Stop aid to Tyrants: It is time to a new development model April 14, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Finfinnee, Food Production, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Land Grabs in Africa, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Poverty, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“Compare free development in Botswana with authoritarian development in Ethiopia. In Ethiopia in 2010, Human Rights Watch documented how the autocrat Meles Zenawi selectively withheld aid-financed famine relief from everyone except ruling-party members. Meanwhile democratic Botswana, although drought-prone like Ethiopia, has enjoyed decades of success in preventing famine. Government relief directed by local activists goes wherever drought strikes.”- http://time.com/23075/william-easterly-stop-sending-aid-to-dictators/
Traditional foreign aid often props up tyrants more than it helps the poor. It’s time for a new model.
Too much of America’s foreign aid funds what I call authoritarian development. That’s when the international community–experts from the U.N. and other bodies–swoop into third-world countries and offer purely technical assistance to dictatorships like Uganda or Ethiopia on how to solve poverty.
Unfortunately, dictators’ sole motivation is to stay in power. So the development experts may get some roads built, but they are not maintained. Experts may sink boreholes for clean water, but the wells break down. Individuals do not have the political rights to protest disastrous public services, so they never improve. Meanwhile, dictators are left with cash and services to prop themselves up–while punishing their enemies.
But there is another model: free development, in which poor individuals, asserting their political and economic rights, motivate government and private actors to solve their problems or to give them the means to solve their own problems.
Compare free development in Botswana with authoritarian development in Ethiopia. In Ethiopia in 2010, Human Rights Watch documented how the autocrat Meles Zenawi selectively withheld aid-financed famine relief from everyone except ruling-party members. Meanwhile democratic Botswana, although drought-prone like Ethiopia, has enjoyed decades of success in preventing famine. Government relief directed by local activists goes wherever drought strikes.
In the postwar period, countries such as Chile, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan have successfully followed the path of free development–often in spite of international aid, not because of it. While foreign policy concerns have often led America to prop up dictatorial regimes, we need a new rule: no democracy, no aid. If we truly want to help the poor, we can’t accept the dictators’ false bargain: ignore our rights abuses, and meet the material needs of those we oppress. Instead, we must advocate that the poor have the same rights as the rich everywhere, so they can aid themselves.
Easterly is the co-director of New York University’s Development Research Institute and author of The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor.
Read further at original source@
http://time.com/23075/william-easterly-stop-sending-aid-to-dictators/
As protestors from Kiev to Khartoum to Caracas take to the streets against autocracy, a new book from economist William Easterly reminds us that Western aid is too often on the wrong side of the battle for freedom and democracy. In The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor, Easterly slams thedevelopment community for supporting autocrats, not democrats, in the name of helping the world’s poorest. Ignoring human rights abuses and giving aid to oppressive regimes, he maintains, harms those in need and in many ways “un-develops” countries.
The Tyranny of Experts takes on the notion that autocracies deliver stronger economic growth than freer societies. Easterly argues that when economic growth occurs under autocratic regimes, it is more often achieved at the local level in spite of the regime’s efforts. In some instances, growth under autocracies can be attributed to relative increases in freedoms. He points to China as an example of this, attributing the country’s phenomenal growth to its adoption of greater personal and economic freedoms, especially compared to the crippling Maoist policies of the past.
Easterly also rejects the myth that dictators are dependable and that a certain level of oppression should be overlooked for the sake of economic growth and overall prosperity. Most recently, the violence and chaos following the 2011 Arab uprisings has made some nostalgic for the stable, if undemocratic, governments that kept civil unrest in check, allowing for a measure of economic development to take hold. Easterly stresses that instability and tumult in the wake of ousting a dictator is not the fault of an emerging democracy, but instead an understandable result of years of autocratic rule. The answer is not to continue to support autocrats in the name of stability, but rather to start the inevitably messy process of democratization sooner.
Easterly is of course not the first to call attention to the importance of prioritizing rights and freedoms in the development agenda. Scholars from Amartya Sen to more recently, Thomas Carothers and Diane de Gramont, have also advocated for a rights-based approach to development. In Pathways to Freedom: Political and Economic Lessons From Democratic Transitions, my coauthors and I similarly found that economic growth and political freedom go hand-in-hand.
Still, the hard questions remain: how to help those without economic and political freedoms? And when should donors walk away from desperately poor people because their government is undemocratic? Easterly argues that the donor community should draw the line with far more scrutiny than it does today – not just at the obvious cases, such as North Korea, but with other undemocratic countries, such as Ethiopia, where human rights abuses are rampant. He debunks the notion that aid can be “apolitical,” arguing that it is inherently political: giving resources to a government allows it to control and allocate (or withhold) resources as it sees fit. The aid community should focus on ways to help oppressed populations without helping their oppressors. For example, scholarship programs, trade, and other people-to-people exchanges can give opportunities to people in need. At the very least, Easterly argues, development actors should not praise oppressive regimes or congratulate them on economic growth they did not create.
Rather than being seduced by “benevolent dictators,” Easterly urges donors to focus their energy on “freedom loving” governments that need help. The Millennium Challenge Corporation is a step in the right direction but, as Easterly pointed out during the CFR meeting, MCC’s approach is undermined by other U.S. aid agencies, such as USAID, that continue to assist countries even when they don’t meet certain good governance and human rights standards.
Easterly also emphasizes the need for aid organizations to be more transparent about where their money is going. Robert Zoellick made strides in this direction during his tenure as World Bank president. But more recent developments suggest that the Bank still has a way to go in becoming more open and accountable. (Easterly noted that an initial invitation to speak about The Tyranny of Experts at the World Bank was later rescinded for “scheduling reasons.”) http://blogs.cfr.org/development-channel/2014/03/14/helping-the-oppressed-not-the-oppressors/#cid=soc-facebook-at-blogs-helping_the_oppressed_not_the_-031414
No democracy, no aid
http://stream.aljazeera.com/story/201403190105-0023568
March 26, 2014 (The Seattle Times) — SOMEHOW — probably my own fault — I have wound up on Bill Gates’ list of the world’s most misguided economists. Gates singled me out by name in his annual 2014 letter to his foundation as an “aid critic” spreading harmful myths about ineffective aid programs.
I actually admire Gates for his generosity and advocacy for the fight againstglobal poverty through the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation in Seattle. We just disagree about how to end poverty throughout the world.
Gates believes poverty will end by identifying technical solutions. My research shows that the first step is not identifying technical solutions, but ensuring poor people’s rights.
Gates concentrates his foundation’s efforts on finding the right fixes to the problems of the world’s poor, such as bed nets to prevent malarial mosquito bites or drought-tolerant varieties of corn to prevent famine. Along with official aid donors, such as USAID and the World Bank, the foundation works together with local, generally autocratic, governments on these technical solutions.
Last year, Gates cited Ethiopia in a Wall Street Journal guest column as an example, a country where he described the donors and government as setting “clear goals, choosing an approach, measuring results, and then using those measurements to continually refine our approach.”
This approach, Gates said, “helps us to deliver tools and services to everybody who will benefit.” Gates then gives credit for progress to the rulers. When the tragically high death rates of Ethiopian children fell from 2005 to 2010, Gates said this was “in large part thanks to” such a measurement-driven program by Ethiopia’s autocrat Meles Zenawi, who had ruled since 1991. Gates later said Meles’ death in August 2012 was “a great loss for Ethiopia.”
Do autocratic rulers like Meles really deserve the credit?
Gates’ technocratic approach to poverty, combining expert advice and cooperative local rulers, is a view that has appealed for decades to foundations and aid agencies. But if technical solutions to poverty are so straightforward, why had these rulers not already used them?
The technical solutions have been missing for so long in Ethiopia and other poor countries because autocrats are more motivated to stay in power than to fix the problems of poverty. Autocracy itself perpetuates poverty.
Meles violently suppressed demonstrations after rigged elections in 2005. He even manipulated donor-financed famine relief in 2010 to go only to his own ruling party’s supporters. The donors failed to investigate this abuse after its exposure by Human Rights Watch, continuing a long technocratic tradition of silence on poor people’s rights.
Rulers only reliably become benevolent when citizens can force them to be so — when citizens exert their democratic rights.
Our own history in the U.S. shows how we can protest bad government actions and reward good actions with our rights to protest and to vote. We won’t even let New Jersey Gov. Chris Christie get away with a traffic jam on a bridge.
Such democratic rights make technical fixes happen, and produce a far better long-run record onreducing poverty, disease and hunger than autocracies. We saw this first in the now-rich countries, which are often unfairly excluded from the evidence base.
Some developing countries such as Botswana had high economic growth through big increases in democratic rights after independence. Botswana’s democrats prevented famines during droughts, unlike the regular famines during droughts under Ethiopia’s autocrats.
Worldwide, the impressive number of developing countries that have shifted to democracy includes successes such as Brazil, Chile, Ghana, South Korea and Taiwan, as well as former Soviet Bloc countries such as the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovenia.
If the democratic view of development is correct, the lessons for Gates are clear: Don’t give undeserved credit and praise to autocrats. Don’t campaign for more official aid to autocrats. Redirect aid to democrats. If the democratic view is wrong, I do deserve to be on Gates’ list of the world’s most misguided economists.
http://ayyaantuu.com/africa/guest-the-flaw-in-bill-gates-approach-to-ending-global-poverty/
Related findings:
The UK government is providing financial aid to human rights abusers in Ethiopia through funding training paramilitaries, who perpetrate summary killings, rape and torture in the impoverished African country, local media reported.
Through its foreign aid budget, the UK government provides financial support to an Ethiopian government security force known as the “special police” as part of its “peace and development programme”, which would cost up to £15 million in five years, The Guardian reported.
The Department for International Development warned in a leaked document of the “reputational risks” of working with organizations that are “frequently cited in human rights violationallegations”, according to the report.
The Ethiopian government’s counter-insurgency campaign in Ogaden, a troubled region largely populated by ethnic Somalis is being enforced by the 14,000-strong special police.
This is while police forces are repeatedly accused by Human Rights Watch of serious human rights abuses.
Claire Beston, the Amnesty International’s Ethiopia researcher, said it was highly concerning that Britain was planning to work with the paramilitary force.
The Historic Inauguration of Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument and Aannoolee Historical Museum: Siidaa Wareegamtoota Aannolee April 12, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument, Dhaqaba Ebba, Finfinnee, Hetosa, Oromia, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo Identity, Oromummaa, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Self determination, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument, African Studies, Economic and Social Freedom, Governance issues, Hetosa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development
2 comments



The Abyssinian war lord Menelik, also known as African Hitler, cut the right hands and breasts of men and women, respectively, during his conquest of Oromia and the rest of today’s people and lands of Southern Ethiopia in 1880s. During Emperor Hailesellasie and Mengistu Hailemariam’s Dergue time the erection of Aannole memorial monument was not thinkable. The present state of Oromia has spent over a million dollar to build the Aanolee Oromo Martyrs’ memorial monument. Many admirers of the genocidal Menelik have opposed to the erection of memorial center but there is nothing they could do to prevent this inauguration. Aannole observed the largest human gathering on the 6th April 2014 on the event of inauguration of the monument and the historical museum.







The Aannolee Oromo Martyrs’ Memorial Monument was unveiled in Hetosa, Arsi, Oromiyaa, on April 6, 2014 – also inaugurated was the Aannolee Cultural/Historical Museum. The Monument commemorates the Oromo martyrs whose limbs and breasts were cut off atrociously by the invading Abyssinian/Shoan Amhara army of Menelik II in 1886. Known as the harmaf harka muraa Aannolee, the Menelik’s Abyssinian/Shoan Amhara army mutilated an unknown number of Oromo men’s right hands and Oromo women’s breasts for resisting Abyssinia’s conquest of the Oromo land.
According to the recently published book by Prof. Abbas H. Gnamo, “Conquest and Resistance in the Ethiopian Empire, 1880-1974 – The Case of the Arsi Oromo,” the Aannolee Oromo Martyrdom has “become the symbol of Oromo resistance.”
Prof. Gnamo continues:
“Of all the brutalities committed by the Shoan army and its leaders against the Oromo, the worst was the Anole mutilation known as harmaf harka muraa Anole (the mutilation of hands and breasts at Anole) – a tragedy on which Ethiopian sources are silent …
… Anole is located about 25km north of Asella, an area where most battles took place and where the Arsi inflicted heavy losses on the Shoan army. Anole seemed to have been chosen to avenge Shoan losses and to teach a lesson to the Arsi who still resisted after their shattering defeat at Azule on September 6, 1886. Arsi strong men and women were assembled under the pretext of concluding peace. All the men and women present, whose exact number was unknown perhaps more than thousand people, were mutilated; their right hands and right breasts were cut off. As a further form of humiliation, fear and terror, the mutilated breasts and hands were tied around the necks of the victims who were then sent back home.”
http://gadaa.com/oduu/25205/2014/04/06/in-pictures-the-unveiling-of-the-aannolee-oromo-martyrs-memorial-monument-in-hetosa-oromiyaa/



THE EXPANSION OF THE AMORPHOUS ADDIS ABABA, THE ENDLESS PERSECUTION AND EVICTION OF TULAMA OROMOO April 6, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo Valley, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny.Tags: African Studies, Finfinnee, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
The deliberate expansion of the amorphous city they call “Addis Ababa” is politically created to divide Oromiyaa into east and west sector. It is not a master plan. It is an evil plan mastered to consummate an evil goal.
