily engaged in agricultural work. During the year the government invested in modernizing agricultural practices and constructing schools to combat the problem of child labor in agricultural sectors.
Child labor remained a serious problem. In both rural and urban areas, children often began working at young ages. Child labor was particularly pervasive in subsistence agricultural production, traditional weaving, fishing, and domestic work. A growing number of children worked in construction. Children in rural areas, especially boys, engaged in activities such as cattle herding, petty trading, plowing, harvesting, and weeding, while other children, mostly girls, collected firewood and fetched water. Children worked in the production of gold. In small-scale gold mining, they dug their own mining pits and carried heavy loads of water. Children in urban areas, including orphans, worked in domestic service, often working long hours, which prevented many from attending school regularly. They also worked in manufacturing, shining shoes, making clothes, as porters, directing customers to taxis, parking, public transport, petty trading, and occasionally herding animals. Some children worked long hours in dangerous environments for little or no wages and without occupational safety protection. Child laborers often faced physical, sexual, and emotional abuse at the hands of their employers.
Also see the Department of Labor’s Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor at http://www.dol.gov/ilab/programs/ocft/tda.htm.
d. Acceptable Conditions of Work
There is no national minimum wage. Some government institutions and public enterprises set their own minimum wages. Public sector employees, the largest group of wage earners, earned a monthly minimum wage of approximately 420 birr ($22). The official estimate for the poverty income level was approximately 315 birr ($16) per month.
Only a small percentage of the population, concentrated in urban areas, was involved in wage-labor employment. Wages in the informal sector generally were below subsistence levels.
The law provides for a 48-hour maximum legal workweek with a 24-hour rest period, premium pay for overtime, and prohibition of excessive compulsory overtime. The country has 13 paid public holidays per year. The law entitles employees in public enterprise and government financial institutions to overtime pay; civil servants receive compensatory time for overtime work. The government, industries, and unions negotiated occupational safety and health standards. Workers specifically excluded by law from unionizing, including domestic workers and seasonal and part-time agricultural workers, generally did not benefit from health and safety regulations in the workplace.
The Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs’ inspection department was responsible for enforcement of workplace standards. The country had 380 labor inspectors, but due to lack of resources, the labor inspectors did not enforce standards effectively. The ministry’s severely limited administrative capacity; lack of an effective mechanism for receiving, investigating, and tracking allegations of violations; and lack of detailed, sector-specific health and safety guidelines hampered effective enforcement of these standards. In addition penalties were not sufficient to deter violations.
Compensation, benefits, and working conditions of seasonal agricultural workers were far below those of unionized permanent agricultural employees. The government did little to enforce the law. Most employees in the formal sector worked a 39-hour workweek. Many foreign, migrant, and informal sector workers worked more than 48 hours per week.
Workers have the right to remove themselves from dangerous situations without jeopardizing their employment. Despite this law most workers feared losing their jobs if they were to do so. Hazardous working conditions existed in the agricultural sector, which was the primary base of the country’s economy. There were also reports of hazardous and exploitative working conditions in the construction and fledgling industrial sectors.
Read further @http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2013/af/220113.htm#
(OPride) — The United States in a scathing report on Thursday accused Ethiopia of curtailing freedom of expression and association, using politically motivated trials, harassment and intimidation of activists and journalists.
Ethiopia holds estimated 70,000-80,000 persons, including some 2,500 women and nearly 600 children incarcerated with their mothers, in severely overcrowded six federal and 120 regional prisons, the U.S. said in its voluminous 2013 Human Rights Reportreleased by Secretary of State John Kerry. “There also were many unofficial detention centers throughout the country, including in Dedessa, Bir Sheleko, Tolay, Hormat, Blate, Tatek, Jijiga, Holeta, and Senkele,” the report said.
While it said pretrial detention in local police stations were marred with poor hygiene and police abuse, the report also highlighted impunity for security forces who often commit politically-motivated killings against dissidents and opposition party members as “a serious problem.” The Ethiopian government rarely, if ever, took actions “to prosecute or otherwise punish officials who committed abuses other than corruption,” the report added.
The report named some of the well-known political prisoners and journalists including Eskinder Nega, Bekele Gerba, Olbana Lelisa, Reeyot Alemu and Woubeshet Taye.“Federal Supreme Court upheld the 2012 convictions under the criminal code of Bekele Gerba and Olbana Lelisa, two well-known political opposition figures from the Oromo ethnic group, for conspiracy to overthrow the government and conspiracy to incite unrest,” the report noted.
“The Supreme Court subsequently determined the Federal High Court did not consider mitigating circumstances and reduced Bekele’s sentence from eight years to three years and seven months. The Supreme Court also reduced Olbana’s sentenced from 13 to 11 years. Courts convicted 69 members of Oromo political opposition parties, charged separately in 2011 under the criminal code with “attacking the political or territorial integrity of the state.”
Gerba, who has fully served out his reduced time, was widely expected to be released last month. However, according to family sources, prison officials gave conflicting reasons for his continued imprisonment, including that his time at the Maekelawi prison doesn’t count or his file was misplaced. Meanwhile, both Gerba and Lelisa are reportedly ill with restricted and limited medical care.
Terminally ill
Lelisa is a longtime Oromo rights activist with Oromo Peoples Congress (OPC), who rose through the ranks of the organization from a sole member to top leadership. He competed in the last three elections representing the Caliya district in West Shewa. He was elected to the Oromia regional parliament in 2005. He was subsequently arrested on concocted charges of plotting to overthrow government by working with the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF), recruiting youth for armed rebellion and for inciting the frequent youth revolt in Ambo and West Shewa.
Lelisa, who has so far served three years of the 11 years sentence, reports being mistreated while in prison. He has repeatedly been beaten by unidentified men at Kaliti prison with orders from security services. He has sustained serious wounds from the beatings by government agents who pose as prisoners, according to OPride sources. Lelisa, who is terminally ill and said to be on a long-term medication for undisclosed condition, had repeatedly appealed to the higher court about his mistreatment but received no response to date.
Singling out the Oromo
While the State Department’s report is short on details, there are several evidences that show the Ethiopian government continues to single out Oromo dissidents. Last year, the OLF released a partial list (independently verified by a reputable OPride source) of 528 individuals sentenced to death and life imprisonment on purely political grounds.
The list includes names of individuals, their gender, and ethnic backgrounds. Underscoring the disproportionate repression of the Oromo, of the 528 individuals who were sentenced to death or life imprisonment by the Ethiopian courts, 459 are Oromo nationals followed by 52 Amhara nationals. “This list clearly indicates that the minority regime in Ethiopia is using its kangaroo courts for destroying Oromo and Amhara nationals who are viewed as potential threat to the regimes hold on to power,” one informant, who asked not to be named, told OPride.
As documented by various international human rights organizations, today, it is a serious crime, under the Tigrean dominated Ethiopian government to support any independent Oromo organization. Thousands of Oromos have been imprisoned, tortured and killed extra-judicially for no apparent reason other than expressing Oromo national feeling and for their support of Oromo organizations such as the OLF.
The selective and systematic targeting of Oromo in Ethiopia by the current began in 1992 when the OLF which jointly ruled Ethiopia from 1991-1992 with the Tigrayan Liberation Front (TPLF) was banned and its members and supporters jailed for years and hundreds executed without due process of law. Although Oromia, the Oromo regional state in Ethiopia, is autonomous in name, the Oromo do not have any meaningful voice in the affairs of their own state, which is totally controlled by the TPLF.
The later represents no more than seven percent of the population of Ethiopia, while the Oromo, who constitute the single largest national group in Ethiopia and the third largest national group in the whole of Africa. The Oromo are denied the basic democratic rights to organize freely and legally and express their political opinions. There is no single independent newspaper or media outlet catering to the Oromo populace in their native tongue.
The TPLF fears the Oromo numerical strength deliberately characterizes all independent Oromo organizations, which it does not control as the “terror wing” of the OLF. The goal for such characterization is to persecute peaceful supporters of the OLF behind the façade of fighting against a “ terrorist organization.” Under the anti-terror law of the current Ethiopian regime, anyone who is suspected of peacefully supporting the OLF, could be sentenced to life imprisonment or executed. The above mentioned 459 Oromo nationals who were sentenced to death or life imprisonment are all suspected OLF supporters.
Destroying the lives of 528 innocent human beings on political ground is a crime against humanity, which must be condemned by all civilized nations. The tearless cry of the U.S. AnnuaL Human Rights report notwithstanding, at this moment no calling is more urgent and more noble and no responsibility greater for those who believe in human rights than raising their voice for pressuring the government of Ethiopia to free the 528 innocent individuals who were sentenced to death and life imprisonment on purely political grounds.
In the last year alone, two Oromo activists have died in prison under mysterious circumnances. Last year, OPride reported about the death in prison of former UNHCR recognized refugee, engineer Tesfahun Chemeda. Last month, a former parliamentary candidate from Chalenqo in Western Hararghe, Ahmed Nejash died in prison. According to an OPC source, Nejash successfully run and challenegd Sufian Ahmed, Ethiopia’s Minister of Finance and Development, during the 2010 elections. He was subsequently arrested in 2011 alleged of being an OLF activist. Although his death recieved scant media coverage even within the Oromo community, a close relative of the late Jarra Abba Gadaa, Nejash is one of the veterans of Oromo people’s struggle. “He was sentenced to seven years, which was also upheld by the higher court,” the OPC told OPride source said. “He was in Zuway with Bekele and Olbana and he was healthy the last time I saw him in 2013.”
http://www.opride.com/oromsis/news/horn-of-africa/3735-us-slams-ethiopia-s-human-rights-abuse
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.
Ethiopia’s Land & Water Grabs Devastate Communities: New Satellite Imagery Shows Extensive Clearance of Land Used By Indigenous People to Make Way for State-Run Sugar Plantations February 25, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Environment, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Hadiya, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Sidama, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Gambella and Omo Valley, Genocide against the Oromo, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Water and Land Grabs in Ormia, World Bank
1 comment so far

‘Ethiopia’s Lower Omo Valley, a UNESCO World Heritage site and home to 200,000 agro-pastoralists, is under development for sugar plantations and processing. The early stages of the development have resulted in the loss of land and livelihoods for thousands of Ethiopia’s most vulnerable citizens. The future of 500,000 agro-pastoralists in Ethiopia and Kenya is at risk.’ – Human Rights Watch
http://www.hrw.org/node/123131
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/lori-pottinger/ethiopia-pushes-river-bas_b_4811584.html
(Nairobi) – New satellite imagery shows extensive clearance of land used by indigenous groups to make way for state-run sugar plantations in Ethiopia’s Lower Omo Valley, Human Rights Watch and International Rivers said today. Virtually all of the traditional lands of the 7,000-member Bodi indigenous group have been cleared in the last 15 months, without adequate consultation or compensation. Human Rights Watch has also documented the forced resettlement of some indigenous people in the area.
The land clearing is part of a broader Ethiopian government development scheme in the Omo Valley, a United National Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Site, including dam construction, sugar plantations, and commercial agriculture. The project will consume the vast majority of the water in the Omo River basin, potentially devastating the livelihoods of the 500,000 indigenous people in Ethiopia and neighboring Kenya who directly or indirectly rely on the Omo’s waters for their livelihoods.
