China, African governments, Debt & Corruption May 12, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa and debt, Africa Rising, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Free development vs authoritarian model, International Trade, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, No to land grabs in Oromia, Theory of Development, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Horn of Africa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, World Bank
add a comment
The message is that African leaders now have licence to oppress their people, clean their national treasuries; and generally rob, loot, rape and plunder because their new masters will not hold them to account on how well or how badly they treat their subjects.http://www.nation.co.ke/oped/Opinion/The-Chinese-did-not-come-here-on-charity/-/440808/2312172/-/11rv0rwz/-/index.html

http://allafrica.com/stories/201405081353.html?utm_source=twitterfeed&utm_medium=twitter
‘Debt and Corruption are an awful mix: The appetite for debt by African governments is particularly concerning given that there does not appear to be any serious action to end the gross mismanagement of public funds. Getting into debt only makes sense if you plan to use the money properly. But if substantial sums of money end up in the pockets of faceless politicians, then Africa is ransoming future earnings with no future benefits. This is self-sabotage at its best. There is no need to belabour the point. Don’t take on billions of dollars of debt if corruption is still an untamed beast…the consequences for Africa’s economy and people will be dire….. ‘Many of the Chinese contracts in Africa lay down that repayments be made in natural resources, with complex institutional contracts that make repayments unpredictable in financial terms’. [2] How can we be comfortable with our governments getting into deals into the billions of dollars and yet these are shrouded in mystery? With no information at hand, we do not really know how deep of a hole we’re digging for ourselves.’
Step away from the debt plate Africa, you need to watch what you’re eating
POSTED ON MAY 12, 2014 @http://anzetsewere.wordpress.com/2014/05/12/step-away-from-the-debt-plate-africa-you-need-to-watch-what-youre-eating/
Africa is bingeing on debt and risks overeating at the buffet of financial offers from China, India, Brazil and many others. Kenya just recently signed a series of financial agreements worth billions with China during Prime Minister Lee Keqiang’s visit to the country this last weekend making it clear that we live in a multipolar world. In this new world order Africa is spoilt for choice with regard to who to partner with to fund development. But we (Africa) seem to have an insatiable appetite for this new money and do not seem to be fully aware of the implications of accepting all these tasty offers of cash. We also don’t seem to be thinking about whether we can, or how we can absorb these volumes of cash. Don’t get me wrong, Africa’s excitement at promises of billions apparently with ‘no conditions’ is understandable. Having spent the past decades grovelling at the doors of donors and investors from Europe and North America, many Africans felt we were giving away our pride for monies tied to what many felt were onerous conditions. So now, we are whistling our way to the bank with our new financials ‘partners’.
But is this truly smart? The reality is that all borrowing has conditions. So allow me to digress briefly and go slightly further with this point. China enjoys talking about about how it provides money with ‘no conditions’, but closer analysis reveals that this is not strictly true. The Chinese government, like any other government, will protect its investments; investments made almost exclusively with African governments…which seems to suggest that if China has to back up (even unpopular or despotic) African governments to protect its investments, it will. Look at the incriminating allegations that China funded Mugabe’s election ‘victory’ last year. Documents from Zimbabwe’s Central Intelligence Organization suggest that the success of Mugabe and his ZANU-PF party, ‘reflected direct intervention by the Chinese Communist Party’. (See more here and here). Perhaps for Zimbabwe the conditions that make China feel most secure in its investments is if Mugabe is in power. So maybe there are some conditions tied to money from China. The point I’m making is that it is important Africans analyse reality and not get spellbound by the rhetoric. But that is an aside; let’s get to the real problems behind Africa’s debt binge
1. We don’t really know the scale of the debt we’re getting into
By ‘we’ I mean Africans not on the inside corridors of power, but on whose behalf these deals are being made. It is absolute madness that in the case of countries such as China, we actually don’t know how much debt we’re getting into. Over the weekend Kenya and China signed several agreements but, ‘The two leaders did not disclose the actual financial value of most of the agreements and protocols signed but their aides said the deals run into billions of Kenya shillings.’[1] Why the secrecy? How much of this money from China is grants vs debt? What are the interest rates (there are references to ‘concessional loans’ but that’s about it), what are the terms of repayment, what are the penalties for defaulting? Also bear in mind that in the past, ‘Many of the Chinese contracts in Africa lay down that repayments be made in natural resources, with complex institutional contracts that make repayments unpredictable in financial terms’. [2] How can we be comfortable with our governments getting into deals into the billions of dollars and yet these are shrouded in mystery? With no information at hand, we do not really know how deep of a hole we’re digging for ourselves.
2. Do we have the absorptive capacity to handle all this money?
We are getting into debt to fund numerous development projects that range from infrastructure to agriculture, to security and wildlife but, pray tell, do we have the absorptive capacity to soak up these billions? Because whether we can absorb the money or not, we will be paying it back. Absorptive capacity here relates to the macro and micro constraints that recipient countries face in using resources, in this case money, effectively.[3] Does Africa have the physical, intellectual and systems-related infrastructure, expertise and culture to competently implement all these projects? For example, do county governments have the technical savoir faire to implement agriculture projects worth millions? One of the issues of serious concern is that investment in educational infrastructure rarely features prominently in these deals. There are very limited (if any) provisions for building the educational capacity of African countries especially at tertiary and vocational levels. So great, we’re getting money to build railways, but how many Africans can be effectively put to task on this, especially at managerial positions? Bear in mind that already, with regards to China, Africa has fallen into a trap where, 1) China is allowed to bring in Chinese nationals to provide labour and, 2) When African labour is used, it is cheap, unskilled labour.[4] This situation is untenable. Africa should be using every single government- funded project to hire Africans and build the capacity of Africans to do the job competently in the future. Africa cannot continue to so fundamentally rely on outsiders to do the basics for us such as building roads. But sadly, African countries seem to be happy with outsourcing all the large-scale projects, sometimes back to companies from the country that gave us the loans in the first place. This leads to the next point.
3. With limited absorptive capacity, Africa will continue to outsource big contracts
Africa is not being very bright. We get loans then outsource the implementation of the projects back to companies from the donor country. In short, we’re paying China to pay itself. Why? Generally however, using outsourcing as the default strategy for large-scale project implementation is problematic in at least two ways: 1) It hides and exacerbates Africa’s skills deficit and, 2) It pumps money out of the country. The first point is obvious, if we continue to rely on others to build our roads, we will continue to lack the skillsets and capacity to competently build and maintain our roads ourselves. But since the roads are being built, we never feel the weight of our incompetence in this area and therefore have no sense urgency to rectify this problem. Secondly, companies implementing projects in Africa make a profit then expatriate the profit. So we’re getting into debt and then haemorrhaging some of that expensive money out of the continent through outsourcing. This makes no long-term sense. Ideally we should use local contractors to implement projects however, as elucidated in point 2, we do not seem to have sufficient volumes of companies capable of absorbing this workload. But rather than fix that, African governments go to the default setting labelled ‘outsource’. We’re getting into a vicious cycle as follows: We don’t have the capacity to implement large-scale projects → we outsource but fail to ensure skills transfer → exacerbates the skills deficit → we don’t have the capacity to implement large-scale projects. African governments should essentially use the development projects led by non-Africans as structured training opportunities for newly qualified professionals as well as building more seasoned professionals into the management structure of projects.
4. Debt and Corruption are an awful mix
The appetite for debt by African governments is particularly concerning given that there does not appear to be any serious action to end the gross mismanagement of public funds. Getting into debt only makes sense if you plan to use the money properly. But if substantial sums of money end up in the pockets of faceless politicians, then Africa is ransoming future earnings with no future benefits. This is self-sabotage at its best. There is no need to belabour the point. Don’t take on billions of dollars of debt if corruption is still an untamed beast…the consequences for Africa’s economy and people will be dire.
5. Overleveraged?
This issue relates to point number 1. There is limited information on the scale of the debt Africa is getting into with certain parties so at what point will we in Africa know when we’re overleveraged? It seems like the answer to that is ‘not any time soon’. The scary part is that some African governments seem to think debt will fix all our problems with Heads of States expecting hearty praise when they secure even more debt for the continent. It is true that structures such as the Debt Sustainability Framework (DSF) exist which seek to stop lenders from lending more money to countries that have exceeded their debt ceilings. But, ‘to work well, the DSF needs close co-ordination between all creditors. This is hard enough to do between public and private lenders from the traditional partners, but is even more difficult with the new lenders [such as China].[5],[6]Sadly, African countries do not seem to be keen on tabulating public debt figures at either national or pan African levels, and sharing them.
Read more from the original sourcce: http://anzetsewere.wordpress.com/2014/05/12/step-away-from-the-debt-plate-africa-you-need-to-watch-what-youre-eating/
Protests, State Violence, and the Manufacture of Dissent in Ethiopia May 6, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, America, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinne is Oromia's land, Finfinnee, Finfinnee is the Capital City of Oromia, Finfinnee n Kan Oromoo ti, Free development vs authoritarian model, Genocidal Master plan of Ethiopia, Hetosa, Human Rights, Human Rights Watch on Human Rights Violations Against Oromo People by TPLF Ethiopia, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Meroetic Oromo, No to land grabs in Oromia, NO to the Evictions of Oromo Nationals from Finfinnee (Central Oromia), Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia wide Oromo Universtiy students Protested Addis Ababa Expansion Master Plan, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo Culture, Oromo Diaspora, Oromo Protests, Oromo Protests in Ambo, Oromo students protests, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromo University students and their national demands, Oromummaa, Say no to the expansions of Addis Ababa, State of Oromia, Stop evicting Oromo people from Cities, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: African Studies, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, The Tyranny of Experts, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
Two things happened simultaneously on May 1st, both involving the U.S. State Department and its relation to Ethiopia. Thing one was the State Department’s news program, Voice of America, broadcasting its brief account of Ethiopian security forces firing upon student demonstrations the previous day (April 30) at three universities resulting in 17 dead and many wounded. Thing two was the Secretary of State John Kerry in Ethiopia giving a speech full of praise for Ethiopia’s rapid economic development as well as the U.S.-Ethiopia partnership in addressing the violence against civilians in neighboring Sudan and Somalia. Apparently, Kerry was unaware that the day before, just a two-hour’s drive down the road from where he was speaking, America’s supposed partner, the Ethiopian government, had committed acts of violence against its citizens. In fact, thousands of individuals at universities and in cities across the Oromia region of Ethiopia had been protesting for days, and as the journalist Mohammed Ademo’s article for Think Africa pointed out on Tuesday (August 29), what they were protesting was precisely the consequences of the rapid economic development and foreign direct investment that Kerry praised in his speech – the eviction and displacement of tenant farmers and poor people due to the expansion of the capital city Addis Ababa into the Oromia region.
We might observe a contradiction here within the same State Department. While the State Department’s news program laments an event and clearly points to the root cause, the State Department’s secretary appears ignorant of the event and also strangely unable to discern the causes of ethnic unrest across Africa. An Al Jazeera op-ed responding to Kerry’s speech suggests that the United States fails to see the contradiction in its policy that talks about democracy and human rights but in practice emphasizes security for foreign direct investment (as per the State Department’s own report on such investment in Ethiopia published shortly before Kerry’s visit.) Noticeably, two contradictory ideas are coming out of the State Department simultaneously. What do we make of that contradiction?
Before I answer that question, I might add on to this strange state of affairs by pointing out that Kerry did criticize the Ethiopian government for using repressive tactics against its journalists — the famous Zone 9 bloggers — but what strikes me is that at the very moment that Kerry criticizes the state of journalism in Ethiopia, the mainstream American news outlets such as CNN, National Public Radio, and the NY Times have for a long time neglected to give any serious coverage of the issues within Ethiopia and in fact did not report on the student demonstrations. The only American media mention of the recent student demonstrations and deaths is a very brief Associated Press article that appeared the day after Kerry’s speech (May 2) and that article embarrassingly gets its facts wrong about what happened and why. Such poor journalism is increasingly perceived to be the norm of America’s once celebrated media whose many factual inaccuracies and lack of any genuine will to truth arguably contributed to the Iraq War back in 2003. Curiously, the only news organization in America that did its job (the VOA) is the news organization intended to serve communities outside of America. Moreover, the VOA is part of the very same “department” that Kerry heads. The quality of mainstream American media coverage might seem excusable if it weren’t for the fact that BBC covered these tragic events in Ethiopia reasonably well, first on its radio program immediately after the massacre (May 1st) and then more comprehensively on its website the following day.
Two things happened simultaneously on May 1st, both involving the U.S. State Department and its relation to Ethiopia. Thing one was the State Department’s news program, Voice of America, broadcasting its brief account of Ethiopian security forces firing upon student demonstrations the previous day (April 30) at three universities resulting in 17 dead and many wounded. Thing two was the Secretary of State John Kerry in Ethiopia giving a speech full of praise for Ethiopia’s rapid economic development as well as the U.S.-Ethiopia partnership in addressing the violence against civilians in neighboring Sudan and Somalia. Apparently, Kerry was unaware that the day before, just a two-hour’s drive down the road from where he was speaking, America’s supposed partner, the Ethiopian government, had committed acts of violence against its citizens. In fact, thousands of individuals at universities and in cities across the Oromia region of Ethiopia had been protesting for days, and as the journalist…
View original post 1,351 more words
Stop aid to Tyrants: It is time to a new development model April 14, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Finfinnee, Food Production, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Land Grabs in Africa, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Poverty, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“Compare free development in Botswana with authoritarian development in Ethiopia. In Ethiopia in 2010, Human Rights Watch documented how the autocrat Meles Zenawi selectively withheld aid-financed famine relief from everyone except ruling-party members. Meanwhile democratic Botswana, although drought-prone like Ethiopia, has enjoyed decades of success in preventing famine. Government relief directed by local activists goes wherever drought strikes.”- http://time.com/23075/william-easterly-stop-sending-aid-to-dictators/
Traditional foreign aid often props up tyrants more than it helps the poor. It’s time for a new model.
Too much of America’s foreign aid funds what I call authoritarian development. That’s when the international community–experts from the U.N. and other bodies–swoop into third-world countries and offer purely technical assistance to dictatorships like Uganda or Ethiopia on how to solve poverty.
Unfortunately, dictators’ sole motivation is to stay in power. So the development experts may get some roads built, but they are not maintained. Experts may sink boreholes for clean water, but the wells break down. Individuals do not have the political rights to protest disastrous public services, so they never improve. Meanwhile, dictators are left with cash and services to prop themselves up–while punishing their enemies.
But there is another model: free development, in which poor individuals, asserting their political and economic rights, motivate government and private actors to solve their problems or to give them the means to solve their own problems.
Compare free development in Botswana with authoritarian development in Ethiopia. In Ethiopia in 2010, Human Rights Watch documented how the autocrat Meles Zenawi selectively withheld aid-financed famine relief from everyone except ruling-party members. Meanwhile democratic Botswana, although drought-prone like Ethiopia, has enjoyed decades of success in preventing famine. Government relief directed by local activists goes wherever drought strikes.
In the postwar period, countries such as Chile, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan have successfully followed the path of free development–often in spite of international aid, not because of it. While foreign policy concerns have often led America to prop up dictatorial regimes, we need a new rule: no democracy, no aid. If we truly want to help the poor, we can’t accept the dictators’ false bargain: ignore our rights abuses, and meet the material needs of those we oppress. Instead, we must advocate that the poor have the same rights as the rich everywhere, so they can aid themselves.
Easterly is the co-director of New York University’s Development Research Institute and author of The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor.
Read further at original source@
http://time.com/23075/william-easterly-stop-sending-aid-to-dictators/
As protestors from Kiev to Khartoum to Caracas take to the streets against autocracy, a new book from economist William Easterly reminds us that Western aid is too often on the wrong side of the battle for freedom and democracy. In The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor, Easterly slams thedevelopment community for supporting autocrats, not democrats, in the name of helping the world’s poorest. Ignoring human rights abuses and giving aid to oppressive regimes, he maintains, harms those in need and in many ways “un-develops” countries.
The Tyranny of Experts takes on the notion that autocracies deliver stronger economic growth than freer societies. Easterly argues that when economic growth occurs under autocratic regimes, it is more often achieved at the local level in spite of the regime’s efforts. In some instances, growth under autocracies can be attributed to relative increases in freedoms. He points to China as an example of this, attributing the country’s phenomenal growth to its adoption of greater personal and economic freedoms, especially compared to the crippling Maoist policies of the past.
Easterly also rejects the myth that dictators are dependable and that a certain level of oppression should be overlooked for the sake of economic growth and overall prosperity. Most recently, the violence and chaos following the 2011 Arab uprisings has made some nostalgic for the stable, if undemocratic, governments that kept civil unrest in check, allowing for a measure of economic development to take hold. Easterly stresses that instability and tumult in the wake of ousting a dictator is not the fault of an emerging democracy, but instead an understandable result of years of autocratic rule. The answer is not to continue to support autocrats in the name of stability, but rather to start the inevitably messy process of democratization sooner.
Easterly is of course not the first to call attention to the importance of prioritizing rights and freedoms in the development agenda. Scholars from Amartya Sen to more recently, Thomas Carothers and Diane de Gramont, have also advocated for a rights-based approach to development. In Pathways to Freedom: Political and Economic Lessons From Democratic Transitions, my coauthors and I similarly found that economic growth and political freedom go hand-in-hand.
Still, the hard questions remain: how to help those without economic and political freedoms? And when should donors walk away from desperately poor people because their government is undemocratic? Easterly argues that the donor community should draw the line with far more scrutiny than it does today – not just at the obvious cases, such as North Korea, but with other undemocratic countries, such as Ethiopia, where human rights abuses are rampant. He debunks the notion that aid can be “apolitical,” arguing that it is inherently political: giving resources to a government allows it to control and allocate (or withhold) resources as it sees fit. The aid community should focus on ways to help oppressed populations without helping their oppressors. For example, scholarship programs, trade, and other people-to-people exchanges can give opportunities to people in need. At the very least, Easterly argues, development actors should not praise oppressive regimes or congratulate them on economic growth they did not create.
Rather than being seduced by “benevolent dictators,” Easterly urges donors to focus their energy on “freedom loving” governments that need help. The Millennium Challenge Corporation is a step in the right direction but, as Easterly pointed out during the CFR meeting, MCC’s approach is undermined by other U.S. aid agencies, such as USAID, that continue to assist countries even when they don’t meet certain good governance and human rights standards.
Easterly also emphasizes the need for aid organizations to be more transparent about where their money is going. Robert Zoellick made strides in this direction during his tenure as World Bank president. But more recent developments suggest that the Bank still has a way to go in becoming more open and accountable. (Easterly noted that an initial invitation to speak about The Tyranny of Experts at the World Bank was later rescinded for “scheduling reasons.”) http://blogs.cfr.org/development-channel/2014/03/14/helping-the-oppressed-not-the-oppressors/#cid=soc-facebook-at-blogs-helping_the_oppressed_not_the_-031414
No democracy, no aid
http://stream.aljazeera.com/story/201403190105-0023568
March 26, 2014 (The Seattle Times) — SOMEHOW — probably my own fault — I have wound up on Bill Gates’ list of the world’s most misguided economists. Gates singled me out by name in his annual 2014 letter to his foundation as an “aid critic” spreading harmful myths about ineffective aid programs.
I actually admire Gates for his generosity and advocacy for the fight againstglobal poverty through the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation in Seattle. We just disagree about how to end poverty throughout the world.
Gates believes poverty will end by identifying technical solutions. My research shows that the first step is not identifying technical solutions, but ensuring poor people’s rights.
Gates concentrates his foundation’s efforts on finding the right fixes to the problems of the world’s poor, such as bed nets to prevent malarial mosquito bites or drought-tolerant varieties of corn to prevent famine. Along with official aid donors, such as USAID and the World Bank, the foundation works together with local, generally autocratic, governments on these technical solutions.
Last year, Gates cited Ethiopia in a Wall Street Journal guest column as an example, a country where he described the donors and government as setting “clear goals, choosing an approach, measuring results, and then using those measurements to continually refine our approach.”
This approach, Gates said, “helps us to deliver tools and services to everybody who will benefit.” Gates then gives credit for progress to the rulers. When the tragically high death rates of Ethiopian children fell from 2005 to 2010, Gates said this was “in large part thanks to” such a measurement-driven program by Ethiopia’s autocrat Meles Zenawi, who had ruled since 1991. Gates later said Meles’ death in August 2012 was “a great loss for Ethiopia.”
Do autocratic rulers like Meles really deserve the credit?
Gates’ technocratic approach to poverty, combining expert advice and cooperative local rulers, is a view that has appealed for decades to foundations and aid agencies. But if technical solutions to poverty are so straightforward, why had these rulers not already used them?
The technical solutions have been missing for so long in Ethiopia and other poor countries because autocrats are more motivated to stay in power than to fix the problems of poverty. Autocracy itself perpetuates poverty.
Meles violently suppressed demonstrations after rigged elections in 2005. He even manipulated donor-financed famine relief in 2010 to go only to his own ruling party’s supporters. The donors failed to investigate this abuse after its exposure by Human Rights Watch, continuing a long technocratic tradition of silence on poor people’s rights.
Rulers only reliably become benevolent when citizens can force them to be so — when citizens exert their democratic rights.
Our own history in the U.S. shows how we can protest bad government actions and reward good actions with our rights to protest and to vote. We won’t even let New Jersey Gov. Chris Christie get away with a traffic jam on a bridge.
Such democratic rights make technical fixes happen, and produce a far better long-run record onreducing poverty, disease and hunger than autocracies. We saw this first in the now-rich countries, which are often unfairly excluded from the evidence base.
Some developing countries such as Botswana had high economic growth through big increases in democratic rights after independence. Botswana’s democrats prevented famines during droughts, unlike the regular famines during droughts under Ethiopia’s autocrats.
Worldwide, the impressive number of developing countries that have shifted to democracy includes successes such as Brazil, Chile, Ghana, South Korea and Taiwan, as well as former Soviet Bloc countries such as the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovenia.
If the democratic view of development is correct, the lessons for Gates are clear: Don’t give undeserved credit and praise to autocrats. Don’t campaign for more official aid to autocrats. Redirect aid to democrats. If the democratic view is wrong, I do deserve to be on Gates’ list of the world’s most misguided economists.
http://ayyaantuu.com/africa/guest-the-flaw-in-bill-gates-approach-to-ending-global-poverty/
Related findings:
The UK government is providing financial aid to human rights abusers in Ethiopia through funding training paramilitaries, who perpetrate summary killings, rape and torture in the impoverished African country, local media reported.
Through its foreign aid budget, the UK government provides financial support to an Ethiopian government security force known as the “special police” as part of its “peace and development programme”, which would cost up to £15 million in five years, The Guardian reported.
The Department for International Development warned in a leaked document of the “reputational risks” of working with organizations that are “frequently cited in human rights violationallegations”, according to the report.
The Ethiopian government’s counter-insurgency campaign in Ogaden, a troubled region largely populated by ethnic Somalis is being enforced by the 14,000-strong special police.
This is while police forces are repeatedly accused by Human Rights Watch of serious human rights abuses.
Claire Beston, the Amnesty International’s Ethiopia researcher, said it was highly concerning that Britain was planning to work with the paramilitary force.
THE EXPANSION OF THE AMORPHOUS ADDIS ABABA, THE ENDLESS PERSECUTION AND EVICTION OF TULAMA OROMOO April 6, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo Valley, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny.Tags: African Studies, Finfinnee, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
The deliberate expansion of the amorphous city they call “Addis Ababa” is politically created to divide Oromiyaa into east and west sector. It is not a master plan. It is an evil plan mastered to consummate an evil goal.
When we see the history of Abyssinian political philosophy, from which we have a written record, it is entirely based on the philosophy of depriving the Oromos from having any right to homeland. To convert Oromummaa to Amaarummaa and ultimately to Itiyophiyawwinnet has been the policy in action up to this very day.
What happened to those Oromos who were living in Finfinnee for centuries? Particular mention has to be made about those Tulama Oromo groups of Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Aabbuu, Jillee. The answer is very simple: They were mercilessly decimated; their villages burnt down, their pasture and arable lands confiscated and shared among the invading Manzian Nagasii families of whom the Dejazmach Mangasha Seifu and the Ras Birru families were the most notorious ones. Thereafter, the Oromo territory occupied by Matcha-Tulama was officially changed to the expanding Kingdom of Showa, a detached enclave from Gonder, Abyssinia. Finfinnee was given a new colonial name “Addis Ababa”, just like Zimbabwe was changed to Rhodesia, Harare to Salisbury. Under this excruciating condition, the conquered Matcha-Tulama region had to lose its historic significance and had to be involuntarily submitted to the colonial name Showa.
Among the major Oromo descent groups, the Matcha-Tulama group has got one of the largest populations, stretching on vast area of land in central and western Oromia. As we are able to learn from our fathers, Matcha and Tulama are Borana brothers, being Tulama angafa (first born) and Matcha qixisuu (second born son). As common to all Oromo ethno-history, the tradition that governs the social role of “angafa and qixisuu”, which begins right from the immediate family unit, has a deep genealogical meaning and social role in re-invigorating the solidarity of the nation. From the earliest time of which we have a tradition hanging down to us,
- Matcha-Tulama Oromo has had a supreme legislative organ known as Chaffe. The Chaffe legislates laws which will eventually be adopted as Seera Gadaa
They have a senatorial council known as “Yaa’ii Saglan Booranaa”, in which elected individuals from major clans are represented. The function of Yaa’ii Saglan Booranaa is to deliberate on issues pertaining to regional issues, resolve inter-clan disputes and oversees how interests of each clan in the confederacies are represented; how local resources are fairly shared and wisely utilised according to the law.
- These two northern Boorana brothers are historically referred to as Boorana Booroo or Boorana Kaabaa
- Among the known five Oromo Odaas, Odaa Nabee and Odaa Bisil are found in Boorana Booroo
However, beginning from the 13th century onward, the Match-Tulama country (Boorana Booroo), adjacent to Abyssinian border, has begun to be ravaged by a group of individuals whose legendary genealogy connects them to a certain King Solomon of non-African origin. They came and settled at a place they call “Manz”.They organised themselves at this place, and started to attack neighbouring villages of Cushitic Oromo family stock of Laaloo, Geeraa and Mammaa. The attacked villages were gradually incorporated into the expanding Manz, which eventually developed to a military outpost known as Showa in the late 18th century. Hereafter, they declared themselves “Ye Negasi Zer, the root of Showa Amhara Dynasty.
After vanquishing Agaw people’s identity and sovereignty on the northern frontier, the Solomonic Negasi Dynasties of Showa intensified their attacks against the Match-Tulama of Borana and the Karrayyu of Barantu Oromos. In such turbulent situation, the rule of yeNegasi Zer entered nineteenth century era, which ushered the era of the Scramble for Africa by European imperialist powers. From Africa, it was only King Minilik of Showa (1866-1889) who was recognised as a partner and invited to attend the Berlin Imperialist Conference of 1884. In this conference, Minilik was represented by his cousin, Ras Mekonnen Tenagneworq Sahile-Sellasie (1852-1906). After completing their mission, King Minilik and the European imperialist powers made concession on border demarcation. After the border demarcation had been completed, a systematic elimination of his prominent general, Ras Goobanaa Daacci (1819-1889), was meticulously carried out. Minilik was so confident to declare himself Emperor of Ethiopia (1889- 1913).This was the Ethiopia, the first time in the history of the region, that brutally annexed and included Oromo, Sidama, Walaita, Kaficho, Beneshangul, Gambella, and others to the expanding of Abyssinia.
The years 1887-89 were the boiling point for Minilik’s declaration of being “Emperor of Ethiopia, yeItiyophiya Nuguse, nägest. Why?
- Because, it was the time when he exterminated the Gullallee Oromo from the marshy-hot spring and pasture land of Finfinnee and collectivised the place under a new colonial name Addis Ababa.
- Because, it was the time when he built full confidence in himself and built his permanent palace at Dhaqaa Araaraa, a sacred hill, where the evicted Oromos peacefully used to sit together and conduct peaceful deliberation for reconciliation.
- It was the time when he annexed three-fourth of southern peoples’ territories, including the Oromo territory, to the expanding Showan Dynasty and put under the iron-fist of his inderases(viceroys).
- It was the time when he assured un-shivering confidence of being continued to be assisted and advised by his European colonial partners: militarily, diplomatically and technically.
Here is the question: What happened to those Oromos who were living in Finfinnee for centuries? Particular mention has to be made about those Tulama Oromo groups of Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Aabbuu, Jillee. The answer is very simple: They were mercilessly decimated; their villages burnt down, their pasture and arable lands confiscated and shared among the invading Manzian Nagasii families of whom the Dejazmach Mangasha Seifu and the Ras Birru families were the most notorious ones. Thereafter, the Oromo territory occupied by Matcha-Tulama was officially changed to the expanding Kingdom of Showa, a detached enclave from Gonder, Abyssinia. Finfinnee was given a new colonial name “Addis Ababa”, just like Zimbabwe was changed to Rhodesia, Harare to Salisbury. Under this excruciating condition, the conquered Matcha-Tulama region had to lose its historic significance and had to be involuntarily submitted to the colonial name Showa.
In addition to the former derogatory term “Galla”, imposed on the conquered Oromos as a whole, the new regional name of Showa is prefixed to the derogatory term Galla. Hence, “ye Showa Galla” came into force as a collective insulting name in addressing the whole Oromo of Matcha-Tulama. This clearly justifies the vertical segregation policy of the conquerors for easy identification of who is who in the newly colonised territory.
Using various forms of oppressive models, Abyssinian colonial tactics and strategies have been going on violently and, now entered into the first half of the 21st century. Since the second half of the 19thcentury in particular, the oppressive models have been amassing massive firearms from European colonialist partners, enjoying diplomatic immunities and profitable political advises.
In the late 19th century, one European writer commented that, if the Abyssinians had not been armed and advised by global colonial powers of the day, notably France and Britain, late alone to defeat the ferocious Oromo forces, they could not have even dared to encroach upon the limits of Oromo borders. He wrote what he witnessed the real situation of the time as follows:
“Against the Galla [Oromo] Menelik has operated with French technicians, French map-makers, French advice on the management of standing army and more French advice as to building captured provinces with permanent garrison of conscripted colonial troops. The French also armed his troops with firearms, and did much else to organize his campaigns. Menelik was at a work on these adventures as King of Shewa during John’s lifetime; adding to his revenues and conscripting the Oromo were thus conquered by the Amhara for the first time in recorded history during the last thirteen years of the nineteenth Century. Without massive European help the Galla [Oromo] would not have been conquered at all.”
The writer further explained what he personally encountered during the campaign in the following unambiguous language:
“A large expedition was sent as far South in Arsi as frontier of Kambata to return with100, 000 head of Cattle. The king’s army fought against tribes who have no other weapons but a lance, a knife and shield, while the Amahras always have in their army several thousand rifles, pistols and often a couple cannon.—-Captive able-bodied males and the elderly were killed. The Severity of the Zamacha [campaign] was aimed at the eradication of all resistance. Whenever the army surged forward, there was the utmost devastation. Houses were burned, crops destroyed, and people executed:”
When we see the history of Abyssinian political philosophy, from which we have a written record, it is entirely based on the philosophy of depriving the Oromos from having any right to homeland. To convert Oromummaa to Amaarummaa and ultimately to Itiyophiyawwinnet has been the policy in action up to this very day. Even though the policy works on all Oromos indiscriminately, the one which has been exercising on the Oromos of Tulama in Finfinnee and surrounding areas has its own unique feature. Some of the unique features are embedded in the formation of “Addis Ababa” itself; as a seat of colonial headquarters with all its oppressive machineries. To have ample space for the settlers, to build army headquarters, to build churches in the name of numerous Saints of Greek and Hebrew origins, to build residences and offices for foreign embassies and missionaries, to build factories and storage houses the crucial demand is land. To fulfil these crucial demands of the customers, helpless Oromo peasants of the area have to be evicted. They have been under routine eviction and land deprivation since the seizure of Burqaa Finfinnee and the establishment of Ethiopian Imperial capital at this place.
It could be incorrect to think of the current TPLF-Arinnet Tigray regime as a detached entity from the whole system of Abyssinian colonial regimes, when we equate what they need against the survival needs of the peoples they generically conquered as “Galla and Shanqilla”. Though since 1991, the Ethiopian imperial system has been overtaken from the Showan Nagasi Dynasty by their junior Tigrean brethren, the life of the colonised Oromo people has been going down from worse to the worst.
What makes TPLF-Arinnet Tigray different from its predecessors is its total monopolisation of resources of the empire, right from the imperial palace to the bottom village levels, from the centre to the periphery. Arable and pasture lands, plain and forest lands, rivers and mining areas are totally under its predatory control. It is routinely evicting peasants from their plots, their only means of existence. They are selling to Chinese, Indians, European, Turkish, Pakistani, Arabians and other companies at the lowest price. In making this huge business, the most preferable area in the empire is Oromoland; of which the land around Finfinee holds rank first.
This politically architected scheme, in the name of investment and development, is daily evicting Oromo peasants around Finfinnee often with meagre or no compensation at all. As a consequence,
- some of the evicted families are migrating to cities like Finfinnee and are becoming beggars
- Some of them are leaving the country for unknown destination and found being refugees in neighbouring countries like Kenya and Yemen.
- Since most of them who have no any alternative, they remain on the sold land and become daily labourers, earning less than half dollar a day.
- Farm lands that had been producing sufficient grains of various types are now turned to produce non-edible flowers and toxic chemicals that contaminate rivers and lakes.
The incumbent Ethiopian regime of TPLF-Arinnet Tigray, more than any other imperial regimes of the past, is committed to make the Oromo people an “African Gypsy”. At one time the deceased prime minister of the Empire and EPDRF leader, Meles Zenawi, refers to the Oromos, who are numerically majority ethnic group in the Empire, said, “It is easy to make them a minority”. They are practically showing us the evil mission they vowed to accomplish. When they become rich of the richest in the Empire, the Oromo peasants they are daily uprooting are becoming poor of the poorest, being reduced to beggary and often deprived of burial sites after death. This evil work, as indicated above, has given priorities to sweep off “garbage” around Finfinnee and ultimately to encompass three-fourth of the region of “Showa” as a domain of “non-garbage” dwellers.
As vividly explained above, the Oromo of Tulama, since the onset of colonisation, have begun to be collectively addressed as “ye Showa Galla”. Those who resisted the derogatory name, the eviction, and the slavery system have been inhumanly executed or hanged. Their land and livestock have been confiscated and shared among the well-armed conquering power.
When Minilik invaded the Gullalle Oromo in Finfinnee, for instance, they remarkably resisted to the last minute but finally defeated. Those who remained behind the massacre had no other option except to leave for other regions against their choice. In their new homes, they have been even treated as collaborators of the invading “Showans” by their own kinsmen, calling them “Goobanaa”.Those able-bodied Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Abbichuu youths were involuntarily conscripted to the colonial army which is typical to all colonial policies. They were forced to go for further campaign to the south, east and west commanded by Showan fitawuraris and dejazmaches
From time to time, all Abyssinian forces, changing forms of their names, swearing in the name of Ethiopian unity and inviolable sovereignty, have never turned down the initial policy of evicting and persecuting the Oromo from their ancestral araddaa. Araddaa Oromoo is the embryonic stage whereOromummaa has begun to radiate from. Hence, by virtue of its original formation, now and then, it could not be integrated into the enforced Abyssinian policy of Itiyophiyawwinnet .
Since the enforced policy has shown no visible success for the past 130 years, this time, it has taken on to shoulder the last option of “sweeping them off” from around what they call “Addis Ababa” as a priority number one. As a consequence, came into being the destruction of Oromo survival relationship with their ancestors’ plot of land. The desecration of their shrines, sacred rivers, sacred mountains and sacred trees of which the case of Odaa and Burqaa Finfinnee, Dhakaa Araaraa and Caffee Tumaa in the vicinity of Finfinnee are quite enough to mention. TPLF’s long range missile policy of destroying Oromos’ relation to their historic araddaa is not the end. It is just the beginning extrapolated to destroy Biyyoo Oromoo.
At this critical time, any concerned Oromo should not be oblivious of the dreadful situation going on in Oromiyaa right now; in Finfinnee and surrounding areas in particular. The deliberate expansion of the amorphous city they call “Addis Ababa” is politically architected to divide Oromiyaa into east and west sector. It is not a master plan. It is an evil plan mastered to consummate an evil goal.
At this critical time, may we believe in the “No life after death”? Rather, may we are for the life right now? Those who are for the life right now are genuinely expected to show discernible power through tangible solidarity to our victimised families at home. Pursuant to our tradition, we have been nurtured learning the wisdom of “Dubbiin haa bultu”. Now, we should redirect this wisdom to “Dubbiin kun hin bultu”,that we ought to swear by great confidence to move in unison against the inhuman act, endless atrocities and perpetual eviction of our families from their ancestral araddaa. Thereof, could we recall the intrinsic wisdom of our fathers’ saying “Tokko dhuufuun namummaadha, lama dhuufuun harrummaadha?”
Urban centers in Oromia:The integration of indigenous Oromo towns into the Ethiopian colonial structure and the formation of garrison and non-garrison cities and towns April 3, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Colonizing Structure, Finfinnee, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo Valley, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development and Change, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Since urban areas and cities are primarily populated by Ethiopian colonial settlers and their collaborators, they are the ones who have access to the limited public facilities such as schools and hospitals. Oromo urbanites like the rural counter parts have been exposed to massive and absolute poverty and have been denied fundamental human rights and needs that Ron Shiffman (1995, 6-8) calls subsistence, protection, affection, and understanding. Most Oromos in urban and rural areas have low levels of subsistence because they lack adequate income, enough food, and livable homes. they do not have protection from disease because they are denied adequate access to health and
medical services.They do not have protection from political violence because the Ethiopian state engages in massive human rights violations and state terrorism ( Jalata 2000). Oromos have been ruled by successive authoritarian-terrorist regimes which have exploited and impoverished them by expropriating their resources. ….The Oromos have been prevented from developing autonomous institutions, organizations, culture, and language, and have been subordinated to the
institutions and organizations of the Habasha colonial settlers in their own cities, towns, and homeland.
Read more @http://works.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1052&context=asafa_jalata
Ethiopia: Farmer gets legal aid from UK to sue Britain for giving aid to the brutal regime of Ethiopia March 30, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa Rising, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Ethnic Cleansing, Hadiya and the Omo Valley, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
An Ethiopian farmer has been given legal aid in the UK to sue Britain – because he claims millions of pounds sent by the UK to his country is supporting a brutal regime that has ruined his life.
He says UK taxpayers’ money – £1.3 billion over the five years of the coalition Government – is funding a despotic one-party state in his country that is forcing thousands of villagers such as him from their land using murder, torture and rape.
The landmark case is highly embarrassing for the Government, which has poured vast amounts of extra cash into foreign aid despite belt-tightening austerity measures at home.
Prime Minister David Cameron claims the donations are a mark of Britain’s compassion.
But the farmer – whose case is set to cost tens of thousands of pounds – argues that huge sums handed to Ethiopia are breaching the Department for International Development’s (DFID) own human rights rules.
He accuses the Government of devastating the lives of some of the world’s poorest people rather than fulfilling promises to help them. The case comes amid growing global concern over Western aid propping up corrupt and repressive regimes.
If the farmer is successful, Ministers might have to review major donations to other nations accused of atrocities, such as Pakistan and Rwanda – and it could open up Britain to compensation claims from around the world.
Ethiopia, a key ally in the West’s war on terror, is the biggest recipient of British aid, despite repeated claims from human rights groups that the cash is used to crush opposition.
DFID was served papers last month by lawyers acting on behalf of ‘Mr O’, a 33-year-old forced to abandon his family and flee to a refugee camp in Kenya after being beaten and tortured for trying to protect his farm.
He is not seeking compensation but to challenge the Government’s approach to aid. His name is being withheld to protect his wife and six children who remain in Ethiopia.
‘My client’s life has been shattered by what has happened,’ said Rosa Curling, the lawyer handling the case. ‘It goes entirely against what our aid purports to stand for.’
Oromia Media Network Launch — Live! March 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Music, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Gadaa System, Hadiya and the Omo Valley, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, Ideas, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Language and Development, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Music, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo Sport, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Poverty, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Self determination, Sidama, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Democratic system, The Oromo Governance System, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Wisdom, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment

Oromia Media Network Launch — Live! 1st March 2014
Millions of Oromos now have the chance to enjoy quality media focusing on the needs and aspirations of the Oromo people.




https://www.oromiamedia.org/donorship/
“The Oromia Media Network (OMN) is an independent, nonpartisan and nonprofit news enterprise whose mission is to produce original and citizen-driven reporting on Oromia, the largest and most populous state in Ethiopia. OMN seeks to offer thought-provoking, contextual, and nuanced coverage of critical public interest issues thereby bringing much needed attention to under-reported stories in the region. Our goal is to create a strong and sustainable multilingual newsroom that will serve as a reliable source of information about the Oromo people, the Ethiopian state, and the greater Horn of Africa region. ” – http://www.oromiamedia.org/
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.
Ethiopia’s government is using imported technology to spy on the phones and computers of Citizens March 26, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Free development vs authoritarian model, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sidama, Slavery, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
Human Rights Watch (HRW) in it recent research report exposes that Ethiopia has built up a large monitoring system for controlling citizens’ network and phone usage. According to this report the government has a sole monopoly of telecommunications and network. And there is no right constraints that prevent the government from gaining an overview of who have contact with anyone on the phone, sms and internet. The government also saves phone calls on a large scale. The authoritarian regime is using imported technology to spy on the phones and computers of its perceived opponents. HRW accuses the government of trying to silence dissent, using software and kit sold by European and Chinese firms. The report says the firms may be guilty of colluding in oppression.
“While monitoring of communications can legitimately be used to combat criminal activity, corruption, and terrorism, in Ethiopia there is little in the way of guidelines or directives on surveillance of communications or use of collected information to ensure such practices are not illegal. In different parts of the world, the rapid growth of information and communications technology has provided new opportunities for individuals to communicate in a manner and at a pace like never before, increasing the space for political discourse and facilitating access to information. However, many Ethiopians have not been able to enjoy these opportunities. Instead, information and
communications technology is being used as yet another method through which the government seeks to exercise complete control over the population, stifling the rights to freedom of expression and association, eroding privacy, and limiting access to information—all of which limit opportunities for expressing contrary opinions and engaging in meaningful debate.”
“Human Rights Watch interviews suggest that a significant number of Oromo individuals have been targeted for unlawful surveillance. Those arrested are invariably accused of being members or supporters of the OLF. In some cases, security officials may have a reasonable suspicion of these individuals being involved with OLF. But in the majority of cases, Oromos were under surveillance because they were organizing cultural associations or trade unions, were involved in celebrating Oromo culture (through music, art, etc.) or were involved in registered political parties.
“Like the OLF, the Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF) was initially a political party, but began a low-level armed insurgency in Ethiopia’s Somali region in response to what it perceived to be the EPRDF’s failure to respect regional autonomy, and to consider demands for self-determination. In 2007, the ONLF scaled up armed attacks against government targets and oil exploration sites, triggering a harsh crackdown by the government. As with the government’s counterinsurgency response to the OLF, the Ethiopian security forces have routinely committed abuses against individuals of Somali ethnicity, including arbitrary detentions, torture, and extrajudicial killings,
based on their ethnicity or perceived support for the ONLF.”“Internet usage in Ethiopia is still in its infancy with less than 1.5 percent of Ethiopians connected to the Internet and fewer than 27,000 broadband subscribers countrywide. By contrast, neighboring Kenya has close to 40 percent access.The majority of Internet users are located in Addis Ababa. According to the ITU, Ethiopia has some of the most expensive broadband in the world. Given these costs, Ethiopians usually access the Internet through the growing number of cybercafés or from their mobile phones.Internet has been available to mobile phone subscribers since 2009.Increasingly available in many of the more expensive hotels and cafes. Connectivity speeds countrywide are quite low, and are prone to frequent outages.”
“State-owned Ethio Telecom is the only telecommunications service provider in Ethiopia. It controls access to the phone network and to the Internet and all phone and Internet traffic must use Ethio Telecom infrastructure. There is no other service provider available in Ethiopia. Ethio Telecom therefore controls access to the Internet backbone that connects Ethiopia to the international Internet. In addition, Internet cafés must apply for a license and purchase service from Ethio Telecom to operate.”
“As Internet access increases, some governments are adopting or compelling use of technologies like “deep packet inspection” (DPI). Deep packet inspection enables the examination of the content of communications (an email or a website) as it is transmitted over an Internet network. Once examined, the communications can be then copied, analyzed, blocked, or even altered. DPI equipment allows Internet service providers—and by extension, governments—to monitor and analyze Internet communications of potentially millions of users in real time. While DPI does have some commercial applications, DPI is also a powerful tool for Internet filtering and blocking and can enable highly intrusive surveillance. Finally, some governments have begun using intrusion software to infiltrate an individual’s computer or mobile phone. Also known as spyware or malware, such software can allow a government to capture passwords (and other text typed into the device), copy or delete files, and even turn on the microphone or camera of the device to eavesdrop. Such software is often unwittingly downloaded when an individual opens a malicious link or file disguised as a legitimate item of interest to the target.”
“The vast majority of the cases documented by Human Rights Watch involving access to phone recordings involved Oromo defendants organizing Oromos in cultural associations, student associations, and trade unions. No credible evidence was presented that would appear to justify their arrest and detention or the accessing of their private phone records. These interrogations took place not only in Addis Ababa, but in numerous police stations and detention centers throughout Oromia and elsewhere in Ethiopia. As described in other publications, the government has gone to great lengths to prevent Oromos and other ethnicities from organizing groups and associations. While the increasing usefulness of the mobile phone to mobilize large groups of people quickly provides opportunities for young people, in particular, to form their own networks, Ethiopia’s monopoly and control over this technology provides Ethiopia with another tool to suppress the formation of these organizations and restrict freedoms of association and peaceful assembly.”
“Ethiopia was the first sub-Saharan African country to begin blocking Internet sites. The first reports of blocked websites appeared in May 2006 when opposition blogs were unavailable, and blocking has become more regular and pervasive ever since. Human Rights Watch and the University of Toronto’s Citizen Lab conducted testing in-country in July and August of 2013 to assess the availability of 171 different URLs that had a higher likelihood of being blocked, based on past testing, on the Ethio Telecom network. A total of 19 tests were run over seven days to ensure reliability of results.”
Read further @
“They Know Everything We Do”
Telecom and Internet Surveillance in Ethiopia
http://www.hrw.org/reports/2014/03/25/they-know-everything-we-do-0
http://thefrontierpost.com/article/84793/Ethiopia-uses-foreign-kit-to-spy-on-opponents-HRW/
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Ethiopia: Silence, Pain, Lies and Abductions March 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Colonizing Structure, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sidama, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, World Bank
add a comment
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-c592hhWlc8
‘This is a regime whose character has the potential to confuse even Jeane J. Kirkpatrick, former Reagan foreign policy advisor, who made a distinction between “authoritarian” and “totalitarian” regimes. In her essay “Dictatorship and Double Standards,” she describes authoritarian dictators as “pragmatic rulers who care about their power and wealth and are indifferent toward ideological issues, even if they pay lip service to some big cause”; while, in contrast, totalitarian leaders are “selfless fanatics who believe in their ideology and are ready to put everything at stake for their ideals”.’
This assessment of the reaction to the article I published on this blog: “Silence and Pain,” is interesting for its exploration of the relationship between the Ethiopian government and the media, even though it overestimates any influence I may have.
Martin
Source: Muktar M. Omer
Ethiopia: Silence, Pain, Lies and Abductions
March 16, 2014
By Muktar M. Omer
Template denials
The Ethiopian Government, through its foreign ministry, responded to Martin Plaut’s article “Silence and Pain: Ethiopia’s human rights record in the Ogaden” with the usual feigned shock and template denial that has long characterized the regime’s political personality. It is the established behavior of aggressive and autocratic regimes to discount well-founded reports of human right violations as propaganda constructs of the ‘enemy’. The response from the Foreign Ministry was thus nothing more than a well memorized and rehearsed Ethiopian way of disregarding documented depravities committed by the regime. As usual…
View original post 2,632 more words
Africa’s youth and the self-seeking repressive elites March 15, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Finfinnee, Food Production, Human Rights, International Economics, International Trade, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromummaa, Poverty, Saudi Arabia, Self determination, Slavery, South Sudan, Specialization, State of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Africa's repressive elites, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, State and Development, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
Africa’s youth will protest to remove self-seeking and repressive elites
“Some examples: authoritarian regimes, as in Ethiopia and Rwanda, are consolidating their positions. In Zambia, Angola and Mozambique, the press, civil society organisations and the opposition are under threat for demanding that the proceeds from raw material exports and billion dollar multinational corporate investments should benefit everyone. ….Short-term greed is, once again, depriving the African populations of the right to share in the continent’s immense riches. No-one can predict the future, but what can be said with certainty is that the possibility of a sustainable long-term and fair development that is currently at hand in Africa is being put at risk. The frustration that is fuelled among populations that are hungry and feel ignored by their rulers will bring about increasingly strident and potentially violent protest. In the near future, this will change the political climate, not least in urban areas. Utilising the internet and their mobile phones, Africa’s youth and forgotten people will mobilise and act together to remove self-seeking and repressive elites. But the situation is not hopeless, on the contrary. Civil society is growing stronger in many places in Africa. The internet makes it possible for people to access and disseminate information in an unprecedented way. However, I get really disappointed when I hear all the ingenuous talk about the possibilities to invest and make quick profits in the ‘New Africa’. What is in reality new in the ‘New Africa’? Today, a worker in a Chinese-owned factory in Ethiopia earns one-tenth of the wage of an employee in China. Unless African governments and investors act more responsibly and ensure long-term sustainable construction for people and the environment ‒ which is currently not the case ‒ we must all ask ourselves if we should not use the consumer power we all possess to exert pressure. There are no excuses for letting African populations and their environment once again pay for the global demand for its raw materials and cheap consumer goods.” – Marika Griehsel, journalist, film-maker and lecturer
“Thousands of people are demonstrating on the streets to protest against low salaries, the highcost of living and an insufficient state safety net. A reaction to austerity measures in Greece? Or a follow-up to the Arab Spring? No, these are protests for greater equality in Sub-Saharan Africa, most recently in Burkina Faso. The widening gap between rich and poor is as troubling in Africa as in the rest of the world. In fact, many Africans believe that inequalities are becoming more marked: A tiny minority is getting richer while the lines of poor people grow out the door. The contrast is all the more striking in Africa since the poverty level has been at a consistently high level for decades, despite the continent’s significant average GDP growth. Some take a plane to get treated for hay fever, while others are pushing up daisies because they can’t afford basic malaria treatment.”
– Global Voices: http://globalvoicesonline.org/2014/03/11/reducing-the-gap-between-africas-rich-and-poor/
It is now evident that the African ‘lion economies’ have hardly even begun the economic and democratic transformation that is absolutely necessary for the future of the continent.
The largest movement ever in Africa of people from rural to urban areas is now taking place. Lagos, Nigeria, and Nairobi, Kenya, are among the world’s fastest growing cities.
The frustration that is fuelled among populations that are hungry and feel ignored by their rulers will bring about increasingly strident and potentially violent protest.
Soon, this will change the political climate, not least in urban areas. Utilising the internet and their phones, Africa’s youth and forgotten people will mobilise to remove self-seeking and repressive elites.
This piece was written in Namibia, where I was leading a tour around one of Africa’s more stable nations. There are several signs confirming the World Bank’s reclassification of Namibia as a middle-income country, which in turn means that many aid donors, including Sweden, have ended their bilateral cooperation.
I see newly constructed, subsidised single-family homes accessible for low-income families. I drive on good roads and meet many tourists, although this is off-season. I hear about a growing mining sector, new discoveries of natural gas and oil deposits. I read about irregularities committed by people in power, in a reasonably free press whose editors are not thrown into jail. There is free primary level schooling and almost free health care.
Most people I talk to are optimistic. A better future for a majority of Namibians is being envisaged. This is in all probability the result of the country having a small population ‒ just above 2 million ‒ and a functioning infrastructure despite its large area.
In Namibia, economic growth can hopefully be matched by implementing policies for long-term, sustainable social and economic development that will benefit more than the élite.
But Namibia is an exception. Because it is now evident that the African ‘lion economies’ have hardly even begun the economic and democratic transformation that is absolutely necessary for the future of the continent.
Some examples: authoritarian regimes, as in Ethiopia and Rwanda, are consolidating their positions. In Zambia, Angola and Mozambique, the press, civil society organisations and the opposition are under threat for demanding that the proceeds from raw material exports and billion dollar multinational corporate investments should benefit everyone.
The International Monetary Fund, IMF, predicts continued high growth rates across Africa with an average of over 6 per cent in 2014. That is of course good news for the continent. Perhaps the best, from a macroeconomic viewpoint, since the 1960s, when many of the former colonies became independent. This growth is mainly driven by the raw material needs of China, India and Brazil.
Meanwhile, the largest movement ever in Africa of people from rural to urban areas is now taking place. Lagos, Nigeria, and Nairobi, Kenya, are among the world’s fastest growing cities. But, in contrast with China, where the migrants from the rural areas get employment in the manufacturing industry, the urban migrants in Africa end up in the growing slums of the big cities.
In a few places, notably in Ethiopia, manufacturing is beginning to take off. But the wages in the Chinese-owned factories are even lower than in China, while the corporations pay minimal taxes to the Ethiopian state.
Short-term greed is, once again, depriving the African populations of the right to share in the continent’s immense riches. No-one can predict the future, but what can be said with certainty is that the possibility of a sustainable long-term and fair development that is currently at hand in Africa is being put at risk.
The frustration that is fuelled among populations that are hungry and feel ignored by their rulers will bring about increasingly strident and potentially violent protest. In the near future, this will change the political climate, not least in urban areas. Utilising the internet and their mobile phones, Africa’s youth and forgotten people will mobilise and act together to remove self-seeking and repressive elites.
But the situation is not hopeless, on the contrary. Civil society is growing stronger in many places in Africa. The internet makes it possible for people to access and disseminate information in an unprecedented way. However, I get really disappointed when I hear all the ingenuous talk about the possibilities to invest and make quick profits in the ‘New Africa’.
What is in reality new in the ‘New Africa’?
Today, a worker in a Chinese-owned factory in Ethiopia earns one-tenth of the wage of an employee in China. Unless African governments and investors act more responsibly and ensure long-term sustainable construction for people and the environment ‒ which is currently not the case ‒ we must all ask ourselves if we should not use the consumer power we all possess to exert pressure.
There are no excuses for letting African populations and their environment once again pay for the global demand for its raw materials and cheap consumer goods.
Some examples: authoritarian regimes, as in Ethiopia and Rwanda, are consolidating their positions. In Zambia, Angola and Mozambique, the press, civil society organisations and the opposition are under threat for demanding that the proceeds from raw material exports and billion dollar multinational corporate investments should benefit everyone.
http://naiforum.org/2014/03/africas-youth-will-protest/
The World Bank paints an optimistic picture of African potential, but warns against persistently high inequalities:
Economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) remains strong with growth forecasted to be 4.9% in 2013. Almost a third of countries in the region are growing at 6% and more, and African countries are now routinely among the fastest-growing countries in the world […] [however the report] notes that poverty and inequality remain “unacceptably high and the pace of reduction unacceptably slow.” Almost one out of every two Africans lives in extreme poverty today.
 http://globalvoicesonline.org/2014/03/11/reducing-the-gap-between-africas-rich-and-poor/
http://globalvoicesonline.org/2014/03/11/reducing-the-gap-between-africas-rich-and-poor/
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights March 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Development, Ethnic Cleansing, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Sidama, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Human Rights Violations in oromia, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromummaa, State of Oromia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights: What is it? Who uses it? Why was it created?
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which was adopted by the UN General Assembly on 10 December 1948, was the result of the experience of the Second World War. With the end of that war, and the creation of the United Nations, the international community vowed never again to allow atrocities like those of that conflict happen again. World leaders decided to complement the UN Charter with a road map to guarantee the rights of every individual everywhere.(http://www.un.org/en/documents/udhr/history.shtml)
http://www.un.org/en/documents/udhr/index.shtml
http://oneworldrights.wordpress.com/2014/02/26/udhr-article-2/
Tweets Ranking Africa: Who tweets most? Who is not? March 12, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Accra, Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Poor, Development, Facebook and Africa, Human Rights, Nairobi, Nelson Mandela, Oromo, South Africa, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Horn of Africa, Oromia, Oromo, Oromummaa, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