When we see the history of Abyssinian political philosophy, from which we have a written record, it is entirely based on the philosophy of depriving the Oromos from having any right to homeland. To convert Oromummaa to Amaarummaa and ultimately to Itiyophiyawwinnet has been the policy in action up to this very day.
What happened to those Oromos who were living in Finfinnee for centuries? Particular mention has to be made about those Tulama Oromo groups of Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Aabbuu, Jillee. The answer is very simple: They were mercilessly decimated; their villages burnt down, their pasture and arable lands confiscated and shared among the invading Manzian Nagasii families of whom the Dejazmach Mangasha Seifu and the Ras Birru families were the most notorious ones. Thereafter, the Oromo territory occupied by Matcha-Tulama was officially changed to the expanding Kingdom of Showa, a detached enclave from Gonder, Abyssinia. Finfinnee was given a new colonial name “Addis Ababa”, just like Zimbabwe was changed to Rhodesia, Harare to Salisbury. Under this excruciating condition, the conquered Matcha-Tulama region had to lose its historic significance and had to be involuntarily submitted to the colonial name Showa.
Among the major Oromo descent groups, the Matcha-Tulama group has got one of the largest populations, stretching on vast area of land in central and western Oromia. As we are able to learn from our fathers, Matcha and Tulama are Borana brothers, being Tulama angafa (first born) and Matcha qixisuu (second born son). As common to all Oromo ethno-history, the tradition that governs the social role of “angafa and qixisuu”, which begins right from the immediate family unit, has a deep genealogical meaning and social role in re-invigorating the solidarity of the nation. From the earliest time of which we have a tradition hanging down to us,
- Matcha-Tulama Oromo has had a supreme legislative organ known as Chaffe. The Chaffe legislates laws which will eventually be adopted as Seera Gadaa
They have a senatorial council known as “Yaa’ii Saglan Booranaa”, in which elected individuals from major clans are represented. The function of Yaa’ii Saglan Booranaa is to deliberate on issues pertaining to regional issues, resolve inter-clan disputes and oversees how interests of each clan in the confederacies are represented; how local resources are fairly shared and wisely utilised according to the law.
- These two northern Boorana brothers are historically referred to as Boorana Booroo or Boorana Kaabaa
- Among the known five Oromo Odaas, Odaa Nabee and Odaa Bisil are found in Boorana Booroo
However, beginning from the 13th century onward, the Match-Tulama country (Boorana Booroo), adjacent to Abyssinian border, has begun to be ravaged by a group of individuals whose legendary genealogy connects them to a certain King Solomon of non-African origin. They came and settled at a place they call “Manz”.They organised themselves at this place, and started to attack neighbouring villages of Cushitic Oromo family stock of Laaloo, Geeraa and Mammaa. The attacked villages were gradually incorporated into the expanding Manz, which eventually developed to a military outpost known as Showa in the late 18th century. Hereafter, they declared themselves “Ye Negasi Zer, the root of Showa Amhara Dynasty.
After vanquishing Agaw people’s identity and sovereignty on the northern frontier, the Solomonic Negasi Dynasties of Showa intensified their attacks against the Match-Tulama of Borana and the Karrayyu of Barantu Oromos. In such turbulent situation, the rule of yeNegasi Zer entered nineteenth century era, which ushered the era of the Scramble for Africa by European imperialist powers. From Africa, it was only King Minilik of Showa (1866-1889) who was recognised as a partner and invited to attend the Berlin Imperialist Conference of 1884. In this conference, Minilik was represented by his cousin, Ras Mekonnen Tenagneworq Sahile-Sellasie (1852-1906). After completing their mission, King Minilik and the European imperialist powers made concession on border demarcation. After the border demarcation had been completed, a systematic elimination of his prominent general, Ras Goobanaa Daacci (1819-1889), was meticulously carried out. Minilik was so confident to declare himself Emperor of Ethiopia (1889- 1913).This was the Ethiopia, the first time in the history of the region, that brutally annexed and included Oromo, Sidama, Walaita, Kaficho, Beneshangul, Gambella, and others to the expanding of Abyssinia.
The years 1887-89 were the boiling point for Minilik’s declaration of being “Emperor of Ethiopia, yeItiyophiya Nuguse, nägest. Why?
- Because, it was the time when he exterminated the Gullallee Oromo from the marshy-hot spring and pasture land of Finfinnee and collectivised the place under a new colonial name Addis Ababa.
- Because, it was the time when he built full confidence in himself and built his permanent palace at Dhaqaa Araaraa, a sacred hill, where the evicted Oromos peacefully used to sit together and conduct peaceful deliberation for reconciliation.
- It was the time when he annexed three-fourth of southern peoples’ territories, including the Oromo territory, to the expanding Showan Dynasty and put under the iron-fist of his inderases(viceroys).
- It was the time when he assured un-shivering confidence of being continued to be assisted and advised by his European colonial partners: militarily, diplomatically and technically.
Here is the question: What happened to those Oromos who were living in Finfinnee for centuries? Particular mention has to be made about those Tulama Oromo groups of Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Aabbuu, Jillee. The answer is very simple: They were mercilessly decimated; their villages burnt down, their pasture and arable lands confiscated and shared among the invading Manzian Nagasii families of whom the Dejazmach Mangasha Seifu and the Ras Birru families were the most notorious ones. Thereafter, the Oromo territory occupied by Matcha-Tulama was officially changed to the expanding Kingdom of Showa, a detached enclave from Gonder, Abyssinia. Finfinnee was given a new colonial name “Addis Ababa”, just like Zimbabwe was changed to Rhodesia, Harare to Salisbury. Under this excruciating condition, the conquered Matcha-Tulama region had to lose its historic significance and had to be involuntarily submitted to the colonial name Showa.
In addition to the former derogatory term “Galla”, imposed on the conquered Oromos as a whole, the new regional name of Showa is prefixed to the derogatory term Galla. Hence, “ye Showa Galla” came into force as a collective insulting name in addressing the whole Oromo of Matcha-Tulama. This clearly justifies the vertical segregation policy of the conquerors for easy identification of who is who in the newly colonised territory.
Using various forms of oppressive models, Abyssinian colonial tactics and strategies have been going on violently and, now entered into the first half of the 21st century. Since the second half of the 19thcentury in particular, the oppressive models have been amassing massive firearms from European colonialist partners, enjoying diplomatic immunities and profitable political advises.
In the late 19th century, one European writer commented that, if the Abyssinians had not been armed and advised by global colonial powers of the day, notably France and Britain, late alone to defeat the ferocious Oromo forces, they could not have even dared to encroach upon the limits of Oromo borders. He wrote what he witnessed the real situation of the time as follows:
“Against the Galla [Oromo] Menelik has operated with French technicians, French map-makers, French advice on the management of standing army and more French advice as to building captured provinces with permanent garrison of conscripted colonial troops. The French also armed his troops with firearms, and did much else to organize his campaigns. Menelik was at a work on these adventures as King of Shewa during John’s lifetime; adding to his revenues and conscripting the Oromo were thus conquered by the Amhara for the first time in recorded history during the last thirteen years of the nineteenth Century. Without massive European help the Galla [Oromo] would not have been conquered at all.”
The writer further explained what he personally encountered during the campaign in the following unambiguous language:
“A large expedition was sent as far South in Arsi as frontier of Kambata to return with100, 000 head of Cattle. The king’s army fought against tribes who have no other weapons but a lance, a knife and shield, while the Amahras always have in their army several thousand rifles, pistols and often a couple cannon.—-Captive able-bodied males and the elderly were killed. The Severity of the Zamacha [campaign] was aimed at the eradication of all resistance. Whenever the army surged forward, there was the utmost devastation. Houses were burned, crops destroyed, and people executed:”
When we see the history of Abyssinian political philosophy, from which we have a written record, it is entirely based on the philosophy of depriving the Oromos from having any right to homeland. To convert Oromummaa to Amaarummaa and ultimately to Itiyophiyawwinnet has been the policy in action up to this very day. Even though the policy works on all Oromos indiscriminately, the one which has been exercising on the Oromos of Tulama in Finfinnee and surrounding areas has its own unique feature. Some of the unique features are embedded in the formation of “Addis Ababa” itself; as a seat of colonial headquarters with all its oppressive machineries. To have ample space for the settlers, to build army headquarters, to build churches in the name of numerous Saints of Greek and Hebrew origins, to build residences and offices for foreign embassies and missionaries, to build factories and storage houses the crucial demand is land. To fulfil these crucial demands of the customers, helpless Oromo peasants of the area have to be evicted. They have been under routine eviction and land deprivation since the seizure of Burqaa Finfinnee and the establishment of Ethiopian Imperial capital at this place.
It could be incorrect to think of the current TPLF-Arinnet Tigray regime as a detached entity from the whole system of Abyssinian colonial regimes, when we equate what they need against the survival needs of the peoples they generically conquered as “Galla and Shanqilla”. Though since 1991, the Ethiopian imperial system has been overtaken from the Showan Nagasi Dynasty by their junior Tigrean brethren, the life of the colonised Oromo people has been going down from worse to the worst.
What makes TPLF-Arinnet Tigray different from its predecessors is its total monopolisation of resources of the empire, right from the imperial palace to the bottom village levels, from the centre to the periphery. Arable and pasture lands, plain and forest lands, rivers and mining areas are totally under its predatory control. It is routinely evicting peasants from their plots, their only means of existence. They are selling to Chinese, Indians, European, Turkish, Pakistani, Arabians and other companies at the lowest price. In making this huge business, the most preferable area in the empire is Oromoland; of which the land around Finfinee holds rank first.
This politically architected scheme, in the name of investment and development, is daily evicting Oromo peasants around Finfinnee often with meagre or no compensation at all. As a consequence,
- some of the evicted families are migrating to cities like Finfinnee and are becoming beggars
- Some of them are leaving the country for unknown destination and found being refugees in neighbouring countries like Kenya and Yemen.
- Since most of them who have no any alternative, they remain on the sold land and become daily labourers, earning less than half dollar a day.
- Farm lands that had been producing sufficient grains of various types are now turned to produce non-edible flowers and toxic chemicals that contaminate rivers and lakes.
The incumbent Ethiopian regime of TPLF-Arinnet Tigray, more than any other imperial regimes of the past, is committed to make the Oromo people an “African Gypsy”. At one time the deceased prime minister of the Empire and EPDRF leader, Meles Zenawi, refers to the Oromos, who are numerically majority ethnic group in the Empire, said, “It is easy to make them a minority”. They are practically showing us the evil mission they vowed to accomplish. When they become rich of the richest in the Empire, the Oromo peasants they are daily uprooting are becoming poor of the poorest, being reduced to beggary and often deprived of burial sites after death. This evil work, as indicated above, has given priorities to sweep off “garbage” around Finfinnee and ultimately to encompass three-fourth of the region of “Showa” as a domain of “non-garbage” dwellers.
As vividly explained above, the Oromo of Tulama, since the onset of colonisation, have begun to be collectively addressed as “ye Showa Galla”. Those who resisted the derogatory name, the eviction, and the slavery system have been inhumanly executed or hanged. Their land and livestock have been confiscated and shared among the well-armed conquering power.
When Minilik invaded the Gullalle Oromo in Finfinnee, for instance, they remarkably resisted to the last minute but finally defeated. Those who remained behind the massacre had no other option except to leave for other regions against their choice. In their new homes, they have been even treated as collaborators of the invading “Showans” by their own kinsmen, calling them “Goobanaa”.Those able-bodied Gullallee, Eekkaa, Galaan, Abbichuu youths were involuntarily conscripted to the colonial army which is typical to all colonial policies. They were forced to go for further campaign to the south, east and west commanded by Showan fitawuraris and dejazmaches
From time to time, all Abyssinian forces, changing forms of their names, swearing in the name of Ethiopian unity and inviolable sovereignty, have never turned down the initial policy of evicting and persecuting the Oromo from their ancestral araddaa. Araddaa Oromoo is the embryonic stage whereOromummaa has begun to radiate from. Hence, by virtue of its original formation, now and then, it could not be integrated into the enforced Abyssinian policy of Itiyophiyawwinnet .