“Ethiopia can develop its land and resources but it shouldn’t run roughshod over the rights of its indigenous communities,” said Leslie Lefkow, deputy Africa director at Human Rights Watch. “The people who rely on the land for their livelihoods have the right to compensation and the right to reject plans that will completely transform their lives.”
A prerequisite to the government’s development plans for the Lower Omo Valley is the relocation of 150,000 indigenous people who live in the vicinity of the sugar plantations into permanent sedentary villages under the government’s deeply unpopular “villagization” program. Under this program, people are to be moved into sedentary villages and provided with schools, clinics, and other infrastructure. As has been seen in other parts of Ethiopia, these movements are not all voluntary.
Satellite images analyzed by Human Rights Watch show devastating changes to the Lower Omo Valley between November 2010 and January 2013, with large areas originally used for grazing cleared of all vegetation and new roads and irrigation canals crisscrossing the valley. Lands critical for the livelihoods of the agro-pastoralist Bodi and Mursi peoples have been cleared for the sugar plantations. These changes are happening without their consent or compensation, local people told Human Rights Watch. Governments have a duty to consult and cooperate with indigenous people to obtain their free and informed consent prior to the approval of any project affecting their lands or territories and other resources.
The imagery also shows the impact of a rudimentary dam built in July 2012 that diverted the waters of the Omo River into the sugar plantations. Water rapidly built up behind the shoddily built mud structure before breaking it twice. The reservoir created behind the dam forced approximately 200 Bodi families to flee to high ground, leaving behind their crops and their homes.
In a 2012 report Human Rights Watchwarned of the risk to livelihoods and potential for increased conflict and food insecurity if the government continued to clear the land. The report also documented how government security forces used violence and intimidation to make communities in the Lower Omo Valley relocate from their traditional lands, threatening their entire way of life with no compensation or choice of alternative livelihoods.
The development in the Lower Omo Valley depends on the construction upstream of a much larger hydropower dam – the Gibe III, which will regulate river flows to support year-round commercial agriculture.
A new film produced by International Rivers, “A Cascade of Development on the Omo River,” reveals how and why the Gibe III will cause hydrological havoc on both sides of the Kenya-Ethiopia border. Most significantly, the changes in river flow caused by the dam and associated irrigated plantations could cause a huge drop in the water levels of Lake Turkana, the world’s largest desert lake and another UNESCO World Heritage site.
Lake Turkana receives 90 percent of its water from the Omo River and is projected to drop by about two meters during the initial filling of the dam, which is estimated to begin around May 2014. If current plans to create new plantations continue to move forward, the lake could drop as much as 16 to 22 meters. The average depth of the lake is just 31 meters.
The river flow past the Gibe III will be almost completely blocked beginning in 2014. According to government documents, it will take up to three years to fill the reservoir, during which the Omo River’s annual flow could drop by as much as 70 percent. After this initial shock, regular dam operations will further devastate ecosystems and local livelihoods. Changes to the river’s flooding regime will harm agricultural yields, prevent the replenishment of important grazing areas, and reduce fish populations, all critical resources for livelihoods of certain indigenous groups.
The government of Ethiopia should halt development of the sugar plantations and the water offtakes until affected indigenous communities have been properly consulted and give their free, prior, and informed consent to the developments, Human Rights Watch and International Rivers said. The impact of all planned developments in the Omo/Turkana basin on indigenous people’s livelihoods should be assessed through a transparent, independent impact assessment process.
“If Ethiopia continues to bulldoze ahead with these developments, it will devastate the livelihoods of half a million people who depend on the Omo River,” said Lori Pottinger, head of International Rivers’ Ethiopia program. “It doesn’t have to be this way – Ethiopia has options for managing this river more sustainably, and pursuing developments that won’t harm the people who call this watershed home.”
Background
Ethiopia’s Lower Omo Valley is one of the most isolated and underdeveloped areas in East Africa. At least eight different groups call the Omo River Valley home and the livelihood of each of these groups is intimately tied to the Omo River and the surrounding lands. Many of the indigenous people that inhabit the valley are agro-pastoralist, growing crops along the Omo River and grazing cattle.
In 2010, Ethiopia announced plans for the construction of Africa’s tallest dam, the 1,870 megawatt Gibe III dam on the Omo River. Controversy has dogged the Gibe III dam ever since. Of all the major funders who considered the dam, only China’s Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) provided financing (the World Bank, African Development Bank, and European Investment Bank all declined to fund it, though the World Bank and African Development Bank have financed related power lines).
The Ethiopian government announced even more ambitious plans for the region in 2011, including the development of at least 245,000 hectares of irrigated state-run sugar plantations. Downstream, the water-intensive sugar plantations, will depend on irrigation canals. Although there have been some independent assessments of the Gibe dam project and its impact on river flow and Lake Turkana, to date the Ethiopian government has not published any environmental or social impact assessments for the sugar plantations and other commercial agricultural developments in the Omo valley.
According to the regional government plan for villagization in Lower Omo, the World Bank-supported Pastoral Community Development Project (PCDP) is funding some of the infrastructure in the new villages. Despite concerns over human rights abuses associated with the villagization program that were communicated to Bank management, in December 2013 the World Bank Board approved funding of the third phase of the PCDP III. PCDP III ostensibly provides much-needed services to pastoral communities throughout Ethiopia, but according to government documents PCDP also pays for infrastructure being used in the sedentary villages that pastoralists are being moved to.
The United States Congress in January included language in the 2014 Appropriations Act that puts conditions on US development assistance in the Lower Omo Valley requiring that there should be consultation with local communities; that the assistance “supports initiatives of local communities to improve their livelihoods”; and that no activities should be supported that directly or indirectly involve forced evictions.
However other donors have not publicly raised concerns about Ethiopia’s Lower Omo development plans. Justine Greening, the British Secretary of State for International Development, in 2012 stated that her Department for International Development (DFID) was not able to “substantiate the human rights concerns” in the Lower Omo Valley despite DFID officials hearing these concerns directly from impacted communities in January 2012.
Ethiopia: Land, Water Grabs Devastate Communities | Human Rights Watch
http://www.hrw.org/news/2014/02/18/ethiopia-land-water-grabs-devastate-communities
A Cascade of Development on the Omo River:Lake Turkana at Risk from Dams and Plantations February 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Culture, Development, Economics, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Gambella and Omo Valley, Gibe III Dam, Gibee River, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Lake Turkana, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Omo River, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, State and Development, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
1 comment so far
Omo River, Lake Turkana at Risk from Dams and Plantations
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/lori-pottinger/ethiopia-pushes-river-bas_b_4811584.html
Dams and irrigated plantations being built in Ethiopia will bring major changes to the flow of the Lower Omo River, which in turn will harm ecosystem functions and local livelihoods all the way to the river’s terminus at Lake Turkana in Kenya. More dams are planned for the basin that would compound the damages.
Here we outline some of the basic changes that can be expected as a result of these developments, and include resources on where to get more information.
The Gibe III reservoir is expected to start filling at the beginning of the next Kiremt rainy season (approximately May 2014); filling the reservoir will take up to three years. During this time, the river’s yearly flow will drop as much as 70%.
The Gibe III will provide stable flows year-round that will enable the growth of large commercial agricultural plantations in the Lower Omo. The Kuraz sugar plantation and additional areas identified for cultivation could eventually take almost half of the Omo River inflow to Lake Turkana.
These projects will cause a decrease in river flow and the size, length, and number of floods, which will be disastrous for downstream users. This is the first year in which runoff from the Kiremt season, which is vital for flood-recession agriculture, restoration of grazing areas, and fisheries production, will be almost completely blocked.
Changes to the flooding regime will disrupt fish spawning cues and decrease productive habitat for fish in Lake Turkana and the river. Lake fish catches may decrease.
Because the Omo River contributes almost all of Lake Turkana’s inflows each year, these developments could cause a big drop in lake water levels. Lake Turkana is projected to drop by about two meters during the initial filling of the dam. If current plans to create new plantations move forward, the lake could drop from 16 to 22 meters. The average depth of the lake is just 31 meters.
Climate change could worsen the water situation in the Omo. More extreme droughts and unpredictable precipitation patterns, combined with higher temperatures (which increase evaporation), could cause further stress to a region that already experiences extreme precipitation variability. There is evidence that there will be a drying trend and warmer temperatures.
The Gibe III and associated irrigation projects will limit people’s mobility and ability to practice diverse livelihoods, which are important ways people in the region have adapted to climate variability in the past.
The primary means of livelihood for about 500,000 people will be dismantled by the Gibe III and large-scale commercial agriculture. Conflicts over scarce resources are expected to increase.
http://www.internationalrivers.org/resources/omo-river-lake-turkana-at-risk-from-dams-and-plantations-8199
http://www.internationalrivers.org/blogs/258/human-rights-must-come-first
Dependency Aid is Dysfunctional: Time for Self-sufficiency February 19, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Food Production, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Aid and Development, Developing country, Development, Development aid, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Land grabbing, Oromia, Social Sciences, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
Against the dysfunctional dependency foreign assistance, Clare Lockhart in World Affairs argues for cheaper, smarter and stronger aid that creates self-sufficiency.
‘Commerce [and] entrepreneurial capitalism take more people out of poverty than aid . . . . It’s not just aid, it’s trade, investment, social enterprise. It’s working with the citizenry so that they can unlock their own domestic resources so that they can do it for themselves. Think anyone in Africa likes aid? Come on.’
Putting these “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches into effect will require some major shifts. It will involve looking not to how much money was disbursed, or how many schools were built, but to value for money and return on investment. And instead of propping up a vast technical assistance industry of varying and often indifferent quality, a higher priority will be placed on conducting a “skills audit” of key personnel—from doctors and teachers to engineers and agronomists—who can be trained internally rather than importing more costly and less invested technical assistance from abroad.
‘It is also important under this new paradigm to distinguish between “aid” (such as life-saving humanitarian assistance and the financial or material donations it requires) and “development engagement,” which is something quite different. Development engagement can be low-budget, and should be designed to move a needy country toward self-sufficiency—so that the state can collect its own revenues and the people can support their own livelihoods—as soon as possible. Many recipient countries have enormous untapped domestic resources, and with some effort devoted to increasing those revenues and building the systems to spend them, could assume much more of the responsibility of meeting their citizens’ needs.’
But a strategy is only as good as its execution. Implementing development policies and programs correctly will require a clear-eyed look at the way programs are designed and implemented, and a re-examination of the reliance on contractors. There is no substitute in the long term for unleashing a society’s domestic potential of human, institutional, and natural capital through a well governed country.