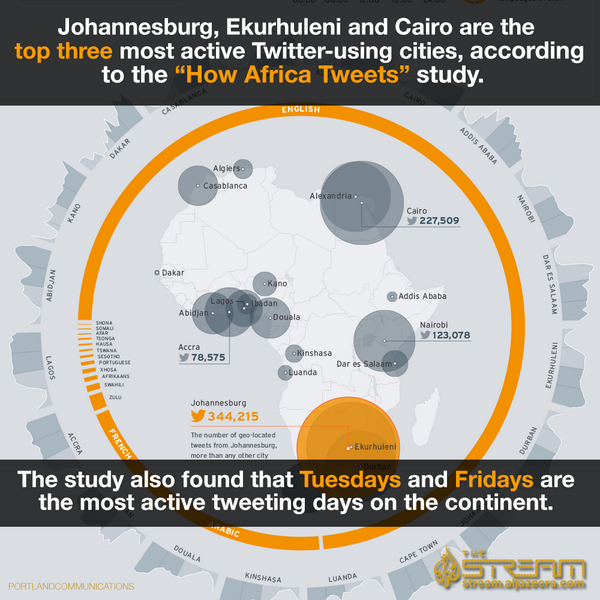
Africa’s largest and second-largest economies, South Africa and Egypt, are Africa’s two most active Twitter countries. Accra, Cairo, Johannesburg and Nairobi are the tweets capitals of Africa. With 344,215 geo-located tweets, Johannesburg is the most active city in Africa.
According to the United Nations International Telecommunication Union (ITU) latest report on information and communications technology in Ethiopia, the country is among the least developed and most expensive in the world. The report placed Ethiopia 151st in ICT development, out of 157 countries, and 152nd out 169 countries in the price of fixed broadband connection. After a decade, in 2012, the internet penetration rate in Ethiopia was a mere 1.1 percent, or 960,331 users and out of this 902,440 are Facebook users. Neighboring Kenya, however, reached a 41 percent penetration rate, with 16.2 million users. As part of its active engagement in curtailing free media, the Ethiopian state is known in making citizen’s use of micro social networkings illegal and blocks internet connections and sites to public.
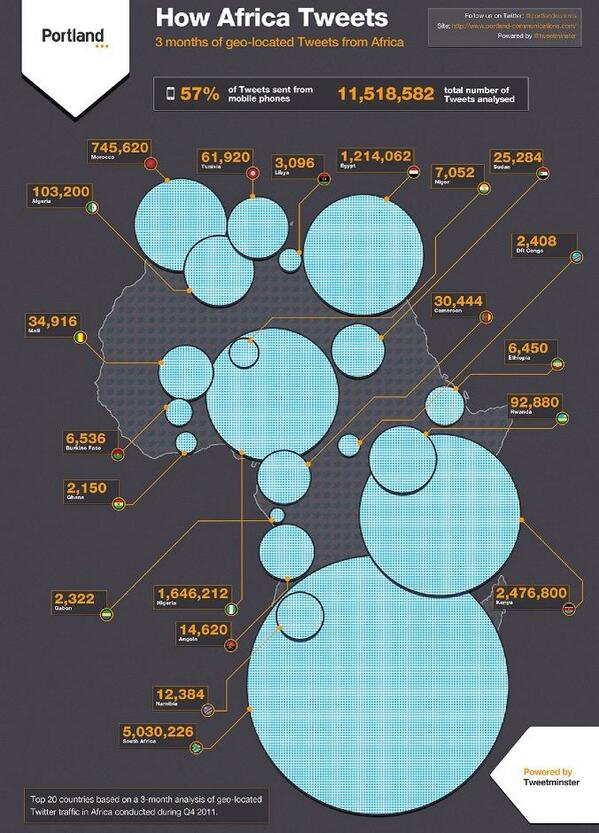
In a follow up to its 2012 study, the London- and Nairobi-based public relations and strategic communications agency Portland analysed geo-located tweets originating from Africa during the final three months of 2013. The second How Africa Tweets study dives deeper into Twitter use on the continent, looking at which cities are the most active, what languages are being used the most and what issues are driving the conversation online.
How Africa Tweets found that, during the final three months of 2013:
Johannesburg is the most active city in Africa, with 344,215 geo-located tweets, followed by Ekurhuleni (264,172) and Cairo (227,509). Durban (163,019) and Alexandria (159,534) make up the remainder of the top five most active cities
Nairobi is the most active city in East Africa and the sixth most active on the continent, with 123,078 geo-located tweets
Accra is the most active city in West Africa and the eight most active on the continent, with 78,575 geo-located tweets
English, French and Arabic are the most common languages on Twitter in Africa, accounting for 75.5% of the total tweets analysed. Zulu, Swahili, Afrikaans, Xhosa and Portuguese are the next most commonly tweeted languages in Africa
Tuesdays and Fridays are the most active tweeting days. Twitter activity rises steadily through the afternoon and evening, with peak volumes around 9pm
The day of Nelson Mandela’s death – 5 December – saw the highest volume of geo-located tweets in Africa
Brands in Africa are becoming increasingly prevalent on Twitter.
Portland tracked major hashtag activity from top brands such as Samsung (#SamsungLove), Adidas (#Adidas) and Magnum ice cream (#MagnumAuction)
Football is the most-discussed topic on Twitter in Africa. Football was discussed more than any other topic, including the death of Nelson Mandela. The most mentioned football team was Johannesburg’s Orlando Pirates (#BlackisBack, #PrayForOrlandoPirates, #OperationFillOrlandoStadium)
Politically-related hashtags were less common than those around other issues, with only four particularly active political hashtags tracked during the time period. This included #KenyaAt50 – celebration of Kenya’s independence – and the competing #SickAt50
Allan Kamau, Head of Portland Nairobi, says: “The African Twittersphere is changing rapidly and transforming the way that Africa communicates with itself and the rest of the world. Our latest research reveals a significantly more sophisticated landscape than we saw just two years ago. This is opening up new opportunities and challenges for companies, campaigning organisations and governments across Africa.”
Mark Flanagan, Head of Digital for Portland, says: “As well as adding diversity of perspective on political and social issues, Africa’s Twitter users are also contributing linguistic diversity. Twitter is now established on the continent as a source of information and a platform for conversation.”http://allafrica.com/stories/201403120080.html
http://allafrica.com/stories/201312230211.html?viewall=1
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
The Oromo are the second largest indigenous population in Africa March 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Afaan Publication, Africa, African Beat, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Colonizing Structure, Development, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Fatuma Roba, Finfinnee, Gadaa System, Haacaaluu Hundeessaa, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, Irreecha, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Language and Development, Nubia, OMN, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Music, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo Sport, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Poverty, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Saudi Arabia, Self determination, Sidama, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oldest Living Person Known to Mankind, The Oromo Democratic system, The Oromo Governance System, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Development, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia and Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, State and Development, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Hard roads to freedom: The Oromo fight for recognition in their new home
refugeeweek
‘We have to tell people we are the second largest indigenous population in Africa
because nobody knows about us.’
 http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/hard-roads-to-freedom-the-oromo-fight-for-recognition-in-their-new-home/
http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/hard-roads-to-freedom-the-oromo-fight-for-recognition-in-their-new-home/
http://advocacy4oromia.files.wordpress.com/2013/05/oromo-fight-for-recognition-in-their-new-home.pdf
The tyranny of experts vs the real cause of poverty:The unchecked power of the state against poor people without rights March 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Poverty, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Aid, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromummaa, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment

How development experts have empowered dictators and helped to trap millions and millions of people in poverty
“Ethiopia, for example, reaps money and plaudits from development giants such as the Gates Foundation while remaining a bastion of authoritarian rule. Economic growth and other positive development outcomes in such states are a mirage, the author argues. His central claim is that no matter how much international aid is poured in, the lives of citizens won’t durably improve without freedom.” -SARAH CHAYES, Book Review, Wall Street Journal
‘The international professionals perpetrate an illusion that poverty is purely a technical problem, distracting attention away from the real cause: the unchecked power of the state against poor people without rights. The dictators whom experts are advising are not the solution — they are the problem. The individual economic and political rights crucial to development include all those we take for granted at home, such as the right to your own property, the right to trade with whomever you wish, the right to protest bad government actions (don’t burn down our houses!), and the right to vote for politicians who do beneficial actions (clean our water!). Technical experts in development sometimes concede some rights and deny others, which disrespects rights for what they are: unalienable. The Uganda story shows the Mubende farmers’ lack of both economic rights (rights to their own property) and political rights (prevented at gunpoint from protesting). The tyranny of experts that neglects rights is first of all a moral tragedy. It reflects a double standard in which we respect rights for the world’s rich — is it conceivable that we would forget these farmers if the story had happened in Ohio? — but not for the poor.
The technocratic approach of dictators advised by experts is also a pragmatic tragedy, because it does not actually work to end poverty. New research by economists on history and modern experience suggest that free individuals with political and economic rights make up remarkably successful problem-solving systems. Such systems based on rights reward a decentralized array of people: Economic entrepreneurs with property rights get to keep the rewards of solving the problems of their consumers. Political entrepreneurs at many government levels and in many departments get rewarded with a longer tenure in office if they solve the citizens’ problems, and they are driven out of office if they don’t. …Focusing on rights yields two perspectives on how development success happens. First, societies that have already attained individual freedom are likely to have already escaped poverty. Economists have gone back deep into our own history to confirm this widely-accepted story for how we in the West escaped our own poverty, but we seem unwilling to consider that the same story could play out in the rest of the world. Second, societies in which there is a positive change in in freedom will likely see a positive change in prosperity (ergo, rapid economic growth and fall in poverty). So what should we do about rights for the poor? Possible starting places for Western policy changes are to not fund dictators, to not support projects that torch farms, to not break promises to investigate rights abuses, and to not let us forget such abuses and missing investigations. But obsessing too much on the “what should we do?” question should not hand the agenda back to the same technical experts who have showed so little interest in the rights of the poor in the first place. The danger of such a tyranny of experts is illustrated by a long history of politicians using technical poverty debates as an excuse to avoid debating rights for the poor. The danger of such a tyranny of experts is illustrated by a long history of politicians using technical poverty debates as an excuse to avoid debating rights for the poor.’ – Read the details and analysis at the original source: http://www.foreignpolicy.com/articles/2014/03/10/the_new_tyranny
Book Review: ‘The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor’ by William Easterly
 The notion of development assistance was born in a period of unabashed racism.
The notion of development assistance was born in a period of unabashed racism.
By SARAH CHAYES
March 7, 2014 (The Wall Street Journal) — Why does poverty persist across so much of the world, despite billions of dollars in international aid and the efforts of armies of development professionals? That is the question that William Easterly explores in “The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor.” His answer: a lack of respect for liberty—not just on the part of governments of impoverished countries but also, more provocatively, on the part of the would-be developers themselves.
Mr. Easterly, an economics professor at New York University, joins other students of international aid in decrying the preference for technical fixes when the political structures of recipient states are built to deny political participation and economic opportunity to most of their citizens. “The technocratic illusion,” he writes, “is that poverty results from a shortage of expertise, whereas poverty is really about a shortage of rights.”
Ethiopia, for example, reaps money and plaudits from development giants such as the Gates Foundation while remaining a bastion of authoritarian rule. Economic growth and other positive development outcomes in such states are a mirage, the author argues. His central claim is that no matter how much international aid is poured in, the lives of citizens won’t durably improve without freedom.
Mr. Easterly recalls that the very notion of development assistance was born in a period of unabashed racism, out of a conjunction of two opposing demands. One was the need for late colonial empires to provide a different rationale than racial superiority for their continued domination of the Third World. The other was the desire of Third World leaders to legitimize seizing authoritarian power themselves.
Touting the virtues of development designed by “experts” and delivered by autocrats proved to be a useful strategy for both camps. “Sun Yat-sen,” writes Mr. Easterly of China in 1924, “suggested the idea of technocratic development to resist European imperialism in China, while at the same time in Versailles, the Allies suggested technocratic development to expand European imperialism in Africa.” And, a few decades later, “the new African leaders found state-led technocratic development to be a justification for their own aspirations to unchecked power.”
This marriage of convenience may have sabotaged democracy’s chances of emerging from the rubble of empire, Mr. Easterly suggests, drawing on evidence from China, Colombia and West Africa. The bias in favor of technocratic fixes, and against fundamental political reform, has certainly helped enable autocratic regimes, which, now as then, capture development aid like any other rent. In Yemen, for example, before counterterrorism security cooperation grew to its current scale, aid was a key source of funding for the Ali Abdullah Saleh regime.
Mr. Easterly’s alternative to the autocrat-driven, technocratic model of development is simple: Apply abroad what we know has worked at home—bottom-up solutions, a free flow of ideas leading to innovative experiments and democratic politics. His positive examples aren’t drawn from the international-assistance realm but rather from the organic emergence of economic prosperity in such environments as 12th-century Italian city-states or the Korean auto industry. Hyundai’s rise is presented as an example of an efficient division of labor engineered almost as a matter of course by free-market forces. Unable to farm his infertile land, Chung Ju Yung, who liked tinkering with cars, set up as a mechanic, thereby exchanging “his problem-solving talents . . . for the problem-solving talents of others in producing food for him.” He would go on to found Hyundai.
Mr. Easterly is hardly the first to criticize the international-development community for its avoidance of politics and fixation on technical solutions. But his belabored insistence that freedom and democracy are the only reliable paths to economic prosperity is too general and thus not very helpful for anyone thinking seriously about how to reform development assistance. While he is right to castigate the many aid efforts undertaken in autocratic contexts, few serious Western development professionals today actively promote dictatorship. Indeed, acceptance of much of Mr. Easterly’s reasoning has driven, from the 1990s on, a sharp increase in support for grass-roots development and democratization efforts.
But Mr. Easterly fails to acknowledge such evolutions. And he thereby misses an opportunity to highlight the obstacles that this approach, in turn, has encountered: the tendency of such grass-roots organizations to respond to the desires of donors rather than their own constituencies, their inability to live up to outsize expectations or, when successful, their tendency to suffer repression at the hands of authoritarian states. Nor does Mr. Easterly contend in detail with the fundamental question raised by his book: What explains the persistence of such a “momentous double standard on rights for the West and not for the Rest?”
Some explanations do emerge in passing. Geostrategic priorities, for example, have impelled the U.S. to use foreign aid to reward autocratic allies in the fights against Communism and terrorism. Racism, blatant or otherwise, has made Westerners doubt non-white non-Westerners’ desire for rights and ability to handle them. The desire to self-perpetuate has also been a powerful motive to stick to the status quo for an industry as large as international assistance—a motive Mr. Easterly doesn’t emphasize. Challenging entrenched power structures is a good way to get thrown out of a country, as a number of democracy-promotion organizations recently learned in Egypt.
Apart from these gaps, and the book’s lack of explicit recommendations, its analysis raises some philosophical problems. It draws too sharp an opposition between individualism and collective values. By depicting a global “East” caught in a feedback loop of autocracy and “collectivist values,” Mr. Easterly falls into Samuel Huntingtonesque generalizations. Similarly, he seems to suggest that geography and climate predisposed the Southern Hemisphere to slave-based or extractive economies.
The generalizations, moreover, evade a lot of contrary nuance. The Nordic countries are widely seen as more respectful of community values than the U.S. or Britain. And many of their health and development outcomes outstrip ours. Some might argue that these are smaller, more homogeneous societies, but so are some of the negative examples of “collectivist values” that Mr. Easterly cites, such as the “Maghribi” network, a 10th-century Cairo-based Jewish trading community. And the world economic meltdown of 2008, with devastating development effects for tens of millions, was the result not of excessively collectivist values but the reverse. Poor development outcomes, in other words, aren’t only a matter of rights, as Mr. Easterly argues. At issue is also the distribution of power—justice as well as liberty.
The book’s argument about the power of freedom and democracy to beget development is made by way of a vast historical tableau. From the 12th-century Italian city-states, the narrative winds past the slave trade, expounds the virtues of migration, explores the ideas of Adam Smith and ruminates on the structure of technological innovation. Supporting anecdotes include a Senegalese religious trading community, the Korean automotive industry and an evolving Manhattan neighborhood.
It is hard to trust an author to command such a welter of detail. And indeed, the result is too often haphazard, self-contradictory or erroneous. For example, while the Maghribi traders are said to demonstrate self-sabotaging collectivist values, the Mourides, a modern Somali religious brotherhood that is organized along nearly the same principles, is cited to illustrate the virtues of migration. The Korean auto industry, depicted as embodying “the amazing potentials of specialization and trade,” emerged under an autocratic government applying protectionist laws.
By my count, finally, about 15% of Mr. Easterly’s text recaps what was just said or announces items from later chapters. Subheadings like “Another Key Moment in This Book” suggest an argument that isn’t tight enough to convince on its own merits. And that’s too bad. Mr. Easterly calls for a profound overhaul of the way powerful nations conceive of and implement aid—and, more important, of the broader foreign-policy decision-making of which aid is a component. That change is needed. It’s just not clear this book is crisp or cogent enough to help advance it.
—Ms. Chayes is a senior associate at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
To buy this book Click Here
The Status of Africa’s Economy and Its Underlying Structural Weakness March 10, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development and Change, Economic, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Horn of Africa, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, World Bank
add a comment
East Asian countries grew rapidly by replicating, in a much shorter time frame, what today’s advanced countries did following the Industrial Revolution. They turned their farmers into manufacturing workers, diversified their economies, and exported a range of increasingly sophisticated goods.
Little of this process is taking place in Africa. As researchers at the African Center for Economic Transformation in Accra, Ghana, put it, the continent is “growing rapidly, transforming slowly.”
In principle, the region’s potential for labor-intensive industrialization is great. A Chinese shoe manufacturer, for example, pays its Ethiopian workers one-tenth what it pays its workers back home. It can raise Ethiopian workers’ productivity to half or more of Chinese levels through in-house training. The savings in labor costs more than offset other incremental costs of doing business in an African environment, such as poor infrastructure and bureaucratic red tape.
But the aggregate numbers tell a worrying story. Fewer than 10% of African workers find jobs in manufacturing, and among those only a tiny fraction – as low as one-tenth – are employed in modern, formal firms with adequate technology. Distressingly, there has been very little improvement in this regard, despite high growth rates. In fact, Sub-Saharan Africa is less industrialized today than it was in the 1980’s. Private investment in modern industries, especially non-resource tradables, has not increased, and remains too low to sustain structural transformation. The underlying problem is the weakness of these economies’ structural transformation.
As in all developing countries, farmers in Africa are flocking to the cities. And yet, as a recent study from the Groningen Growth and Development Center shows, rural migrants do not end up in modern manufacturing industries, as they did in East Asia, but in services such as retail trade and distribution. Though such services have higher productivity than much of agriculture, they are not technologically dynamic in Africa and have been falling behind the world frontier.
Consider Rwanda, a much-heralded success story where GDP has increased by a whopping 9.6% per year, on average, since 1995 (with per capita incomes rising at an annual rate of 5.2%). Xinshen Diao of the International Food Policy Research Institute has shown that this growth was led by non-tradable services, in particular construction, transport, and hotels and restaurants. The public sector dominates investment, and the bulk of public investment is financed by foreign grants. Foreign aid has caused the real exchange rate to appreciate, compounding the difficulties faced by manufacturing and other tradables.
None of this is to dismiss Rwanda’s progress in reducing poverty, which reflects reforms in health, education, and the general policy environment. Without question, these improvements have raised the country’s potential income. But improved governance and human capital do not necessarily translate into economic dynamism. What Rwanda and other African countries lack are the modern, tradable industries that can turn the potential into reality by acting as the domestic engine of productivity growth.
The African economic landscape’s dominant feature – an informal sector comprising microenterprises, household production, and unofficial activities – is absorbing the growing urban labor force and acting as a social safety net. But the evidence suggests that it cannot provide the missing productive dynamism. Studies show that very few micro enterprises grow beyond informality, just as the bulk of successful established firms do not start out as small, informal enterprises.
Optimists say that the good news about African structural transformation has not yet shown up in macroeconomic data. They may well be right. But if they are wrong, Africa may confront some serious difficulties in the decades ahead.
Half of Sub-Saharan Africa’s population is under 25 years of age. According to the World Bank, each year an additional five million turn 15, “crossing the threshold from childhood to adulthood.” Given the slow pace of positive structural transformation, the Bank projects that over the next decade only one in four African youth will find regular employment as a salaried worker, and that only a small fraction of those will be in the formal sector of modern enterprises.
Two decades of economic expansion in Sub-Saharan Africa have raised a young population’s expectations of good jobs without greatly expanding the capacity to deliver them. These are the conditions that make social protest and political instability likely. Economic planning based on simple extrapolations of recent growth will exacerbate the discrepancy. Instead, African political leaders may have to manage expectations downward, while working to increase the rate of structural transformation and social inclusion. – Dani Rodrik, Africa’s Structural Transformation Challenge
Related Article from the Economist:-
EVERY boom has its boosters and detractors. So it is with sub-Saharan Africa’s economic advance in the past 15 years. GDP across the region has risen by an average 5.1% a year. The IMF forecasts further growth of almost 6% this year and next. Optimists say growth now has an unstoppable momentum. But naysayers point out that a similar spurt in the 1960s and early 1970s gave way to two decades of stagnation. How can Africa make sure it does not repeat that dismal pattern?
A version of this question was posed by Yaw Ansu, chief economist of the Africa Centre for Economic Transformation (ACET), an Accra-based think-tank, as he unveiled a detailed report on Africa’s progress and prospects. The answer from Mr Ansu, who worked for 26 years at the World Bank before joining ACET, is that Africa must focus on “economic transformation” or put more simply “growth built on solid grounds”. His study draws on the experience of eight middle-income countries (six from Asia plus Brazil and Chile) that were as poor 30-40 years ago as Africa is now. The lesson is that GDP growth is not enough. For prosperity to last, economies must also become more diverse, export-oriented and constantly upgrade their technology.
This is a familiar wish-list. But unlike many development blueprints, the ACET report is grounded in economic reality. The road out of poverty, it says, must be linked to Africa’s endowment of abundant cheap labour, land and minerals. For instance the way to ensure that oil, gas and metal deposits are a blessing and not a curse, says ACET, is first to be sure to get the best deal for exploiting minerals and then to use the money well. That means countries should invest in geological surveys so they know as much about their mineral deposits as prospectors do. Cutting a back-room deal for a mining concession is to invite a rip-off. So rights should instead be sold by auction. Countries such as Norway and Chile can be tapped for their know-how in collecting mineral revenue and salting it away.
All too often a natural-resource boom works against lasting development. The mining industry uses lots of machinery and creates relatively few jobs. In good times the foreign earnings from mineral sales push up the value of the local currency making it harder for other kinds of exporters to survive. And mineral-rich countries can become too dependent on a few sources of income which can dry up when world prices suddenly change. A lack of diversity in earnings is a big concern for Africa. The ACET report shows that five exports account for 64% of all exports in Africa compared with an average of 44% in the eight middle-income countries used as a benchmark.
A strong message from the ACET report is that Africa needs more factories if it is to keep up its progress. Manufacturing has greater spillovers for the rest of the economy than mining does and gives variety to export income. While there are gulfs between Africa and richer countries in a wide variety of indicators, the lack of manufacturing muscle is one of the largest. Its share of Africa’s GDP was around 9% in 2010 compared with 24% among the eight middle-income countries.
Africa has lots of surplus labour. What it needs are jobs-intensive industries, such as garment-making and component assembly, to soak it up. The growing middle class in Africa should make this an easy sell to multinational firms. A businesses would be “crazy not to consider building a processing plant in Africa just to supply the local market demand,” says one of the executives surveyed by ACET. Indeed there are recent signs of a manufacturing revival in Africa. But the same executive goes on to say “the challenges are too large for us to be comfortable to invest.” Business folk surveyed by ACET spoke of unhelpful policies, shortages of skills and the small size of markets as particular barriers.
Among the fixes for these ills suggested by ACET are special economic zones (in which some rules are relaxed); training colleges to cater to specific company’s needs, such as the ones run in Kenya and Nigeria by Samsung, an electronics giant; and more effort to cut tariffs within Africa’s regional trading zones. Indeed there is no shortage of advice for Africa’s would-be lions. The lessons from the success of Asia’s tigers are fairly well understood. The tricky part is to implement them.
http://www.economist.com/blogs/baobab/2014/03/development-africa?fsrc=scn/tw_ec/how_to_make_it_last
US Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor 2013 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Ethiopia February 28, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, African Poor, Colonizing Structure, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Ethiopia, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Ethiopia:2013 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices
By US Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor
27 February 2014
- The most significant human rights problems included: restrictions on freedom of expression and association, including through arrests; detention; politically motivated trials; harassment; and intimidation of opposition members and journalists, as well as continued restrictions on print media.
- Other human rights problems included arbitrary killings; allegations of torture, beating, abuse, and mistreatment of detainees by security forces; reports of harsh and, at times, life-threatening prison conditions; arbitrary arrest and detention; detention without charge and lengthy pretrial detention; a weak, overburdened judiciary subject to political influence; infringement on citizens’ privacy rights, including illegal searches; allegations of abuses in the implementation of the government’s “villagization” program; restrictions on academic freedom; restrictions on freedom of assembly, association, and movement; alleged interference in religious affairs; limits on citizens’ ability to change their government; police, administrative, and judicial corruption; violence and societal discrimination against women and abuse of children; female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C); trafficking in persons; societal discrimination against persons with disabilities; clashes between ethnic minorities; discrimination against persons based on their sexual orientation and against persons with HIV/AIDS; limits on worker rights; forced labor; and child labor, including forced child labor.
- Impunity was a problem. The government, with some reported exceptions, usually did not take steps to prosecute or otherwise punish officials who committed abuses other than corruption.
- Members of the security forces reportedly committed killings. On August 8, security forces in Addis Ababa detained more than one thousand Muslims participating in Eid al-Fitr celebrations. Authorities released most of the detainees shortly thereafter, but there were credible allegations some of the detainees died while in detention. There continued to be reports of abuses, including killings, by the Somali Region Special Police.
- A few domestic human rights groups operated, but with significant government restrictions. The government was generally distrustful and wary of domestic human rights groups and international observers. State-controlled media were critical of international human rights groups such as Human Rights Watch.
- The CSO law prohibits charities, societies, and associations (NGOs or CSOs) that receive more than 10 percent of their funding from foreign sources from engaging in activities that advance human and democratic rights or promote equality of nations, nationalities, peoples, genders, and religions; the rights of children and persons with disabilities; conflict resolution or reconciliation; or the efficiency of justice and law enforcement services. The implementation of the law continued to result in the severe curtailment of NGO activities related to human rights. In July 2012 the UN high commissioner for human rights expressed concern that civil society space “has rapidly shrunk” since the CSO law’s enactment.
- The country has more than 80 ethnic groups, of which the Oromo, at approximately 35 percent of the population, is the largest. The federal system drew boundaries roughly along major ethnic group lines. Most political parties remained primarily ethnically based.
- Clashes between ethnic groups during the year resulted in injury and death. In January ethnic clashes broke out at Addis Ababa University reportedly due to anti-Oromo graffiti. The clashes resulted in injury to as many as 20 persons.
- The government, controlled by the ruling EPRDF, restricted media freedom and arrested opposition members. Constituent parties of the EPRDF conferred advantages upon their members; the parties directly owned many businesses and were broadly perceived to award jobs and business contracts to loyal supporters. Several opposition political parties reported difficulty in renting homes or buildings in which to open offices, citing visits by EPRDF members to the landlords to persuade or threaten them not to rent property to these parties. There were reports authorities had terminated the employment of teachers and other government workers if they belonged to opposition political parties.
- According to sources, the ruling party via the Ministry of Education continued to give preference to students loyal to the party in assignments to postgraduate programs. Some university staff members commented that priority for employment after graduation in all fields was given to students who joined the party. Authorities limited teachers’ ability to deviate from official lesson plans. Numerous anecdotal reports suggested non-EPRDF members were more likely to be transferred to undesirable posts and bypassed for promotions. There were unspecified reports of teachers not affiliated with the EPRDF being summarily dismissed for failure to attend unscheduled meetings. There continued to be a lack of transparency in academic staffing decisions, with numerous complaints from individuals in the academic community alleging bias based on party membership, ethnicity, or religion. According to multiple credible sources, teachers and high school students in grade 10 and above were required to attend training on the concepts of revolutionary democracy and EPRDF party ideology.
- The state-owned Ethio Telecom was the only internet service provider in the country. The government restricted access to the internet and blocked several websites, including blogs; opposition websites; and websites of Ginbot 7, the OLF, and the ONLF. The government also temporarily blocked news sites such as al-Jazeera. Websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and Yahoo! were temporarily inaccessible at times. Several news blogs and websites run by opposition diaspora groups were not accessible. These included Addis Neger, Nazret, Ethiopian Review, CyberEthiopia, Quatero Amharic Magazine, Tensae Ethiopia, and the Ethiopian Media Forum. Authorities took steps to block access to Virtual Private Network providers that let users circumvent government screening of internet browsing and e-mail. According to the International Telecommunication Union, approximately 1.5 percent of individuals used the internet in 2012. In March, Citizen Lab, a Canadian research center at the University of Toronto, identified 25 countries, including Ethiopia, that host servers linked to FinFisher surveillance software. According to the report, “FinFisher has gained notoriety because it has been used in targeted attacks against human rights campaigners and opposition activists in countries with questionable human rights records.”
- Estimates by human rights groups and diplomatic missions regarding the number of political prisoners varied. The government did not permit access by international human rights organizations.
- All of the Ethiopian journalists, opposition members, and activists previously convicted and jailed under the antiterrorism proclamation remained in prison.
- On January 8, the Federal Court of Cassation denied journalist Reyot Alemu’s appeal of her conviction on the charge of participating in the promotion or communication of a terrorist act. She was serving a five-year prison sentence.
- On May 2, the Federal Supreme Court upheld the sentences of journalist and blogger Eskinder Nega and vice chairman of the opposition front Medrek Andualem Arage for terrorism and treason. In September 2012 the government announced it asked the Federal High Court to freeze the assets of Eskinder and Andualem while investigating whether their assets were used in conjunction with the commission of the crimes for which they were convicted. The court had not issued a decision by year’s end.
- The Federal Supreme Court upheld the 2012 convictions under the criminal code of Bekele Gerba and Olbana Lelisa, two well-known political opposition figures from the Oromo ethnic group, for conspiracy to overthrow the government and conspiracy to incite unrest. The Supreme Court subsequently determined the Federal High Court did not consider mitigating circumstances and reduced Bekele’s sentence from eight years to three years and seven months. The Supreme Court also reduced Olbana’s sentenced from 13 to 11 years. Courts convicted 69 members of Oromo political opposition parties, charged separately in 2011 under the criminal code with “attacking the political or territorial integrity of the state.”
http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2013/af/220113.htm#
– See more at: http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/humanrightsreport/index.htm?dlid=220113&year=2013#wrapper
Ethiopia is a federal republic. The ruling Ethiopian Peoples’ Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF), a coalition of four ethnically based parties, controls the government. In September 2012, following the death of former Prime Minister Meles Zenawi, parliament elected Hailemariam Desalegn as prime minister. In national parliamentary elections in 2010, the EPRDF and affiliated parties won 545 of 547 seats to remain in power for a fourth consecutive five-year term. Although the relatively few international officials allowed to observe the elections concluded that technical aspects of the vote were handled competently, some also noted that an environment conducive to free and fair elections was not in place prior to the election. Authorities generally maintained control over the security forces, although Somali Region Special Police and local militias sometimes acted independently. Security forces committed human rights abuses.
The most significant human rights problems included: restrictions on freedom of expression and association, including through arrests; detention; politically motivated trials; harassment; and intimidation of opposition members and journalists, as well as continued restrictions on print media. On August 8, during Eid al-Fitr celebrations, security forces temporarily detained more than one thousand persons in Addis Ababa. The government continued restrictions on activities of civil society and nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) imposed by the Charities and Societies Proclamation (the CSO law).
Other human rights problems included arbitrary killings; allegations of torture, beating, abuse, and mistreatment of detainees by security forces; reports of harsh and, at times, life-threatening prison conditions; arbitrary arrest and detention; detention without charge and lengthy pretrial detention; a weak, overburdened judiciary subject to political influence; infringement on citizens’ privacy rights, including illegal searches; allegations of abuses in the implementation of the government’s “villagization” program; restrictions on academic freedom; restrictions on freedom of assembly, association, and movement; alleged interference in religious affairs; limits on citizens’ ability to change their government; police, administrative, and judicial corruption; violence and societal discrimination against women and abuse of children; female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C); trafficking in persons; societal discrimination against persons with disabilities; clashes between ethnic minorities; discrimination against persons based on their sexual orientation and against persons with HIV/AIDS; limits on worker rights; forced labor; and child labor, including forced child labor.
Impunity was a problem. The government, with some reported exceptions, usually did not take steps to prosecute or otherwise punish officials who committed abuses other than corruption.
Factions of the Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF), an ethnically based, violent, and fragmented separatist group operating in the Somali Region, were responsible for abuses.
SECTION 1. RESPECT FOR THE INTEGRITY OF THE PERSON, INCLUDING FREEDOM FROM:
a. Arbitrary or Unlawful Deprivation of Life
Members of the security forces reportedly committed killings.
On August 8, security forces in Addis Ababa detained more than one thousand Muslims participating in Eid al-Fitr celebrations. Authorities released most of the detainees shortly thereafter, but there were credible allegations some of the detainees died while in detention.
There continued to be reports of abuses, including killings, by the Somali Region Special Police.
Scattered fighting continued between government forces – primarily regional government-backed militias – and elements of the ONLF. Clashes between ethnic groups resulted in injury and death.
b. Disappearance
There were several reported cases of disappearances of civilians after clashes between security forces and rebel groups.
Security forces detained at least 12 residents of Alamata town in the northern Tigray Region in January following protests against government plans to demolish illegal housing units. The whereabouts of the detainees remained unknown at year’s end.
c. Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment
The constitution and law prohibit such practices; however, there were reports security officials tortured and otherwise abused detainees.
Authorities reportedly tortured Solomon Kebede, a columnist with Muslim Affairs magazine (see section 2.a.).
Sources widely believed police investigators often used physical abuse to extract confessions in Maekelawi, the central police investigation headquarters in Addis Ababa. Human Rights Watch reported abuses, including torture, occurred at Maekelawi. In an October report the NGO described beatings, stress positions, the hanging of detainees by their wrists from the ceiling, prolonged handcuffing, the pouring of water over detainees, verbal threats, and solitary confinement at the facility. Authorities continued to restrict access by diplomats and NGOs to Maekelawi.
In 2010 the UN Committee Against Torture reported it was “deeply concerned” about “numerous, ongoing, and consistent allegations” concerning “the routine use of torture” by police, prison officers, and other members of the security forces – including the military – against political dissidents and opposition party members, students, alleged terrorists, and alleged supporters of violent separatist groups like the ONLF and the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF). The committee reported that such acts frequently occurred with the participation of, at the instigation of, or with the consent of commanding officers in police stations, detention centers, federal prisons, military bases, and unofficial or secret places of detention. Some reports of such abuses continued during the year.
Prison and Detention Center Conditions
Prison and pretrial detention center conditions remained harsh and, in some cases, life threatening. There were numerous reports that authorities beat prisoners. Medical attention following beatings reportedly was insufficient in some cases.
Physical Conditions: As of September 2012 there were 70,000-80,000 persons in prison, of whom approximately 2,500 were women and nearly 600 were children incarcerated with their mothers. Authorities sometimes incarcerated juveniles with adults and sometimes incarcerated small children with their mothers. Male and female prisoners generally were separated.
Severe overcrowding was common, especially in prison sleeping quarters. The government provided approximately eight birr ($0.42) per prisoner per day for food, water, and health care. Many prisoners supplemented this amount with daily food deliveries from family members or by purchasing food from local vendors, although there were unspecified reports officials prevented some prisoners from receiving supplemental food from their families. Medical care was unreliable in federal prisons and almost nonexistent in regional prisons. Prisoners had limited access to potable water, as did many in the country. Also water shortages caused unhygienic conditions, and most prisons lacked appropriate sanitary facilities. Many prisoners had serious health problems in detention but received little treatment. Information released by the Ministry of Health in 2012 reportedly stated that nearly 62 percent of inmates in various jails across the country suffered from mental health problems as a result of solitary confinement, overcrowding, and lack of adequate health care facilities and services.
The country had six federal and 120 regional prisons. The Ethiopian NGO Justice For All-Prison Fellowship Ethiopia (JFA-PFE) ran model prisons in Adama and Mekele, with significantly better conditions than those found in other prisons. There also were many unofficial detention centers throughout the country, including in Dedessa, Bir Sheleko, Tolay, Hormat, Blate, Tatek, Jijiga, Holeta, and Senkele. Most were located at military camps.
Pretrial detention often occurred in police station detention facilities, where the conditions varied widely. Reports regarding pretrial detention in police stations indicated poor hygiene and police abuse of detainees.
Administration: It was difficult to determine if recordkeeping was adequate due to the lack of transparency regarding incarceration. Authorities did not employ alternative sentencing for nonviolent offenders. Prisons did not have ombudspersons to respond to complaints. Legal aid clinics existed in some prisons for the benefit of prisoners. Authorities allowed the submission by detainees of complaints to judicial authorities without censorship. Courts sometimes declined to hear such complaints. The Ethiopian Human Rights Commission (EHRC) and the Federal Police Commission sometimes investigated allegations of abuse, although there were reports that detainees’ discussions with them were not done in private, which could limit their ability to speak freely.
Authorities generally permitted prisoners to have visitors, although some police stations did not allow pretrial detainees access to visitors (including family members and legal counsel). In some cases authorities restricted family visits to prisoners to a few per year. Family members of prisoners charged with terrorist activity alleged instances of blocked access to the prisoners. There were also reports authorities denied those charged with terrorist activity visits with their lawyers, or with representatives of the political parties to which they belonged. In June prison authorities temporarily granted full visitation privileges to imprisoned journalist/blogger Eskinder Nega; previously, Eskinder was been permitted visits by a select group of individuals. Prison officials limited the number of individuals permitted to visit journalist Reyot Alemu.
Prisoners generally were permitted religious observance, but this varied by prison, and even by section within a prison, at the discretion of prison management. There were some allegations that while in custody authorities denied detainees adequate locations in which to pray. Prisoners were permitted to voice complaints about prison conditions or treatment to the presiding judge during their trials.
Independent Monitoring: During the year the International Committee of the Red Cross visited regional prisons throughout the country.
Regional authorities allowed government and NGO representatives to meet regularly with prisoners without third parties present. The government-established EHRC, which is funded by parliament and subject to parliamentary review, monitored federal and regional detention centers and interviewed prison officials and prisoners in response to allegations of widespread human rights abuses. The JFA-PFE was granted access to various prison and detention facilities.
Improvements: The government and prison authorities generally cooperated with efforts of the JFA-PFE to improve prison conditions. Reports indicated prison conditions, including the treatment of prisoners, improved upon the completion of a local legal aid clinic, although specific data was not available.
d. Arbitrary Arrest or Detention
Although the constitution and law prohibit arbitrary arrest and detention, the government often ignored these provisions. There were multiple reports of arbitrary arrest and detention by police and security forces throughout the country.
Civilians, international NGOs, and other aid organizations operating in the Somali Region reported government security forces, local militias, and the ONLF committed abuses such as arbitrary arrest.
ROLE OF THE POLICE AND SECURITY APPARATUS
The Federal Police reports to the Ministry of Federal Affairs, which is subject to parliamentary oversight. The oversight was loose. Each of the country’s nine regions has a state or special police force that reports to the regional civilian authorities. Local militias operated across the country in loose coordination with regional and federal police and the military, with the degree of coordination varying by region. In many cases these militias functioned as extensions of local EPRDF political bosses.
Security forces were effective, but impunity remained a serious problem. The mechanisms used to investigate abuses by the federal police were not known. There continued to be reports of abuse, including killings, by the Somali Region Special Police. The government rarely publicly disclosed the results of investigations into abuses by local security forces, such as arbitrary detention and beatings of civilians.
The government continued its efforts to provide human rights training for police and army recruits. The EHRC trained more than 100 police officers and prison officials during the year and in 2012 on basic human rights concepts and prisoner treatment. The government continued to accept assistance from the JFA-PFE and the EHRC to improve and professionalize its human rights training and curriculum by including more material on the constitution and international human rights treaties and conventions.
ARREST PROCEDURES AND TREATMENT OF DETAINEES
Although the constitution and law require that detainees be brought to court and charged within 48 hours of arrest, authorities did not always respect this requirement. With court approval, persons suspected of serious offenses may be detained for 14 days without being charged and for additional 14-day periods if an investigation continues. Under the antiterrorism proclamation, police may request to hold persons without charge for 28-day periods, up to a maximum of four months, while an investigation is conducted. The law prohibits detention in any facility other than an official detention center; however, local militias and other formal and informal law enforcement entities used dozens of unofficial local detention centers.
A functioning bail system was in place. Bail was not available for persons charged with murder, treason, and corruption. In most cases authorities set bail between 500 and 10,000 birr ($26 and $530), which most citizens could not afford. The government provided public defenders for detainees unable to afford private legal counsel, but only when their cases went to court. While detainees were in pretrial detention, authorities sometimes allowed them little or no contact with legal counsel, did not provide full information on their health status, and did not provide for family visits.
Arbitrary Arrest: Authorities regularly detained persons without warrants.
On May 24, in the western state of Benishangul-Gumuz, local police detained Muluken Tesfaw, a journalist for the Ethio-Mihdar newspaper, who was investigating allegations that local officials unlawfully evicted ethnic Amhara residents from their homes. The journalist reportedly was not carrying his press credentials. On May 31, authorities released Muluken without charge.
Pretrial Detention: Some detainees reported being held for several years without being charged and without trial. Information on the percentage of detainee population in pretrial detention and the average length of time held was not available. Trial delays were most often caused by lengthy legal procedures, the large numbers of detainees, judicial inefficiency, and staffing shortages.
Amnesty: On September 11, in keeping with a long-standing tradition of issuing pardons at the Ethiopian new year, the federal government pardoned 498 prisoners. Regional governments also pardoned persons during the year. For example, the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People’s Region (SNNPR) regional government pardoned 1,984 prisoners, the Oromia regional government pardoned 2,604 prisoners, and the Amhara regional government pardoned 2,084 prisoners.
e. Denial of Fair Public Trial
The law provides for an independent judiciary. Although the civil courts operated with a large degree of independence, the criminal courts remained weak, overburdened, and subject to political influence. The constitution recognizes both religious and traditional or customary courts.
TRIAL PROCEDURES
By law accused persons have the right to a fair public trial by a court of law within a “reasonable time,” a presumption of innocence, the right to be represented by legal counsel of their choice, and the right to appeal. The law provides defendants the right against self-incrimination. The law gives defendants the right to present witnesses and evidence in their defense, cross-examine prosecution witnesses, and access government-held evidence. The government did not always allow defendants the right of access to evidence it held. The court system does not use jury trials. Judicial inefficiency and lack of qualified staff often resulted in serious delays in trial proceedings and made the application of the law unpredictable. The government continued to train lower court judges and prosecutors and made effective judicial administration the primary focus of this training. Defendants were often unaware of the specific charges against them until the commencement of the trial; this also caused defense attorneys to be unprepared to provide an adequate defense.
The Public Defender’s Office provided legal counsel to indigent defendants, although its scope and quality of service remained limited due to the shortage of attorneys. Numerous free legal aid clinics around the country, based primarily at universities, provided advice to clients. In certain areas of the country the law allows volunteers, such as law students and professors, to represent clients in court on a pro bono basis.
On January 22, citing national security concerns, the Federal High Court closed the trial of 28 Muslims identified with July 2012 protests and one Muslim accused of accepting funds illegally from a foreign embassy. On December 12, the Federal High Court dismissed charges against 10 of the defendants and reduced charges against 18 others. Although the Federal High Court also closed the trial of 28 additional Muslims the government alleged to have links to al-Qaida and al-Shabaab, the court reopened the trial to the public on October 29. Both trials continued at year’s end.
Many citizens residing in rural areas generally had little access to formal judicial systems and relied on traditional mechanisms of resolving conflict. By law all parties to a dispute must agree to use a traditional or religious court before such a court may hear a case, and either party may appeal to a regular court at any time. Sharia (Islamic law) courts may hear religious and family cases involving Muslims. Sharia courts received some funding from the government and adjudicated the majority of cases in the Somali and Afar regions, which are predominantly Muslim. In addition other traditional systems of justice, such as councils of elders, continued to function. Some women stated they lacked access to free and fair hearings in the traditional justice system because they were excluded by custom from participation in councils of elders and because there was strong gender discrimination in rural areas.
POLITICAL PRISONERS AND DETAINEES
Estimates by human rights groups and diplomatic missions regarding the number of political prisoners varied. The government did not permit access by international human rights organizations.
All of the Ethiopian journalists, opposition members, and activists previously convicted and jailed under the antiterrorism proclamation remained in prison.
On January 8, the Federal Court of Cassation denied journalist Reyot Alemu’s appeal of her conviction on the charge of participating in the promotion or communication of a terrorist act. She was serving a five-year prison sentence.
On May 2, the Federal Supreme Court upheld the sentences of journalist and blogger Eskinder Nega and vice chairman of the opposition front Medrek Andualem Arage for terrorism and treason. In September 2012 the government announced it asked the Federal High Court to freeze the assets of Eskinder and Andualem while investigating whether their assets were used in conjunction with the commission of the crimes for which they were convicted. The court had not issued a decision by year’s end.
The Federal Supreme Court upheld the 2012 convictions under the criminal code of Bekele Gerba and Olbana Lelisa, two well-known political opposition figures from the Oromo ethnic group, for conspiracy to overthrow the government and conspiracy to incite unrest. The Supreme Court subsequently determined the Federal High Court did not consider mitigating circumstances and reduced Bekele’s sentence from eight years to three years and seven months. The Supreme Court also reduced Olbana’s sentenced from 13 to 11 years. Courts convicted 69 members of Oromo political opposition parties, charged separately in 2011 under the criminal code with “attacking the political or territorial integrity of the state.”
CIVIL JUDICIAL PROCEDURES AND REMEDIES
The law provides citizens the right to appeal human rights violations in civil court. No such cases were filed during the year.
f. Arbitrary Interference with Privacy, Family, Home, or Correspondence
The law requires authorities to obtain judicial warrants to search private property; police often ignored the law, and there were no records of courts excluding evidence found without warrants.
There were periodic reports throughout the year police carried out nighttime raids of Muslims’ homes in Addis Ababa to collect evidence against persons they alleged to be terrorists. The government claimed the police had warrants.
Opposition political party leaders reported suspicions of telephone tapping and other electronic eavesdropping, and alleged government agents attempted to lure them into illegal acts by calling and pretending to be representatives of groups – designated by the country’s parliament as terrorist organizations – interested in making financial donations.
The government reportedly used a widespread system of paid informants to report on the activities of particular individuals. During the year opposition members reported ruling party operatives and militia members made intimidating and unwelcome visits to their homes and offices.
Security forces continued to detain family members of persons sought for questioning by the government. There were reports unemployed youths who were not affiliated with the ruling coalition sometimes had trouble receiving the “support letters” from their kebeles (neighborhoods or wards) necessary to get jobs.
The national government and regional governments continued to put in place “villagization” plans in the Afar, Benishangul-Gumuz, Gambella, SNNPR, and Somali regions. These plans involved the relocation by regional governments of scattered rural populations from arid or semiarid lands vulnerable to recurring droughts into designated clusters. The stated purposes of villagization were to improve the provision of government services (i.e., health care, education, and clean water), protect vulnerable communities from natural disasters and attacks, and change environmentally destructive patterns of shifting cultivation. Some observers stated the purpose was to enable the large-scale leasing of land for commercial agriculture. The government described the villagization program as strictly voluntary.
International donors reported that assessments from more than 16 visits to villagization sites since 2011 did not corroborate allegations of systematic human rights violations in this program. They did find problems such as delays in establishing promised infrastructure from rushed program implementation. Communities and individual families appeared to have agreed to move based on assurances from authorities of food aid, services, and land, although in some instances communities moved before adequate basic services and shelter were in place in the new locations. International human rights organizations, however, continued to express concern regarding the villagization process. A report by the Oakland Institute in February stated that the military forcibly relocated communities and committed human rights violations in the Omo Valley. A report by the Oakland Institute in July asserted that, during a January 2012 assessment in the Lower Omo Valley, donor representatives heard testimony from community members regarding human rights violations.
SECTION 2. RESPECT FOR CIVIL LIBERTIES, INCLUDING:
a. Freedom of Speech and Press
The constitution and law provide for freedom of speech and press; however, authorities arrested, detained, and prosecuted journalists and other persons whom they perceived as critical of the government.
Freedom of Speech: Authorities arrested and harassed persons for criticizing the government. The government attempted to impede criticism through various forms of intimidation, including detention of journalists and opposition activists and monitoring and interference in the activities of political opposition groups. Some persons feared authorities would retaliate against them for discussing security force abuses.
Press Freedoms: The government continued to take actions to close independent newspapers. Regulators revoked the operating licenses of Addis Times magazine and Li-Elina newspaper in February and March, respectively, after independent editor Temesgen Dessalegn acquired them. The remaining 14 newspapers had a combined weekly circulation in Addis Ababa of more than 140,000. Most newspapers were printed on a weekly or biweekly basis, with the exception of the state-owned Amharic and English dailies.
The government controlled the only television station that broadcast nationally, which, along with radio, was the primary source of news for much of the population. Four private FM radio stations broadcast in the capital city, one private radio station broadcast in the northern Tigray Region, and at least 16 community radio stations broadcast in the regions. State-run Ethiopian Radio had the largest reach in the country, followed by Fana Radio, which was affiliated with the ruling party.
Government-controlled media closely reflected the views of the government and the ruling EPRDF. The government periodically jammed foreign broadcasts. The law prohibits political and religious organizations and foreigners from owning broadcast stations.
Violence and Harassment: The government continued to arrest, harass, and prosecute journalists. This included the prosecution of three persons associated with the defunct Muslim Affairs magazine under the antiterrorism proclamation.
On January 17, authorities arrested Solomon Kebede, columnist and managing editor of Muslim Affairs. They charged him along with 27 other Muslims in April under the antiterrorism proclamation.
The case against Temesgen Dessalegn, editor in chief of the defunct Feteh newspaper, continued. Charges against him included inciting and agitating the country’s youth to engage in violence, defamation of the government, and destabilizing the public by spreading false reports. Mastewal Berhanu, former publisher and managing director of Feteh, reportedly left the country due to government harassment.
Censorship or Content Restrictions: Government harassment caused journalists to avoid reporting on sensitive topics. Many private newspapers reported informal editorial control by the government through article placement requests and calls from government officials concerning articles perceived as critical of the government. Private sector and government journalists routinely practiced self-censorship.
Libel Laws/National Security: The government used the antiterrorism proclamation to suppress criticism. Journalists feared covering five groups designated by parliament in 2011 as terrorist organizations (Ginbot 7, the ONLF, the OLF, al-Qaida, and al-Shabaab), citing ambiguity on whether reporting on these groups might be punishable under the law. Several journalists, both local and foreign correspondents, reported an increase in self-censorship.
The government used libel laws during the year to suppress criticism.
On May 15, police in Addis Ababa questioned Ferew Abebe, editor in chief of the Sendek newspaper, about 2012 articles that alleged the widow of former prime minister Meles Zenawi refused to vacate the prime minister’s official residence after the death of her husband. Police requested that Ferew reveal his sources to them and would not disclose who initiated the libel claim against Ferew. Ferew posted bail and was released; authorities did not file formal charges by year’s end.
INTERNET FREEDOM
The state-owned Ethio Telecom was the only internet service provider in the country. The government restricted access to the internet and blocked several websites, including blogs; opposition websites; and websites of Ginbot 7, the OLF, and the ONLF. The government also temporarily blocked news sites such as al-Jazeera. Websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and Yahoo! were temporarily inaccessible at times. Several news blogs and websites run by opposition diaspora groups were not accessible. These included Addis Neger, Nazret, Ethiopian Review, CyberEthiopia, Quatero Amharic Magazine, Tensae Ethiopia, and the Ethiopian Media Forum. Authorities took steps to block access to Virtual Private Network providers that let users circumvent government screening of internet browsing and e-mail. According to the International Telecommunication Union, approximately 1.5 percent of individuals used the internet in 2012.
In March, Citizen Lab, a Canadian research center at the University of Toronto, identified 25 countries, including Ethiopia, that host servers linked to FinFisher surveillance software. According to the report, “FinFisher has gained notoriety because it has been used in targeted attacks against human rights campaigners and opposition activists in countries with questionable human rights records.” A “FinSpy” campaign in the country allegedly “used pictures of Ginbot 7, an Ethiopian opposition group, as bait to infect users.”
In March police arrested university student Manyazewal Eshetu, for posting allegations of government corruption on Facebook. Authorities later released Manyazewal without charge.
ACADEMIC FREEDOM AND CULTURAL EVENTS
The government restricted academic freedom, including through decisions on student enrollment, teachers’ appointments, and the curriculum. Authorities frequently restricted speech, expression, and assembly on university and high school campuses.
According to sources, the ruling party via the Ministry of Education continued to give preference to students loyal to the party in assignments to postgraduate programs. Some university staff members commented that priority for employment after graduation in all fields was given to students who joined the party.
Authorities limited teachers’ ability to deviate from official lesson plans. Numerous anecdotal reports suggested non-EPRDF members were more likely to be transferred to undesirable posts and bypassed for promotions. There were unspecified reports of teachers not affiliated with the EPRDF being summarily dismissed for failure to attend unscheduled meetings. There continued to be a lack of transparency in academic staffing decisions, with numerous complaints from individuals in the academic community alleging bias based on party membership, ethnicity, or religion.
According to multiple credible sources, teachers and high school students in grade 10 and above were required to attend training on the concepts of revolutionary democracy and EPRDF party ideology.
A Ministry of Education directive prohibits private universities from offering degree programs in law and teacher education. The directive also requires public universities to align their curriculum offerings with the ministry’s policy of a 70-to-30 ratio between science and social science academic programs. As a result the number of students studying social sciences and the humanities at public institutions continued to decrease, and private universities focused heavily on the social sciences.
b. Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Association
FREEDOM OF ASSEMBLY
The constitution and law provide for freedom of assembly; however, the government did not respect this right. Organizers of large public meetings or demonstrations must notify the government 48 hours in advance and obtain a permit. Authorities may not refuse to grant a permit but may require that the event be held at a different time or place for reasons of public safety or freedom of movement. If authorities determine an event should be held at another time or place, the law requires that organizers be notified in writing within 12 hours of the time of submission of their request.
The government denied some requests by the Semayawi (Blue) Party and Medrek, the largest opposition coalition, to hold protests in Addis Ababa, although the government officially permitted a June 2 Semayawi Party demonstration. The march was widely reported as the first mass outpouring of discontent permitted by the government since protests in 2005. The government subsequently allowed additional protests to take place in Addis Ababa and several other cities, although organizers in most cases alleged government interference, and authorities required several of the protests to move to different dates or locations from those the organizers requested. Protest organizers alleged the government’s claims of needing to move the protests based on public safety concerns were not credible.
Local government officials, almost all of whom were affiliated with the EPRDF, controlled access to municipal halls, and there were many complaints from opposition parties that local officials denied or otherwise obstructed the scheduling of opposition parties’ use of halls for lawful political rallies. There were numerous credible reports that owners of hotels and other large facilities cited unspecified internal rules forbidding political parties from utilizing their space for gatherings.
Regional governments, including the Addis Ababa regional administration, were reluctant to grant permits or provide security for large meetings.
The government arrested persons in relation to opposition demonstrations. This included a March 17 protest and a planned August 31 protest by the Semayawi Party. Authorities also arrested Unity for Democracy and Justice Party members before and after a July 17 protest.
On August 31, security forces raided the headquarters of the Semayawi Party to prevent a demonstration planned for the following day. Authorities reportedly temporarily detained 60 to 90 persons and beat some of them. The demonstration would have coincided with a mass public rally promoting interfaith tolerance organized by the government.
Beginning in late 2011 and continuing throughout the year, some members of the Muslim community held peaceful protests following Friday prayers at several of Addis Ababa’s largest mosques, the Aweliya Islamic Center in Addis Ababa, and at other locations throughout the country. Most demonstrations occurred without incident, although police met some with arrests and alleged use of unnecessary force. For example, on August 8, security forces in Addis Ababa detained more than one thousand Muslims participating in Eid al-Fitr celebrations.
FREEDOM OF ASSOCIATION
Although the law provides for freedom of association and the right to engage in unrestricted peaceful political activity, the government limited this right.
A report of the UN Special Rapporteur on the Rights to Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Association stated, “The enforcement of these [the CSO law] provisions has a devastating impact on individuals’ ability to form and operate associations effectively.”
The CSO law bans anonymous donations to NGOs. All potential donors were therefore aware their names would be public knowledge. The same was true concerning all donations made to political parties.
International NGOs seeking to operate in the country had to submit an application via Ethiopian embassies abroad, which was then submitted by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to the Charities and Societies Agency.
c. Freedom of Religion
See the Department of State’s International Religious Freedom Report at http://www.state.gov/j/drl/irf/rpt/.
d. Freedom of Movement, Internally Displaced Persons, Protection of Refugees, and Stateless Persons
Although the law provides for freedom of internal movement, foreign travel, emigration, and repatriation, the government restricted some of these rights.
The government cooperated with the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and other humanitarian organizations in providing protection and assistance to internally displaced persons (IDPs), refugees, returning refugees, asylum seekers, stateless persons, and other persons of concern; however, at times authorities, armed groups and the situation of insecurity limited the ability of humanitarian organizations to operate.
According to the UN, humanitarian organizations reported 36 incidents that impeded humanitarian work in the first six months of the year compared with 34 during the same period in 2012; 32 of these cases were in the Somali Region. The incidents included violence and hostility against humanitarian personnel, theft of assets, interference with the implementation of humanitarian programs, and restrictions on importation of personnel and goods into the country for humanitarian work. This data referred broadly to humanitarian work and were not limited to activities focusing on IDPs or refugees.
Although the Somali regional government granted several organizations access to Nogob (formerly Fik) to start humanitarian operations, access to areas in the Somali Region remained challenging due to continuing clashes between government forces and the ONLF, as well as reports of al-Shabaab elements operating in and around Somali refugee camps in Dolo Ado. Cases were noted in which NGOs were denied access to areas of operation despite agreements with regional officials. In numerous cases NGOs deferred travel to program activity sites due to insecurity. On June 13, suspected ONLF gunmen fired on a mobile health and nutrition team supported by the UN Children’s Fund in Korahe zone and seriously injured one person.
In-country Movement: The government continued to relax but did not completely remove restrictions on the movement of persons into and within the Somali Region, continuing to argue the ONLF posed a security threat (see section 2.d., Internally Displaced Persons). Security concerns forced a temporary halt of deliveries of food and medicine in the limited areas affected by fighting.
The government continued a policy that allowed refugees to live outside of a camp. According to the Administration for Returnees and Refugee Affairs (ARRA), which managed the out-of-camp program, 3,412 refugees lived outside of the camps in 2012, compared with 1,294 in 2011. Prior to this policy the government gave such permission primarily to attend higher education institutions, undergo medical treatment, or avoid security threats at the camps.
Foreign Travel: On October 23, the government enacted a temporary ban on citizens travelling to the Middle East for employment. The ban did not affect citizens travelling for investment or business reasons. The government stated it issued the ban to prevent harassment, intimidation, and trauma suffered by those working abroad as domestic employees.
Exile: Several citizens sought political asylum in other countries or remained abroad in self-imposed exile.
INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS (IDPS)
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) estimated the total number of IDPs in the country as of June to be 363,141, an increase of 71,487 from the period January through March. The increase was mostly due to conflict and flooding in the Somali and Gambella regions. Drought also caused displacements during the year.