Since the enforced policy has shown no visible success for the past 130 years, this time, it has taken on to shoulder the last option of “sweeping them off” from around what they call “Addis Ababa” as a priority number one. As a consequence, came into being the destruction of Oromo survival relationship with their ancestors’ plot of land. The desecration of their shrines, sacred rivers, sacred mountains and sacred trees of which the case of Odaa and Burqaa Finfinnee, Dhakaa Araaraa and Caffee Tumaa in the vicinity of Finfinnee are quite enough to mention. TPLF’s long range missile policy of destroying Oromos’ relation to their historic araddaa is not the end. It is just the beginning extrapolated to destroy Biyyoo Oromoo.
At this critical time, any concerned Oromo should not be oblivious of the dreadful situation going on in Oromiyaa right now; in Finfinnee and surrounding areas in particular. The deliberate expansion of the amorphous city they call “Addis Ababa” is politically architected to divide Oromiyaa into east and west sector. It is not a master plan. It is an evil plan mastered to consummate an evil goal.
At this critical time, may we believe in the “No life after death”? Rather, may we are for the life right now? Those who are for the life right now are genuinely expected to show discernible power through tangible solidarity to our victimised families at home. Pursuant to our tradition, we have been nurtured learning the wisdom of “Dubbiin haa bultu”. Now, we should redirect this wisdom to “Dubbiin kun hin bultu”,that we ought to swear by great confidence to move in unison against the inhuman act, endless atrocities and perpetual eviction of our families from their ancestral araddaa. Thereof, could we recall the intrinsic wisdom of our fathers’ saying “Tokko dhuufuun namummaadha, lama dhuufuun harrummaadha?”
The Quest for Oromo’s Indigenous Knowledge and Institutions April 3, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Abbush Zallaqaa, Afaan Publication, Africa, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Finfinnee, Free development vs authoritarian model, Gadaa System, Haile Fida, Humanity and Social Civilization, Irreecha, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Language and Development, Oral Historian, Oromia, Oromia Satelite Radio and TV Channels, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo Sport, Oromummaa, Self determination, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oldest Living Person Known to Mankind, The Oromo Democratic system, The Oromo Governance System, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Toltu Tufa, Uncategorized, Wisdom.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Gadaa, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Human Rights and Liberties, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
By Iddoosaa Ejjetaa, Ph.D.*
The classical definition of knowledge was given by Plato as “justified true belief.” There are many philosophical theories to explain knowledge. The online Oxford dictionaries define knowledge as a theoretical or practical understanding of a subject [online]. The same source explain knowledge that can be implicit (as with practical skill or expertise) or explicit (as with the theoretical understanding of a subject); it can be more or less formal or systematic. According to Stanley Cavell, “Knowing and Acknowledging” the “knowledge acquisition involves complex cognitive processes: perception, communication, association and reasoning; while knowledge is also said to be related to the capacity of acknowledgment in human beings.” I am not here to write the theory of knowledge, but trying to bring the human society acknowledgement and recognition for the Oromoo nation’s indigenous knowledge.
The Oromoo Gadaa System (OGS) is an indigenous knowledge reserve institution of the Oromoo nation. It is an organic system, which is self-refining every eight years (in two four-year terms) to meet the needs of the society. The OGS is a well-structured and organized indigenous knowledge reserve that encompasses social, political, economic and military institutions that operate mainly based on self-reliance principles while Oromummaa is an act of embracing these institutions and applying the indigenous knowledge to manifest an authentic Oromoo’s cultural and national identity.
The essence of scientific education is to understand Mother Nature, daachee haadha marggoo, and human experience in relation to Mother Nature. Through scientific education we can ask questions and try to investigate or do research to find out the facts and report the new knowledge about the subject. For example, who is responsible for the creation of human being, other living and non-living things as a part of the whole nature? What if I told you that the answer to the question is Mother Nature? I guess, you would not be satisfied with the answer because it leads to another subsequent philosophical questions such as who is responsible for the creation of the Mother Nature. Again, what if I told you the answer is a God? This time, probably you would be settled and agree with me. But how do you know for sure that it is a God who is responsible for the creation of nature?
I have thought deeply about these questions and tried to find the best possible answers. I would like to share the final answer with you later on if you continue the journey with me through reading and thinking about the perplexities of human life experience.
The purpose of this paper is to share my points of view with you and highlight that the Oromoo Gadaa System is the prima source of Oromo indigenous knowledge reserve that every Oromoo person should safeguard it and reclaim it as a shared-value that can be manifested through applied Oromoo knowledge and life experience, which is often called Oromummaa. Hence, the Oromoo Qubee generation are highly encouraged to embark their scientific studies and discoveries on our forefathers’ indigenous knowledge and bring it to light to show the world that our forefathers had made significant contribution to human society and civilization by creating and developing a comprehensive and complex democratic system: the Oromoo Gadaa System and its Institutions. For the qubee Oromoo generation, I would say they have a gold mining opportunity on their own backyards and they have to go for it.
Oromoo’s Indigenous Knowledge
Indigenous knowledge is local by nature. It is primarily based on social skills and production techniques. Both social skills and production techniques employ indigenous knowledge that in turn involves the process of life-long learning and teaching. The Oromoo Gadaa System provides such indigenous knowledge reserve so as to enable the new generation to learn from and teach the generations to come. For example, Oromummaa is a social skill. The Oromoo children learn social skills: respect, love, sympathy, empathy, ethics (Safuu), sharing, helping others, communications, etc from their parents and through well-organized Gadaa institutions such as the Age group (Hiriyyaa) and Qalluu.
Like every society, the Oromoo Gadaa Society had engaged in production of goods and services for long time or millenniums. They have millennium years of farming and animal husbandry experience and knowledge. The Oromoo farmers were the first people who domesticated barley as cereal crop in the region and a coffee plant and used the coffee beans in the world. This means the Oromoo farmers had possessed a primary indigenous knowledge about these crops. This indigenous knowledge reserve, however, needs a substantial effort in the field of scientific research and documentation for learning and teaching purposes by present and future Oromoo generations.
The lack of self-ruling political right in Ethiopian Empire and the decline of the Oromoo Gadaa System of Self-governance lead to the deterioration of the Indigenous knowledge and Institutions. In addition, the absence of curiosities from the Oromoo educated class for long time and self-inflicted prejudices against Oromoo indigenous knowledge had played a significant role on its underdevelopment. The educated class is the first social group who run away from their villages and turn their back to their culture and traditional ways of life. Consequently they find themselves in the garrison cities where almost everything is imitation of modernity that has no root in the local culture or traditions. Moreover, the educated elites had been played an agent role to introduce exogenous values including foreign religion, culture of conspicuous consumption and other copy-cut life styles from the West, and Middle-East world.
As I mentioned above, because of the lack of basic human right the Oromoo as a nation has no formal indigenous institutions yet. Instead, the institutions are maintained by the Oromoo Gadaa fathers and mothers who have been serving as Oromo indigenous knowledge reserve as institution. . This means the Qubee generation scientific research and discoveries are highly dependent on the existence of Gadaa Oromoo fathers and mothers (abbootii Gadaa Oromoo) and time because if they die the institutions and knowledge will die with them. For many of them, a biological time is about running out now. One day they will leave us for good. So it is responsibilities and sacred duties of this generation to secure and backup these precious indigenous “documents” that had been inherited form the previous generations.
As JF Kennedy said, the purpose of education is to advance human knowledge and dissemination of truth. However, contrary he said, the education system in Ethiopia has been harboring ignorance, distortion and denial of the truth that effectively disabled the process of learning, thinking and bringing positive changes to our society. So I suggest to the new generation regardless of their ethnic and cultural background to use the best three doses of pills/prescription for ignorance, distortion and denial of history. They are: genuine education, genuine education, and genuine education (3-GE). Through genuine education one can learn the true essence of love (jaalala), which is unselfishness, the creator, and creatures, uumaa fi uumammaa.
Generally, indigenous knowledge (IK) are the outcome of true and genuine collective human experience. It could be knowledge about culture, tradition, history, philosophy, belief system, art, farming, biodiversity, medicine, family, economic distribution, etc. The Oromoo Gadaa System is one of such collective human experience that need to be learned as universal value to human society and pass down to the next generations.
The Predicaments of Indigenous Knowledge in Ethiopia Politically speaking, Ethiopia as a nation had never been colonized and maintained its independence while all African countries had been colonized by European states. To some extent, this is true. Practically, however, the Ethiopian Empire State had been constructed and maintained by European states and continued to operate under indirect-colonialism of Anglo-American and European States. Like all African Republics or States, the Ethiopia’s government structure, military structure, religious institutions, political and social, educational, and legal systems are highly influenced mainly by Anglo-American and European institutions including British, France, Italian, Germany, American, Japan, China, etc. Consequently, indigenous knowledge had been systematically marginalized and ignored, unfairly criticized as primitive, static and simple idea by semi-literate domestic elites or agents of exogenous institutions.
These exogenous institutions such as the Orthodox Coptic Church officials (clergy/priests) and collusion of feudal neftenyaa and self-serving local balabats in Ethiopia, for instance, had played a key role in dismantling indigenous institutions, discrediting and condemning indigenous knowledge and even blessing Menelik’s genocidal and unjust war against our people and indigenous people of the south. Here one must note that the local Oromoo balabats had played a primary role in sponsoring, defending and assigning a commanding site Oromoland to the Orthodox Churches in Oromiyaa today. In addition to the neftenyaa system, these social class is accountable historically for the decline of the Oromoo Gadaa System and underdevelopment of its Institutions. Beside this, at present the decedent of these social class still maintained their loyalty to the Orthodox Church and Ethiopia’s empire state. Some individuals even have been involving in the Oromoo liberation struggle by dressing a sheep skin to saboteur the genuine aspiration of Oromians for freedom and independence. This author suspect that this very social class had contributed to the weakness of Oromia liberation camp.
The Impacts of Church Education on Indigenous knowledge
The Orthodox Coptic church jealously dominated the education system in Ethiopia. The Orthodox Coptic Church in Ethiopia had provided training in reading and writing in Ge’ez and Amarigna (Amharic) at primary school level to limited areas and people of the country. To summarize the church education in Ethiopia: elementary pupils had to learn to read, write, and recite the Dawit Medgem (Psalms of David). There are 15 sections, called negus (kings), which normally took two years to master. Next they learned to sing kum zema (church hymns), which took four years, and msaewait zema (advanced singing), which took an additional year to learn. Liturgical dancing and systrum holding required three years. Qine (poetry) and law required five years to learn. The interpretation of the Old and New Testaments, as well as the Apostles’ Creed, took four years on average, while the interpretation of the works of learned monks and priests took three years. When a student knew the psalms by heart, he had mastered the “house of reading” and was now considered an elementary school graduate. As one can see there is no a single grain of indigenous knowledge or belief system had been taught by the Orthodox Church.
The Orthodox Coptic Tewahido Church is considered by government as indigenous institution, when it is imported and imposed on native culture. Both religions Christian and Islam were imported and imposed on native population, such as the early Christianized ethnic Tigray and Amhara and then ethnic Oromoo, Sidama, and other people of the south, by few clergies and foreign religious crusaders. These institutions had replaced the indigenous belief system, institutions and knowledge over time. As a result, the majority, if not the entire population, ethnic Tigray and Amhara believe that Bible is the source of their history and culture. As one can easily understand, the people of Tigray and Amhara have lived far more years than the bible does, which is two thousand years. As people who residing in East Africa, the Tigray and Amhara people must have had indigenous culture and knowledge. What are they?
Despite the claim of three thousand years history of civilization, Ethiopians exposed to non-church education or modern education in 1920s. The ministry of education established in 1930s. Secondary schools established in 1940s, and higher education, Addis Ababa University, established in 1960s. In similar way, the modern education system had also failed in teaching and conducting research on indigenous knowledge so as to integrate it into the modern education. As a result, creativity, inventions and innovations have seen as odd culture to our society. On the contrary, receiving aid, economic migration, conspicuous consumption of imported goods including education and dependency on Western advanced societies or institutions have become a culture.
Therefore, it is up to the Habesha (Tigre and Amhara), the Oromoo and other ethnic groups of the new generation to dig deep down to find out their respective indigenous knowledge that deep rooted in their culture and traditions and pass down from one generation to other generations by their native ancestors if any and re-evaluate the existing very controversial written history, which is biased and by large based on fiction history. The cycle of self-discrimination must end by the new generation. By doing this they can find shared human values that would allow them to live in peace without disrespecting one another as good neighbors and citizens of their respective nation. So one must understand that no one would agree on imported history that was written by the followers and supporters of Christianity crusaders, war lords, kings, dictators and agents of the Western discriminatory and racist institutions of the time as shared human value and history of our respective people in our time. The time and world have changed forever.