‘Having judged the development programs of the last decade to be failures, many in the US now call for development budget cuts and wearily espouse isolationism. But it is a classic example of throwing the baby out with the bathwater. Failed methods do not mean that the goal of international development must be abandoned. Development needn’t be an indulgent venture in charity, or risky business, or a road to nowhere paved with good intentions. A more hardheaded approach, one that creates self-sufficiency rather than dependency, is the new beginning that the development world has been waiting for.’ – http://www.worldaffairsjournal.org/article/fixing-us-foreign-assistance-cheaper-smarter-stronger
In 2002, during the early stages of Afghanistan’s reconstruction process, I sat in a remote part of Bamiyan Province with a group of villagers who told me how excited they had been several months before, when a $150 million housing program from a UN agency had been announced on the radio. They felt the program, which promised to bring shelter to their communities, would transform their lives. They were shocked, however, to discover soon after that this program had already come and gone—with very little change to their lives. Indignant, as well as curious, they decided to track the money and find out what had happened to the program that, as far as they were concerned, had never been. Becoming forensic accountants, they went over the files and figures and found that the original amount granted by the UN had first gone through an aid agency in Geneva that took twenty percent off the top before sub-contracting to a Washington-based agency that took another twenty percent. The funds were passed like a parcel from agency to agency, NGO to NGO, until they limped to their final destination—Afghanistan itself. The few remaining funds went to buy wood from Iran, shipped via a trucking cartel at above-market rates. Eventually some wooden beams did reach the village, but they were too heavy for the mud walls used in construction there. All the villagers said they could do was cut up the wood for firewood, sending $150 million literally up in smoke.
With examples like this, it’s really no surprise that a growing chorus of commentators claims that foreign development is expensive, ineffective, and often resented by the intended beneficiaries. In The White Man’s Burden, for instance, William Easterly provides a searing critique of this do-good mentality, which he shows often causes more harm than help. In The Crisis Caravan, Linda Polman documents the unintended consequences of humanitarian assistance. In Dead Aid, Dambisa Moyo argues that aid serves to fuel corruption and lack of accountability among elites.
Critics of US assistance build on this narrative to paint a picture of an America overstretched and in decline, wasting money abroad in a futile effort to serve its uncertain foreign policy objectives, and call for cutbacks and disengagement.
The US has spent $100 billion in nonmilitary funds to rebuild Afghanistan. Yet, after a decade of mind-bending mismanagement and unaccountability, it seems all for naught.
Some of America’s recent engagements abroad have indeed been marked by extraordinary waste and poor design. As Joel Brinkley described in an article in this publication one year ago (“Money Pit,” January/February 2013), American aid to Afghanistan has at times been extravagantly wasteful, as when a contractor overbilled the US government by $500 million. Brinkley also points to the general practice of outsourcing aid projects to contractors with little oversight. Such failures undermine confidence in the very notion of US efforts in confronting poverty and call into question our ability to deal with conflict through “soft power.”
But this criticism misses an important distinction: it is not the principle of engagement, but the way many development projects work that has led to failure. There is, in fact, an alternative way of engaging abroad to promote stability and prosperity with more lasting effect and at a far lower cost than what has become a discredited status quo.
This alternative approach recognizes that there is no shortcut to development that circumvents the citizens and governing institutions of the country. It recognizes the prominent role of entrepreneurial and civic activity. It demonstrates an understanding that institutional change requires years, not months. It has been practiced by a number of farsighted development programs that have reinforced principles of partnership and local ownership of the policy agenda. This “Learn to Fish for a Lifetime” model seeks to build up local institutions that provide security, good governance, and other elements of self-sustaining economic growth. It takes advantage of the things that America knows how to do well: mobilizing investors, firms, universities, and other potent but underused tools that leverage private capital to deliver a kind of development that far outlasts the initial intervention. Many of the activities undertaken with this model actually generate enough revenue to pay back the initial investment, meaning that foreign development projects could someday operate at or close to “net zero” expenditure to the US taxpayer, a particularly appealing prescription in an era of harsh fiscal realities.
Putting “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches into practice, however, requires rejecting the prevailing approach, which makes for a complicated and ultimately self-defeating operation, in favor of one that emphasizes return on investment, both financially and in terms of improved conditions on the ground.
My own wake-up call to the yawning gap between the intentions and impact of major development programs came in that remote part of Afghanistan, soon after the Taliban had fled. Stories similar to the one I heard have been documented by the US special inspectors general for Iraq and Afghanistan reconstruction. But it is not just in combat zones where billions of taxpayers’ funds have created disappointment. After Haiti’s tragic earthquake in January 2010, world powers promised to “build back better” and citizens internationally joined them in committing billions of dollars to that country’s reconstruction. Aid programs in Haiti were notoriously dysfunctional even before the earthquake, but in the scramble to provide help after the catastrophe, funds and opportunities were squandered on an even grander scale. More than three years on, results have fallen far short of the promise. It is what one commentator and Haiti expert, Jonathan Katz, bleakly referred to in the title of his book on the aftermath of the earthquake: The Big Truck That Went By: How the World Came to Save Haiti and Left Behind a Disaster.
Haitian President Michel Martelly has been vocal in his criticisms of the effort, too: “Where has the money given to Haiti after the earthquake gone? . . . Most of the aid was used by nongovernmental organizations for emergency operations, not for the reconstruction of Haiti . . . . Let’s look this square in the eye so we can implement a better system that yields results.”
As Mark Schuller documents in his book Killing with Kindness, foreign donors directed the money to a network of NGOs that bypassed the Haitian government’s policy framework and the implementation capacity of its private sector, and thereby failed to meet the priorities of its citizens. Haitian organizations saw very little of the investment they needed to rebuild their society, but instead were overwhelmed by a vast aid machinery that parachuted down upon them with its own rules and priorities and complex bureaucracy.
Failure, as Haiti showed, does not come from a shortage of money or goodwill. Rather, the aid business has been afflicted by a set of institutional pathologies that almost guarantee failure. Projects designed in national capitals and foreign embassies are often divorced from the realities of the local lives of the people they intend to help, while the long time frames and rigidity of design mean that by the time a project rolls out, it is often irrelevant, even if money actually arrives after the overhead is paid to the food chain of delivery organizations. Multiple contractual layers mean too much of the original project money never even leaves international capital regions—especially Washington.
In Banda Aceh, Indonesia, analysts report how an NGO spent nearly $1 million of European Commission money on a project to construct eleven boatyards intended to stimulate the livelihoods of local fishermen, but in the end only created ten boats, none of them seaworthy.
Somewhere along the way, incentives have become skewed. Project managers and contractors alike are monitored mainly for whether the money in their charge can be tracked, rather than for whether aid activities have any transformational power. For many aid agencies, moreover, running projects has become the goal, rather than seeking to foster institutions and build productive partnerships among governments, firms, and communities. The metrics track whether a project was completed and the money disbursed, not whether sustainable institutions were left after the money had come and gone.
Finally, much of what has become standard procedure in the development business distorts local markets and displaces market activity. Every time a wheat consignment is distributed for free, for instance, local farmers see the market price for their locally grown wheat decrease. In Afghanistan in 2003, after a large-scale World Food Program wheat distribution, farmers threw up their hands and simply let their crops rot because aid had collapsed the market. Nor is it only farmers who are affected by thoughtless charity. Every time solar panels, water pumps, tractors, or cell phones are handed out for free, a local supplier can no longer sell and install his inventory, and a small business that might have long-range prospects for hiring and supporting several people is smothered.
The perversity of incentives operating in the aid and development field is no longer a trade secret. It has caught the attention of even some of the founders of the modern aid movement. “Aid is just a stopgap,” the pop star Bono, one of the forces behind putting charity to Africa on the map through the Live Aid concerts, told an audience at Georgetown University in November 2012. “Commerce [and] entrepreneurial capitalism take more people out of poverty than aid . . . . It’s not just aid, it’s trade, investment, social enterprise. It’s working with the citizenry so that they can unlock their own domestic resources so that they can do it for themselves. Think anyone in Africa likes aid? Come on.”
In an apparent one-eighty from his earlier focus on simply mobilizing aid donations, Bono’s Live Aid partner, Sir Bob Geldof, has followed suit by launching an infrastructure investment firm for Africa, proclaiming, “I want to leave behind me firms, farms, and factories.”
While the stories of what didn’t work in Afghanistan have grabbed the headlines, there have also been several examples of successful development engagement there. The National Solidarity Program in Afghanistan, for example, has directly reached more than thirty-eight thousand villages since 2003. Under its approach, a block grant, ranging from $20,000 to $60,000, goes directly to a bank account held by the village council, or Community Development Council. The village doesn’t have to apply for the funds, but if it wants to, it must follow three simple rules: elect or appoint the council, ensure a quorum of residents attend meetings to choose projects, and post the accounts in a public place. To date, the program has disbursed more than $1.6 billion, and the village councils have completed more than seventy thousand projects—roads to the local markets, water canals, and generators and microhydro systems that electrify the area.
In one case, thirty-seven villages trying to combat the loss of women in childbirth got together and pooled their money to build a maternity hospital. In another case, one hundred and eighty-five villages pooled their money to create a watershed management system, vastly expanding the land they could cultivate. NGOs are involved in these projects as facilitators who support the village through the complex transactions that it must undertake, but unlike in the traditional model of development, they don’t hold the purse strings or oversee the implementation of projects. The US Agency for International Development is now part of an international consortium that contributes to the program costs.
Similar projects exist at even greater scale in Indonesia and Pakistan. In Indonesia, the National Program for Community Empowerment (PNPM) works in more than eighty thousand villages across the nation. The program formed in 1998, in the wake of the Asian financial crisis, with the imperative to benefit communities directly with cash. Neither the government’s social safety nets nor the NGOs could do this alone, and so a partnership between governments and communities was established. Over time, the program has evolved to include micro-finance and other investment facilities, barefoot lawyers programs, and the construction of schools—all managed directly by the villages themselves.
According to official numbers, one of the PNPM programs, PNPM Mandiri Rural, reached four thousand three hundred and seventy-one sub-districts by 2009, and saw the construction or rehabilitation of ten thousand kilometers of road, two thousand and six bridges, two thousand nine hundred and eighty-six health facilities, and three thousand three hundred and seventy-two schools, in addition to the construction of public sanitation facilities and irrigation systems. These projects increased per capita consumption gains by eleven percent and reduced unemployment by one and a half percent. PNPM can accomplish all of this because of an open planning process by which projects are targeted to meet demand as expressed by the community rather than by officials thousands of miles away.
In a similar operation in Pakistan, the Rural Support Programs Network (RSPN) partners with three hundred and twenty thousand community organizations, covering five million households and thirty-three million people. These organizations have led responses to the earthquakes and floods, organized micro-finance and health insurance schemes, and built and operated schools, clinics, roads, and hydropower schemes.
This family of homegrown programs in Afghanistan, Indonesia, and Pakistan, and similar ones in Colombia, Mexico, and India, have proven it is possible to reach communities directly and at scale, cutting out the layers of contractors and NGOs that function as middlemen, while making communities the implementers of their own development in projects that achieve real results.
We really don’t need to look far afield to find approaches that work. There are a number of distinctly American approaches to development that have delivered in the past but have fallen unaccountably into disuse. Take the Economic Cooperation Act of 1948, a framework that for a while worked exceptionally well, but whose practices have been strangely forgotten in recent decades. At its core was the idea of facilitating “the achievement by the countries . . . of a healthy economy independent of extraordinary outside assistance.” The act’s programs, including the tremendously successful Marshall Plan, were geared toward the institutional and economic self-sufficiency of the recipients, with a central premise that the program could be judged a success only if it reduced the need for aid, rather than perpetuating it.