In January conflict between ethnic Oromos and Somalis over border demarcation and land ownership displaced approximately 55,000 persons from Gursum, Meyu, Kimbi, and Chinaksen districts in Oromia Region. Insecurity resulted in the delay of humanitarian assistance. The impacted population remained displaced at year’s end.
Heavy rainfall in the Somali Region from late March to early April resulted in severe flooding in Faafan, Jerer, Korahe, Nogob, and Shebele zones, destroying homes and displacing thousands. Joint assessments by the United Nations, NGOs, and the government reported the floods affected 500 households in Kebredihar and 5,756 in the Mustahil, Ferfer, and Kelafo districts of Shebelle zone. Flooding from April to June displaced an additional 36,792 individuals in Ferfer, Kelafo, and Mustahil, and 6,657 individuals in the Kebrediar and Dobowein districts of Korahe zone.
During the year drought caused the displacement of more than 22,000 persons in Afar.
According to the IOM, an estimated 80 percent of all IDPs were considered “protracted” IDPs, for whom durable solutions (return to home areas, local integration, and resettlement in other parts of the country) were not possible at the time. This was due to lack of resolution of the conflict, lack of political decision or resources to support local integration, or undesirability of resettlement to other areas of the country.
The government, through the Disaster Risk Management Food Security Sector (DRMFSS) and regional and district administrations, encouraged humanitarian responses to internal displacement and facilitated assessments to determine humanitarian needs. Humanitarian organizations usually provided assistance received by IDPs. For example, both the DRMFSS and the local government helped to coordinate the humanitarian response following conflict between ethnic Somali and Oromo residents of East Hararghe zone, Oromia Region.
PROTECTION OF REFUGEES
Access to Asylum: The law provides for the granting of asylum or refugee status, and the government has established a system for providing protection to refugees.
According to the UNHCR, the country hosted 423,851 refugees as of September. The majority of refugees were from Somalia (242,588), with others coming from Sudan (31,951), South Sudan (67,958), Eritrea (77,083), and other countries particularly Kenya (4,271).
The UNHCR, the ARRA, and humanitarian agencies continued to care for Sudanese arrivals fleeing from conflict in Sudan’s Blue Nile State. The government also extended support to South Sudanese asylum seekers from South Sudan’s Jonglei State; 5,776 of these asylum seekers crossed into the country by July, raising the total of South Sudanese asylum seekers to more than 67,000.
Eritrean asylum seekers continued to arrive in the country. This included a large number of unaccompanied minors. Many Eritreans who arrived in the country regularly departed for secondary migration through Egypt and Sudan to go to Israel, Europe, and other final destinations.
Employment: The government did not grant refugees work permits.
Access to Basic Services: The UNHCR and ARRA, with support from NGOs, provided refugees in camps with basic services such as health, education, water, sanitation, and hygiene. For those outside of camps, there were no reports of discrimination in access to public services.
Durable Solutions: The government granted refugee status to asylum seekers from Eritrea, Somalia, South Sudan, and Sudan. The government welcomed refugees to settle permanently in the country but did not offer a path to citizenship or facilitate integration. It permitted Eritrean refugees to live outside refugee camps provided they sustained themselves financially. The government provided some support for Eritreans who were pursuing higher education. During the first half of the year, approximately 2,600 refugees departed the country for resettlement.
SECTION 3. RESPECT FOR POLITICAL RIGHTS: THE RIGHT OF CITIZENS TO CHANGE THEIR GOVERNMENT
The constitution and law provide citizens the right to change their government peacefully. The ruling party’s electoral advantages limited this right.
Elections and Political Participation
Recent Elections: In August 2012, following the death of Prime Minister Meles Zenawi, the ruling EPRDF elected Hailemariam Desalegn to take Meles’s place as chairman of the party and subsequently nominated him for the post of prime minister. In September 2012 parliament elected Hailemariam as prime minister.
In the 2010 national parliamentary elections, the EPRDF and affiliated parties won 545 of 547 seats to remain in power for a fourth consecutive five-year term. Government restrictions severely limited independent observation of the vote. Although the relatively few international officials allowed to observe the elections concluded technical aspects of the vote were handled competently, some also noted the lack of an environment conducive to free and fair elections prior to election day. Several laws, regulations, and procedures implemented since the 2005 national elections created a clear advantage for the EPRDF throughout the electoral process. There was ample evidence that unfair government tactics, including intimidation of opposition candidates and supporters, influenced the extent of the EPRDF victory. In addition, voter education was limited to information about technical voting procedures and was done only by the National Electoral Board just days before voting began.
The African Union, whose observers arrived one week before the vote, deemed the elections to be free and fair. The EU, some of whose observers arrived a few months before the vote, concluded the elections fell short of international standards for transparency and failed to provide a level playing field for opposition parties. The EU observed a “climate of apprehension and insecurity,” noting that the volume and consistency of complaints of harassment and intimidation by opposition parties was “a matter of concern” and had to be taken into consideration “in the overall assessment of the electoral process.”
The EPRDF’s continued dominance was demonstrated in nationwide elections to local and city council positions held in April. EPRDF-affiliated parties won all but five of 3.6 million seats; 33 opposition parties boycotted the elections.
Political Parties: Political parties were predominantly ethnically based. The government, controlled by the ruling EPRDF, restricted media freedom and arrested opposition members. Constituent parties of the EPRDF conferred advantages upon their members; the parties directly owned many businesses and were broadly perceived to award jobs and business contracts to loyal supporters. Several opposition political parties reported difficulty in renting homes or buildings in which to open offices, citing visits by EPRDF members to the landlords to persuade or threaten them not to rent property to these parties.
There were reports authorities had terminated the employment of teachers and other government workers if they belonged to opposition political parties. According to Oromo opposition groups, the Oromia regional government continued to threaten to dismiss opposition party members, particularly teachers, from their jobs. Government officials alleged that many members of legitimate Oromo opposition political parties were secretly OLF members and more broadly that members of many opposition parties had ties to Ginbot 7. At the university level members of Medrek and its constituent parties were able to teach.
Registered political parties must receive permission from regional governments to open and occupy local offices.
Participation of Women and Minorities: No laws or cultural or traditional practices prevented women or minorities from voting or participating in political life on the same basis as men or nonminority citizens, although women were significantly underrepresented in both elected and appointed positions. The Tigray Regional Council held the highest proportion of women nationwide, at 48.5 percent.
The government’s policy of ethnic federalism led to the creation of individual constituencies to provide for representation of all major ethnic groups in the House of People’s Representatives. There were more than 80 ethnic groups, and small groups lacked representation in the legislature. There were 24 nationality groups in six regional states (Tigray, Amhara, Beneshangul-Gumuz, the SNNPR, Gambella, and Harar) that did not have a sufficient population to qualify for constituency seats based on the 2007 census; however, in the 2010 elections, individuals from these nationality groups competed for 24 special seats in the House of People’s Representatives. Additionally these 24 nationality groups have one seat each in the House of Federation.
Women held three federal government ministerial positions and 152 of 547 seats in the national parliament.
SECTION 4. CORRUPTION AND LACK OF TRANSPARENCY IN GOVERNMENT
The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials. Despite the government’s prosecution of numerous officials for corruption, some officials continued to engage in corrupt practices. Corruption, especially the solicitation of bribes, remained a problem among low-level bureaucrats. Police and judicial corruption also continued to be problems. Some government officials appeared to manipulate the privatization process, and state- and party-owned businesses received preferential access to land leases and credit.
Corruption: The Ministry of Justice has primary responsibility for combating corruption, largely through the Federal Ethics and Anticorruption Commission (FEACC).
During the year the FEACC initiated criminal proceedings against the director general of the Ethiopian Revenues and Customs Authority, his deputy, and as many as 60 other government officials and private business leaders for alleged corrupt practices. Most trials continued at year’s end, although some cases were dropped due to lack of evidence.
Whistleblower Protection: The law provides protection to public and private employees for making internal disclosures or lawful public disclosures of evidence of illegality, such as the solicitation of bribes or other corrupt acts, gross waste or fraud, gross mismanagement, abuse of power, or substantial and specific dangers to public health and safety. The law also specifically bars appointed or elected officials and public servants from making direct or indirect reprisals against whistleblowers.
Financial Disclosure: The law requires all government officials and employees officially register their wealth and personal property. The president and prime minister registered their assets. By the end of 2012, a total of 32,297 federal government officials registered their assets, according to the FEACC. The FEACC held financial disclosure records. According to the law, any person seeking access to these records may do so by making a request in writing, although access to information on family assets may be restricted unless the FEACC deems the disclosure necessary. The law includes financial and criminal sanctions for noncompliance.
Public Access to Information: The law provides for public access to government information, but access was largely restricted. The law includes a sufficiently narrow list of exceptions outlining the grounds for nondisclosure. Responses generally must be made within 30 days of a written request, and fees may not exceed the actual cost of responding to the request. The law includes mechanisms for punishing officials for noncompliance, as well as appeal mechanisms for review of disclosure denials. Information on the number of disclosures or denials during the year was not available.
The government publishes its laws and regulations in the national gazette prior to their taking effect. The Government Communications Affairs Office managed contacts between the government, the press, and the public; the private press reported the government rarely responded to its queries.
SECTION 5. GOVERNMENTAL ATTITUDE REGARDING INTERNATIONAL AND NONGOVERNMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF ALLEGED VIOLATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS
A few domestic human rights groups operated, but with significant government restrictions. The government was generally distrustful and wary of domestic human rights groups and international observers. State-controlled media were critical of international human rights groups such as Human Rights Watch.
The CSO law prohibits charities, societies, and associations (NGOs or CSOs) that receive more than 10 percent of their funding from foreign sources from engaging in activities that advance human and democratic rights or promote equality of nations, nationalities, peoples, genders, and religions; the rights of children and persons with disabilities; conflict resolution or reconciliation; or the efficiency of justice and law enforcement services. The implementation of the law continued to result in the severe curtailment of NGO activities related to human rights. In July 2012 the UN high commissioner for human rights expressed concern that civil society space “has rapidly shrunk” since the CSO law’s enactment.
Some human rights defender organizations continued to register either as local charities, meaning they could not raise more than 10 percent of their funds from foreign donors but could act in the specified areas, or as resident charities, which allowed foreign donations above 10 percent but prohibited activities in those areas.
One of several sets of the law’s implementing regulations, commonly known as the 70/30 rule, caps administrative spending at 30 percent of an organization’s operating budget. The regulations define training of teachers, agricultural and health extension workers, and other government officials as an “administrative” cost, contending the training does not directly affect beneficiaries, thus limiting the number of training programs that can be provided by development assistance partners who prefer to employ train-the-trainer models to reach more persons. The government addressed application of this regulation on a case-by-case basis. A Civil Society Sector Working Group cochaired by the Ministry of Federal Affairs and a representative of the donor community convened periodically to monitor and discuss challenges that arose as the law was implemented.
The government denied most NGOs access to federal prisons, police stations, and political prisoners. The government permitted the JFA-PFE, one of four organizations granted an exemption enabling them to raise unlimited funds from foreign sources and to engage in human rights advocacy, to visit prisoners. The JFA-PFE played a positive role in improving prisoners’ chances for clemency.
Authorities limited the access of human rights organizations, the media, humanitarian agencies, and diplomatic missions to conflict-affected areas, although it eased such restrictions. Humanitarian access in the Somali Region improved in particular. The government lacked a clear policy on NGO access to sensitive areas, leading regional government officials and military officials frequently to refer requests for access to the federal government. Officials required journalists to register before entering conflict regions. There were isolated reports of regional police or local militias blocking NGOs’ access to particular locations on particular days, citing security concerns. Some agencies limited project activities for security reasons.
Some persons feared authorities would retaliate against them if they met with NGOs and foreign government officials who were investigating allegations of abuse.
UN and Other International Bodies: Requests to visit the country from the UN special rapporteur on torture and other cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment remained outstanding.
Government Human Rights Bodies: The EHRC investigated human rights complaints and produced annual and thematic reports. The commission operated 112 legal aid centers in collaboration with 17 universities and two civil society organizations, the Ethiopian Women Lawyers’ Association and the Ethiopian Christian Lawyers Fellowship. The commission also completed the preparatory measures to sign collaborative agreements with two additional universities. The EHRC reported its Addis Ababa headquarters resolved 90 percent of the 952 complaints submitted to it during 2012.
The Office of the Ombudsman has authority to receive and investigate complaints with respect to administrative mismanagement by executive branch offices. From September 2011 to September 2012, the office received 2,094 complaints. Of these, the ombudsman opened investigations into 784, and the office reported it resolved the remaining cases through alternative means. The majority of complaints dealt with social security, labor, housing, and property disputes. The Office of the Ombudsman did not compile nationwide statistics.
SECTION 6. DISCRIMINATION, SOCIETAL ABUSES, AND TRAFFICKING IN PERSONS
The constitution provides all persons equal protection without discrimination based on race, nation, nationality or other social origin, color, gender, language, religion, political or other opinion, property, birth, or status, but the government did not fully promote and protect these rights. The constitution does not address discrimination based on disability, sexual orientation, or gender identity.
Women
Rape and Domestic Violence: The law criminalizes rape and provides for penalties of five to 20 years’ imprisonment, depending on the severity of the case; the law does not expressly address spousal rape. The government did not fully enforce the law, partially due to widespread underreporting. Recent statistics on the number of abusers prosecuted, convicted, or punished were not available. Anecdotal evidence suggested reporting of rapes had increased since the 2004 revision of the criminal code but the justice system was unable to keep up with the number of cases.
Domestic violence, including spousal abuse, was a pervasive social problem.
Although women had recourse to the police and the courts, societal norms and limited infrastructure prevented many women from seeking legal redress, particularly in rural areas. The government prosecuted offenders on a limited scale. Domestic violence is illegal, but government enforcement of laws against rape and domestic violence was inconsistent. Depending on the severity of damage inflicted, legal penalties range from small fines to imprisonment for up to 10 to 15 years.
Domestic violence and rape cases often were delayed significantly and given low priority. In the context of gender-based violence, significant gender gaps in the justice system remained, due to poor documentation and inadequate investigation. “Child friendly” benches hear cases involving violence against children and women. Police officers were required to receive domestic violence training from domestic NGOs and the Ministry of Women, Children, and Youth Affairs. There was a commissioner for women and children’s affairs in the EHRC.
Women and girls experienced gender-based violence, but it was underreported due to cultural acceptance, shame, fear, or a victim’s ignorance of legal protections.
Harmful Traditional Practices: The most prevalent harmful traditional practices were FGM/C, uvula cutting, tonsil scraping and milk tooth extraction, early marriage, and marriage by abduction.
Marriage by abduction is illegal, although it continued in some regions despite the government’s attempts to combat the practice. A 2009 Population Council study of seven regions found that 2.6 percent of married female youth reported their marriage occurred through abduction. The study found the rate to be 12.9 percent in the SNNPR, 4.4 percent in Oromia, 3 percent in Afar, and less than 1percent in Beneshangul Gumuz. The study did not include the Gambella or Somali regions. Forced sexual relationships accompanied most marriages by abduction, and women often experienced physical abuse during the abduction. Abductions led to conflicts among families, communities, and ethnic groups. In cases of marriage by abduction, the perpetrator did not face punishment if the victim agreed to marry the perpetrator.
Female Genital Mutilation/Cutting (FGM/C): FGM/C is illegal, but the government did not actively enforce this prohibition or punish those who practiced it.
Sexual Harassment: Sexual harassment was widespread. The penal code prescribes penalties of 18 to 24 months’ imprisonment, but authorities generally did not enforce harassment laws.
Reproductive Rights: Individuals and couples have the right to decide freely and responsibly the number, spacing, and timing of children and to have the information and means to do so free from discrimination, coercion, and violence. The 2011 Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) indicated a modern contraceptive prevalence of 27 percent nationwide among married women, a twofold increase from the survey done six years earlier. The survey found 25.3 percent of married girls and women ages 15 to 49 had unmet family planning needs. The 2011 DHS indicated the maternal mortality rate was 676 deaths per 100,000 live births as compared with 673 per 100,000 reported in the 2005 DHS. The immediate causes of maternal mortality included excessive bleeding, infection, hypertensive complications, and obstructed labor, with the underlying cause being the prevalence of home births and lack of access to emergency obstetric care. Only 9 percent of women reported delivering in a health facility or with a skilled birth attendant.
Discrimination: Discrimination against women was a problem and was most acute in rural areas, where an estimated 85 percent of the population lived. The law contains discriminatory regulations, such as the recognition of the husband as the legal head of the family and the sole guardian of children more than five years old. Courts generally did not consider domestic violence by itself a justification for granting a divorce. Irrespective of the number of years the marriage existed, the number of children raised, and joint property, the law entitled women to only three months’ financial support if a relationship ended. There was limited legal recognition of common-law marriage. A common-law husband had no obligation to provide financial assistance to his family, and as a result, women and children sometimes faced abandonment. Traditional courts continued to apply customary law in economic and social relationships.
According to the constitution all land belongs to the government. Both men and women have land-use rights, which they may pass on as an inheritance. Land law varies among regions. All federal and regional land laws empower women to access government land. Inheritance laws also enable widowed women to inherit joint property they acquired during marriage.
In urban areas women had fewer employment opportunities than men, and the jobs available did not provide equal pay for equal work. Women’s access to gainful employment, credit, and the opportunity to own or manage a business was further limited by their generally lower level of education and training and by traditional attitudes.
The Ministry of Education reported female participation in undergraduate and postgraduate programs increased to 144,286 during the 2011-12 academic year, compared with 123,706 in 2010-11, continuing the trend of increasing female participation in higher education.
Children
Birth registration: Citizenship is derived from one’s parents. The law requires all children to be registered at birth. Children born in hospitals were registered while most children born outside of hospitals were not. The overwhelming majority of children, particularly in rural areas, were born at home.
Education: As a policy, primary education was universal and tuition-free; however, there were not enough schools to accommodate the country’s youth, particularly in rural areas. The cost of school supplies was prohibitive for many families, and there was no legislation to enforce compulsory primary education. The number of students enrolled in schools expanded faster than trained teachers could be deployed.
Child Abuse: Child abuse was widespread. A 2009 study conducted by the African Child Policy Forum revealed prosecuting offenders for sexual violence against children was difficult due to inconsistent interpretation of laws among legal bodies and the offender’s right to bail, which often resulted in the offender fleeing or coercing the victim or the victim’s family to drop the charges. “Child friendly” benches heard cases involving violence against children and women. During the year the Federal Court of First Instance announced that tribunals hearing cases relating to families and children would keep extended hours to accommodate children’s school schedules. There was a commissioner for women and children’s affairs in the EHRC.
Forced or Early Marriage: The law sets the legal marriage age for girls and boys at 18; however, authorities did not enforce this law uniformly, and rural families sometimes were unaware of this provision. In several regions it was customary for older men to marry young girls, although this traditional practice continued to face greater scrutiny and criticism.
According to the 2011 DHS, the median age of first marriage among women surveyed between the ages of 20 and 49 was 17.1 years. The age of first marriage appeared to be rising. In 2005 the median age of marriage for women surveyed between 20 and 24 was 16.5 years, and while 39 percent of women between 45 and 49 reported being married by age 15, only 8 percent of young women between 15 and 19 years of age reported being or having been married.
In the Amhara and Tigray regions, girls were married routinely as early as age seven. Child marriage was most prevalent in the Amhara Region, where the median first marriage age was 15.1 years, according to the 2011 DHS, compared with 14.7 years in 2005. Regional governments in Amhara and, to a lesser extent, Tigray offered programs to educate young women on problems associated with early marriage.
Harmful Traditional Practices: Societal abuse of young girls continued to be a problem. Harmful practices included FGM/C, early marriage, marriage by abduction, and food and work prohibitions.
The majority of girls in the country have undergone some form of FGM/C, although the results of the 2009 Population Council survey suggested its prevalence had declined. Sixty-six percent of female respondents ages 21 to 24 reported they were subjected to FGM/C compared with 56 percent of those ages 15 to 17. Of the seven regions surveyed, the study found the rates to be highest in Afar (90.3 percent), Oromia (77.4 percent), and the SNNPR (74.6 percent).
FGM/C was much less common in urban areas, where only 15 percent of the population lived. Girls typically experienced clitoridectomies seven days after birth (consisting of an excision of the clitoris, often with partial labial excision) and infibulation (the most extreme and dangerous form of FGM/C) at the onset of puberty. The penal code criminalizes practitioners of clitoridectomy, with imprisonment of at least three months or a fine of at least 500 birr ($26). Infibulation of the genitals is punishable with imprisonment of five to 10 years. No criminal charges have ever been brought for FGM/C. The government discouraged the practice of FGM/C through education in public schools, the Health Extension Program, and broader mass media campaigns.
Sexual Exploitation of Children: The minimum age for consensual sex is 18 years, but authorities did not enforce this law. The law provides for three to 15 years in prison for sexual intercourse with a minor. The law provides for one year in prison and a fine of 10,000 birr ($530) for trafficking in indecent material displaying sexual intercourse by minors. The law prohibits profiting from the prostitution of minors and inducing minors to engage in prostitution; however, commercial sexual exploitation of children continued, particularly in urban areas. Girls as young as age 11 reportedly were recruited to work in brothels. Customers often sought these girls because they believed them to be free of sexually transmitted diseases. Young girls were trafficked from rural to urban areas. They also were exploited as prostitutes in hotels, bars, resort towns, and rural truck stops. Reports indicated family members forced some young girls into prostitution.
Infanticide or Infanticide of Children with Disabilities: Ritual and superstition-based infanticide continued in remote tribal areas, particularly South Omo. Local governments worked to educate communities against the practice.
Displaced Children: According to a 2010 report by the Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs, approximately 150,000 children lived on the streets, of whom 60,000 were in the capital. The ministry’s report stated families’ inability to support children due to parental illness or insufficient household income exacerbated the problem. These children begged, sometimes as part of a gang, or worked in the informal sector.
A 2010 Population Council Young Adult Survey found that 82.3 percent of boys who lived or worked on the streets had been to or had enrolled in school, 26.4 percent had lost one parent, and 47.2 percent had lost both parents. Among these boys, 72 percent worked for pay at some point in their lives. Government and privately run orphanages were unable to handle the number of street children.
Institutionalized Children: There were an estimated 5.4 million orphans in the country, according to a 2010 report by the Central Statistics Authority. The vast majority lived with extended family members. Government orphanages were overcrowded, and conditions were often unsanitary. Due to severe resource constraints, hospitals and orphanages often overlooked or neglected abandoned infants. Institutionalized children did not receive adequate health care.
International Child Abductions: The country is not a party to the 1980 Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction.
Anti-Semitism
The Jewish community numbered approximately 2,000 persons. There were no reports of anti-Semitic acts.
Trafficking in Persons
See the Department of State’s Trafficking in Persons Report at http://www.state.gov/j/tip/.
Persons with Disabilities
The constitution does not mandate equal rights for persons with disabilities. The law prohibits discrimination against persons with physical and mental disabilities in employment and mandates access to buildings. It is illegal for deaf persons to drive.
The law prohibits employment discrimination based on disability. It also makes employers responsible for providing appropriate working or training conditions and materials to persons with disabilities. The law specifically recognizes the additional burden on women with disabilities. The government took limited measures to enforce the law, for example, by assigning interpreters for hearing-impaired civil service employees.
The law mandates building accessibility and accessible toilet facilities for persons with physical disabilities, although specific regulations that define the accessibility standards were not adopted. Buildings and toilet facilities were usually not accessible. Landlords are required to give persons with disabilities preference for ground-floor apartments, and this was respected.
Women with disabilities were more disadvantaged than men with disabilities in education and employment. An Addis Ababa University study from 2008 showed that female students with disabilities were subjected to a heavier burden of domestic work than their male peers. The 2010 Population Council Young Adult Survey found young persons with disabilities were less likely to have ever attended school than young persons without disabilities. The survey indicated girls with disabilities were less likely than boys with disabilities to be in school; 23 percent of girls with disabilities were in school, compared to 48 percent of girls without disabilities and 55 percent of boys without disabilities. Overall, 47.8 percent of young persons with disabilities surveyed reported not going to school due to their disability. Girls with disabilities also were much more likely to suffer physical and sexual abuse than girls without disabilities. Of sexually experienced girls with disabilities, 33 percent reported having experienced forced sex. According to the same survey, some 6 percent of boys with disabilities had been beaten in the three months prior to the survey, compared with 2 percent of boys without disabilities.
There were several schools for hearing and visually impaired persons and several training centers for children and young persons with intellectual disabilities. There was a network of prosthetic and orthopedic centers in five of the nine regional states.
The Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs worked on disability-related problems. The CSO law continued to affect negatively several domestic associations, such as the Ethiopian National Association of the Blind, the Ethiopian National Association of the Deaf, and the Ethiopian National Association of the Physically Handicapped, like other civil society organizations.
National/Racial/Ethnic Minorities
The country has more than 80 ethnic groups, of which the Oromo, at approximately 35 percent of the population, is the largest. The federal system drew boundaries roughly along major ethnic group lines. Most political parties remained primarily ethnically based.
Clashes between ethnic groups during the year resulted in injury and death. In January ethnic clashes broke out at Addis Ababa University reportedly due to anti-Oromo graffiti. The clashes resulted in injury to as many as 20 persons. In February clashes between members of the Afar, Somali, and Oromo ethnic groups in the eastern town of Awash Arba reportedly resulted in the deaths of more than 20 persons.
Authorities in the western region of Benishangul-Gumuz forcibly evicted as many as 8,000 ethnic Amhara residents from their homes; some of those evicted alleged police beat and harassed them because of their ethnicity. The regional president publically stated the evictions were a mistake and called on the evictees to return. Government officials also stated that victims would be compensated for lost property and any injuries sustained. Authorities dismissed several local officials from their government positions because of their alleged involvement in the evictions, and charged some of these officials with criminal offenses.
Societal Abuses, Discrimination, and Acts of Violence Based on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
Consensual same-sex sexual activity is illegal and punishable by imprisonment under the law. There is no law prohibiting discrimination against lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) individuals. There were some reports of violence against LGBT individuals; reporting was limited due to fear of retribution, discrimination, or stigmatization. There are no hate crime laws or other criminal justice mechanisms to aid in the investigation of abuses against LGBT persons. Persons did not identify themselves as LGBT persons due to severe societal stigma and the illegality of consensual same-sex sexual activity. Activists in the LGBT community stated they were followed and at times feared for their safety. There were periodic detentions of some in the LGBT community, combined with interrogation and alleged physical abuse.
The AIDS Resource Center in Addis Ababa reported the majority of self-identified gay and lesbian callers, most of whom were male, requested assistance in changing their behavior to avoid discrimination. Many gay men reported anxiety, confusion, identity crises, depression, self-ostracism, religious conflict, and suicide attempts.
Other Societal Violence or Discrimination
Societal stigma and discrimination against persons living with or affected by HIV/AIDS continued in the areas of education, employment, and community integration. Persons living with or affected by HIV/AIDS reported difficulty accessing services. Despite the abundance of anecdotal information, there were no statistics on the scale of the problem.
SECTION 7. WORKER RIGHTS
a. Freedom of Association and the Right to Collective Bargaining
The constitution and the law provide workers, except for certain categories of workers primarily in the public sector, with the right to form and join unions, conduct legal strikes, and bargain collectively, although other laws severely restrict or excessively regulate these rights. The law specifically prohibits managerial employees, teachers, health care workers, and civil servants (including judges, prosecutors, and security service workers) from organizing unions. Other workers specifically excluded by law from unionizing include domestic workers and seasonal and part-time agricultural workers.
A minimum of 10 workers is required to form a union. While the law provides all unions with the right to register, the government may refuse to register trade unions that do not meet its registration requirements. The law stipulates a trade union organization may not act in an overtly political manner. The law allows administrative authorities to appeal to the courts to cancel union registration for engaging in prohibited activities, such as political action. While the law prohibits antiunion discrimination by employers and provides for reinstatement for workers fired for union activity, it does not prevent an employer from creating or supporting a workers’ organization for the purpose of controlling it.
Other laws and regulations that explicitly or potentially infringe upon workers’ rights to associate freely and to organize include: the CSO law; Council of Ministers Regulation No. 168/2009 on Charities and Societies to reinforce the CSO law; Proclamation No. 652/2009 on Antiterrorism. During the year the International Labor Organization (ILO) Committee of Experts on the Application of Conventions and Recommendations noted the CSO law gives the government power to interfere in the right of workers to organize, including through the registration, internal administration, and dissolution of organizations, and that the Antiterrorism Proclamation could become a means of punishing the peaceful exercise of freedom of expression and the right to organize.
While the law recognizes the right of collective bargaining, this right was severely restricted. Negotiations aimed at amending or replacing a collective agreement must be completed within three months of its expiration, or the provisions on wages and other benefits cease to apply. Civil servants, including public school teachers, have the right to establish and join professional associations, but are not allowed to negotiate for better wages or working conditions. Furthermore, the arbitration procedures in the public sector are more restrictive than those in the private sector.
Although the constitution and law provide workers with the right to strike to protect their interests, the law contains detailed provisions prescribing excessively complex and time-consuming formalities that make legal strike actions difficult to carry out. The law requires aggrieved workers to attempt reconciliation with employers before striking and includes a lengthy dispute settlement process. These provisions applied equally to an employer’s right to lock workers out. Two-thirds of the workers involved must support a strike for it to occur. If a case has not already been referred to a court or labor relations board, workers retain the right to strike without resorting to either of these options, provided they give at least 10 days’ notice to the other party and the Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs and make efforts at reconciliation.
The law also prohibits strikes by workers who provide essential services, including air transport and urban bus service workers, electric power suppliers, gas station personnel, hospital and pharmacy personnel, firefighters, telecommunications personnel, and urban sanitary workers. The list of essential services exceeds the ILO definition of essential services. The law prohibits retribution against strikers, but also provides for excessive civil or penal sanctions against unions and workers involved in unauthorized strike actions. Unions may be dissolved for carrying out strikes in “essential services.”
The informal labor sector, including domestic workers, is not unionized and is not protected by labor laws. Lack of adequate staffing prevented the government from effectively enforcing applicable laws during the year. Court procedures were subject to lengthy delays and appeals.
Freedom of association and the right to collective bargaining were not respected. Although the government permits unions, the government established and controlled the major trade unions. As it had for more than four years, the government continued to use its authority to refuse to register the National Teachers’ Association (NTA) on the grounds that a national teacher association already existed, and that the NTA’s registration application was not submitted in accordance with the CSO law. According to the Education International report to the ILO in 2011, government security agents subjected members of the NTA to surveillance and harassment, with the goal of intimidating teachers to abandon the NTA and forcing them to give up their long-standing demand for the formation of an independent union. In November 2012 the ILO’s Committee on Freedom of Association expressed its concern with regard to serious violations of the NTA’s trade union rights, including continuous interference in its internal organization that prevented it from functioning normally, as well as interference by way of threats, dismissals, arrest, detention, and mistreatment of NTA members. The committee urged the government to register the NTA without delay; to ensure the CSO law was not applicable to workers’ and employers’ organizations; and to undertake civil service reform to fully protect the right of civil servants to establish and join organizations of their own choosing.
While the government allowed citizens to exercise the right of collective bargaining freely, representatives negotiated wages only at the plant level. It was common for employers to refuse to bargain. Unions in the formal industrial sector made some efforts to enforce labor regulations.
Despite the law prohibiting antiunion discrimination, unions reported employers fired union activists. There were reports most Chinese employers generally did not allow workers to form unions and often transferred or fired union leaders, and intimidated and pressured members to leave unions. Lawsuits alleging unlawful dismissal often take years to resolve because of case backlogs in the courts. Employers found guilty of antiunion discrimination were required to reinstate workers fired for union activities and generally did so. While the law prohibits retribution against strikers, most workers were not convinced the government would enforce this protection. Labor officials reported that, due to high unemployment and long delays in the hearing of labor cases, some workers were afraid to participate in strikes or other labor actions. Antiunion activities occurred but were rarely reported.
b. Prohibition of Forced or Compulsory Labor
The law prohibits most forms of forced or compulsory labor, including by children, but it also permits courts to order forced labor as a punitive measure. The government did not effectively enforce the forced labor prohibition, and forced labor occurred. Both adults and children were forced to engage in street vending, begging, traditional weaving, or agricultural work. Children also worked in forced domestic labor. Situations of debt bondage also occurred in traditional weaving, pottery, cattle herding, and other agricultural activities, mostly in rural areas.
Also see the Department of State’s Trafficking in Persons Report at http://www.state.gov/j/tip/.
c. Prohibition of Child Labor and Minimum Age for Employment
By law the minimum age for wage or salary employment is 14 years. The minimum age provisions, however, only apply to contractual labor and do not apply to self-employed children or children who perform unpaid work. Special provisions cover children between the ages of 14 and 18, including the prohibition of hazardous or night work. The law defines hazardous work as work in factories or involving machinery with moving parts or any work that could jeopardize a child’s health. Prohibited work sectors include passenger transport, electric generation plants, underground work, street cleaning, and many other sectors. The law expressly excludes children under age 16 attending vocational schools from legal protection with regard to the prohibition on young workers performing hazardous work. The law does not permit children between the ages of 14 and 18 to work more than seven hours per day, between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m., on public holidays or rest days, or on overtime.
The government did not effectively enforce these laws. The lack of labor inspectors and controls prevented the government from enforcing the law. The resources for inspections and the implementation of penalties were extremely limited. Despite the introduction of labor inspector training at Gondar University in 2011, insufficient numbers of labor inspectors and inspections resulted in lax enforcement of occupational safety and health measures and in increased numbers of children working in prohibited work sectors, particularly construction. The National Action Plan to Eliminate the Worst Forms of Child Labor was signed at the end of 2012.
While primary education is free, it is not compulsory, and net school enrollment was low, particularly in rural areas. To underscore the importance of attending school, joint NGO and government-led community-based awareness raising activities targeted communities where children were heavily engaged in agricultural work. During the year the government invested in modernizing agricultural practices and constructing schools to combat the problem of child labor in agricultural sectors.
Child labor remained a serious problem. In both rural and urban areas, children often began working at young ages. Child labor was particularly pervasive in subsistence agricultural production, traditional weaving, fishing, and domestic work. A growing number of children worked in construction. Children in rural areas, especially boys, engaged in activities such as cattle herding, petty trading, plowing, harvesting, and weeding, while other children, mostly girls, collected firewood and fetched water. Children worked in the production of gold. In small-scale gold mining, they dug their own mining pits and carried heavy loads of water. Children in urban areas, including orphans, worked in domestic service, often working long hours, which prevented many from attending school regularly. They also worked in manufacturing, shining shoes, making clothes, as porters, directing customers to taxis, parking, public transport, petty trading, and occasionally herding animals. Some children worked long hours in dangerous environments for little or no wages and without occupational safety protection. Child laborers often faced physical, sexual, and emotional abuse at the hands of their employers.
Also see the Department of Labor’s Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor at http://www.dol.gov/ilab/programs/ocft/tda.htm.
d. Acceptable Conditions of Work
There is no national minimum wage. Some government institutions and public enterprises set their own minimum wages. Public sector employees, the largest group of wage earners, earned a monthly minimum wage of approximately 420 birr ($22). The official estimate for the poverty income level was approximately 315 birr ($16) per month.
Only a small percentage of the population, concentrated in urban areas, was involved in wage-labor employment. Wages in the informal sector generally were below subsistence levels.
The law provides for a 48-hour maximum legal workweek with a 24-hour rest period, premium pay for overtime, and prohibition of excessive compulsory overtime. The country has 13 paid public holidays per year. The law entitles employees in public enterprise and government financial institutions to overtime pay; civil servants receive compensatory time for overtime work. The government, industries, and unions negotiated occupational safety and health standards. Workers specifically excluded by law from unionizing, including domestic workers and seasonal and part-time agricultural workers, generally did not benefit from health and safety regulations in the workplace.
The Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs’ inspection department was responsible for enforcement of workplace standards. The country had 380 labor inspectors, but due to lack of resources, the labor inspectors did not enforce standards effectively. The ministry’s severely limited administrative capacity; lack of an effective mechanism for receiving, investigating, and tracking allegations of violations; and lack of detailed, sector-specific health and safety guidelines hampered effective enforcement of these standards. In addition penalties were not sufficient to deter violations.
Compensation, benefits, and working conditions of seasonal agricultural workers were far below those of unionized permanent agricultural employees. The government did little to enforce the law. Most employees in the formal sector worked a 39-hour workweek. Many foreign, migrant, and informal sector workers worked more than 48 hours per week.
Workers have the right to remove themselves from dangerous situations without jeopardizing their employment. Despite this law most workers feared losing their jobs if they were to do so. Hazardous working conditions existed in the agricultural sector, which was the primary base of the country’s economy. There were also reports of hazardous and exploitative working conditions in the construction and fledgling industrial sectors.
Read further @http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2013/af/220113.htm#
(OPride) — The United States in a scathing report on Thursday accused Ethiopia of curtailing freedom of expression and association, using politically motivated trials, harassment and intimidation of activists and journalists.
Ethiopia holds estimated 70,000-80,000 persons, including some 2,500 women and nearly 600 children incarcerated with their mothers, in severely overcrowded six federal and 120 regional prisons, the U.S. said in its voluminous 2013 Human Rights Reportreleased by Secretary of State John Kerry. “There also were many unofficial detention centers throughout the country, including in Dedessa, Bir Sheleko, Tolay, Hormat, Blate, Tatek, Jijiga, Holeta, and Senkele,” the report said.
While it said pretrial detention in local police stations were marred with poor hygiene and police abuse, the report also highlighted impunity for security forces who often commit politically-motivated killings against dissidents and opposition party members as “a serious problem.” The Ethiopian government rarely, if ever, took actions “to prosecute or otherwise punish officials who committed abuses other than corruption,” the report added.
The report named some of the well-known political prisoners and journalists including Eskinder Nega, Bekele Gerba, Olbana Lelisa, Reeyot Alemu and Woubeshet Taye.“Federal Supreme Court upheld the 2012 convictions under the criminal code of Bekele Gerba and Olbana Lelisa, two well-known political opposition figures from the Oromo ethnic group, for conspiracy to overthrow the government and conspiracy to incite unrest,” the report noted.
“The Supreme Court subsequently determined the Federal High Court did not consider mitigating circumstances and reduced Bekele’s sentence from eight years to three years and seven months. The Supreme Court also reduced Olbana’s sentenced from 13 to 11 years. Courts convicted 69 members of Oromo political opposition parties, charged separately in 2011 under the criminal code with “attacking the political or territorial integrity of the state.”
Gerba, who has fully served out his reduced time, was widely expected to be released last month. However, according to family sources, prison officials gave conflicting reasons for his continued imprisonment, including that his time at the Maekelawi prison doesn’t count or his file was misplaced. Meanwhile, both Gerba and Lelisa are reportedly ill with restricted and limited medical care.
Terminally ill
Lelisa is a longtime Oromo rights activist with Oromo Peoples Congress (OPC), who rose through the ranks of the organization from a sole member to top leadership. He competed in the last three elections representing the Caliya district in West Shewa. He was elected to the Oromia regional parliament in 2005. He was subsequently arrested on concocted charges of plotting to overthrow government by working with the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF), recruiting youth for armed rebellion and for inciting the frequent youth revolt in Ambo and West Shewa.
Lelisa, who has so far served three years of the 11 years sentence, reports being mistreated while in prison. He has repeatedly been beaten by unidentified men at Kaliti prison with orders from security services. He has sustained serious wounds from the beatings by government agents who pose as prisoners, according to OPride sources. Lelisa, who is terminally ill and said to be on a long-term medication for undisclosed condition, had repeatedly appealed to the higher court about his mistreatment but received no response to date.
Singling out the Oromo
While the State Department’s report is short on details, there are several evidences that show the Ethiopian government continues to single out Oromo dissidents. Last year, the OLF released a partial list (independently verified by a reputable OPride source) of 528 individuals sentenced to death and life imprisonment on purely political grounds.
The list includes names of individuals, their gender, and ethnic backgrounds. Underscoring the disproportionate repression of the Oromo, of the 528 individuals who were sentenced to death or life imprisonment by the Ethiopian courts, 459 are Oromo nationals followed by 52 Amhara nationals. “This list clearly indicates that the minority regime in Ethiopia is using its kangaroo courts for destroying Oromo and Amhara nationals who are viewed as potential threat to the regimes hold on to power,” one informant, who asked not to be named, told OPride.
As documented by various international human rights organizations, today, it is a serious crime, under the Tigrean dominated Ethiopian government to support any independent Oromo organization. Thousands of Oromos have been imprisoned, tortured and killed extra-judicially for no apparent reason other than expressing Oromo national feeling and for their support of Oromo organizations such as the OLF.
The selective and systematic targeting of Oromo in Ethiopia by the current began in 1992 when the OLF which jointly ruled Ethiopia from 1991-1992 with the Tigrayan Liberation Front (TPLF) was banned and its members and supporters jailed for years and hundreds executed without due process of law. Although Oromia, the Oromo regional state in Ethiopia, is autonomous in name, the Oromo do not have any meaningful voice in the affairs of their own state, which is totally controlled by the TPLF.
The later represents no more than seven percent of the population of Ethiopia, while the Oromo, who constitute the single largest national group in Ethiopia and the third largest national group in the whole of Africa. The Oromo are denied the basic democratic rights to organize freely and legally and express their political opinions. There is no single independent newspaper or media outlet catering to the Oromo populace in their native tongue.
The TPLF fears the Oromo numerical strength deliberately characterizes all independent Oromo organizations, which it does not control as the “terror wing” of the OLF. The goal for such characterization is to persecute peaceful supporters of the OLF behind the façade of fighting against a “ terrorist organization.” Under the anti-terror law of the current Ethiopian regime, anyone who is suspected of peacefully supporting the OLF, could be sentenced to life imprisonment or executed. The above mentioned 459 Oromo nationals who were sentenced to death or life imprisonment are all suspected OLF supporters.
Destroying the lives of 528 innocent human beings on political ground is a crime against humanity, which must be condemned by all civilized nations. The tearless cry of the U.S. AnnuaL Human Rights report notwithstanding, at this moment no calling is more urgent and more noble and no responsibility greater for those who believe in human rights than raising their voice for pressuring the government of Ethiopia to free the 528 innocent individuals who were sentenced to death and life imprisonment on purely political grounds.
In the last year alone, two Oromo activists have died in prison under mysterious circumnances. Last year, OPride reported about the death in prison of former UNHCR recognized refugee, engineer Tesfahun Chemeda. Last month, a former parliamentary candidate from Chalenqo in Western Hararghe, Ahmed Nejash died in prison. According to an OPC source, Nejash successfully run and challenegd Sufian Ahmed, Ethiopia’s Minister of Finance and Development, during the 2010 elections. He was subsequently arrested in 2011 alleged of being an OLF activist. Although his death recieved scant media coverage even within the Oromo community, a close relative of the late Jarra Abba Gadaa, Nejash is one of the veterans of Oromo people’s struggle. “He was sentenced to seven years, which was also upheld by the higher court,” the OPC told OPride source said. “He was in Zuway with Bekele and Olbana and he was healthy the last time I saw him in 2013.”
http://www.opride.com/oromsis/news/horn-of-africa/3735-us-slams-ethiopia-s-human-rights-abuse
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.
21 Things They Never Tell You About Poverty & Poor Countries February 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromo people, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
- Poverty-as-rule-not -exception is difficult to bend our minds around because we tend to base our views about the world on direct experience. If people around us seem mostly well-fed and content, then why shouldn’t everybody else be? We still don’t know as much as we should about poverty and we try to ignore poor people. Most people’s experience of the global poor is the waiter at their table or the pool attendant, the ones lucky enough to have jobs. Only by direct experience and immersion in local circumstances is it possible to have a vague inkling of what it might be like to be genuinely destitute. There’s no obligation on holidaymakers to go wandering around in slums, but anybody who claims knowledge about deprivation should experience or observe it first-hand for themselves, ideally for a long time.
- Which undermines my first four points. As Morten Jerven says in his book Poor Numbers: How We Are Misled By African Development Statistics And What To Do About It, “the most basic metric of development, GDP, should not be treated as an objective number but rather as a number that is a product of a process in which a range of arbitrary and controversial assumptions are made.” Jerven finds that the discrepancy between different GDP estimates is up to a half in some cases. This supports my experience from working in the least developed countries, where statistics offices are usually underfunded and don’t have the resources to collect data often or well enough.
- There’s a kind of false scientism: foreign academic economists spend ages refining complicated econometric models despite the raw material being rubbish. In the absence of good numbers, the only immediate alternative is to live in a country, to use good theory and to rely where necessary on case studies and even anecdote.
- A report from Oxfam last month pointed out that 85 people, about as many as would fit on a double-decker bus, own as much wealth as the bottom half of the world’s population.
- The Spirit Level by Kate Pickett and Richard Wilkinson shows that equality is good for everyone. Redistribution reduces poverty and makes life better for the rich in the form of less crime, better education and a more cohesive society. Global inequality is getting worse, not better. If we don’t radically reduce inequality the poor will eat us, so aid isn’t an option, and it’s not about the rich world “saving” the poor. It’s essential for everyone.
- Although things are improving, a huge chunk of the world’s population remain poor. Over a fifth of humans, 1.29 billion, are considered extremely poor . In effect the equivalent of every man, woman and child in Europe, the United States and the Middle East scrape by on 75 British pence a day adjusted for the cost of living in each country. About a third of the world lives on less than $2 a day. The poorest half of the world – 3.5 billion people – own only 0.71% of the world’s wealth between them.
- A billion people live in chronic hunger. Nearly a third of all children are chronically malnourished, which unless addressed before the age of two often leaves them stunted and mentally impaired. A sixth of the world’s adults can’t read or write and many more have only rudimentary literacy. Sub-Saharan Africa has only two doctors for every 10,000 people, which is partly why on average its inhabitants live to an average age of 56.
- Rather than a term like “developing” to describe these people and countries, the travel writer Dervla Murphy’s phrase “majority world” is more accurate.
- “The four basic needs: food, housing, clothes and medicine must be cheap and easy for everybody. That’s civilisation”, says Jon Jandai, a farmer from northeast Thailand. I’d add primary, secondary and tertiary education, too.
- Lower income countries have leapfrogged some technologies. For example many will never install fixed telephone lines because mobile coverage is so good. Vast numbers of people will never touch a PC, doing all their computing on a smartphone or tablet.
- The governments of poor countries should be more adventurous, leapfrogging ideologies too. Some proponents of economic growth argue that environmental sustainability and a focus on happiness will handicap poverty reduction. But it could enable some countries to prioritise the important things in life. Endless growth is impossible and undesirable.
- Beyond a certain point rich inefficiency is the real problem. Why do developing countries ape the development paths and economic structures of the West? We are wage slaves who perform bullshit jobs so that we can service our mortgages. The advance of the car ruined everyone’s quality of life so that a minority can sit in air-conditioned metal boxes in jams. Clever though-leadership in the majority world could lead the way for the rich. Bhutan’s idea of Gross National Happiness is an example.
- There’s plenty of food to go round. World agriculture produces 17% more calories per person today than it did 30 years ago despite a 70% population increase, due to rising yields, higher farming intensity and more use of land. The real problems are the system of distribution and energy use. If the rich world didn’t hog all the food and produce it inefficiently there’d be enough for everyone.
- The amount officially spent on each poor person globally is US$20 a year, according to the World Bank. The amount has doubled in the last decade following a dip in the late 1990s. But several opinion polls show that rich country inhabitants think they’re much more generous than they really are. Americans think that their government spends 28% of the budget on aid when it’s really about 1%. Brits are almost as bad. The result of this widespread overestimation of generosity is that many people in rich countries want to cut aid.
http://emergenteconomics.com/2014/02/24/21-things-they-never-tell-you-about-poor-countries/
Prompted by Bill Gates’s annual letter and the response from the Overseas Development Institute I thought I’d list some of the things that in my experience seem to be less understood about poor countries. (I wanted to list 23 things like Ha-Joon Chang on capitalism but I couldn’t think of another two). I use the word poor on purpose because although the word risks sounding patronising or dismissive, euphemisms like developing and less-developed can be worse. Thoughts are welcome.
1. Poverty is the rule, not the exception.For most people life just isn’t as good as it is for you and I, the comfortable people from a country rich enough to allow us the literacy, time and Internet access to read blogs written by well-meaning left liberals. Poverty-as-rule-not -exception is difficult to bend our minds around because we tend to base our views about the world on direct experience. If…
View original post 3,098 more words
The ‘Africa Rising’ Narrative: A Single Optimist Narrative Masks Growing Inequality in the Continent February 24, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Economics, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, International Economics, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, South Sudan, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo culture, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
“Compare that with the mean wealth of a South African at $11,310, Libyan ($11,040) and Namibian ($10,500). While the average Ethiopian has his asset base standing at a mere $260 despite years of economic growth and foreign investment – wealth has not filtered through to the people. With this kind of glaring inequality between and within countries, the “Africa Rising” narrative risks masking the realities of millions of Africans struggling to get by in continent said to be on the move.” http://www.africareview.com//Blogs/Africa-is-rising-but-not-everywhere/-/979192/2219854/-/12at0a8/-/index.html?relative=true
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Africa Rising” is now a very popular story – a near-universal belief that the continent is the next investment frontier after more than a decade of sustained high growth rates and increased foreign direct investment.
We even now have memes for this new narrative.
But some people have their doubts about this whole “Afro-optimism” talk – they say Africa isn’t really rising.
They argue that Africa’s low levels of manufacturing and industrialisation discredit the continent’s “growth miracle”. Its share of world trade is remains very small compared to Asia.
Well, Africa cannot be reduced to a single narrative. We have been victims of this before – for hundreds of years the continent has always been seen in a kind of Hobbesian way – where life is poor, nasty, brutish and short.
Now, there is a minority global elite working round the clock trying to turn this long-held view of a continent.
While I do not begrudge them for their PR efforts – we cannot mask the glaring inequality in Africa by developing a new optimist narrative about the continent.
There are many stories about Africa. Not just one.
Genocide
While the sun shines bright in Namibia, not the same can be said of Malawi where the government is bankrupt or the Central African Republic (CAR) where sectarian violence is increasingly becoming genocidal.
Pretty much everyone else in the world seems accustomed to the living hell that is Somalia.
But we have also come to a consensus that Botswana and Ghana are the model countries in Africa.
South Africa is a member of the BRICS. While the petro-dollars are changing the fortunes of Angola – it has grown its wealth per capita by 527 per cent since the end of the civil war in 2002.
Not much can be said of South Sudan. Oil has not done anything despite pronouncements by the liberation leaders that independence holds much promise for the young nation’s prosperity.
The country imploded barely three years into into its independence.
This is the problem of a single narrative – it is indifferent to the growing and glaring inequality in Africa and its various political contexts.
Many Africans still have no access to the basic necessities of life. Millions go to bed without food and die from preventable diseases.
Others live in war-ravaged countries in constant fear for their lives. You can bet the last thing on their mind is not a blanket “rising” narrative about Africa and the promise it holds. That is not their Africa, its someone else’s.
Yes. “Africa Rising” may be real. But only to a small minority.
Wealth distribution
A report by New World Wealth highlights the variations in wealth distribution across the continent’s 19 wealthiest countries.
Africa’s total wealth stood at $2.7 trillion last year down from $3 trillion in 2007 after taking a hit from the global financial crisis.
These 19 countries control 76 per cent while the remaining 35 scrape over $648 billion. And most of this wealth is concentrated in northern and southern Africa.
The western, central and eastern regions have some of the poorest individuals on the continent with the highest per capita wealth from this group – with the exception of Angola – coming from Nigeria at $1,350.
Compare that with the mean wealth of a South African at $11,310, Libyan ($11,040) and Namibian ($10,500).
While the average Ethiopian has his asset base standing at a mere $260 despite years of economic growth and foreign investment – wealth has not filtered through to the people.
With this kind of glaring inequality between and within countries, the “Africa Rising” narrative risks masking the realities of millions of Africans struggling to get by in continent said to be on the move.
The sun may be shining bright in Africa – but only in favoured parts of it.
Read further @:
How to end poverty? February 22, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, Self determination, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo people, Parliament, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“Nations fail economically because of extractive institutions. These institutions keep poor countries poor and prevent them from embarking on a path to economic growth. This is true today in Africa, in South America, in Asia, in the Middle East and in some ex-Soviet Union nations. While having very different histories, languages and cultures, poor countries in these regions have similar extractive institutions designed by their elites for enriching themselves and perpetuating their power at the expense of the vast majority of the people on those societies. No meaningful change can be expected in those places until the exclusive extractive institutions, causing the problems in the first place, will become more inclusive.” http://otrazhenie.wordpress.com/2014/02/16/how-to-end-poverty/#
“If we are to build grassroots respect for the institutions and processes that constitute democracy,” Mo Ibrahim writes for Project Syndicate, “the state must treat its citizens as real citizens, rather than as subjects. We cannot expect loyalty to an unjust regime. The state and its elites must be subject, in theory and in practice, to the same laws that its poorest citizens are.” http://www.huffingtonpost.com/dr-mo-ibrahim/africa-needs-rule-of-law_b_4810286.html?utm_hp_ref=tw