The present suspicion, political conflicts and all forms of problems in our region will not be solved without recognizing and applying indigenous knowledge. The lasting resolutions for the problems can be achieved if every member of our society or nation adults learn and teach their younger generation good social skills, which are critical to successfully functioning society. Basic social skills enable adults and children to know what to say, how to make good choices, and how to behave in adverse situations. The extent to which young people possess good social skills can influence their adult behavior in decision making, conflict management and problem solving. Social skills are also linked to the quality of the school environment. The Church and modern education in Ethiopia, unfortunately, had been denying members of our society these good basic skills such as respect, appreciation, empathy, apology, truthfulness, positive attitude about others, etc. Instead, the system allowed social ignorance such disrespect, occupational despise, ethnic chauvinism, fear, the divine right of the kings and honor for ruling class. As a result, the Ethiopian empire has produced highly educated class like Dr. Getachew Haile without basic and good social skills; it seems that he passed through poor socialization as one can understand the meaning of his name, ‘lord of …power’, which is false-self has given to him by his parents
and trying his best to make them proud by being discourteous and rude to the Oromoo people. Dr. Getachew Haile, be nice!
The black people or African descents are subject to institutional discrimination and racism more than any other races in the world including the holy land- Israel and Saud Arabia. Do you know why? The reasons can be many, but one of the reasons is imitation of ideas. The black people are the most imitating of other societies’ idea. They did not protect and develop their own indigenous institutions (political, religious, cultural and socio-economic institutions) to shape their lifestyle and influence others. No other nations are imitating Africans’ culture, religion, lifestyles but the Africans tend to imitate others about everything that life needs. Some African or extremists trying to be more imitator and more knowledgeable about the culture, religion and ideology than the original inventor or creator of the idea. It is understandable that human being has ability to imitate and all cultures imitate ideas from original culture. The question I would like ask the readers is why the changes are in one direction only. Why African descents imitate ideas of the other culture when the other culture do not imitate the African idea or world view?
For example, black Africans including Ethiopians has been pretending as if they have better known about the Jesus of Nazareth more than the Israelis and Prophet Muhammad more than the Arabs; Marxism and Leninism or communism more than Russians; democracy more than Americans and Western societies. These blind optimists about other’s idea are cynical at the same time about their own indigenous knowledge; they are willing to abuse, jail, torture and murder their own innocent people for the authenticity of imported ideas, religious and political ideology. In the case of Ethiopia, the king Menelik II and Yohanness II – holy war and wildish conquests were a case in point. They had imitated from the history of European middle-age idea of religious crusaders and empire builders. The Abyssinian kings had been acted as proxy war lords of European colonial powers and committed incalculable atrocity against the Oromo people and other black people in East Africa. In addition, these Abyssinian kingdom were one of the worst Africa’s kingdoms who sold Africans, their own race, to British, Arabs and other European white race for the exchange of European firearms to conquer the land of other nations and subjugate the people and build the empirical institutions based on European ideas and political model. What most disgracing is when people like Dr. Getachew Haile and his like trying to keep the truth elusive and misrepresent the history of the black people and glorifying the history of the White colonial proxy war lords like Menelik II as great black king, who was cowardly cut women’s breast, mutilate men’s hand and embarrassingly sold his own black race to the European white race.
In conclusion, the quest for truth shall continue by present and future Oromo generations. The root cause for conflicts in Africa is an imported knowledge and imitation of ideas. In many cases, imitation represent a false-self or an act to hiding a true-self. Discriminatory and racist attitude against black people had been partly brought up by European’s colonial power proxy war lords in Africa such as Menelik II of Abyssinia/Ethiopia kingdom. Although most black people tend to cherish and assimilate their cultural identity into the Middle-Eastern and Western cultural identity and ways of life, the very culture of the societies they imitating have been reciprocating or holding discrimination against them based on race, stereotypes and historical disadvantages. Institutional racism still exist and there are also significant number of individuals who think that Africans have not yet acquired culture and civilization. The imitation of others’ ideas, belief system and political institutions by Africans including my fellow Oromoo has kept the racist believes alive. It is suffice to mention the 2013 incidents against African immigrants in Saud Arabia and recently in Israel. The majority of Africans believed that embracing Christianity and Islam would lead to heaven via holy land. Unfortunately, it turned out differently; they end up in hell in the holy land. So, the lasting solution would be revitalizing indigenous knowledge and institutions that demands for real efforts, courage and sacrifices. As to the Oromo’s quest for indigenous knowledge and institutions, revitalization of the Gadaa Republic of Oromia and its institutions would be the lasting solution for century old colonial extraction, subjugation and embarrassment.
___________________
* About the author: Iddoosaa Ejjetaa, Ph.D., native to Oromiyaa, Ethiopia. Independent and Naturalist Thinker; An activist and advocator for the revitalization of Authentic Oromummaa, Oromoo Indigenous knowledge and institutions, and for the formation of Biyyaa Abbaa Gadaa,Oromiyaa-The Gadaa Republic of Oromia.
Read more @
http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/the-quest-for-oromos-indigenous-knowledge-and-institutions/
Urban centers in Oromia:The integration of indigenous Oromo towns into the Ethiopian colonial structure and the formation of garrison and non-garrison cities and towns April 3, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Colonizing Structure, Finfinnee, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo Valley, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromian Voices, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development and Change, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Since urban areas and cities are primarily populated by Ethiopian colonial settlers and their collaborators, they are the ones who have access to the limited public facilities such as schools and hospitals. Oromo urbanites like the rural counter parts have been exposed to massive and absolute poverty and have been denied fundamental human rights and needs that Ron Shiffman (1995, 6-8) calls subsistence, protection, affection, and understanding. Most Oromos in urban and rural areas have low levels of subsistence because they lack adequate income, enough food, and livable homes. they do not have protection from disease because they are denied adequate access to health and
medical services.They do not have protection from political violence because the Ethiopian state engages in massive human rights violations and state terrorism ( Jalata 2000). Oromos have been ruled by successive authoritarian-terrorist regimes which have exploited and impoverished them by expropriating their resources. ….The Oromos have been prevented from developing autonomous institutions, organizations, culture, and language, and have been subordinated to the
institutions and organizations of the Habasha colonial settlers in their own cities, towns, and homeland.
Read more @http://works.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1052&context=asafa_jalata
In Ethiopia 40.2% of population are undernourished and the country is one of the world’s 10 hungriest countries April 2, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Ethnic Cleansing, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia.Tags: African culture, Developing country, Development, Economic development, Economic growth, Ethiopia, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Hunger, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromiyaa, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
- There are over 870 million people in the world who are hungry right now. I’m not talking about could use a snack before lunch hungry, not even didn’t have time for breakfast hungry, but truly, continually, hungry. Of these 870 million people, it’s been estimated by the World Food Programme that 98% live in developing countries, countries that perversely produce most of the world’s food stocks. So why is this the case?
- In Ethiopia an alarming 40.2% of population are undernourished.The 2011 Horn of Africa drought left 4.5 million people in Ethiopia in need of emergency food assistance. Pastoralist areas in southern and south-eastern Ethiopia were most severely affected by the drought. At the same time, cereal markets experienced a supply shock, and food prices rose substantially, resulting in high food insecurity among poor people. By the beginning of 2012, the overall food security situation had stabilized thanks to the start of the Meher harvest after the June-to-September rains resulting in improved market supply — and to sustained humanitarian assistance. While the number of new arrivals in refugee camps has decreased significantly since the height of the Horn of Africa crisis, Ethiopia still continues to receive refugees from Somalia, Sudan and South Sudan. The Humanitarian Requirements Document issued by the government and humanitarian partners in September 2012 estimates that 3.76 million people require relief food assistance from August to December 2012. The total net emergency food and non-food requirement amounts to US$189,433,303. Ethiopia remains one of the world’s least developed countries, ranked 174 out of 187 in the 2011 UNDP Human Development Index.
Read more @ http://www.globalcitizen.org/Content/Content.aspx?id=d7f0ac9b-e3a3-4233-8103-0348bb35e127
Ethiopia: Farmer gets legal aid from UK to sue Britain for giving aid to the brutal regime of Ethiopia March 30, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa Rising, Aid to Africa, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Ethnic Cleansing, Hadiya and the Omo Valley, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
An Ethiopian farmer has been given legal aid in the UK to sue Britain – because he claims millions of pounds sent by the UK to his country is supporting a brutal regime that has ruined his life.
He says UK taxpayers’ money – £1.3 billion over the five years of the coalition Government – is funding a despotic one-party state in his country that is forcing thousands of villagers such as him from their land using murder, torture and rape.
The landmark case is highly embarrassing for the Government, which has poured vast amounts of extra cash into foreign aid despite belt-tightening austerity measures at home.
Prime Minister David Cameron claims the donations are a mark of Britain’s compassion.
But the farmer – whose case is set to cost tens of thousands of pounds – argues that huge sums handed to Ethiopia are breaching the Department for International Development’s (DFID) own human rights rules.
He accuses the Government of devastating the lives of some of the world’s poorest people rather than fulfilling promises to help them. The case comes amid growing global concern over Western aid propping up corrupt and repressive regimes.
If the farmer is successful, Ministers might have to review major donations to other nations accused of atrocities, such as Pakistan and Rwanda – and it could open up Britain to compensation claims from around the world.
Ethiopia, a key ally in the West’s war on terror, is the biggest recipient of British aid, despite repeated claims from human rights groups that the cash is used to crush opposition.
DFID was served papers last month by lawyers acting on behalf of ‘Mr O’, a 33-year-old forced to abandon his family and flee to a refugee camp in Kenya after being beaten and tortured for trying to protect his farm.
He is not seeking compensation but to challenge the Government’s approach to aid. His name is being withheld to protect his wife and six children who remain in Ethiopia.
‘My client’s life has been shattered by what has happened,’ said Rosa Curling, the lawyer handling the case. ‘It goes entirely against what our aid purports to stand for.’
Africa Rising: So What? March 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Food Production, Free development vs authoritarian model, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, Genocide, Governance issues, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
This study critically discuses the “Africa rising” story and the sub-narratives it carries, including the rise of the African woman, the rise of the African middle class and the power of innovation. The articles included inform that, in too many cases, it is not the wider population but small segments and interested parties, such as the local political elite and foreign investors, who are benefiting from economic growth and resource wealth. Social cohesion, political freedom and environmental protection carry little importance in the comforting world of impressive growth statistics. The glamorous images of Africa’s prominent women and rising middle class produced and re-produced in the media prevent the less attractive and more complex stories about ordinary people’s daily struggles from being heard.
GDP tells us nothing about health of an economy, let alone its sustainability and the overall impact on GDP is simply a measure of market consumption, which has been improperly adopted to assess economic performance. Rebuilding Libya after the civil war has been a blessing for its GDP. But does that mean that Libya is on an enviable growth path? When there is only one brick left in a country devastated by war or other disasters, then just making another brick means doubling the economy (100 percent growth). Another problem is the reliability of GDP statistics in Africa. Economic growth figures for most African countries are incomplete, thus undermining any generalisation about overall economic performance in the continent. Besides statistical problems, there are important structural reasons why one should be suspicious of the ‘Africa rising’ mantra. Most fast- growing Africa economies are heavily dependent on exports of commodities.
Read the full articles @:
Click to access perspectives_feb_2014_web1.pdf
“About 30% of sub-Saharan Africa’s annual GDP has been moved to secretive tax havens.”
http://www.fairobserver.com/article/africa-illicit-outflow-84931
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Oromia Media Network Launch — Live! March 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Music, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Gadaa System, Hadiya and the Omo Valley, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, Ideas, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Language and Development, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Music, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo Sport, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Poverty, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Self determination, Sidama, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Democratic system, The Oromo Governance System, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Wisdom, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment

Oromia Media Network Launch — Live! 1st March 2014
Millions of Oromos now have the chance to enjoy quality media focusing on the needs and aspirations of the Oromo people.




https://www.oromiamedia.org/donorship/
“The Oromia Media Network (OMN) is an independent, nonpartisan and nonprofit news enterprise whose mission is to produce original and citizen-driven reporting on Oromia, the largest and most populous state in Ethiopia. OMN seeks to offer thought-provoking, contextual, and nuanced coverage of critical public interest issues thereby bringing much needed attention to under-reported stories in the region. Our goal is to create a strong and sustainable multilingual newsroom that will serve as a reliable source of information about the Oromo people, the Ethiopian state, and the greater Horn of Africa region. ” – http://www.oromiamedia.org/
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.
Ethiopia: Silence, Pain, Lies and Abductions March 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Colonizing Structure, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Free development vs authoritarian model, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sidama, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, World Bank
add a comment
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-c592hhWlc8
‘This is a regime whose character has the potential to confuse even Jeane J. Kirkpatrick, former Reagan foreign policy advisor, who made a distinction between “authoritarian” and “totalitarian” regimes. In her essay “Dictatorship and Double Standards,” she describes authoritarian dictators as “pragmatic rulers who care about their power and wealth and are indifferent toward ideological issues, even if they pay lip service to some big cause”; while, in contrast, totalitarian leaders are “selfless fanatics who believe in their ideology and are ready to put everything at stake for their ideals”.’
This assessment of the reaction to the article I published on this blog: “Silence and Pain,” is interesting for its exploration of the relationship between the Ethiopian government and the media, even though it overestimates any influence I may have.