The Marshall Plan worked for the countries it sought to benefit and worked for the donor as well, paying the US back dividends both economically and in security terms far above its costs. This did not happen by chance. One of the participants in this plan, the political scientist Herbert Simon, describes in Administrative Behavior the painstaking organizational design that went into fine-tuning its approach. George Kennan, in a now-declassified memo from 1947, argued that “it is absolutely essential that people in Europe should make the effort to think out their problems and should have forced upon them a sense of direct responsibility for the way the funds are expended. Similarly, it is important that people in this country should feel that a genuine effort has been made to achieve soundness of concept in the way United States funds are to be spent.”
Other lesser-known US development programs similarly brought impressive results with moderate or no cost to the US taxpayer.
In the aftermath of the Korean War, South Korea had one of the lowest GDPs on earth, but between 1966 and 1989, it raised its GDP by an average of eight percent per year. Behind this story lies a dedicated effort to foster local capacity and industrial-led growth, backed by a US partnership. In 1966, President Lyndon Johnson agreed with President Park Chung-hee of South Korea to help establish the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and assembled a team of leading scientists and technical experts to form and plan the institute. KIST aimed to nurture Korea’s own technical and managerial capacity to lay the basis for its economic transformation, rather than remain dependent on foreign management and input for its projects and companies. Korea is now one of a handful of nations that combine GDP per capita in excess of $20,000 with a population of more than fifty million people.
The South Korean government and the US government each contributed $10 million to KIST at its founding, and Washington used a similar model when it helped establish the Saudi Arabian National Center for Science and Technology (SANCST) in 1977. Saudi funds went to the US Treasury, which in turn paid for the technical assistance required for the center and a range of other initiatives.
Many of the best development initiatives are not directed by governments, but by the private sector and its use of market mechanisms. One example is the involvement of the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) in the Afghan telecom sector. In 2002, Afghanistan had sparse telephone coverage, with access only either through a small number of fixed lines or very expensive satellite coverage. The UN proposed that the telecom sector should be addressed through an aid-driven approach, whereby funds would be used to contract with a major cell phone provider to set up services that would provide coverage to key embassies and aid agencies, at an estimated cost in the tens of millions of dollars. But, in line with how cell phone services are organized in any developed country, it was decided instead that rather than being paid by the government or aid agencies, the telephone company would bid for the license to operate a commercial service, with the proviso that services include a certain level of coverage and standard of quality.
The tender process went ahead. Several international companies registered their interest, but many expressed reservations about the level of risk they would be undertaking. This is where OPIC stepped in to draw up a risk guarantee for possible political and security problems. With an expenditure of just $20 million, this agreement provided sufficient confidence in the telecom sector for investment to proceed. By now, several billion dollars have been invested, more than sixteen million phones purchased, significant revenues generated via taxes to the Afghan government—and the $20 million guarantee was never called upon because the risks feared by the private companies never materialized. In this case, a risk instrument was able to pave the way for new market opportunities and to provide an essential service. Contrast that with the typical aid approach, which would have distorted the market, squandered money, and likely produced, at best, ambiguous results.
A similar example came out of the Caribbean. Before 2007, individual insurance companies were reluctant to insure Caribbean islands for hurricane and earthquake damage, the liability being considered commercially too risky. But then the World Bank’s Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility (CCRIF) was created, pooling risk to enable governments in the area to purchase affordable insurance. CCRIF was designed to protect Caribbean countries from the financial fallout of a natural disaster, offering each country timely and flexible payouts. The group can respond more quickly and more efficiently to a member country in need than can the sort of chaos of good intentions that descended on Haiti, as was demonstrated in its response to Hurricane Tomas in 2010. Barbados, St. Lucia, and St. Vincent and the Grenadines received fifty percent of their payouts within days.
In contrast to a top-down, statist aid paradigm, these “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches are all designed to unlock and leverage the value from within the society, state, and market. They all start with the operating principle of co-designing programs with the citizens and leaders from the country concerned. Where there is a market, they do not seek to use grant capital. Once the initial intervention is over, success is judged by whether or not the innovations designed for the crisis are sustainable. This approach is geared toward increasing the self-sufficiency of the country concerned, and in particular boosting its economy and generating its own revenue and tax base.
While the treasuries of most Western countries may be afflicted by the constraints of austerity budgeting, there are vast amounts of private investment capital looking for opportunities. Many of the countries that are seen as the neediest destinations for aid are also considered by emerging market investors as the fastest-growing in the world—Rwanda, Nepal, Indonesia, and India. Infrastructure projects from power to roads and ports can and do attract private capital, and public funds can be used for risk guarantees or as co-investments rather than grant aid for these projects. Rather than seeking to maximize aid, such an approach seeks to maximize the return on investment to the society concerned.
Putting these “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches into effect will require some major shifts. It will involve looking not to how much money was disbursed, or how many schools were built, but to value for money and return on investment. And instead of propping up a vast technical assistance industry of varying and often indifferent quality, a higher priority will be placed on conducting a “skills audit” of key personnel—from doctors and teachers to engineers and agronomists—who can be trained internally rather than importing more costly and less invested technical assistance from abroad.
It is also important under this new paradigm to distinguish between “aid” (such as life-saving humanitarian assistance and the financial or material donations it requires) and “development engagement,” which is something quite different. Development engagement can be low-budget, and should be designed to move a needy country toward self-sufficiency—so that the state can collect its own revenues and the people can support their own livelihoods—as soon as possible. Many recipient countries have enormous untapped domestic resources, and with some effort devoted to increasing those revenues and building the systems to spend them, could assume much more of the responsibility of meeting their citizens’ needs. Getting the toolbox right requires instruments that can best support this approach: the OPIC, enterprise funds, chambers of commerce, public diplomacy, scholarships, international financial institutions, trade measures, and the National Academies, among others.
But a strategy is only as good as its execution. Implementing development policies and programs correctly will require a clear-eyed look at the way programs are designed and implemented, and a re-examination of the reliance on contractors. There is no substitute in the long term for unleashing a society’s domestic potential of human, institutional, and natural capital through a well governed country.
Having judged the development programs of the last decade to be failures, many in the US now call for development budget cuts and wearily espouse isolationism. But it is a classic example of throwing the baby out with the bathwater. Failed methods do not mean that the goal of international development must be abandoned. Development needn’t be an indulgent venture in charity, or risky business, or a road to nowhere paved with good intentions. A more hardheaded approach, one that creates self-sufficiency rather than dependency, is the new beginning that the development world has been waiting for.
Clare Lockhart is the coauthor, with Ashraf Ghani, of Fixing Failed States and the director of the Institute for State Effectiveness, an organization devoted to finding, documenting, and facilitating better approaches to engaging abroad.
Read further at original source:
http://www.worldaffairsjournal.org/article/fixing-us-foreign-assistance-cheaper-smarter-stronger
Africa: Agribusiness Feeds the Rich; Small Farmers Feed the Rest February 18, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Domestic Workers, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Family Farm in Africa, Industrial Agriculture, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromo, Oromo people, Small Farm, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, World Bank
add a comment
“Agribusiness feeds the rich; small farmers feed the rest. Yet we have a strong interest in feeding the world and are concerned that food conferences dominated by agribusiness directly threaten our ability to produce affordable, healthy, local food.Solving world hunger is not about industrial agriculture producing more food – our global experience of the green revolution has shown that the drive towards this industrial model has only increased the gap between the rich and the poor. Feeding the world is about increasing access to resources like land and water, so that people have the means to feed themselves, their families and their communities. Small family farms produce the majority of food on the planet – 70% of the world’s food supply! If conferences, like this one, exclude the voice of small farmers, then the debate about feeding the world is dominated by the rich and the solutions proposed will only feed their profits.”
A farming revolution is under way in Africa, pushed by giant corporations and the UK’s aid budget. It will surely be good for the global economy, writes Sophie Morlin-Yron, but will Africa’s small farmers see the benefit?
Many millions of small farmers that were once merely poor, will be propelled into destitution, the chaff of a neoliberal market revolution as pitiless as it is powerful.
World leaders in agriculture and development gathered in London last week at the The Economist’s ‘Feeding the World Summit’ to discuss global solutions to tackling Africa’s food security crisis.
At the event, which cost between £700 and £1,000 to attend, industry leaders spoke of new innovations and initiatives which would help fight poverty, world hunger and malnutrition, and transform the lives of millions of farmers worldwide.
Just one farmer
But there was only one farmer among the speakers, Rose Adongo, with barely a handful more in the audience. A Ugandan beef and honey farmer, Adongo was unimpressed by the technical solutions offered by the corporate speakers.
For her, the main issue was land ownership for farmers – and desperately needed changes in Ugandan law, under which women have no right to land ownership even though 80% of the country’s farmers are women, and they produce 60% of the food.
If only a woman could own land – currently passed down from father to son “she can produce more food”. Besides that she wanted cheaper fertilisers and an end to the desperate toil of hand working in the fields. Much of the land is currently plowed by hand which “can take weeks to do”.
Among the excluded …
But many were excluded from the event – and desperately wanted their voices to be heard. Among them was Jyoti Fernandes, from The Landworkers’ Alliance (member of La Via Campesina), a producer-led organisation representing small-scale agroecological producers in the UK.
“Agribusiness feeds the rich; small farmers feed the rest”, she said. “None of our members could afford to attend the Feeding the World Summit.
“Yet we have a strong interest in feeding the world and are concerned that food conferences dominated by agribusiness directly threaten our ability to produce affordable, healthy, local food.
Solving world hunger, she insisted, “is not about industrial agriculture producing more food – our global experience of the green revolution has shown that the drive towards this industrial model has only increased the gap between the rich and the poor.”
Improving access to land and water
“Feeding the world is about increasing access to resources like land and water, so that people have the means to feed themselves, their families and their communities.
“Small family farms produce the majority of food on the planet – 70% of the world’s food supply! If conferences, like this one, exclude the voice of small farmers, then the debate about feeding the world is dominated by the rich and the solutions proposed will only feed their profits.”
As Graciela Romero of War on Want commented in The Ecologist last week, it is that small farmers are feeding the world – not corporations:
“Millions of small-scale farmers produce 70% of the world’s food. Yet they remain excluded and forgotten from exchanges which affect their livelihoods or concern how to end world hunger.”
Private investment
Among the 27 speakers at the event were Nestlé Head of Agriculture Hans Joehr, Monsanto CEO Hugh Grant, Cargill Vice-Chairman Paul Conway, UN Secretary General for Food Security and Nutrition David Nabarro, and representatives from the World Food Program and World Vision.
And despite the involvement of some NGOs, academics UN officials, the main topic of discussion was private sector investment in agriculture.
Lynne Featherstone, a junior UK minister for International Development, said the way forward is newly developed efficient fertilisers, pest tolerant crops and private sector investment:
“There is substantial room for improvement, and helping farmers increase productivity while consuming fewer inputs is a priority. With partners such as CGIAR we have developed more efficient fertilisers and pest tolerant crop varieties.”