I was always wondering about the most effective way to help move billions of people from the rut of poverty to prosperity. More philanthropy from the wealthy nations of the West? As J.W. Smith points it, with the record of corruption within impoverished countries, people will question giving them money as such ‘donations’ rarely ‘reach the target’. Building industries instead? While that approach seems to provide better results (see few examples described by Ray Avery in his book ‘Rabel with a cause‘), it still did not provide a silver bullet solution, as it does not address the roots of poverty and prosperity.

From Christian Bowe
In their book ‘Why nations fail?‘, that examines the origin of poverty and prosperity, Daron Acemoglu and James Robinson conclusively show that it is man-made political and economic institutions that underlie economic success (or the lack of it). Therefore only the development of inclusive…
View original post 844 more words
Africa Must Industrialize: The Time IS Now February 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Oromo, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Horn of Africa, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Social Sciences, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
As the current economic growth did not result from value addition and increased manufacturing, but instead from increases in world commodity prices, it makes the region susceptible to commodity price volatility. If commodity prices fall, Africa’s impressive economic growth might grind to a halt — thus, the dire need for diversification through industrialization. Even if commodity prices stay high, natural resources are not infinite and they must be managed with sagacity.
As recommended by the 2013 Africa Progress report, it is advantageous for African governments to fully implement the Accelerated Industrial Development for Africa (AIDA) plan, signed in 2008 in Addis-Ababa. The AIDA is a comprehensive framework for achieving the industrialization of the continent. If Africa can successfully steward its natural resource wealth, investing it wisely and using some to industrialize, then whether the resources run out or not or whether commodity prices fall, Africa would be on a good economic footing.
Moreover, not only will industrialization create the environment for adding value to Africa’s natural resources, but it will also provide much needed employment at various stages of the value adding chain for Africa’s 1.1 billion people — leading to wealth creation.
Industrialization will address many development gaps in sub-Saharan Africa. Some of these gaps, as noted in a UNECA Southern Africa Office Expert Group Meeting Report, include:
Africa’s high dependence on primary products
Low value addition to commodities before exports
High infrastructure deficit
High exposure to commodity price volatility
Limited linkage of the commodities sector to the local economy
Poorly developed private sector, which is highly undercapitalized
Limited commitment to implement industrial policies
Limited investment in R&D, science, innovation and technology
Low intra-Africa trade
Slow progress towards strengthening regional integration
The Time is Now
Is Africa ready? The answer is an emphatic yes. The phenomenal growth is one reason why Africa is ready, but growth on its own is not enough. Other conditions need to be considered: Does the continent have access to enough raw materials for production? What is the proximity of these natural resources to the continent? Is there adequate land, labor, and capital? These are the traditional factors of production or inputs to the production process.
Yes, Africa has access to the raw materials necessary for production. Unlike already industrialized nations who have to import raw materials from Africa and elsewhere over long distances, Africa enjoys close proximity to these resources.
With regards to the factors of production, Africa is the world’s second largest continent and therefore is home to plenty of land — most of which is arable.
Africa is also the world’s second most populous continent. The average age of an African in Africa is under 19 years. This means Africa has enough manpower or labor to industrialize.
Capital refers to man-made products used in the production process such as buildings, machinery and tools. Africa does have a measure of this, but instead needs to do more in this area — hence the need for greater infrastructural and skills development. In fact, African policymakers as well as their counterparts in the developed world should realize that it is high time for a shift in the nature of aid to the continent — from primarily monetary aid to the type of capital aid needed for industrialization.
Finally, when Africa successfully undergoes industrial development, its huge populace will serve as a market for the outputs of its production processes; any excess supply can be exported and swapped for foreign exchange. Africa is ready and the time for it to industrialize is now.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Fair Observer’s editorial policy.
read more@
As The 1960s Euphorea, The Current Africa Rising Optimism Is Illusionary Than Real: Let Us Actually Think How Africa Can Become Truly Prosperous. February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Culture, Development, Dictatorship, Economics, Food Production, Human Rights, Ideas, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Self determination, Slavery, South Sudan, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Africa Rising, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