Martin
Source: Muktar M. Omer
Ethiopia: Silence, Pain, Lies and Abductions
March 16, 2014
By Muktar M. Omer
Template denials
The Ethiopian Government, through its foreign ministry, responded to Martin Plaut’s article “Silence and Pain: Ethiopia’s human rights record in the Ogaden” with the usual feigned shock and template denial that has long characterized the regime’s political personality. It is the established behavior of aggressive and autocratic regimes to discount well-founded reports of human right violations as propaganda constructs of the ‘enemy’. The response from the Foreign Ministry was thus nothing more than a well memorized and rehearsed Ethiopian way of disregarding documented depravities committed by the regime. As usual…
View original post 2,632 more words
Tribute to the Late Dr. Paul Baxter (1925-2014) March 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Afaan Publication, African Beat, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Colonizing Structure, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.1 comment so far
The Oromo Studies Association’s Tribute to the Late Dr. Paul Baxter (1925-2014)
It is with great sadness that the Oromo Studies Association (OSA) informs the Oromo and friends of Oromo about the passing away of Dr. Paul Baxter on March 2, 2014. He was 89. Dr. Paul Baxter was a distinguished British anthropologist who devoted his life to Oromo studies. He is one of the finest human being, who contributed immensely to the development of Oromo studies at the time when the scholarship on the Oromo people was extremely discouraged in Ethiopia. His death is a significant loss for his family, all those who knew and were touched by his humanity and kindness, and for the students of Oromo studies. Dr. Paul Baxter is survived by his wife, Pat Baxter, his son, Adam Baxter, and his three grandsons and their children.
Born on January 30, 1925 in England, Paul Trevor William Baxter, popularly known as Paul Baxter or P.T.W. Baxter, earned his BA degree from Cambridge University. Influenced by famous scholars such as Bronisław Kasper Malinowski, Charles Gabriel Seligman, and Evans Pritchard, Paul Baxter had a solid affection for social anthropology. He went to the famous Oxford University to study social anthropology.
It was at the zenith of the Amharization project of Emperor Haile Selassie that he developed a strong interest to study the social organization of the Oromo people. In fact, in 1952, he wanted to go to Ethiopia to study the Oromo Gada system. Let alone tolerating this type of research, Ethiopia was in the middle of the massive project to eradicate the memory of the Oromo from their historic and indigenous territories. The Assimilation policy was in the full swing. Little spared from an attempt was made to change everything Oromo into Amharic. Even the Oromo names of urban centers were rechristened into Amharic names. It is no wonder that Ethiopia was reluctant to welcome a researcher like Baxter who was looking for the soul of the Oromo culture in the homogenizing Ethiopian Empire. Nonetheless, the challenge did not bother the young and exuberant Baxter to pursue his studies. He was determined more than ever to study the social fabric of the Oromo nation. Failed to get permission to do research among the Oromo in Ethiopia, he went to the British Colony Kenya to study the Borana Oromo social organization in northern Kenya. He spent two years (1952 and 1953) among them, which resulted in his PhD dissertation: ‘The Social Organization of the Oromo of Northern Kenya’, in 1954. This research became a foundation for more of his researches to come and a reference for the students of Oromo studies. Besides, the research disqualified many of the myths and pseudo facts that assume the Oromos were a people without civilization, culture, and history. Dr. Paul Baxter did not stop here. He continued with his studies and spent several decades studying different aspects of the Oromo society. It was through his extended research among the Oromos that he deconstructed some of the myths that portrayed the Oromo people as a “warlike” or “barbarian” nation. The title of essays in his honor, in 1994, “A River of Blessings” speaks to his perception and reality of the Oromo as a peace-loving nation. In his article, “Ethiopia’s Unacknowledged Problem: The Oromo,” he highlighted some of the Oromophobic and barbaric manners of the Ethiopian Empire, and he suggested that peace with the Oromo nation was the only lasting panacea to the Ethiopian political sickening.
In his long academic and research career, he studied the Oromo from northern Kenya to Wallo and Arsi to Guji and so on. He edited a number of books on Oromo studies and published many other articles and book chapters in the field of social anthropology. He participated several times on OSA annual conferences. During the 1960s and 1970s, Dr. Paul Baxter was known as the finest living social anthropologist in the United Kingdom. Besides his impressive scholarship on the Oromo society, Dr. Paul Baxter’s lasting legacy is that he educated so many scholars who have studied Oromo culture both in Kenya and Ethiopia. Dr. Paul Baxter’s passion and determination will inspire the generation of students of the Oromo studies. Our prayers and thoughts are with his family, friends, and Oromos and friends of Oromo studies during this difficult time.
Ibrahim Elemo, M.D., M.P.H
President, the Oromo Studies Association
Mohammed Hassen, Ph.D.
Board Chairman, the Oromo Studies Association
———————-
A partial list of his scholarly works on the Oromo includes the followings:
1. “The Social Organization of the [Oromo] of Northern Kenya,” Ph.D. Dissertation, Oxford University, 1954.
2. “Repetition in Certain Boran Ceremonies” In African Systems of Thought, ed. M. Fortes and G. Dieterlin, (London: Oxford University Press for International African Institute, 1960), 64-78.
3. “Acceptance and Rejection of Islam among the Boran of the Northern Frontier District of Kenya” In Islam in Tropical Africa, edited by I.O. Lewis (London: Oxford University Press, 1966), 233-250.
4. “Stock Management and the Diffusion of Property Rights among the Boran” In Proceedings of the Third International Conference of Ethiopian Studies, (Addis Ababa: Institute of Ethiopian Studies, Haile Selassie I University, 1966), 116-127.
5. “Some Preliminary Observations on a type of Arssi Song” In Proceedings of the Third International Congress of Ethiopian Studies, ed. E. Cerulli (Rome: 1972).
6. “Boran Age-Sets and Generation-set: Gada, a Puzzle or a maze?” In Age Generation and time: Some Features of East African Age Oroganisations, ed. P.T.W. Baxter and U. Almagor, ( London: C. Hurst, 1978), 151-182.
7. “Ethiopia’s Unacknowledged Problem: The Oromo”, African Affairs, Volume 77, Number 208 (1978): 283-296.
8. “Atete: A Congregation of Arssi Women” North East African Studies, Volume I (1979), 1-22.
9. Boran Age-Sets and Warfare”, in Warfare among East African Herders, ed. D. Turton and K. Fukui, Senri Ethnological Studies, Number 3, Osaka: National Museum of Ethnology( 1979), 69-95.
10. “Always on the outside looking in: A view of the 1969 Ethiopian elections from a rural constituency” Ethnos, Number 45(1980): 39-59.
11. “The Problem of the Oromo or the Problem for the Oromo” in Nationalism and Self-Determination in the Horn of Africa, ed. I.M. Lewis, (London: Ithaca Press, 1983), 129-150.
12. “Butter for Barley and Barley for Cash: Petty Transactions and small Transformations in an Arssi Market” In Proceedings of Seventh Congress of Ethiopian Studies (Lund: 1984), 459-472.
13. “The Present State of Oromo Studies: a Resume,” Bulletin des Etudes africaine de l’ Inalco, Vol. VI, Number 11(1986): 53-82.
14. “Giraffes and Poetry: Some Observations on Giraffe Hunting among the Boran” Paiduma: Mitteilungen fur Kulturkunde Volume 32 (1986), 103-115.
15. “Some Observations on the short Hymns sung in Praise of Shaikh Nur Hussein of Bale” In The Diversity of the Muslim Community, ed. Ahmed el –Shahi, (London: Ithaca Press, 1987), 139-152.
16. “L’impact de la revolution chez les Oromo: Commentl’ont-ils percu, comment ont-ils reagi?” In La Revolution ethiopienne comme phenomene de societe, edited by Joseph Tubiana, (Paris: l’Harmattan, Bibliotheque Peiresc, 1990), 75-92.
17. “Big men and cattle licks in Oromoland” Social change and Applied Anthropology; Essays in Honor of David David W. Brokensha, edited by Miriam Chaiken & Anne K. Fleuret,( Boulder: Westview Press, 1990), 246-261.
18. “Oromo Blessings and Greetings” In The Creative Communion, edited by Anita Jacoson-Widding & W. Van Beek (Uppsala, Uppsala Studies in Cultural Anthropology , 1990), 235-250.
19. “Introduction “In Guji Oromo Culture in Southern Ethiopia by J. Van de Loo, ( Berli: ReinMer, 1991).
20. “Ethnic Boundaries and Development: Speculations on the Oromo Case” In Inventions and Boundaries: Historical and Anthropological Approaches to the Study of Ethnicity & Nationalism, edited by Kaarsholm Preben & Jan Hultin, (Denmark: Roskilde University, 1994): 247-260.
21. “The Creation & Constitution of Oromo Nationality” In Ethnicity & Conflict in the Horn of Africa, edited by Fukui Katsuyoshi & John Markarkis, (London: James Currey, 1994): 166-86.
22. “Towards a Comparative Ethnography of the Oromo” In Being and Becoming Oromo: Historical & Anthropological Enquiries, edited by Paul Baxter et al, (Uppsala: Nordiska Afikanistitutet, 1996): 178-189.
23. “Components of moral Ethnicity: The case of the Oromo.” In Ethnicity and the state in Eastern Africa, edited by Mohammed Salih & John Markarkis, (Uppsala: OSSREA & SIAS, 1998).
http://gadaa.com/oduu/24792/2014/03/03/the-oromo-studies-associations-tribute-to-the-late-dr-paul-baxter-1925-2014/
“…The efflorescence of feelings of common nationhood and of aspirations of self-determination among the the cluster of peoples who speak Oromo has not been much commented upon. Yet the problem of the Oromo people has been a major and central one in the Ethiopian Empire ever since it was created by Menelik in the last two decades of the nineteenth century. If the Oromo people only obtain a portion of the freedoms which they seek the balance of political power will be completely altered. If the Oromo act with unity they must necessarily constitute a powerful force. … If the Ogaden and Eritrea were detached Ethiopia would merely be diminished, but if the Oromo were to detach themselves, then it is not just that the centre could not hold, the centre would be part of the detached Oromo land. The Empire, which Menelik stuck together and Haile Selassie held together, would just fall apart. The Amhara would then forced back to their barren and remote hills. … The slogan of the Oromo Liberation Front is ‘Let Oromo freedom flower today! (addi bilisumma Oromo Ha’dararuu!).This may be a very over-optimistic hope but, if not today, the time of flowering and fruiting cannot be delayed forever.”
Professor Paul Baxter, Manchester University, in his article
Ethiopia’s Unacknowledged Problem: The Oromo
African Affairs 1978 Volume LXXVII (pp. 283-296) Published for Royal African Society by Oxford University Press.
Baxter daadhiin jala haa yaatu
http://www.opride.com/oromsis/news/horn-of-africa/3737-baxter-daadhiin-jala-haa-yaatu
My friend, the social anthropologist PTW (Paul) Baxter, who has died aged 89, made a significant contribution to western understanding of the Oromo peoples of northern Kenya and Ethiopia and championed their culture, which was frequently denigrated by colonial and local elites.
His work on the plight of the Ethiopian Oromo became a standard text in Oromo studies and a rallying point for the Oromo cause. Paul was not always comfortable with the praise he received as a result, and was often self-deprecating, describing himself as the world’s most unpublished anthropologist. That was a harsh judgment, since a complete list of his output is respectably long. He also made a wider contribution by editing the journal Africa and sitting on the Royal African Society board.
Born in Leamington Spa – his father was a primary school headteacher in the town – Paul attended Warwick school. Academic ambitions were put aside when he joined the commandos in 1943, serving in the Netherlands and occupied Germany. He married Pat, whom he had met at school, in 1944, and after the war went to Downing College, Cambridge, studying English under FR Leavis before switching to anthropology.
On graduation he moved to Oxford, where anthropology under EE Evans-Pritchard was flourishing. Field research on the pastoral Borana people in northern Kenya followed for two years, accompanied by Pat and their son, Timothy. He gained his DPhil in 1954 and more fieldwork followed among the Kiga of Uganda.
With UK jobs scarce, he took a position at the University College of Ghana. This was a happy time for the family, who found Ghana delightful. Returning to the UK in 1960, he was offered a one-year lectureship at the University of Manchester by the sociology and social anthropology head, Max Gluckman, after a recommendation by Evans-Pritchard. He then spent two years at the University College of Swansea (now Swansea University) before returning permanently to the University of Manchester. Over the next 26 years Paul contributed significantly to anthropological studies and to Oromo research, spending 12 months among the Arssi Oromo of Ethiopia before retiring in 1989.
Paul was never interested in winning academic prizes; instead his focus was on helping people. Generations of students, both at home and overseas, benefited from friendship and, often, a warm welcome in his home.