UK spending £280m to support private sector engagement
She also outlined the Government plans to invest £280m from its aid budget funding in businesses and organisations under the Alliance for Food Security and Nutrition (AFNC).
This private sector initiative – which has also involves 14 Governments – ostensibly aims to lift 50 million people in Africa out of poverty by 2022, by attracting more private investment in agriculture. Featherstone explained the rationale:
“Economic growth in these countries is best achieved through agricultural growth, which has the power of raising incomes and getting people out of poverty. And the private sector can catalyse that agricultural growth with sustainable agricultural investment.”
But is it really about land grabs?
But critics fear that is has rather more to do with getting governments on-side so corporations can carry out land grabs – taking the best watered and most fertile land away from African farmers and delivering it up to investors to plant cash crops across the continent, while turning once independent small farmers into a a proletarian underclass of landless plantation workers and rootless urban workers.
Paulus Verschuren, Special Envoy on Food and Nutrition Security, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, The Netherlands attempted to strike a balance:
“We are not going to fix the zero-hunger challenge without involving the private sector, but we need to set the criteria for these transformational partnerships. They need to have a business outcome and a development outcome.”
Corporations keen to help small farmers …
Representatives of major food corporations also insisted that they wanted to work with small farmers and help them to produce their crops efficiently while meeting development objectives.
Nestlé’s Corporate Head of Agriculture, Hans Jöhr, claimed to be willing to work with small farmers as well as large to fulfil development objectives and improving resource efficiency:
“The issue of feeding the world has to been seen in perspective of rural development, and not only technology”, he said. “And it’s definitely not about talking small versus big farmers, I think that was really the yesterday talk. It’s about people, individuals, it’s about farmers.
We cannot go on polluting and destroying
“So in this meeting about farmers, when we are talking about farmers, we are going back to what we have listened to, the restrictions we all face in business is natural resources, natural capital. It’s not only about the land, it’s mainly about water.
“This leads us to looking into production systems and methods and understanding that we cannot continue to go on with polluting destroying and depleting natural resources and with wasting them.
“Farmers who don’t know how to farm waste a tremendous amount of natural resources and agricultural materials because they don’t know how to store, and are not linked to an outlet to markets. That means that we have to help them better understand the production systems.”
Productivity must be raised
Vice Chairman of Cargill, Paul Conway, emphasised the importance of secure land ownership: “The number one thing here isn’t technology, it isn’t finance, it’s security of tenure of the land, which is absolutely critical.”
And Monsanto’s CEO Hugh Grant played down the importance of genetic modification in improving crop yields in Africa, from 20 bushels of grain per hectare to India’s typical level of 100 bushels.
“There is no reason Africa shouldn’t be close to India, it’s all small-holder agriculture. Why is it 20 today and not 90? Now forget biotech, that’s eminently achievable with some sensible husbandry and land reform ownership, the tools are in hand today.”
“We have set goals to double yields in the next 30 years with a third less water, agriculture gets through an enormous amount of water. The first 70 per cent of which goes to agriculture, the next 30 per cent goes to Coke, Pepsi, swimming pools and everything you drink and all of industry, and that isn’t sustainable.
We believe our sole focus on agriculture is vital as the world looks to produce enough nutritious food to feed a growing population while conserving, or even decreasing, the use of precious natural inputs such as land, water and energy.”
Farmers ‘invisible and irrelevant’
But Mariam Mayet, Director of African Safety for Biosafety – which campaigns against genetic engineering, privatisation, industrialisation and private sector control of African agriculture – was not convinced.
To the constellation of famous speakers and corporate representatives, she said, small farmers were a simple obstruction to progress:
“We know that all of African farmers are invisible and irrelevant to those at this summit. These producers are seen as inefficient and backwards, and if they have any role at all, it is to be forced out of agriculture to becoming mere passive consumers of industrial food products.
“Africa is seen as a possible new frontier to make profits, with an eye on land, food and biofuels in particular.
“The recent investment wave must be understood in the context of consolidation of a global food regime dominated by large corporations in input supply such as seed and agrochemicals especially, but also increasingly in processing, storage, trading and distribution.
“Currently African food security rests fundamentally on small-scale and localised production. The majority of the African population continue to rely on agriculture as an important, if not the main, source of income and livelihoods.”
Can the chasm be bridged?
If we take the sentiments expressed by corporate bosses at face value – and why not? – then we do not see any overt determination to destroy Africa’s small farmers. On the contrary, they want to help them to farm better, more productively and efficiently, and more profitably.
And perhaps we should not be surprised. After all that suits their interests, to have a growing and prosperous farming sector in Africa that can both buy their products and produce reliable surpluses for sale on global food markets.
The rather harder question is, what about those farmers who lack the technical or entrepreneurial ability, the education, the desire, the extent of land, the security of land tenure, to join that profitable export-oriented sector? And who simply want to carry on as mainly subsistence farmers, supporting their families, producing only small surpluses for local sale?
The small subsistence farmer has no place
Stop and think about it, and the answer is obvious. They have no place in the new vision of agriculture that is sweeping across the continent, with the generous support of British aid money.
Their role in this process is to be forced off their land – whether expelled by force or by market forces – and deliver it up to their more successful neighbour, the corporation, the urban agricultural entrepreneur, to farm it at profit for the market.
And then, either to leave their village homes and join the displaced masses in Africa’s growing cities, or to stay on as landless workers, serving their new masters.
This all represents ‘economic progress’ and increases in net production. But look behind the warm words – and many millions of small farmers that were once merely poor, will be propelled into destitution, the chaff of a neoliberal market revolution as pitiless as it is powerful.
Is this really how the UK’s aid funds should be invested?
Sophie Morlin-Yron is a freelance journalist.
Oliver Tickell edits The Ecologis
http://www.theecologist.org/News/news_analysis/2287243/africas_farm_revolution_who_will_benefit.html
A landmark G8 initiative to boost agriculture and relieve poverty has been damned as a new form of colonialism after African governments agreed to change seed, land and tax laws to favour private investors over small farmers.
Ten countries made more than 200 policy commitments, including changes to laws and regulations after giant agribusinesses were granted unprecedented access to decision-makers over the past two years.
The pledges will make it easier for companies to do business in Africathrough the easing of export controls and tax laws, and through governments ringfencing huge chunks of land for investment.
The Ethiopian government has said it will “refine” its land law to encourage long-term land leases and strengthen the enforcement of commercial farm contracts. In Malawi, the government has promised to set aside 200,000 hectares of prime land for commercial investors by 2015, and in Ghana, 10,000 hectares will be made available for investment by the end of next year. In Nigeria, promises include the privatisation of power companies.
A Guardian analysis of companies’ plans under the initiative suggests dozens of investments are for non-food crops, including cotton, biofuels and rubber, or for projects explicitly targeting export markets.
Companies were invited to the table through the G8 New Alliance for Food Security and Nutrition initiative that pledges to accelerate agricultural production and lift 50 million people out of poverty by 2022.
But small farmers, who are supposed to be the main beneficiaries of the programme, have been shut out of the negotiations.
Olivier de Schutter, the UN special rapporteur on the right to food, said governments had been making promises to investors “completely behind the screen”, with “no long-term view about the future of smallholder farmers” and without their participation.
He described Africa as the last frontier for large-scale commercialfarming. “There’s a struggle for land, for investment, for seed systems, and first and foremost there’s a struggle for political influence,” he said.
Zitto Kabwe, the chairman of the Tanzanian parliament’s public accountscommittee, said he was “completely against” the commitments his government has made to bolster private investment in seeds.
“By introducing this market, farmers will have to depend on imported seeds. This will definitely affect small farmers. It will also kill innovation at the local level. We have seen this with manufacturing,” he said.
“It will be like colonialism. Farmers will not be able to farm until they import, linking farmers to [the] vulnerability of international prices. Big companies will benefit. We should not allow that.”
Tanzania’s tax commitments would also benefit companies rather than small farmers, he said, adding that the changes proposed would have to go through parliament. “The executive cannot just commit to these changes. These are sensitive issues. There has to be enough debate,” he said.
Million Belay, the head of the Alliance for Food Sovereignty in Africa (AFSA), said the initiative could spell disaster for small farmers in Africa. “It clearly puts seed production and distribution in the hands of companies,” he said.
“The trend is for companies to say they cannot invest in Africa without new laws … Yes, agriculture needs investment, but that shouldn’t be used as an excuse to bring greater control over farmers’ lives.
“More than any other time in history, the African food production system is being challenged. More than any other time in history outside forces are deciding the future of our farming systems.”
AFSA has also denounced the G8 initiative as ushering in a new wave of colonialism on the continent.
http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/feb/18/g8-new-alliance-condemned-new-colonialism
As The 1960s Euphorea, The Current Africa Rising Optimism Is Illusionary Than Real: Let Us Actually Think How Africa Can Become Truly Prosperous. February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Culture, Development, Dictatorship, Economics, Food Production, Human Rights, Ideas, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Self determination, Slavery, South Sudan, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Africa Rising, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


‘Much of the “Africa Rising” narrative is based on the cyclical growth in income revenues from commodities. But who knows how long this will last? Dr Moghalu wants African governments to grasp hold of their future by creating industrial manufacturing so that Africans can consume what they produce. If that could be achieved, the continent will have moved away from being an import-driven consumer-driven economy. It is only then, he argues, that we can say Africa has truly risen.’
The term “Africa Rising” is on the lips of many these days particularly as seven of the world’s fastest growing economies are believed to be African. But can this current wave of Afro-optimism bring genuine prosperity to the African continent? Dr Kingsley Chiedu Moghalu, the Deputy Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria thinks not.
“Hope is good,” he says. “But hope must be based on concrete substantive strategy going forward, so I pour a little bit of cold water of the Africa Rising phenomenon. I think it could lead to illusionary thinking. I recall that when African countries became independent that there was a huge sense of euphoria around the continent that independence guaranteed economic growth, political development and stability. But this did not happen in the following 30 to 40 years.”
In his latest book, Emerging Africa: How the Global Economy’s ‘Last Frontier’ can prosper and matter, Dr Moghalu presents his own ideas on how Africa can become truly prosperous. He describes it as “a vision for Africa’s future based on a fundamental analysis of why Africa has fallen behind in the world economy”.
In doing so, the LSE alumnus discusses some fundamental misunderstandings about which African states need to revise their assumptions.
The first is the idea that globalisation is automatically good. Rather, Dr Moghalu describes it as a huge and influential reality which Africans must engage with a sense of sophistication and self-interest. It is important to find a way to break that stranglehold because globalisation is neither benign in its intention nor agnostic in its belief. It is driven by an agenda and there are people who drive it.
Economist Dambisa Moyo caused controversy with her first book, Dead Aid: Why foreign aid isn’t working and how there is another way for Africa. Dr Moghalu echoes some of her arguments describing foreign aid as one of the leading reasons why Africa is impoverished. “It has removed the incentive of many African nations to seek solutions for their economic challenges and create wealth for their citizens,” he argues. “Instead it has perpetuated poverty because they are simply content to survive from one day to the next.”