‘Much of the “Africa Rising” narrative is based on the cyclical growth in income revenues from commodities. But who knows how long this will last? Dr Moghalu wants African governments to grasp hold of their future by creating industrial manufacturing so that Africans can consume what they produce. If that could be achieved, the continent will have moved away from being an import-driven consumer-driven economy. It is only then, he argues, that we can say Africa has truly risen.’
The term “Africa Rising” is on the lips of many these days particularly as seven of the world’s fastest growing economies are believed to be African. But can this current wave of Afro-optimism bring genuine prosperity to the African continent? Dr Kingsley Chiedu Moghalu, the Deputy Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria thinks not.
“Hope is good,” he says. “But hope must be based on concrete substantive strategy going forward, so I pour a little bit of cold water of the Africa Rising phenomenon. I think it could lead to illusionary thinking. I recall that when African countries became independent that there was a huge sense of euphoria around the continent that independence guaranteed economic growth, political development and stability. But this did not happen in the following 30 to 40 years.”
In his latest book, Emerging Africa: How the Global Economy’s ‘Last Frontier’ can prosper and matter, Dr Moghalu presents his own ideas on how Africa can become truly prosperous. He describes it as “a vision for Africa’s future based on a fundamental analysis of why Africa has fallen behind in the world economy”.
In doing so, the LSE alumnus discusses some fundamental misunderstandings about which African states need to revise their assumptions.
The first is the idea that globalisation is automatically good. Rather, Dr Moghalu describes it as a huge and influential reality which Africans must engage with a sense of sophistication and self-interest. It is important to find a way to break that stranglehold because globalisation is neither benign in its intention nor agnostic in its belief. It is driven by an agenda and there are people who drive it.
Economist Dambisa Moyo caused controversy with her first book, Dead Aid: Why foreign aid isn’t working and how there is another way for Africa. Dr Moghalu echoes some of her arguments describing foreign aid as one of the leading reasons why Africa is impoverished. “It has removed the incentive of many African nations to seek solutions for their economic challenges and create wealth for their citizens,” he argues. “Instead it has perpetuated poverty because they are simply content to survive from one day to the next.”
Foreign aid does have its place, Dr Moghalu admits, but “it should always be within a limited time frame and it should focus on economic wealth creation activities rather than just helping people survive”. On the day we meet, the UK Secretary of State for International Development Justine Greening is in the news revealing that there will be a radical shift in future UK aid into economic development, concentrating on economic growth and jobs. Dr Moghalu expressed great pleasure at this announcement remarking that “it is very interesting that British policy is catching up with the recommendations in my book”.
Another fundamental understanding that the central banker develops in his book is the importance of understanding the four different kinds of capitalism and the implications they have for Africa’s growth. The first is state capitalism which is not very common, although it is practised by China. It is, in fact, an oxymoron. Many African states do not have the capacity to run state capitalism because you need an all-knowing state with a huge reserve of strategic thinking capacity to be able to direct wealth creation for the purposes defined by the state. There is also oligarchic or crony capitalism in Russia and some African states. This can be turned into strategic activity if cronyism is not rampant. South Korea did that by creating the Chaebols, the family-held businesses which today dominate the South Korea economy. Welfare capitalism is the norm is Europe. Some African states have practised welfare capitalism without generating the type of revenue that will sustain it into the future. Now it is out of favour. Entrepreneurial capitalism is what made America wealthy and this is what Dr Moghalu recommends for most African economies because it suits the African culture. Along with a certain amount of oligarchic and welfare capitalism, it would do Africa a world of good, he adds.
Much of the “Africa Rising” narrative is based on the cyclical growth in income revenues from commodities. But who knows how long this will last? Dr Moghalu wants African governments to grasp hold of their future by creating industrial manufacturing so that Africans can consume what they produce. If that could be achieved, the continent will have moved away from being an import-driven consumer-driven economy. It is only then, he argues, that we can say Africa has truly risen. http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/africaatlse/2014/02/12/afro-optimism-will-not-transform-africa/
US Congress Takes a Historic Stance Against Land Grabs-Related Forced Evictions in Ethiopia February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromummaa, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Genocide against the Oromo, Gibe Valley, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Lower Omo, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
See the Omnibus Appropriations Bill (p. 1295-1296) @
http://docs.house.gov/billsthisweek/20140113/CPRT-113-HPRT-RU00-h3547-hamdt2samdt_xml.pdf
Oakland, CA – In a historic move, the US Congress has taken a stance on land grabs-related human rights abuses in Ethiopia. The 2014 Omnibus Appropriations Bill contains provisions that ensure that US development funds are not used to support forced evictions in Ethiopia.
The bill prevents US assistance from being used to support activities that directly or indirectly involve forced displacement in the Lower Omo and Gambella regions. It further requires US assistance in these areas be used to support local community initiatives aimed at improving livelihoods and be subject to prior consultation with affected populations. The bill goes further and even instructs the directors of international financial institutions to oppose financing for any activities that directly or indirectly involve forced evictions in Ethiopia.
According to Anuradha Mittal, Executive Director of the Oakland Institute, “We welcome this move as it aims to address one major flaw of US assistance to Ethiopia. The step taken by the US Congress is very significant, as it signals to both the Ethiopian government and the US administration that turning a blind eye to human rights abuses in the name of development is no longer an option.”
Several reports from the Oakland Institute have raised alarm about the scale, rate, and negative impacts of large-scale land acquisitions in Ethiopia that would result in the forced displacement of over 1.5 million people. This relocation process through the government’s villagization scheme is destroying the livelihoods of small-scale farmers and pastoralist communities. Ethiopian security forces have beaten, arrested, and intimidated individuals who have refused to relocate and free the lands for large-scale agricultural plantations.
Ethiopia’s so-called development programs cannot be carried out without the support of international donors, primarily the US, one of its main donors. Oakland Institute’s on-the-ground research has documented the high toll paid by local people as well as the role of donor countries such as the US in supporting the Ethiopian policy.
This language represents an important first step towards Congress initiating a comprehensive examination of US development practices in Ethiopia. As the oversight authority of the State Department, Congress must now ensure that the law is fully upheld and implemented. This warrants thorough scrutiny of USAID programs to Ethiopia and their contribution to forced resettlements and human rights abuses.
With this bill, USAID, the State Department, as well as the World Bank, will have to reconsider the terms and modalities of the support they provide to the Ethiopian government. According to Frederic Mousseau, Oakland Institute’s Policy Director, “This is a light of hope for the millions of indigenous people in Ethiopia who have sought international support from the international community to recognize their very destruction as communities and people.” Read Further @
USAID’s cover-up of Ethiopia abuses overruled by Congress 12 February 2014
The United States Congress has acted to prevent its aid to Ethiopia being used to fund forced evictions of tribal peoples in the south west of the country.
The provisions in the Omnibus Appropriations Bill for 2014 represent a slap in the face for USAID, which last month said that ‘there are no reports of widespread or systematic human rights abuses’ in the region.
In fact, tribes of the Lower Omo Valley are being violently evicted from their villages by the government to make way for lucrative cotton, palm oil, and sugarcane plantations whose irrigation will be made possible by the controversial Gibe III dam. Transferred to designated resettlement areas, the once self-sufficient tribes will be left with no access to their livestock or lands and, consequently, will be unable to sustain themselves. Intimidation tactics, such as rape and beatings, have reportedly been used against those who resist resettlement.
One Mursi man told Survival International, ‘We are waiting to die. We are crying. When the government collects people into one village there will be no place for crops, and my children will be hungry and have no food.’
The Ethiopian government has not consulted any indigenous communities over its aggressive plantation plans in the Omo Valley, and very few were consulted over the construction of the Gibe III dam.