Paul’s life was touched by sadness, particularly Timothy’s death from multiple sclerosis in 2005, but he took great pleasure in his family. He is survived by Pat, their son Adam, four grandchildren and three great-grandchildren.
http://www.theguardian.com/science/2014/mar/18/ptw-baxter-obituary#
Africa: Legacy of Pre-colonial Empires and Colonialism March 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Afaan Publication, Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Culture, Development, Dhaqaba Ebba, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Haacaaluu Hundeessaa, Hadiya, Hadiya and the Omo Valley, Haile Fida, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Language and Development, Nubia, Ogaden, OMN, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo Sport, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Poverty, Self determination, Sidama, Sirna Gadaa, South Sudan, Specialization, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oldest Living Person Known to Mankind, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Tyranny, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, economics, Ethiopia, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
‘Our knowledge of the nature of identity relations in pre-colonial Africa is less than complete. However, there is little doubt that many parts of the continent were torn apart by various wars, during that era. Many of the pre-colonial wars revolved around state formation, empire building, slave raids, and control over resources and trade routs. The slave raiding and looting empires and kingdoms, including those of the 19th century, left behind complex scars in inter-identity relations. It is beyond the scope of this paper to discuss in detail the nature of pre-colonial empires in Africa. The examples of the Abyssinian Empire and the Mahdiyya state in Sudan provide a glimpse of the impacts of pre-colonial empires on the prevailing problems in inter-identity relations. The Abyssinian Empire, for example, is credited for creating the modern Ethiopian state during the second half of the 19th century and defending it from European colonialism. However, it also left behind a deeply divided country where the populations in the newly incorporated southern parts of the country were ravaged by slave raids and lootings and, in many cases, reduced into landless tenants, who tilled the land for northern landlords (Pankhurst, 1968). The Empire also established a hierarchy of cultures where the non-Abyssinian cultures in the newly incorporated territories were placed in a subordinate position. There are claims, for instance, that it was not permissible to publish, preach, teach or broadcast in Oromiya [Afaan Oromo] (language of the Oromo people) in Ethiopia until the end of the reign of Emperor Haile Selassie (Baxter, 1978, 228). It requires a great deal of sensitivity to teach Ethiopian history in the country’s schools, since the empire-builders of the 19th century are heroes to some identities while they are viewed as villains who brought destruction and oppression by others. Similarly, Sudan’s Mahdiyya state, which professed Arab identity and was supported by slave raiding communities, left behind complex scars in inter-identity relations, which still plague the country (Francis Deng, 2010).’ pp 10-12
Diversity Management in Africa: Findings from the African Peer Review Mechanism
and a Framework for Analysis and Policy-Making , 2011.
http://www.uneca.org/sites/default/files/publications/3-diversity-management.pdf
Click to access 3-diversity-management.pdf
Related articles:
A country is not about its leaders but of its people. It goes without saying that the people are the symbolic mirror of their nation. That is exactly why foreigners particularly the development partners assess and evaluate a nation through its people. In other words, a happy people are citizen of not only a peaceful and happy nation but one which accepts the principles of democracy, rule of law and human and people’s right. On the contrast, heartbroken, timid and unhappy people are subjects of dictatorial, callous and brutal regimes. Such people are robbed of their humanity and identity through systematic harassment, intimidation, unlawful detention, extra judicial killing and disappearances by the leaders who transformed themselves into creators of human life or lords. The largest oromo nation in Ethiopia through the 22years of TPLF/EPRDF repressive leadership has turned into a nation sobbing in the dark. One does not need to be a rocket scientist to figure this out. All it takes is a closer look at any Oromos in the face. The story is the same on all the faces: fear, uncertainty, and an unquenchable thirst for freedom. The disturbing melody of the sobs in the dark echo the rhythmic desire to break free from TPLF dictatorial shackles.
The Horn African region of the Ethiopia is home to just 90 million people, it is also home to one of the world’s most ruthless, and eccentric, tyrannical regime .TPLF/EPRDF is ruling the nation particularly the Oromos with an iron fist for the past two decades and yet moving on. Today dissents in Oromia are frequently harassed, arrested, tortured, murdered and put through sham trials, while the people are kept in a constant state of terror through tight media control, as repeatedly reported by several human rights groups. It has been long time since the Woyane government bans most foreign journalists and human rights organizations and NGOs from operating in the country for the aim of hiding its brutal governance from the world. While the people in Ethiopia are being in terrorized by TPLF gangs, the western powers are yet looking at the country as a very strategic place to fight the so called terrorism in horn African region. But In today’s Ethiopia; as an Oromo, No one can speak out against the dictatorship in that country. You can be killed. You can be arrested. You can be kept in prison for a long time. Or you can disappear in thin air. Nobody will help. Intimidations, looting Oromo resources and evicting Oromos from their farm lands have become the order of the day everywhere across Oromia.
No Oromo has constitutional or legal protection from the killing machinery of the TPLF securities. The recent murdering of Tesfahun Chemeda in kallitti prison is a case book of the current Circumstance.
The So called EPRDF constitution, as all Ethiopian constitutions had always been under the previous Ethiopian regimes, is prepared not to give legal protections to the Oromo people, but to be used against the Oromo people. Prisons in the Ethiopia have become the last home to Oromo nationalists, human right activists or political opponent of the regime. Yet the international community is either not interested or have ignored the numerous Human Right abuses in Ethiopia simply because, they think there is stability in the country. Is there no stability in North Korea? I don’t understand why the international community playing double standard with dining and wining with Ethiopian brutal dictators while trying to internationally isolate other dictators. For crying out loud, all dictators are dangerous to humanity and shaking their hands is even taboo much more doing business with them.
Without the support of the USA and EU, major pillars of the regime would have collapsed. Because one reason why TPLF is sustaining in power is through the budgetary support and development funding of the EU, the United States and offered diplomatic validation by the corrupted African Union. Foremost, the US and EU as the largest partners are responsible for funding the regime’s sustainability and its senseless brutality against ordinary citizens. They would have the capacity to disrupt the economic might of this regime without negatively impacting ordinary citizens, and their failure to do so is directly responsible for the loss of many innocent lives, the torture of many and other grievous human rights abuses. Helping dictators while they butcher our people is what I cannot understand. What I want to notify here is, on the way of struggling for freedom it is very essential to call on the western powers to stop the support they are rendering to dictators in the name of fighting the so called terrorism in Horn Africa, otherwise it will remain an obstacle for the struggle.
Holding elections alone does not make a country democratic. Where there is no an independent media, an independent judiciary (for the rule of law), an independent central bank, an independent electoral commission (for a free and fair vote); neutral and professional security forces; and an autonomous (not a rubber stamp) parliament, no one should expect that the pseudo election will remove TPLF from power. The so-called “Ethiopian constitution” is a façade that is not worth the paper which it is written on. It does not impose the rule of law; and does not effectively limit governmental power. No form of dissent is tolerated in the country.
As my understanding and as we have observed for more than two decades, it is unthinkable to remove TPLF regime without a military struggle or without popular Uprisings. They are staying, staying, and staying in power – 10, 20, 22 and may be 30 or 40 years. They have developed the mentality of staying on power as their own family and ethnic property. So that they are grooming their clans, their wives, sons, cats, dogs and even goats to succeed them. They are simply the worst mafia regime and the most politically intolerant in the Africa. It is impossible to remove them electorally because we have been witnessing that the electoral system is fundamentally flawed and indomitably skewed in favor them. Every gesture and every words coming from TPLF gangs in the last several years have confirmed that to remove them by election is nothing but like to dream in daylight.
The late dictator “Meles Zenawi” had once said that TPLF “shall rule for a thousand years”, asserting that elections SHALL NOT remove his government. He also said: “the group who want the power must go the forest and fight to achieve power”. Therefore, taking part in Pseudo election will have no impact on reducing the pain of the oppressed people. Evidently, the opposition and civil societies have been rendered severely impotent, as any form of dissent attracts the ultimate penalty in Ethiopia. Furthermore, we are watching that this regime is intensifying its repression of democracy each day, and ruling strictly through the instrument of paralyzing fear and the practice of brutality against ordinary citizens.
As we are learning from history, Dictators are not in a business of allowing election that could remove them from their thrones. The only way to remove this TPLF dictatorship is through a military force, popular uprising, or a rebel insurgency: Egypt (2011), Ivory Coast (2011), Tunisia (2011), Libya (2011), Rwanda (1994), Somalia (1991), Liberia (1999), etc. A high time to fire up resistance to the TPLF killings and resource plundering in Oromia, is now. To overthrow this brutal TPLF dictatorship and to end the 22 years of our pain, it is a must to begin the resistance with a nationwide show of defiance including distributing postures of resistance against their brutality across Oromia and the country. Once a national campaign of defiance begins, it will be easy to see how the TPLF regime will crumble like a sand castle. Besides, we the Oromo Diaspora need to work on strengthening the struggle by any means we can. It is the responsibility of the Diaspora to advance the Oromo cause, and at the same time to determine how our efforts can be aided by the international community. As well, it is a time for every freedom thirsty Oromo to take part in supporting our organization Oromo liberation Front by any means we can.
These days, TPLF regime is standing on one foot and removing it is easier than it appears. Let all oppressed nations organize for the final push to liberty. The biggest fear of Woyane regime is people being organized and armed with weapons of unity, knowledge, courage, vigilance, and justice. What is needed is a unified, dedicated struggle for justice and sincerity. Oromo’s are tired of the dying, the arrests, the detentions, the torture, the brutality and the forced disappearances. This should come to an end! DEATH FOR TPLF LEADERES ,.long live FOR OROMIYA
_____________________________________
The author, ROBA PAWELOS, can be reached by bora1273@yahoo.com
Africa’s spin doctors (mostly American and European) deliberately choose to represent what the Free Africa Foundation’s George Ayittey so refreshingly describes as “Swiss-bank socialists”, “crocodile liberators”, “quack revolutionaries”, and “briefcase bandits”. Mr Ayittey – a former political prisoner from Ghana – pulls us a lot closer to the truth.
If the mainstream media adopts Mr Ayittey’s language, the free governments of the world would be forced to face the truth and take necessary steps to tie their aid and trade deals to democratic reform for the benefit of Africa’s population. Sunlight is the best disinfectant, and we must combat the work of firms that provide “reputation management” to oppressive states by exposing their role in abetting injustice.
Those firms may want to consider atoning by volunteering for the civil society groups, human rights’ defenders and economic opportunity organisations working to make Africa free and prosperous.’…………………………………………………
A number of African governments accused of human rights abuses have turned to public relations companies to salvage the image of their countries.
The BBC’s Focus on Africa magazine asked two experts whether “reputation management” is mostly a cover-up for bad governance.
NO: Thor Halvorssen is president of the New York-based Human Rights Foundation and founder of the Oslo Freedom Forum.
Thor Halvorssen has published extensively on the subject of lobbying
For Public Relations (PR) companies and their government clients, “reputation management” can be a euphemism of the worst sort. In many cases across Africa, it often means whitewashing the human rights violations of despotic regimes with fluff journalism and, just as easily, serving as personal PR agents for rulers and their corrupt family members.
But they also help governments drown out criticism, often branding dissidents, democratic opponents and critics as criminals, terrorists or extremists.
Today, with the preponderance of social media, anyone with an opinion, a smart phone and a Facebook account can present their views to an audience potentially as large as any major political campaign can attract.
This has raised citizen journalism to a level of influence unknown previously. Yet, this communication revolution has also resulted in despotic governments smearing not just human rights advocates, but individuals with blogs as well as Twitter, YouTube and Facebook accounts. This undermines the power and integrity of social media.
And as PR firms help regimes “astroturf” with fake social media accounts, they do more damage than just muddling legitimate criticism with false comments and tweets linking back to positive content – they also make the general public sceptical about social media.
It is no surprise that ruthless governments that deny their citizens basic freedoms would wish to whitewash their reputations. But PR professionals who spin for them should be exposed as amoral.
It is no surprise that ruthless governments that deny their citizens basic freedoms would wish to whitewash their reputations”
For instance, Qorvis Communications, a PR and lobbying firm in the United States, represents Equatorial Guinea – among other allegedly repressive governments – for a reported $55,000 a month. The firm is said to have amassed more than $100 million by helping their clients with “reputation management”.
By burying opposing public opinions or spinning false, positive stories of stability and economic growth on behalf of President Teodoro Obiang Nguema’s brutal regime, the firm is seriously hampering the progress of human rights in the country.
In response, Qorvis says that customers with troublesome human rights records are a very small part of its client base, and that these governments are using Qorvis as a means to be heard in the “court of public opinion”.
Washington Media Group, another American PR firm, was hired in 2010 by the Tunisian government. The autocracy was subsequently described in various media outlets as a “stable democracy” and a “peaceful, Islamic country with a terrific story to share with the world”. Only after the regime’s snipers began picking off protesters did Washington Media Group end its $420,000 contract.