Foreign aid does have its place, Dr Moghalu admits, but “it should always be within a limited time frame and it should focus on economic wealth creation activities rather than just helping people survive”. On the day we meet, the UK Secretary of State for International Development Justine Greening is in the news revealing that there will be a radical shift in future UK aid into economic development, concentrating on economic growth and jobs. Dr Moghalu expressed great pleasure at this announcement remarking that “it is very interesting that British policy is catching up with the recommendations in my book”.
Another fundamental understanding that the central banker develops in his book is the importance of understanding the four different kinds of capitalism and the implications they have for Africa’s growth. The first is state capitalism which is not very common, although it is practised by China. It is, in fact, an oxymoron. Many African states do not have the capacity to run state capitalism because you need an all-knowing state with a huge reserve of strategic thinking capacity to be able to direct wealth creation for the purposes defined by the state. There is also oligarchic or crony capitalism in Russia and some African states. This can be turned into strategic activity if cronyism is not rampant. South Korea did that by creating the Chaebols, the family-held businesses which today dominate the South Korea economy. Welfare capitalism is the norm is Europe. Some African states have practised welfare capitalism without generating the type of revenue that will sustain it into the future. Now it is out of favour. Entrepreneurial capitalism is what made America wealthy and this is what Dr Moghalu recommends for most African economies because it suits the African culture. Along with a certain amount of oligarchic and welfare capitalism, it would do Africa a world of good, he adds.
Much of the “Africa Rising” narrative is based on the cyclical growth in income revenues from commodities. But who knows how long this will last? Dr Moghalu wants African governments to grasp hold of their future by creating industrial manufacturing so that Africans can consume what they produce. If that could be achieved, the continent will have moved away from being an import-driven consumer-driven economy. It is only then, he argues, that we can say Africa has truly risen. http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/africaatlse/2014/02/12/afro-optimism-will-not-transform-africa/
US Congress Takes a Historic Stance Against Land Grabs-Related Forced Evictions in Ethiopia February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromummaa, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Genocide against the Oromo, Gibe Valley, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Lower Omo, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
See the Omnibus Appropriations Bill (p. 1295-1296) @
http://docs.house.gov/billsthisweek/20140113/CPRT-113-HPRT-RU00-h3547-hamdt2samdt_xml.pdf
Oakland, CA – In a historic move, the US Congress has taken a stance on land grabs-related human rights abuses in Ethiopia. The 2014 Omnibus Appropriations Bill contains provisions that ensure that US development funds are not used to support forced evictions in Ethiopia.
The bill prevents US assistance from being used to support activities that directly or indirectly involve forced displacement in the Lower Omo and Gambella regions. It further requires US assistance in these areas be used to support local community initiatives aimed at improving livelihoods and be subject to prior consultation with affected populations. The bill goes further and even instructs the directors of international financial institutions to oppose financing for any activities that directly or indirectly involve forced evictions in Ethiopia.
According to Anuradha Mittal, Executive Director of the Oakland Institute, “We welcome this move as it aims to address one major flaw of US assistance to Ethiopia. The step taken by the US Congress is very significant, as it signals to both the Ethiopian government and the US administration that turning a blind eye to human rights abuses in the name of development is no longer an option.”
Several reports from the Oakland Institute have raised alarm about the scale, rate, and negative impacts of large-scale land acquisitions in Ethiopia that would result in the forced displacement of over 1.5 million people. This relocation process through the government’s villagization scheme is destroying the livelihoods of small-scale farmers and pastoralist communities. Ethiopian security forces have beaten, arrested, and intimidated individuals who have refused to relocate and free the lands for large-scale agricultural plantations.
Ethiopia’s so-called development programs cannot be carried out without the support of international donors, primarily the US, one of its main donors. Oakland Institute’s on-the-ground research has documented the high toll paid by local people as well as the role of donor countries such as the US in supporting the Ethiopian policy.
This language represents an important first step towards Congress initiating a comprehensive examination of US development practices in Ethiopia. As the oversight authority of the State Department, Congress must now ensure that the law is fully upheld and implemented. This warrants thorough scrutiny of USAID programs to Ethiopia and their contribution to forced resettlements and human rights abuses.
With this bill, USAID, the State Department, as well as the World Bank, will have to reconsider the terms and modalities of the support they provide to the Ethiopian government. According to Frederic Mousseau, Oakland Institute’s Policy Director, “This is a light of hope for the millions of indigenous people in Ethiopia who have sought international support from the international community to recognize their very destruction as communities and people.” Read Further @
USAID’s cover-up of Ethiopia abuses overruled by Congress 12 February 2014
The United States Congress has acted to prevent its aid to Ethiopia being used to fund forced evictions of tribal peoples in the south west of the country.
The provisions in the Omnibus Appropriations Bill for 2014 represent a slap in the face for USAID, which last month said that ‘there are no reports of widespread or systematic human rights abuses’ in the region.
In fact, tribes of the Lower Omo Valley are being violently evicted from their villages by the government to make way for lucrative cotton, palm oil, and sugarcane plantations whose irrigation will be made possible by the controversial Gibe III dam. Transferred to designated resettlement areas, the once self-sufficient tribes will be left with no access to their livestock or lands and, consequently, will be unable to sustain themselves. Intimidation tactics, such as rape and beatings, have reportedly been used against those who resist resettlement.
One Mursi man told Survival International, ‘We are waiting to die. We are crying. When the government collects people into one village there will be no place for crops, and my children will be hungry and have no food.’
The Ethiopian government has not consulted any indigenous communities over its aggressive plantation plans in the Omo Valley, and very few were consulted over the construction of the Gibe III dam.

The region’s top human rights body, the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights, has written to the Ethiopian government asking it to halt the forced resettlement of the Lower Omo tribes while it investigates Survival’s submission regarding human rights violations in the area.
Ethiopia is one of the biggest recipients of American and British aid through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and the UK Department for International Development (DFID).
Although the provisions in the recent spending bill will force USAID to reevaluate the funding given to Ethiopia, it will ultimately be the responsibility of Congress to guarantee that the terms are upheld.
Survival International Director Stephen Corry said today, ‘This bill is a huge step in the right direction, and shows that USAID’s shameful denials of the human rights abuses being committed in the Lower Omo simply haven’t been believed.
‘American taxpayers want to be sure that their money isn’t going toward the destruction of tribal peoples’ lives. Hopefully the historic provisions in this year’s spending bill will ensure that’s the case. It is now high time that British parliamentarians follow suit and ensure that DFID does not use UK taxpayers’ money to fund human rights violations in the Lower Omo.’ http://www.survivalinternational.org/news/9983
Further References on land grabs in Africa
Around 90 percent of the population of 87 million still suffers from numerous deprivations, ranging from insufficient access to education to inadequate health care; average incomes are still well below $1500 a year; and more than 30 million people still face chronic food shortages.
And while there are a number of positive and genuine reasons for the growth spurt – business and legislative reforms, more professional governance, the achievements of a thriving service sector – many critics say that the growth seen in agriculture, which accounts for almost half of Ethiopia’s economic activity and a great deal of its recent success, is actually being driven by an out of control ‘land grab’, as multinational companies and private speculators vie to lease millions of acres of the country’s most fertile territory from the government at bargain basement prices.
At the ministry of agriculture in Addis Ababa, this land-lease programme is often described as a “win-win” because it brings in new technologies and employment and, supposedly, makes it easier to improve health care, education and other services in rural areas.
“Ethiopia needs to develop to fight poverty, increase food supplies and improve livelihoods and is doing so in a sustainable way,” said one official.
But according to a host of NGO’s and policy advocates, including Oxfam, Human Rights Watch and the Oakland Institute, the true consequences of the land grabs are almost all negative. They say that in order to make such huge areas available for foreign investors to grow foodstuffs and bio-fuels for export – and in direct contravention of Ethiopia’s obligations under international law – the authorities are displacing hundreds of thousands of indigenous peoples, abusing their human rights, destroying their traditions, trashing the environment, and making them more dependent on food aid than ever before.
“The benefits for the local populations are very little,” said renowned Ethiopian sociologist Dessalegn Rahmato. “They’ve taken away their land. They’ve taken away their natural resource, because these investors are clearing the land, destroying the forest, cutting down the trees. The government claims that one of the aims of this investment was to enable local areas to benefit by investing in infrastructure, social services … but these benefits are not included in the contract. It’s only left up to the magnanimity of the investor.”
And those investors, he continued, are simply not interested in anything other than serving their own needs: “They can grow any crop they want, when they want it, they can sell in any market they want, whether it’s a global market or a local market. In fact most of them are not interested in the local markets.”
He cited as an example a massive Saudi-owned plantation in the fertile Gambella region of south west Ethiopia, a prime target area for investors: “They have 10,000 hectares and they are producing rice. This rice is going to be exported to the Middle East, to Saudi Arabia and other places. The local people in that area don’t eat rice.”
But the most controversial element of the government’s programme is known as ‘villagisation’ – the displacement of people from land they have occupied for generations and their subsequent resettlement in artificial communities.
In Gambella, where two ethnic groups, the Anuaks and the Nuers, predominate, it has meant tens of thousands of people have been forced to abandon a traditional way of life. One such is Moot, an Anuak farmer who now lives in a government village far from his home.
“When investors showed up, we were told to pack up our things and to go to the village. If we had decided not to go, they would have destroyed our crops, our houses and our belongings. We couldn’t even claim compensation because the government decided that those lands belonged to the investors. We were scared … if you get upset and say that someone stole your land, you are put in prison. If you complain about being arrested, they will kill you. It’s not our land anymore; we have been deprived of our rights.”
Despite growing internal opposition and international criticism, the Ethiopian government shows no sign of scaling the programme back. According to the Oakland Institute, since 2008, an area the size of France has already been handed over to foreign corporations. Over the next few years an area twice that size is thought to be earmarked for leasing to investors.
So what does all this mean for the people on the ground? In Ethiopia – Land for Sale, filmmakers Veronique Mauduy and Romain Pelleray try and find out.
http://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/peopleandpower/2014/01/ethiopia-land-sale-20141289498158575.html
Farming and food in Africa and the battle over land, water and resource rights
Africa is being heralded as the new frontier for commercial farming but, as governments and investors sign deals, a counter movement of family farmers is promoting alternative pathways to development.
The International Year of Family Farming is now underway, and never before have family farmers in Africa been more under threat.
Large land deals between African governments and usually foreign (and sometimes domestic) investors have seen swathes of the countryside leased or conceded, often for as much as 50-99 years. From Senegal in West Africa to Ethiopia in the Horn, and down to Mozambique in the south, land considered idle and available has changed hands, with profound implications for local people and the environment.