The region’s top human rights body, the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights, has written to the Ethiopian government asking it to halt the forced resettlement of the Lower Omo tribes while it investigates Survival’s submission regarding human rights violations in the area.
Ethiopia is one of the biggest recipients of American and British aid through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and the UK Department for International Development (DFID).
Although the provisions in the recent spending bill will force USAID to reevaluate the funding given to Ethiopia, it will ultimately be the responsibility of Congress to guarantee that the terms are upheld.
Survival International Director Stephen Corry said today, ‘This bill is a huge step in the right direction, and shows that USAID’s shameful denials of the human rights abuses being committed in the Lower Omo simply haven’t been believed.
‘American taxpayers want to be sure that their money isn’t going toward the destruction of tribal peoples’ lives. Hopefully the historic provisions in this year’s spending bill will ensure that’s the case. It is now high time that British parliamentarians follow suit and ensure that DFID does not use UK taxpayers’ money to fund human rights violations in the Lower Omo.’ http://www.survivalinternational.org/news/9983
Further References on land grabs in Africa
Around 90 percent of the population of 87 million still suffers from numerous deprivations, ranging from insufficient access to education to inadequate health care; average incomes are still well below $1500 a year; and more than 30 million people still face chronic food shortages.
And while there are a number of positive and genuine reasons for the growth spurt – business and legislative reforms, more professional governance, the achievements of a thriving service sector – many critics say that the growth seen in agriculture, which accounts for almost half of Ethiopia’s economic activity and a great deal of its recent success, is actually being driven by an out of control ‘land grab’, as multinational companies and private speculators vie to lease millions of acres of the country’s most fertile territory from the government at bargain basement prices.
At the ministry of agriculture in Addis Ababa, this land-lease programme is often described as a “win-win” because it brings in new technologies and employment and, supposedly, makes it easier to improve health care, education and other services in rural areas.
“Ethiopia needs to develop to fight poverty, increase food supplies and improve livelihoods and is doing so in a sustainable way,” said one official.
But according to a host of NGO’s and policy advocates, including Oxfam, Human Rights Watch and the Oakland Institute, the true consequences of the land grabs are almost all negative. They say that in order to make such huge areas available for foreign investors to grow foodstuffs and bio-fuels for export – and in direct contravention of Ethiopia’s obligations under international law – the authorities are displacing hundreds of thousands of indigenous peoples, abusing their human rights, destroying their traditions, trashing the environment, and making them more dependent on food aid than ever before.
“The benefits for the local populations are very little,” said renowned Ethiopian sociologist Dessalegn Rahmato. “They’ve taken away their land. They’ve taken away their natural resource, because these investors are clearing the land, destroying the forest, cutting down the trees. The government claims that one of the aims of this investment was to enable local areas to benefit by investing in infrastructure, social services … but these benefits are not included in the contract. It’s only left up to the magnanimity of the investor.”
And those investors, he continued, are simply not interested in anything other than serving their own needs: “They can grow any crop they want, when they want it, they can sell in any market they want, whether it’s a global market or a local market. In fact most of them are not interested in the local markets.”
He cited as an example a massive Saudi-owned plantation in the fertile Gambella region of south west Ethiopia, a prime target area for investors: “They have 10,000 hectares and they are producing rice. This rice is going to be exported to the Middle East, to Saudi Arabia and other places. The local people in that area don’t eat rice.”
But the most controversial element of the government’s programme is known as ‘villagisation’ – the displacement of people from land they have occupied for generations and their subsequent resettlement in artificial communities.
In Gambella, where two ethnic groups, the Anuaks and the Nuers, predominate, it has meant tens of thousands of people have been forced to abandon a traditional way of life. One such is Moot, an Anuak farmer who now lives in a government village far from his home.
“When investors showed up, we were told to pack up our things and to go to the village. If we had decided not to go, they would have destroyed our crops, our houses and our belongings. We couldn’t even claim compensation because the government decided that those lands belonged to the investors. We were scared … if you get upset and say that someone stole your land, you are put in prison. If you complain about being arrested, they will kill you. It’s not our land anymore; we have been deprived of our rights.”
Despite growing internal opposition and international criticism, the Ethiopian government shows no sign of scaling the programme back. According to the Oakland Institute, since 2008, an area the size of France has already been handed over to foreign corporations. Over the next few years an area twice that size is thought to be earmarked for leasing to investors.
So what does all this mean for the people on the ground? In Ethiopia – Land for Sale, filmmakers Veronique Mauduy and Romain Pelleray try and find out.
http://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/peopleandpower/2014/01/ethiopia-land-sale-20141289498158575.html
Farming and food in Africa and the battle over land, water and resource rights
Africa is being heralded as the new frontier for commercial farming but, as governments and investors sign deals, a counter movement of family farmers is promoting alternative pathways to development.
The International Year of Family Farming is now underway, and never before have family farmers in Africa been more under threat.
Large land deals between African governments and usually foreign (and sometimes domestic) investors have seen swathes of the countryside leased or conceded, often for as much as 50-99 years. From Senegal in West Africa to Ethiopia in the Horn, and down to Mozambique in the south, land considered idle and available has changed hands, with profound implications for local people and the environment.
Oromia: OSGA Invited to the UN to report on human rights abuses February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sirna Gadaa, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Democratic system, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


HCH is working in conjunction with the Oromia Support Group of Australia (OSGA), one of our long standing community partners, to raise urgently required funds toward a unique opportunity to
present serious allegations of human rights abuses in Ethiopia, at the highest level; the United Nations Universal Periodic Review (UPR).
Human rights organisations have long been reporting human rights abuses committed by the Ethiopian government, which include rape, torture, arbitrary detention and kidnapping. OSGA is an Australian based organisation that was established in 2008 to report on and raise awareness of these violations.
They have recently been offered a significant opportunity to send a delegate to the 19th session of the UN Human Rights Council’s UPR in April, 2014. There they will present a first-hand account of human rights abuses committed by the Ethiopian government.
This opportunity, to report first-hand accounts of torture, arbitrary imprisonment and rape to senior UN officials, will enable them to forward these concerns to the Ethiopian government during the official UPR process. This process will require the Ethiopian government to answer the accusations.
OSGA is raising urgently needed funds to send a representative from the Ethiopian community in Australia. The estimated total cost is approximately $5,000. If you can help, OSGA can provide a receipt, and will also report on the acquisition of any funds. Any contribution would greatly assist this effort.
If you can contribute, please contact info@osgaustralia
Stop Clearing Oromo from their Land in the Name of Boosting Economic Development: Who Will Stand for the Oromo People Living on the Outskirts of Finfinnee? February 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Culture, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Food Production, Gadaa System, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, ICC, Ideas, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, economics, Ethiopia, Finfinnee, Gadaa System, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Raya under destruction, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, World Bank
add a comment


It is to be recalled that Finfinnee (Addis Ababa) was founded as the present capital city the so called Ethiopian in 1886 by a man called Minilik II. During this time, the area was inhabited by the Oromo people and the area was almost covered with natural forest. Initially the Shawa government made it seat at Ankober. Hence, before the founding of Finfinee as a political and economic capital of the king, all the areas within the present Finfinnee and the surround areas was free like any other Oromia lands. However, after 1886 the Semitic people from the northern segments and others had taken the land and the Oromo people who were used to live in these areas were forced lost their land through time.
For example, according to Central Statistics Agency of Ethiopia (2007) Out of the 2,738,248 100% total population living in Finfinnee, the total number of the Oromo people living in the city was only 534,255 (19.51%). Since its founding as a capital, Finfinnee remained the capital city for the successive Ethiopian regimes (Menilik II, Lij Eyassu, Zawuditu, Hailesillasse I, Mengistu, Melles and HaileMariam). Through time, the number of inhabitants increased and urbanization expanded greatly. The deliberate and implicitly planned mission and decision of the Semitic people to erase any sign of Oromo history from Finfinnee was started during the forcefully integration of Oromo people into Ethiopia as second-class citizens and the process has continued in the present government.
Different people mostly from the northern part of the so called Ethiopia have come from the various ethnic groups come and settled in the capital owing to its supper suitable agro-climatic and exploit the natural within the outside today’s Finfinne from the near distance in the name of work and investment. Where did those Oromo farmers go when Finfinnee became the property of new invaders? Be in mind that the Oromo’s are pushed to the peripheral areas of the capital and the number of Oromo people inhabitants decreased from time to time, as the above data depicts. The indigenous people of the land were pushed out one after the other and were replaced by the invaders from the north. What is happening to the Oromo people living on the outskirt of Finfinne today? It is simply the continuation of a process, which had resulted in a massive displacement of an indigenous Oromo people.
B. The New Master Plan of Fifinnee and Areas to be Incorporated
For the last 100 or so years the Master Plan of Finfinnee city was revised several times. The recent proposal of preparing new Master Plan for City administration that planned to incorporates all the towns and districts lying within the range of 1 hour commuting distance from the Finfinnee, justifies the blatant violation of the constitution and their voracious appetite to systematically replacing resource and land deficient people to these fertile lands owned by the Oromo people. According to the proposed plan of established the “Integrated Regional Development Plan”, an additional 36 towns and 17 districts currently administered by the Oromia regional State will be merged with Finfinnee so that the right of the land use will be determined by the central mayor .
The new Master Plan was intended to incorporate Oromia’s land locating in 100kms around the Finfinnee city. According to Ethiopia Government preparation, the following 36 Towns and 17 Districts are included in the newly planned Master plan. (See the figure 1.)
Some of the Towns are: Adama, Sodere, Mojo, Wenji Adama, Ejere, Alem Tena, Koka, Adulala, Bushoftu, Dukem, Gelen, Akaki Beseka, Godino, Chefe Donsa, Sebeta , Sendafa, Milkewa, Wendoda, Sirti, Duber,Gorfo, Chancho, Mulo, Debra,Muger , Ulo, Adis Alem, Holota, Burayu,Debre Genet, Illu Teji, Tefki, Sebeta, Boneya, Melka Kunture and etc.
Some of the Districts areas are: Adama, Dodota, Bora, Lome, Liben chukala, Adea (around Bushoftu), Akaki, Gimbichu, Bereh(around Sebeta), Aleltu, Jida, Sulultu, Ejere, Welmera, Illu, Sebeta Hawas and etc.
Today, when the world is concerned about preserving ecology and wild life in their natural habitat, it is an Ethiopian Government that is clearing an indigenous Oromo people from their home Land in the name of inequitable Economic Development. Hence, who should stand and speak for these innocent people and argue to preserve the right of the extremely vulnerable Oromo people living in the proposed territories and to preserve the indigenous Oromo people, culture, Languages and etc. Otherwise sooner than latter these great people will be marginalized and lost their identities.

Figure 1: The newly Developed and proposed Master Plan of the tomorrow’s Finfinne over the coming 25 years
C. The Agenda behind the “Integrated Regional Development Plan (IRDP)”
An office called “Addis Ababa and the surrounding Oromia Integrated Development Plan” prepared an International and National Conference on June 2013 at Adama Town, Galma Abba Gadaa. The Objective of organizing the conference of the top ranking government cadres (mostly OPDO’s) was to work on the manifesting of the proposed Integrated Regional Development Plan (IRDP) and prepare the cadre’s to work on the people.
On the Conference, it was stated that, the Purposes of the “IRDP” are:
Instrumental to unleashing Regional Development Potentials
Enables localities addressing their mutual development challenges
Enables localities addressing their mutual development challenges
Strengthens complementarities and interconnection of localities
These purposes can be the explicit or clear objectives of the plan. However, the plan have hidden or implicit agenda. Systematically bringing the land under their custody so that, it will sooner or later scramble among their impoverished people in their region. For example, the Finfinnee City Administration and Finfinnee Special Zone can address their mutual development challenges without being incorporated into one master plan. However, the Master plan is not prepared on mutual benefit as the plan is solely prepared by Finfinnee City Administration, despite the name of the office. Hence, though development is boldly emphasized, the main purpose seems to clear the Oromo farmers from their lands in the name of unfair Economic Development.
It was also stated that the Pillars of the Integrated Regional Development Plan are:
Regional Infrastructure Networks
Natural Resource and Environment Stewardship
Cross – Boundary Investments/ e.g FDI)
Joint Regional Projects
However, there seem hidden agenda behind these pillars. For example, in the name of cross-Boundary Investments, local Oromo farmers are going to lose their land for the so-called “investors” and under the pretext of promoting national economy through FDI initiatives In addition, if the plan is going to be realized natural and environmental degradation is inevitable.
In addition, the Basic Principles of the Integrated Regional Development Plan are:
Ensuring Mutual Benefits
A joint development Framework – not a substitute for local plans
An Integrated Regional Plan voluntarily accepted by participating partners
Differences resolved through negotiation and under in-win scenario
Nevertheless, the plan will not ensure a mutual benefit at it is largely intended to displace Oromo farmers from their land. In additions, the populations of the two areas are not homogenous. Hence, they have no common interest. Even though it is said the “IRDP’ will be voluntarily accepted by participating partners, the top cadres in Oromia themselves have strongly opposed the plan on the conference. Beside, the implicit objective of the plan is to remove/avoid the differences in language and culture there by to plant “Ethiopianism or Tigreans” on Oromo land. The plan is intended to say good bye to Oromo Culture and language. The other thing is that the differences between Oromo and others cannot be resolved as it is intended to eradicate Oromo identity, culture and language. As we know from history, Oromo’s never compromised on these issues. Hence, if the plan is to be implemented, peaceful co-existence may not be there.
D. Problems that may come because of the Integrated Regional Development Plan
As different sources shown, many Oromo’s living in Special Zone has already lost their land in the name of foreign direct investment and land grasping. This is because of several fa3ctories are constructed in the special zone by taking the Lands from local Oromo farmers. It is not new to see Oromo labor workers or guards in their own land. Family members are highly displaced by this measure. Many went to street. Not only the displaced Oromos damaged by this. It is said chemical coming out of the factories are also hurting the health of the remaining Oromos. It is said that “In Central Oromia, thousands of people and their livestock died due to the industrial pollution directly released to rivers and lakes.”
Taking the above as an experience, there also different reasons why the newly Master plan of Finfinne should not be implemented on Oromo people. Some of the reasons are:
1. It will bring Extreme Poverty: It is inevitable that the local Oromo farmers lost their land in the name of investment and urbanization. This means that the Oromos are systematically cleaned from their own land, as they were cleaned from Finfinnee in earlier days. Hence, the local farmers lose their land which is part of their permanent asset. After the lose their land, the farmers will going to work for 300 birrr in the factory or serve as house servant or home guard, which is already started. By doing so, the farmers face extreme poverty. In addition, the gap between rich and poor will very high. For example, one writer described the impact of “investment” saying:
“The current regime has sold out more than 3 million hectares of fertile land to the foreigner investors after forcefully displacing Oromo farmers from their ancestral land. The grabbing of land ended the indigenous people without shelter and foods. This displacement of the Oromo people accompanied by limitless human rights violations set the Oromo to be the vast number of immigrants in the Horn of Africa.”
2. Family displacement and disintegration: Members of a family will be displaced and disintegrated as a result of loosing their land. In addition, the workers of Finfinnee special zone will be displaced as they are working in Afan Oromo.
3. Abuse of constitutional rights: After long year of struggle and sacrifice of thousands of Life, Afan Oromo given constitution right to be used in administration, school and other sectors in Oromia region. This is one of the basic objectives that Oromos has been struggling. However, if the master plan is going to be implemented, working language of Finfinnee City, Amharic, is going to be used in the areas. By doing so, the local people will be forced to learn new language to use it for different purpose. The measure will take back Oromo to the “Atse” region. The Federal Constitution states “Every people, nation and nationality have the right to speak, to write and to develop their own language, as well as to express, to develop and to promote their culture and history.Article 39” will be clearly violated. The Oromo living in Finfinnee Special Zone will lose the rights that the FDRE constitution guarantees them.
4. Academic and psychological impacts on Oromo students: If the newly proposed master plan of Finfinnee City is going to be implemented, Oromo students living in the surrounding area will attend their education in Amharic, which is second language to the students. It is strongly argued that using the native languages of students as a medium of instruction is a decisive factor for effective learning However, this situation, failure to give a role to native languages and largely depending on second/foreign language instruction, brought various difficulties to students. The students are expected to entangle not only with learning the subject matters but also the language itself. It also creates difficulty to students in expressing themselves and as a result it limits their classroom participation as there is fear of making mistakes. In addition, it is a barrier to smooth classroom communication. It is also argued that use of a second/foreign language in education negatively affects the ability and the ease with which knowledge is acquired by students. It also affects the performance of students and creates difficulties in developing their cognitive skills. Moreover, giving low status to native languages of students in educational setting leads to marginalization of majority of the citizens from active engagement in the development arena. In general, the master plan will have negative impacts on Oromo students in various academic aspects.
5. Impact on Identity and Culture of Local Oromo People: The new plan will make Oromos to lose their identity and culture, like the previous regimes did. This is because people having different identity and culture are going to settle on Oromo land. The settlers will push out the Oromo identity and replace by their own. The Oromo’s will have very limited opportunity to exercise their cultural value and linguistic form. The language and cultural development will be also hampered by the new plan.
6. Economic impact: If the master plan is going to be realized, the Finfinnee City Adminstration will control all economic aspects of the areas. The income that is collected from different factories will be taken. The Oromiya government will loose great income to Finfinnee city administration.
7. Impact on Natural Resource and Environment: As the result of the plan, there will be overspread ground and surface water pollution. In addition, there will be severe deforestation and natural resource depletion.
8. Cutting Oromia into East and West Regions: The new Master Plan of Finfinne city will cut the current Oromia into two parts i.e. Eastern and Western. This is because the Central and great part of Oromia is proposed to be taken and incorporated into Finfinnee. Hence, the Central part that joins East and West will be taken.
D. What Should be done to Save the Oromo People around Finfinnee
As shown above, the master plan is so disadvantage for Oromia. In general, if we see the plan, it will affect local Oromo people in various aspects. However, the government who is supposed to represent the Oromo people is unable to see the danger. So we kindly ask the Oromos at home and Diaspora and other concerned bodies to forward ways and mechanisms to stop the intended plan. We ask the Oromo people and international communities, who will stand for the Oromo’s living around Finfinnee??
If we read an honest history of the present and past Governments of Ethiopia, we would conclude that the present Government is truly facing a difficult dilemma. At the dawn of the 21st century, we can neither run away from ourselves nor hide our realities. We have to face our generation and the historical realities of our time. It is undeniable that today, people demand respect for their human and national rights. Above all, people will not rest until their identity and their sovereignty over what is theirs is ensured. These are the peoples’ most burning issues. They realize that they have to make utmost effort of their own. It is within the context of the above-mentioned framework that the Oromo people resolutely demand their rights and freedom. It is to those who want to deny the rights and freedoms of the people that we are most bitterly opposed. It is a crime to deny the national identity and sovereignty of a people no matter how sophisticated the tactics used to do so. It is equally wrong to see the national desire of a people from a selfish perspective. It is based on the above concepts and precepts that the Oromo people continue their unceasing and bitter struggle against being treated as second class citizens. We know that our struggle is just for it is motivated by our desire to preserve our dignity and identity as a people.
We, the sons and daughters of the Oromo people, strenuously oppose the implementation of new Master Plan for Finfinne administration because we fully understand the historical development of the desire of other people to displace the Oromo people in order to benefit the non-Oromo new comers and their lackeys in this country. This highly orchestrated conspiracy, the present Oromo generation shall not tolerate at any cost. It will steadfastly and resolutely resist the conspiracy.
We also request international communities to put pressure on FDRE/TPLF Government and Finfinnee City Administration to stop the proposed Master Plan, which directly or indirectly harm the Oromo people.
We call on the Federal Government of Ethiopia, House of Peoples’ Representatives, the Federation Council, the Oromia Council to stop clearing Oromo people from their home Land in the name of inequitable Development and replacing others on their land.
Please generate comments as many as possible on what should be done about the plan.
May Waaq Gurraacha help us!
From: Sabbontoota Oromoo, Oromia.
We are always Oromo First!!!!
Sabbontoota Oromo can be reached at sabboontotaaoromo@yahoo.in
Ethiopia: Raya under destruction
 Raya refers a tract of land stretching from Ala wuha in the south to Alaje in the north. That is bigger than Adwa and Axum awrajas combined. Historically, this is where the Weyane rebellion started in 1928 as a spontaneous reaction to a repressive system of the time. Originating in their present day Kobo wereda, the revolt would quickly spread to cover the entire Raya and Wejerat provinces. Later, the inhabitants of Enderta joined the revolt and a sort of quasi-organized alliance was formed after a decade of Raya and Wejerat rebellion. This alliance, Weyane, would emerge so potent that by its heyday it practically liberated the provinces of Raya, Wejerat and Enderta. The imperial government with the support of British Air force resorted to aerial bombardment of the rebel held areas which caused a wide-spread damage, including complete erasure of villages. However, the most detrimental factor that actually caused the demise of Weyane was to come from none other than Adwa people. In 1943, Dejazmach Gebrehiwot Meshesha along with a dozen of Adwans exploited the trust vested on them to assassinate the leaders of the Weyane movement. This is significant for in the Ethiopian tradition, at least until then, if one manages to kill the leader one will win the battle. Meshesha and co. breach of the traditional trust and value was so venomous that even to this date mistrust and resentment runs high in Raya. It is to be noted that if not for Meshesha of Adwa, the people were in a very strong bargaining position and if one has to look how similar revolts in Bale and other regions were resolved, the rebels demand for better governance was within reach. As a thank you for their contribution, Meshesha and his fellow Adwans were rewarded heavily by Haileselasse while a series of punitive attacks continued on the ‘originators’ of Weyane and ultimately Raya was divided between Wollo and Tigray.
Raya refers a tract of land stretching from Ala wuha in the south to Alaje in the north. That is bigger than Adwa and Axum awrajas combined. Historically, this is where the Weyane rebellion started in 1928 as a spontaneous reaction to a repressive system of the time. Originating in their present day Kobo wereda, the revolt would quickly spread to cover the entire Raya and Wejerat provinces. Later, the inhabitants of Enderta joined the revolt and a sort of quasi-organized alliance was formed after a decade of Raya and Wejerat rebellion. This alliance, Weyane, would emerge so potent that by its heyday it practically liberated the provinces of Raya, Wejerat and Enderta. The imperial government with the support of British Air force resorted to aerial bombardment of the rebel held areas which caused a wide-spread damage, including complete erasure of villages. However, the most detrimental factor that actually caused the demise of Weyane was to come from none other than Adwa people. In 1943, Dejazmach Gebrehiwot Meshesha along with a dozen of Adwans exploited the trust vested on them to assassinate the leaders of the Weyane movement. This is significant for in the Ethiopian tradition, at least until then, if one manages to kill the leader one will win the battle. Meshesha and co. breach of the traditional trust and value was so venomous that even to this date mistrust and resentment runs high in Raya. It is to be noted that if not for Meshesha of Adwa, the people were in a very strong bargaining position and if one has to look how similar revolts in Bale and other regions were resolved, the rebels demand for better governance was within reach. As a thank you for their contribution, Meshesha and his fellow Adwans were rewarded heavily by Haileselasse while a series of punitive attacks continued on the ‘originators’ of Weyane and ultimately Raya was divided between Wollo and Tigray.When the TPLF started the armed insurrection in Ethiopia, it took little time to transform itself as an Adwa-only club by the same inherited act of treachery. The legacy of resentment that Meshesha and co. left means TPLF-Adwa had hard time to set foot in Raya. Hence, they needed to come up with a trick and did it so by cosmetically inserting the word Weyane in the Tigrigna version of its name. Taken with the harsher realities under DERG, Rayans reluctantly sided with TPLF on the principle of the lesser devil. Soon, tens of thousands of Raya youth joined the TPLF, including forming the majority and the backbone of Hadush “Hayelom” Ariaya’s fighting force that brought the little known“Hayelom” into prominence. However, if the experience of my village is anything, it is fair to conclude that almost all the Raya recruits ended up as cannon fodders. Those who survived, especially the independent and rational ones, would have never escaped the Meles-Sebhat death squad. In Raya, for example, it is not uncommon to talk to your relative TPLF fighter over the phone in the morning only to be notified of his death of “natural” consequences on the same day. I will say more on the motives next time. But for now, I want to draw your attention to the following Table, which is taken from the 1994 and 2007 population census of Ethiopia. I think this illustrates how the Raya and Adwa are faring under the TPLF-Adwa administration.

Clearly, 7 towns (Robit, Gobiye, Waja, Mersa, Korem, Wedisemro, Chelena) of Raya from the total 11, i.e., 64% of the town that existed in the 1994 Census Ethiopia have died or are dying. Well, with Adwa awraja towns the figures show a hard-to-believe growth registering as ridiculous as 1033% for Gerhusenay, Idegaarbi(377%), Nebelet(266%); even noticeable is the emergence of a novel city (Diobdibo) in the 2007 census, attesting to the developmental and modernization campaigns in Adwa rural areas as well. The bar graph of the rate at which towns are expanding (Adwa) or shrinking (Raya) shown below can only be a proof that in the so-called Tigray “killil” both, depending on the area, de-constructive and constructive policies are in operation. To the unsuspecting, it may occur that this might have to do with the pre-1991 TPLF bandit caused civil war. However, it is not quite so for, for instance, there was no single bomb that was dropped on Adwa towns nor was a confrontation in populated areas in the entire Adwa awraja. There was insignificant causality as far as the civilian population of Adwa is concerned for the TPLF military engagement tactic in Adwa/Axum area was totally different from the rest awrajas. For example, Korem town alone might have received far more arial bombardment than the entire Adwa awraja. From SehulMikael (the Godfather of Ethiopia’s disintegration), to Meshesha-Sebhat-Meles-Sebhat(again), there exist very little dissimilarity. Right now, Alamata, the only remaining city not to die fast enough as Adwans would have liked to see, is under open destruction. The residents never complained on the absence of developmental activity but never expected that the Adwa administration of the city will come-up with a destruction agenda. Surprised by the revelation, the unsuspecting residents went to Mekelle to air their grievances in the hope that the big men there might be rational and take proper action. However, Abay Woldu’s administration did not give it a second to listen; just ordered more Bulldozers, armored tanks and a battalion to effectively carry out the planned destruction. Worse, those who complained the demolishing of their belonging are rounded-up and now languish in Adwa operated secret Tigrayan jails
Right now, Alamata, the only remaining city not to die fast enough as Adwans would have liked to see, is under open destruction. The residents never complained on the absence of developmental activity but never expected that the Adwa administration of the city will come-up with a destruction agenda. Surprised by the revelation, the unsuspecting residents went to Mekelle to air their grievances in the hope that the big men there might be rational and take proper action. However, Abay Woldu’s administration did not give it a second to listen; just ordered more Bulldozers, armored tanks and a battalion to effectively carry out the planned destruction. Worse, those who complained the demolishing of their belonging are rounded-up and now languish in Adwa operated secret Tigrayan jails
Reference:
- Central Statistical Authority Ethiopia: The 1994 populaion and Housing Census of Ethiopia. Results for Tigray region, Volume 1, Statistical report.Table 2.2, Page 11
- Central Statistical Authority Ethiopia: The 1994 populaion and Housing Census of Ethiopia. Results for Amhara Region, Volume 1, Statistical report.Table 2.2, Page 13
- The 2007 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia: Statistical Report for Tigray Region, Table 2.1, page 7
- The 2007 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia: Statistical Report for Amhara Region, Table 2.2, page 11
http://ethiofreespeech.blogspot.co.uk/2014/02/ethiopia-raya-under-destruction.html?spref=fb











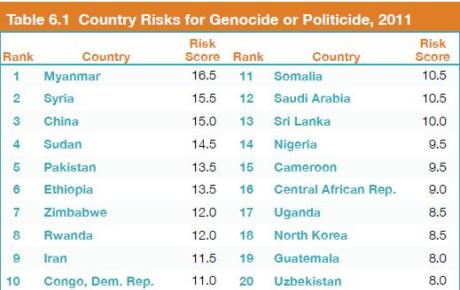






















You must be logged in to post a comment.