‘Limited engagement’
When a PR firm spins a dictator’s story, it does not just present a different viewpoint, as the firm might want you to believe; rather, it undermines the resources from which people can draw opinions. If a website or magazine commends the government, how is an average citizen to know for certain if the information is accurate or true?
President Teodoro Obiang Nguema
Teodoro Obiang Nguema is accused of leading a brutal regime in Equatorial Guinea
Many firms that operate, or have done, on behalf of kleptocracies in Africa are based not only in the US but also in the United Kingdom. They include Bell Pottinger (Hosni Mubarak’s Egypt), Brown Lloyd James (Muammar Gaddafi’s Libya) and Hill & Knowlton (Yoweri Museveni’s Uganda).
There are likely many more that continue to do this work under the cover of corporate secrecy. When firms get caught or criticised for their activities many say it is “limited engagement” for only a few months or that the task only involved “tourism” or “economic progress”.
If, for instance, a firm served the questionable government in the Democratic Republic of the Congo they would probably insist they are “consultants” helping to create “economic opportunity” and, no doubt, providing a “guiding hand” to the current president as he improves the lot of the Congolese poor.
Yet the spin doctors most probably ignore the fact that President Joseph Kabila’s security forces killed Floribert Chebeya, arguably the DR Congo’s leading human rights defender, and likely “disappeared” his driver (he is still missing). Only after an international uproar were the policemen directly responsible for the killing brought to justice.
Meanwhile, political opponents routinely disappear, journalists are arrested for criticising the government and any comprehensive human rights report contains appalling anecdotes and painful analysis about a country with little judicial independence and respect for the rule of law.
PR agents do not create “economic opportunities” – they alter reality so that certain deals and foreign aid can flow faster and in larger quantities – all the while being rewarded handsomely.
‘Briefcase bandits’
Africa’s spin doctors (mostly American and European) deliberately choose to represent what the Free Africa Foundation’s George Ayittey so refreshingly describes as “Swiss-bank socialists”, “crocodile liberators”, “quack revolutionaries”, and “briefcase bandits”.
Mr Ayittey – a former political prisoner from Ghana – pulls us a lot closer to the truth.
If the mainstream media adopts Mr Ayittey’s language, the free governments of the world would be forced to face the truth and take necessary steps to tie their aid and trade deals to democratic reform for the benefit of Africa’s population.
Sunlight is the best disinfectant, and we must combat the work of firms that provide “reputation management” to oppressive states by exposing their role in abetting injustice.
Those firms may want to consider atoning by volunteering for the civil society groups, human rights’ defenders and economic opportunity organisations working to make Africa free and prosperous.

Tweets Ranking Africa: Who tweets most? Who is not? March 12, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Accra, Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, African Poor, Development, Facebook and Africa, Human Rights, Nairobi, Nelson Mandela, Oromo, South Africa, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tweets and Africa, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Horn of Africa, Oromia, Oromo, Oromummaa, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


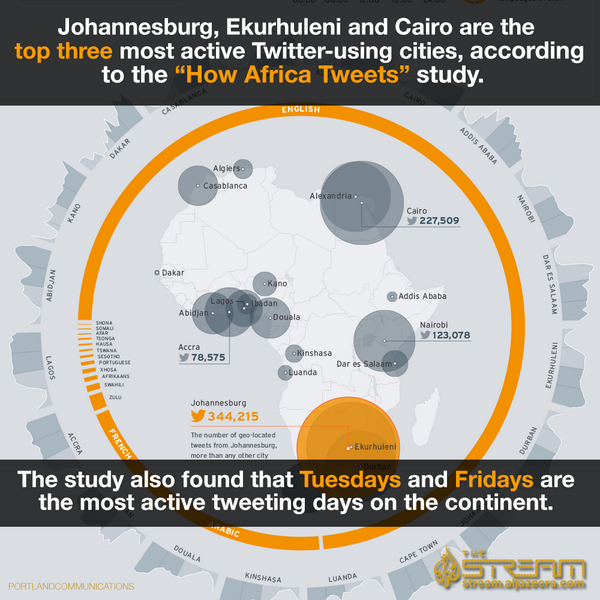
Africa’s largest and second-largest economies, South Africa and Egypt, are Africa’s two most active Twitter countries. Accra, Cairo, Johannesburg and Nairobi are the tweets capitals of Africa. With 344,215 geo-located tweets, Johannesburg is the most active city in Africa.
According to the United Nations International Telecommunication Union (ITU) latest report on information and communications technology in Ethiopia, the country is among the least developed and most expensive in the world. The report placed Ethiopia 151st in ICT development, out of 157 countries, and 152nd out 169 countries in the price of fixed broadband connection. After a decade, in 2012, the internet penetration rate in Ethiopia was a mere 1.1 percent, or 960,331 users and out of this 902,440 are Facebook users. Neighboring Kenya, however, reached a 41 percent penetration rate, with 16.2 million users. As part of its active engagement in curtailing free media, the Ethiopian state is known in making citizen’s use of micro social networkings illegal and blocks internet connections and sites to public.
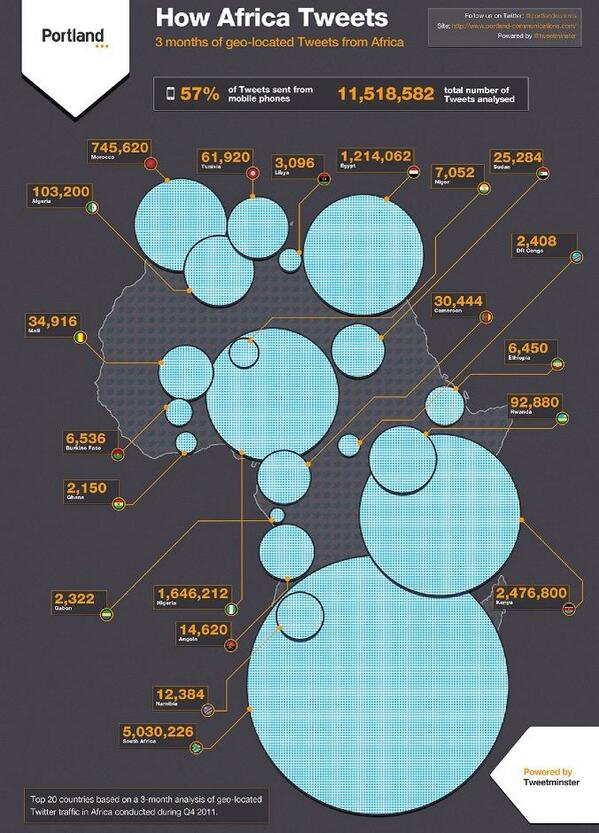
In a follow up to its 2012 study, the London- and Nairobi-based public relations and strategic communications agency Portland analysed geo-located tweets originating from Africa during the final three months of 2013. The second How Africa Tweets study dives deeper into Twitter use on the continent, looking at which cities are the most active, what languages are being used the most and what issues are driving the conversation online.
How Africa Tweets found that, during the final three months of 2013:
Johannesburg is the most active city in Africa, with 344,215 geo-located tweets, followed by Ekurhuleni (264,172) and Cairo (227,509). Durban (163,019) and Alexandria (159,534) make up the remainder of the top five most active cities
Nairobi is the most active city in East Africa and the sixth most active on the continent, with 123,078 geo-located tweets
Accra is the most active city in West Africa and the eight most active on the continent, with 78,575 geo-located tweets
English, French and Arabic are the most common languages on Twitter in Africa, accounting for 75.5% of the total tweets analysed. Zulu, Swahili, Afrikaans, Xhosa and Portuguese are the next most commonly tweeted languages in Africa
Tuesdays and Fridays are the most active tweeting days. Twitter activity rises steadily through the afternoon and evening, with peak volumes around 9pm
The day of Nelson Mandela’s death – 5 December – saw the highest volume of geo-located tweets in Africa
Brands in Africa are becoming increasingly prevalent on Twitter.
Portland tracked major hashtag activity from top brands such as Samsung (#SamsungLove), Adidas (#Adidas) and Magnum ice cream (#MagnumAuction)
Football is the most-discussed topic on Twitter in Africa. Football was discussed more than any other topic, including the death of Nelson Mandela. The most mentioned football team was Johannesburg’s Orlando Pirates (#BlackisBack, #PrayForOrlandoPirates, #OperationFillOrlandoStadium)
Politically-related hashtags were less common than those around other issues, with only four particularly active political hashtags tracked during the time period. This included #KenyaAt50 – celebration of Kenya’s independence – and the competing #SickAt50
Allan Kamau, Head of Portland Nairobi, says: “The African Twittersphere is changing rapidly and transforming the way that Africa communicates with itself and the rest of the world. Our latest research reveals a significantly more sophisticated landscape than we saw just two years ago. This is opening up new opportunities and challenges for companies, campaigning organisations and governments across Africa.”
Mark Flanagan, Head of Digital for Portland, says: “As well as adding diversity of perspective on political and social issues, Africa’s Twitter users are also contributing linguistic diversity. Twitter is now established on the continent as a source of information and a platform for conversation.”http://allafrica.com/stories/201403120080.html
http://allafrica.com/stories/201312230211.html?viewall=1
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Ranking Africa by literacy rate March 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Beat, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Culture, Development, Dictatorship, Humanity and Social Civilization, Language and Development, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Education and Development
add a comment
 “Barely anyone — one to two percent of the population — could read in ancient Rome and nobody thought more people should. Now we recognize that literacy is a human right; that being able to read and write is personally empowering and, in a world that relies more and more on technology, simply necessary.” Kristina Chew
“Barely anyone — one to two percent of the population — could read in ancient Rome and nobody thought more people should. Now we recognize that literacy is a human right; that being able to read and write is personally empowering and, in a world that relies more and more on technology, simply necessary.” Kristina Chew
The study by The African Economist demonstrates that the top 5 literate countries in Africa are: Zimbabwe, Equatorial Guinea, South Africa, Kenya and Namibia.
Ethiopian is among the lowest literate 11. It is 42nd (with 42.7% literacy rate) of the 52. Burkina Faso is the 52nd. An other robust research shows that Ethiopia is one of the 1o countries in the world with worst literacy rates (with literacy rate of 39%). This study informs that 54 of the 76 million illiterate young women come from nine countries, most in south and west Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa and not necessarily those with high rates of adult illiteracy: India (where almost 30 million young women are illiterate), Pakistan, Nigeria, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the United Republic of Tanzania, Egypt and Burkina Faso. http://www.care2.com/causes/10-countries-with-the-worst-literacy-rates-in-the-world.html#ixzz2vhIgCozN
The African Economist’s analysis:
‘Information on literacy, while not a perfect measure of educational results, is probably the most easily available and valid for international comparisons. It is impossible to overstate the importance of education especially in Africa. Low levels of literacy, and education in general, can impede the economic development of a country in the current rapidly changing, technology-driven world. … This entry includes a definition of literacy and Census Bureau percentages for the total population, males, and females. There are no universal definitions and standards of literacy. Unless otherwise specified, all rates are based on the most common definition – the ability to read and write at a specified age (15 and above). Detailing the standards that individual countries use to assess the ability to read and write is beyond the scope of this article.’
Below is the ranking of African countries by the literacy rate:
Country Literacy Rate
1. Zimbabwe 90.70
2. Equatorial Guinea 87.00
3.South Africa 86.40
4.Kenya 85.10
5.Namibia 85.00
6.Sao Tome and Principe 84.90
7. Lesotho 84.80
8.Mauritius 84.40
9.Congo, Republic of the 83.80
10. Libya 82.60
11.Swaziland 81.60
12. Botswana 81.20
13.Zambia 80.60
14.Cape Verde 76.60
15. Tunisia 74.30
16. Egypt 71.40
17. Rwanda 70.40
18. Algeria 69.90
19. Tanzania 69.40
20. Madagascar 68.90
21. Nigeria 68.00
22. Cameroon 67.90
23. Djibouti 67.90
24. Angola 67.40
25.Congo, Democratic Republic of the 67.20
26. Uganda 66.80
27. Gabon 63.20
28. Malawi 62.70
29.Sudan 61.10
30. Togo 60.90
31. Burundi 59.30
32.Eritrea 58.60
33.Ghana 57.90
34.Liberia 57.50
35. Comoros 56.50
36. Morocco 52.30
37. Mauritania 51.20
38. Cote d’Ivoire 48.70
39. Central African Republic 48.60
40. Mozambique 47.80
41.Mali 46.40
42. Ethiopia 42.70
43. Guinea-Bissau 42.40
44. Gambia, The 40.10
45. Senegal 39.30
46. Somalia 37.80
47. Sierra Leone 35.10
48. Benin 34.70
49. Guinea 29.50
50. Niger 28.70
51. Chad 25.70
52. Burkina Faso 21.80
10 Countries With the Worst Literacy Rates in the World
Barely anyone – one to two percent of the population — could read in ancient Rome and nobody thought more people should. Now we recognize that literacy is a human right; that being able to read and write is personally empowering and, in a world that relies more and more on technology, simply necessary.