Stop Clearing Oromo from their Land in the Name of Boosting Economic Development: Who Will Stand for the Oromo People Living on the Outskirts of Finfinnee? February 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Culture, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Food Production, Gadaa System, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, ICC, Ideas, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, economics, Ethiopia, Finfinnee, Gadaa System, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Raya under destruction, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, World Bank
add a comment


It is to be recalled that Finfinnee (Addis Ababa) was founded as the present capital city the so called Ethiopian in 1886 by a man called Minilik II. During this time, the area was inhabited by the Oromo people and the area was almost covered with natural forest. Initially the Shawa government made it seat at Ankober. Hence, before the founding of Finfinee as a political and economic capital of the king, all the areas within the present Finfinnee and the surround areas was free like any other Oromia lands. However, after 1886 the Semitic people from the northern segments and others had taken the land and the Oromo people who were used to live in these areas were forced lost their land through time.
For example, according to Central Statistics Agency of Ethiopia (2007) Out of the 2,738,248 100% total population living in Finfinnee, the total number of the Oromo people living in the city was only 534,255 (19.51%). Since its founding as a capital, Finfinnee remained the capital city for the successive Ethiopian regimes (Menilik II, Lij Eyassu, Zawuditu, Hailesillasse I, Mengistu, Melles and HaileMariam). Through time, the number of inhabitants increased and urbanization expanded greatly. The deliberate and implicitly planned mission and decision of the Semitic people to erase any sign of Oromo history from Finfinnee was started during the forcefully integration of Oromo people into Ethiopia as second-class citizens and the process has continued in the present government.
Different people mostly from the northern part of the so called Ethiopia have come from the various ethnic groups come and settled in the capital owing to its supper suitable agro-climatic and exploit the natural within the outside today’s Finfinne from the near distance in the name of work and investment. Where did those Oromo farmers go when Finfinnee became the property of new invaders? Be in mind that the Oromo’s are pushed to the peripheral areas of the capital and the number of Oromo people inhabitants decreased from time to time, as the above data depicts. The indigenous people of the land were pushed out one after the other and were replaced by the invaders from the north. What is happening to the Oromo people living on the outskirt of Finfinne today? It is simply the continuation of a process, which had resulted in a massive displacement of an indigenous Oromo people.
B. The New Master Plan of Fifinnee and Areas to be Incorporated
For the last 100 or so years the Master Plan of Finfinnee city was revised several times. The recent proposal of preparing new Master Plan for City administration that planned to incorporates all the towns and districts lying within the range of 1 hour commuting distance from the Finfinnee, justifies the blatant violation of the constitution and their voracious appetite to systematically replacing resource and land deficient people to these fertile lands owned by the Oromo people. According to the proposed plan of established the “Integrated Regional Development Plan”, an additional 36 towns and 17 districts currently administered by the Oromia regional State will be merged with Finfinnee so that the right of the land use will be determined by the central mayor .
The new Master Plan was intended to incorporate Oromia’s land locating in 100kms around the Finfinnee city. According to Ethiopia Government preparation, the following 36 Towns and 17 Districts are included in the newly planned Master plan. (See the figure 1.)
Some of the Towns are: Adama, Sodere, Mojo, Wenji Adama, Ejere, Alem Tena, Koka, Adulala, Bushoftu, Dukem, Gelen, Akaki Beseka, Godino, Chefe Donsa, Sebeta , Sendafa, Milkewa, Wendoda, Sirti, Duber,Gorfo, Chancho, Mulo, Debra,Muger , Ulo, Adis Alem, Holota, Burayu,Debre Genet, Illu Teji, Tefki, Sebeta, Boneya, Melka Kunture and etc.
Some of the Districts areas are: Adama, Dodota, Bora, Lome, Liben chukala, Adea (around Bushoftu), Akaki, Gimbichu, Bereh(around Sebeta), Aleltu, Jida, Sulultu, Ejere, Welmera, Illu, Sebeta Hawas and etc.
Today, when the world is concerned about preserving ecology and wild life in their natural habitat, it is an Ethiopian Government that is clearing an indigenous Oromo people from their home Land in the name of inequitable Economic Development. Hence, who should stand and speak for these innocent people and argue to preserve the right of the extremely vulnerable Oromo people living in the proposed territories and to preserve the indigenous Oromo people, culture, Languages and etc. Otherwise sooner than latter these great people will be marginalized and lost their identities.

Figure 1: The newly Developed and proposed Master Plan of the tomorrow’s Finfinne over the coming 25 years
C. The Agenda behind the “Integrated Regional Development Plan (IRDP)”
An office called “Addis Ababa and the surrounding Oromia Integrated Development Plan” prepared an International and National Conference on June 2013 at Adama Town, Galma Abba Gadaa. The Objective of organizing the conference of the top ranking government cadres (mostly OPDO’s) was to work on the manifesting of the proposed Integrated Regional Development Plan (IRDP) and prepare the cadre’s to work on the people.
On the Conference, it was stated that, the Purposes of the “IRDP” are:
Instrumental to unleashing Regional Development Potentials
Enables localities addressing their mutual development challenges
Enables localities addressing their mutual development challenges
Strengthens complementarities and interconnection of localities
These purposes can be the explicit or clear objectives of the plan. However, the plan have hidden or implicit agenda. Systematically bringing the land under their custody so that, it will sooner or later scramble among their impoverished people in their region. For example, the Finfinnee City Administration and Finfinnee Special Zone can address their mutual development challenges without being incorporated into one master plan. However, the Master plan is not prepared on mutual benefit as the plan is solely prepared by Finfinnee City Administration, despite the name of the office. Hence, though development is boldly emphasized, the main purpose seems to clear the Oromo farmers from their lands in the name of unfair Economic Development.
It was also stated that the Pillars of the Integrated Regional Development Plan are:
Regional Infrastructure Networks
Natural Resource and Environment Stewardship
Cross – Boundary Investments/ e.g FDI)
Joint Regional Projects
However, there seem hidden agenda behind these pillars. For example, in the name of cross-Boundary Investments, local Oromo farmers are going to lose their land for the so-called “investors” and under the pretext of promoting national economy through FDI initiatives In addition, if the plan is going to be realized natural and environmental degradation is inevitable.
In addition, the Basic Principles of the Integrated Regional Development Plan are:
Ensuring Mutual Benefits
A joint development Framework – not a substitute for local plans
An Integrated Regional Plan voluntarily accepted by participating partners
Differences resolved through negotiation and under in-win scenario
Nevertheless, the plan will not ensure a mutual benefit at it is largely intended to displace Oromo farmers from their land. In additions, the populations of the two areas are not homogenous. Hence, they have no common interest. Even though it is said the “IRDP’ will be voluntarily accepted by participating partners, the top cadres in Oromia themselves have strongly opposed the plan on the conference. Beside, the implicit objective of the plan is to remove/avoid the differences in language and culture there by to plant “Ethiopianism or Tigreans” on Oromo land. The plan is intended to say good bye to Oromo Culture and language. The other thing is that the differences between Oromo and others cannot be resolved as it is intended to eradicate Oromo identity, culture and language. As we know from history, Oromo’s never compromised on these issues. Hence, if the plan is to be implemented, peaceful co-existence may not be there.
D. Problems that may come because of the Integrated Regional Development Plan
As different sources shown, many Oromo’s living in Special Zone has already lost their land in the name of foreign direct investment and land grasping. This is because of several fa3ctories are constructed in the special zone by taking the Lands from local Oromo farmers. It is not new to see Oromo labor workers or guards in their own land. Family members are highly displaced by this measure. Many went to street. Not only the displaced Oromos damaged by this. It is said chemical coming out of the factories are also hurting the health of the remaining Oromos. It is said that “In Central Oromia, thousands of people and their livestock died due to the industrial pollution directly released to rivers and lakes.”
Taking the above as an experience, there also different reasons why the newly Master plan of Finfinne should not be implemented on Oromo people. Some of the reasons are:
1. It will bring Extreme Poverty: It is inevitable that the local Oromo farmers lost their land in the name of investment and urbanization. This means that the Oromos are systematically cleaned from their own land, as they were cleaned from Finfinnee in earlier days. Hence, the local farmers lose their land which is part of their permanent asset. After the lose their land, the farmers will going to work for 300 birrr in the factory or serve as house servant or home guard, which is already started. By doing so, the farmers face extreme poverty. In addition, the gap between rich and poor will very high. For example, one writer described the impact of “investment” saying:
“The current regime has sold out more than 3 million hectares of fertile land to the foreigner investors after forcefully displacing Oromo farmers from their ancestral land. The grabbing of land ended the indigenous people without shelter and foods. This displacement of the Oromo people accompanied by limitless human rights violations set the Oromo to be the vast number of immigrants in the Horn of Africa.”
2. Family displacement and disintegration: Members of a family will be displaced and disintegrated as a result of loosing their land. In addition, the workers of Finfinnee special zone will be displaced as they are working in Afan Oromo.
3. Abuse of constitutional rights: After long year of struggle and sacrifice of thousands of Life, Afan Oromo given constitution right to be used in administration, school and other sectors in Oromia region. This is one of the basic objectives that Oromos has been struggling. However, if the master plan is going to be implemented, working language of Finfinnee City, Amharic, is going to be used in the areas. By doing so, the local people will be forced to learn new language to use it for different purpose. The measure will take back Oromo to the “Atse” region. The Federal Constitution states “Every people, nation and nationality have the right to speak, to write and to develop their own language, as well as to express, to develop and to promote their culture and history.Article 39” will be clearly violated. The Oromo living in Finfinnee Special Zone will lose the rights that the FDRE constitution guarantees them.
4. Academic and psychological impacts on Oromo students: If the newly proposed master plan of Finfinnee City is going to be implemented, Oromo students living in the surrounding area will attend their education in Amharic, which is second language to the students. It is strongly argued that using the native languages of students as a medium of instruction is a decisive factor for effective learning However, this situation, failure to give a role to native languages and largely depending on second/foreign language instruction, brought various difficulties to students. The students are expected to entangle not only with learning the subject matters but also the language itself. It also creates difficulty to students in expressing themselves and as a result it limits their classroom participation as there is fear of making mistakes. In addition, it is a barrier to smooth classroom communication. It is also argued that use of a second/foreign language in education negatively affects the ability and the ease with which knowledge is acquired by students. It also affects the performance of students and creates difficulties in developing their cognitive skills. Moreover, giving low status to native languages of students in educational setting leads to marginalization of majority of the citizens from active engagement in the development arena. In general, the master plan will have negative impacts on Oromo students in various academic aspects.
5. Impact on Identity and Culture of Local Oromo People: The new plan will make Oromos to lose their identity and culture, like the previous regimes did. This is because people having different identity and culture are going to settle on Oromo land. The settlers will push out the Oromo identity and replace by their own. The Oromo’s will have very limited opportunity to exercise their cultural value and linguistic form. The language and cultural development will be also hampered by the new plan.
6. Economic impact: If the master plan is going to be realized, the Finfinnee City Adminstration will control all economic aspects of the areas. The income that is collected from different factories will be taken. The Oromiya government will loose great income to Finfinnee city administration.
7. Impact on Natural Resource and Environment: As the result of the plan, there will be overspread ground and surface water pollution. In addition, there will be severe deforestation and natural resource depletion.
8. Cutting Oromia into East and West Regions: The new Master Plan of Finfinne city will cut the current Oromia into two parts i.e. Eastern and Western. This is because the Central and great part of Oromia is proposed to be taken and incorporated into Finfinnee. Hence, the Central part that joins East and West will be taken.
D. What Should be done to Save the Oromo People around Finfinnee
As shown above, the master plan is so disadvantage for Oromia. In general, if we see the plan, it will affect local Oromo people in various aspects. However, the government who is supposed to represent the Oromo people is unable to see the danger. So we kindly ask the Oromos at home and Diaspora and other concerned bodies to forward ways and mechanisms to stop the intended plan. We ask the Oromo people and international communities, who will stand for the Oromo’s living around Finfinnee??
If we read an honest history of the present and past Governments of Ethiopia, we would conclude that the present Government is truly facing a difficult dilemma. At the dawn of the 21st century, we can neither run away from ourselves nor hide our realities. We have to face our generation and the historical realities of our time. It is undeniable that today, people demand respect for their human and national rights. Above all, people will not rest until their identity and their sovereignty over what is theirs is ensured. These are the peoples’ most burning issues. They realize that they have to make utmost effort of their own. It is within the context of the above-mentioned framework that the Oromo people resolutely demand their rights and freedom. It is to those who want to deny the rights and freedoms of the people that we are most bitterly opposed. It is a crime to deny the national identity and sovereignty of a people no matter how sophisticated the tactics used to do so. It is equally wrong to see the national desire of a people from a selfish perspective. It is based on the above concepts and precepts that the Oromo people continue their unceasing and bitter struggle against being treated as second class citizens. We know that our struggle is just for it is motivated by our desire to preserve our dignity and identity as a people.
We, the sons and daughters of the Oromo people, strenuously oppose the implementation of new Master Plan for Finfinne administration because we fully understand the historical development of the desire of other people to displace the Oromo people in order to benefit the non-Oromo new comers and their lackeys in this country. This highly orchestrated conspiracy, the present Oromo generation shall not tolerate at any cost. It will steadfastly and resolutely resist the conspiracy.
We also request international communities to put pressure on FDRE/TPLF Government and Finfinnee City Administration to stop the proposed Master Plan, which directly or indirectly harm the Oromo people.
We call on the Federal Government of Ethiopia, House of Peoples’ Representatives, the Federation Council, the Oromia Council to stop clearing Oromo people from their home Land in the name of inequitable Development and replacing others on their land.
Please generate comments as many as possible on what should be done about the plan.
May Waaq Gurraacha help us!
From: Sabbontoota Oromoo, Oromia.
We are always Oromo First!!!!
Sabbontoota Oromo can be reached at sabboontotaaoromo@yahoo.in
Ethiopia: Raya under destruction
 Raya refers a tract of land stretching from Ala wuha in the south to Alaje in the north. That is bigger than Adwa and Axum awrajas combined. Historically, this is where the Weyane rebellion started in 1928 as a spontaneous reaction to a repressive system of the time. Originating in their present day Kobo wereda, the revolt would quickly spread to cover the entire Raya and Wejerat provinces. Later, the inhabitants of Enderta joined the revolt and a sort of quasi-organized alliance was formed after a decade of Raya and Wejerat rebellion. This alliance, Weyane, would emerge so potent that by its heyday it practically liberated the provinces of Raya, Wejerat and Enderta. The imperial government with the support of British Air force resorted to aerial bombardment of the rebel held areas which caused a wide-spread damage, including complete erasure of villages. However, the most detrimental factor that actually caused the demise of Weyane was to come from none other than Adwa people. In 1943, Dejazmach Gebrehiwot Meshesha along with a dozen of Adwans exploited the trust vested on them to assassinate the leaders of the Weyane movement. This is significant for in the Ethiopian tradition, at least until then, if one manages to kill the leader one will win the battle. Meshesha and co. breach of the traditional trust and value was so venomous that even to this date mistrust and resentment runs high in Raya. It is to be noted that if not for Meshesha of Adwa, the people were in a very strong bargaining position and if one has to look how similar revolts in Bale and other regions were resolved, the rebels demand for better governance was within reach. As a thank you for their contribution, Meshesha and his fellow Adwans were rewarded heavily by Haileselasse while a series of punitive attacks continued on the ‘originators’ of Weyane and ultimately Raya was divided between Wollo and Tigray.
Raya refers a tract of land stretching from Ala wuha in the south to Alaje in the north. That is bigger than Adwa and Axum awrajas combined. Historically, this is where the Weyane rebellion started in 1928 as a spontaneous reaction to a repressive system of the time. Originating in their present day Kobo wereda, the revolt would quickly spread to cover the entire Raya and Wejerat provinces. Later, the inhabitants of Enderta joined the revolt and a sort of quasi-organized alliance was formed after a decade of Raya and Wejerat rebellion. This alliance, Weyane, would emerge so potent that by its heyday it practically liberated the provinces of Raya, Wejerat and Enderta. The imperial government with the support of British Air force resorted to aerial bombardment of the rebel held areas which caused a wide-spread damage, including complete erasure of villages. However, the most detrimental factor that actually caused the demise of Weyane was to come from none other than Adwa people. In 1943, Dejazmach Gebrehiwot Meshesha along with a dozen of Adwans exploited the trust vested on them to assassinate the leaders of the Weyane movement. This is significant for in the Ethiopian tradition, at least until then, if one manages to kill the leader one will win the battle. Meshesha and co. breach of the traditional trust and value was so venomous that even to this date mistrust and resentment runs high in Raya. It is to be noted that if not for Meshesha of Adwa, the people were in a very strong bargaining position and if one has to look how similar revolts in Bale and other regions were resolved, the rebels demand for better governance was within reach. As a thank you for their contribution, Meshesha and his fellow Adwans were rewarded heavily by Haileselasse while a series of punitive attacks continued on the ‘originators’ of Weyane and ultimately Raya was divided between Wollo and Tigray.When the TPLF started the armed insurrection in Ethiopia, it took little time to transform itself as an Adwa-only club by the same inherited act of treachery. The legacy of resentment that Meshesha and co. left means TPLF-Adwa had hard time to set foot in Raya. Hence, they needed to come up with a trick and did it so by cosmetically inserting the word Weyane in the Tigrigna version of its name. Taken with the harsher realities under DERG, Rayans reluctantly sided with TPLF on the principle of the lesser devil. Soon, tens of thousands of Raya youth joined the TPLF, including forming the majority and the backbone of Hadush “Hayelom” Ariaya’s fighting force that brought the little known“Hayelom” into prominence. However, if the experience of my village is anything, it is fair to conclude that almost all the Raya recruits ended up as cannon fodders. Those who survived, especially the independent and rational ones, would have never escaped the Meles-Sebhat death squad. In Raya, for example, it is not uncommon to talk to your relative TPLF fighter over the phone in the morning only to be notified of his death of “natural” consequences on the same day. I will say more on the motives next time. But for now, I want to draw your attention to the following Table, which is taken from the 1994 and 2007 population census of Ethiopia. I think this illustrates how the Raya and Adwa are faring under the TPLF-Adwa administration.

Clearly, 7 towns (Robit, Gobiye, Waja, Mersa, Korem, Wedisemro, Chelena) of Raya from the total 11, i.e., 64% of the town that existed in the 1994 Census Ethiopia have died or are dying. Well, with Adwa awraja towns the figures show a hard-to-believe growth registering as ridiculous as 1033% for Gerhusenay, Idegaarbi(377%), Nebelet(266%); even noticeable is the emergence of a novel city (Diobdibo) in the 2007 census, attesting to the developmental and modernization campaigns in Adwa rural areas as well. The bar graph of the rate at which towns are expanding (Adwa) or shrinking (Raya) shown below can only be a proof that in the so-called Tigray “killil” both, depending on the area, de-constructive and constructive policies are in operation. To the unsuspecting, it may occur that this might have to do with the pre-1991 TPLF bandit caused civil war. However, it is not quite so for, for instance, there was no single bomb that was dropped on Adwa towns nor was a confrontation in populated areas in the entire Adwa awraja. There was insignificant causality as far as the civilian population of Adwa is concerned for the TPLF military engagement tactic in Adwa/Axum area was totally different from the rest awrajas. For example, Korem town alone might have received far more arial bombardment than the entire Adwa awraja. From SehulMikael (the Godfather of Ethiopia’s disintegration), to Meshesha-Sebhat-Meles-Sebhat(again), there exist very little dissimilarity. Right now, Alamata, the only remaining city not to die fast enough as Adwans would have liked to see, is under open destruction. The residents never complained on the absence of developmental activity but never expected that the Adwa administration of the city will come-up with a destruction agenda. Surprised by the revelation, the unsuspecting residents went to Mekelle to air their grievances in the hope that the big men there might be rational and take proper action. However, Abay Woldu’s administration did not give it a second to listen; just ordered more Bulldozers, armored tanks and a battalion to effectively carry out the planned destruction. Worse, those who complained the demolishing of their belonging are rounded-up and now languish in Adwa operated secret Tigrayan jails
Right now, Alamata, the only remaining city not to die fast enough as Adwans would have liked to see, is under open destruction. The residents never complained on the absence of developmental activity but never expected that the Adwa administration of the city will come-up with a destruction agenda. Surprised by the revelation, the unsuspecting residents went to Mekelle to air their grievances in the hope that the big men there might be rational and take proper action. However, Abay Woldu’s administration did not give it a second to listen; just ordered more Bulldozers, armored tanks and a battalion to effectively carry out the planned destruction. Worse, those who complained the demolishing of their belonging are rounded-up and now languish in Adwa operated secret Tigrayan jails
Reference:
- Central Statistical Authority Ethiopia: The 1994 populaion and Housing Census of Ethiopia. Results for Tigray region, Volume 1, Statistical report.Table 2.2, Page 11
- Central Statistical Authority Ethiopia: The 1994 populaion and Housing Census of Ethiopia. Results for Amhara Region, Volume 1, Statistical report.Table 2.2, Page 13
- The 2007 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia: Statistical Report for Tigray Region, Table 2.1, page 7
- The 2007 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia: Statistical Report for Amhara Region, Table 2.2, page 11
http://ethiofreespeech.blogspot.co.uk/2014/02/ethiopia-raya-under-destruction.html?spref=fb



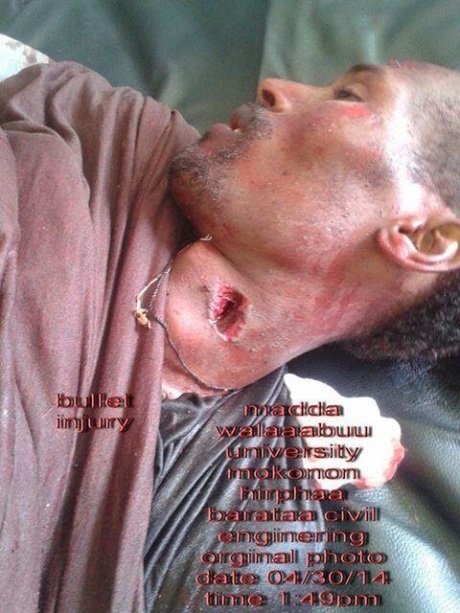

































You must be logged in to post a comment.