Nonetheless, millions of children, the majority of whom are girls, still never learn to read and write today (pdf). This Sunday, September 8, is International Literacy Day, an event that Unesco has been observing for more than 40 years to highlight how essential literacy is to learning and also “for eradicating poverty, reducing child mortality, curbing population growth, achieving gender equality and ensuring sustainable development, peace and democracy.”
774 million people aged 15 and older are illiterate, an infographic (pdf) from Unesco details. 52 percent (pdf) live in south and west Asia and 22 percent in sub-Saharan Africa. The latter region is where most of the countries with the lowest literacy rates in the world are located, according to data from the C.I.A.:
1. Burkina Faso: 21.8 percent of the adults in this West African country are literate.
2. South Sudan: This country in east Africa, which became an independent state in 2011, has a literary rate of 27 percent.
3 Afghanistan: 28.1 percent of this country’s population are literate with a far higher percentage of men (43.1 percent) than women (12.6 percent) able to read.
4. Niger: The ratio of men to women in this landlocked western African country is also lopsided: the literacy rate is 42.9 percent for men, 15.1 percent for women and 28.7 percent overall.
5. Mali: Niger’s neighbor on the west, the literacy rate in Mali is 33.4 percent. 43.1 percent of the adult male population can read and 24.6 percent of the country’s women.
6. Chad: This west African country is Niger’s neighbor on its eastern border; 34.5 percent of its population is literate.
7. Somalia: Long beset by civil war and famine, 37.8 of Somalia’s population is literate. 49.7 percent of the adult male population is literate but only 25.8 percent of adult females.
8. Ethiopia: Somalia’s neighbor to the north, the literacy rate in Ethiopia is 39 percent.
9. Guinea: 41 percent of this west African country’s population is literate. More than half (52 percent) of adult males are literature and only 30 percent of women.
10. Benin: 42.4 percent of Benin in West Africa are literate.
Around the world, two-thirds of adults who are illiterate are female, meaning that there are 493 women unable to read and write.
54 of the 76 million illiterate young women come from nine countries, most in south and west Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa and not necessarily those with high rates of adult illiteracy: India (where almost 30 million young women are illiterate), Pakistan, Nigeria, Ethiopia, Bangladesh, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the United Republic of Tanzania, Egypt and Burkina Faso.
Why Literacy Is a Human Right
Those who cannot read and write are “destined to be on the social and economic margins of our world,” Unesco reminds us. Being able to read and write has profound benefits not only on a person’s educational opportunities but also for their health, economic prospects and their children.
My late grandmother, who emigrated from southern China to Oakland in the early 20th century, never learned to read or write anything beyond her first and last name. She relied completely on her children or grandchildren to read the instructions on a bottle of medicine, to open her mail and pay her bills. Once when she was in her 90s and still living alone in Oakland Chinatown, a strange man knocked on her door, showed her some official-looking documents and insisted that he had to enter her house. She shut the door in his face and immediately called my dad.
Had my grandmother been able to read the papers the man had in his hand, she could have known what he was up to. As a girl in rural China at the start of the previous century, no one gave a thought to teaching her to read or write. She worked for most of her life (she was still sewing piecework for clothing manufacturers into her 90s). Like many older adults, she simply never had time to devote her energies to learn to read and write.
In 2010, the literacy rate was higher for young people (89.6 percent) than for adults (84.1 percent), according to a report from Unesco (pdf). It’s essential that as many children as possible go to school, learn to read and write and acquire the numeracy skills necessary to thrive in our technology-drive world. This year’s International Literacy Day is specifically dedicated to “literacies for the 21st century,” in recognition that we not only need to need to provide “basic literacy skills for all” but also “equip everyone with more advanced literacy skills as part of lifelong learning.”
The Oromo are the second largest indigenous population in Africa March 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Afaan Publication, Africa, African Beat, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Colonizing Structure, Development, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Facebook and Africa, Fatuma Roba, Finfinnee, Gadaa System, Haacaaluu Hundeessaa, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Humanity and Social Civilization, Irreecha, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Language and Development, Nubia, OMN, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Media Network, Oromo Music, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo Sport, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Poverty, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Saudi Arabia, Self determination, Sidama, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oldest Living Person Known to Mankind, The Oromo Democratic system, The Oromo Governance System, The Oromo Library, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Development, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia and Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo people, Oromummaa, poverty, State and Development, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Hard roads to freedom: The Oromo fight for recognition in their new home
refugeeweek
‘We have to tell people we are the second largest indigenous population in Africa
because nobody knows about us.’
 http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/hard-roads-to-freedom-the-oromo-fight-for-recognition-in-their-new-home/
http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/hard-roads-to-freedom-the-oromo-fight-for-recognition-in-their-new-home/
http://advocacy4oromia.files.wordpress.com/2013/05/oromo-fight-for-recognition-in-their-new-home.pdf
The tyranny of experts vs the real cause of poverty:The unchecked power of the state against poor people without rights March 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Poverty, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Aid, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromummaa, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment

How development experts have empowered dictators and helped to trap millions and millions of people in poverty
“Ethiopia, for example, reaps money and plaudits from development giants such as the Gates Foundation while remaining a bastion of authoritarian rule. Economic growth and other positive development outcomes in such states are a mirage, the author argues. His central claim is that no matter how much international aid is poured in, the lives of citizens won’t durably improve without freedom.” -SARAH CHAYES, Book Review, Wall Street Journal
‘The international professionals perpetrate an illusion that poverty is purely a technical problem, distracting attention away from the real cause: the unchecked power of the state against poor people without rights. The dictators whom experts are advising are not the solution — they are the problem. The individual economic and political rights crucial to development include all those we take for granted at home, such as the right to your own property, the right to trade with whomever you wish, the right to protest bad government actions (don’t burn down our houses!), and the right to vote for politicians who do beneficial actions (clean our water!). Technical experts in development sometimes concede some rights and deny others, which disrespects rights for what they are: unalienable. The Uganda story shows the Mubende farmers’ lack of both economic rights (rights to their own property) and political rights (prevented at gunpoint from protesting). The tyranny of experts that neglects rights is first of all a moral tragedy. It reflects a double standard in which we respect rights for the world’s rich — is it conceivable that we would forget these farmers if the story had happened in Ohio? — but not for the poor.
The technocratic approach of dictators advised by experts is also a pragmatic tragedy, because it does not actually work to end poverty. New research by economists on history and modern experience suggest that free individuals with political and economic rights make up remarkably successful problem-solving systems. Such systems based on rights reward a decentralized array of people: Economic entrepreneurs with property rights get to keep the rewards of solving the problems of their consumers. Political entrepreneurs at many government levels and in many departments get rewarded with a longer tenure in office if they solve the citizens’ problems, and they are driven out of office if they don’t. …Focusing on rights yields two perspectives on how development success happens. First, societies that have already attained individual freedom are likely to have already escaped poverty. Economists have gone back deep into our own history to confirm this widely-accepted story for how we in the West escaped our own poverty, but we seem unwilling to consider that the same story could play out in the rest of the world. Second, societies in which there is a positive change in in freedom will likely see a positive change in prosperity (ergo, rapid economic growth and fall in poverty). So what should we do about rights for the poor? Possible starting places for Western policy changes are to not fund dictators, to not support projects that torch farms, to not break promises to investigate rights abuses, and to not let us forget such abuses and missing investigations. But obsessing too much on the “what should we do?” question should not hand the agenda back to the same technical experts who have showed so little interest in the rights of the poor in the first place. The danger of such a tyranny of experts is illustrated by a long history of politicians using technical poverty debates as an excuse to avoid debating rights for the poor. The danger of such a tyranny of experts is illustrated by a long history of politicians using technical poverty debates as an excuse to avoid debating rights for the poor.’ – Read the details and analysis at the original source: http://www.foreignpolicy.com/articles/2014/03/10/the_new_tyranny
Book Review: ‘The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor’ by William Easterly
 The notion of development assistance was born in a period of unabashed racism.
The notion of development assistance was born in a period of unabashed racism.
By SARAH CHAYES
March 7, 2014 (The Wall Street Journal) — Why does poverty persist across so much of the world, despite billions of dollars in international aid and the efforts of armies of development professionals? That is the question that William Easterly explores in “The Tyranny of Experts: Economists, Dictators, and the Forgotten Rights of the Poor.” His answer: a lack of respect for liberty—not just on the part of governments of impoverished countries but also, more provocatively, on the part of the would-be developers themselves.
Mr. Easterly, an economics professor at New York University, joins other students of international aid in decrying the preference for technical fixes when the political structures of recipient states are built to deny political participation and economic opportunity to most of their citizens. “The technocratic illusion,” he writes, “is that poverty results from a shortage of expertise, whereas poverty is really about a shortage of rights.”
Ethiopia, for example, reaps money and plaudits from development giants such as the Gates Foundation while remaining a bastion of authoritarian rule. Economic growth and other positive development outcomes in such states are a mirage, the author argues. His central claim is that no matter how much international aid is poured in, the lives of citizens won’t durably improve without freedom.
Mr. Easterly recalls that the very notion of development assistance was born in a period of unabashed racism, out of a conjunction of two opposing demands. One was the need for late colonial empires to provide a different rationale than racial superiority for their continued domination of the Third World. The other was the desire of Third World leaders to legitimize seizing authoritarian power themselves.
Touting the virtues of development designed by “experts” and delivered by autocrats proved to be a useful strategy for both camps. “Sun Yat-sen,” writes Mr. Easterly of China in 1924, “suggested the idea of technocratic development to resist European imperialism in China, while at the same time in Versailles, the Allies suggested technocratic development to expand European imperialism in Africa.” And, a few decades later, “the new African leaders found state-led technocratic development to be a justification for their own aspirations to unchecked power.”
This marriage of convenience may have sabotaged democracy’s chances of emerging from the rubble of empire, Mr. Easterly suggests, drawing on evidence from China, Colombia and West Africa. The bias in favor of technocratic fixes, and against fundamental political reform, has certainly helped enable autocratic regimes, which, now as then, capture development aid like any other rent. In Yemen, for example, before counterterrorism security cooperation grew to its current scale, aid was a key source of funding for the Ali Abdullah Saleh regime.
Mr. Easterly’s alternative to the autocrat-driven, technocratic model of development is simple: Apply abroad what we know has worked at home—bottom-up solutions, a free flow of ideas leading to innovative experiments and democratic politics. His positive examples aren’t drawn from the international-assistance realm but rather from the organic emergence of economic prosperity in such environments as 12th-century Italian city-states or the Korean auto industry. Hyundai’s rise is presented as an example of an efficient division of labor engineered almost as a matter of course by free-market forces. Unable to farm his infertile land, Chung Ju Yung, who liked tinkering with cars, set up as a mechanic, thereby exchanging “his problem-solving talents . . . for the problem-solving talents of others in producing food for him.” He would go on to found Hyundai.
Mr. Easterly is hardly the first to criticize the international-development community for its avoidance of politics and fixation on technical solutions. But his belabored insistence that freedom and democracy are the only reliable paths to economic prosperity is too general and thus not very helpful for anyone thinking seriously about how to reform development assistance. While he is right to castigate the many aid efforts undertaken in autocratic contexts, few serious Western development professionals today actively promote dictatorship. Indeed, acceptance of much of Mr. Easterly’s reasoning has driven, from the 1990s on, a sharp increase in support for grass-roots development and democratization efforts.
But Mr. Easterly fails to acknowledge such evolutions. And he thereby misses an opportunity to highlight the obstacles that this approach, in turn, has encountered: the tendency of such grass-roots organizations to respond to the desires of donors rather than their own constituencies, their inability to live up to outsize expectations or, when successful, their tendency to suffer repression at the hands of authoritarian states. Nor does Mr. Easterly contend in detail with the fundamental question raised by his book: What explains the persistence of such a “momentous double standard on rights for the West and not for the Rest?”
Some explanations do emerge in passing. Geostrategic priorities, for example, have impelled the U.S. to use foreign aid to reward autocratic allies in the fights against Communism and terrorism. Racism, blatant or otherwise, has made Westerners doubt non-white non-Westerners’ desire for rights and ability to handle them. The desire to self-perpetuate has also been a powerful motive to stick to the status quo for an industry as large as international assistance—a motive Mr. Easterly doesn’t emphasize. Challenging entrenched power structures is a good way to get thrown out of a country, as a number of democracy-promotion organizations recently learned in Egypt.
Apart from these gaps, and the book’s lack of explicit recommendations, its analysis raises some philosophical problems. It draws too sharp an opposition between individualism and collective values. By depicting a global “East” caught in a feedback loop of autocracy and “collectivist values,” Mr. Easterly falls into Samuel Huntingtonesque generalizations. Similarly, he seems to suggest that geography and climate predisposed the Southern Hemisphere to slave-based or extractive economies.
The generalizations, moreover, evade a lot of contrary nuance. The Nordic countries are widely seen as more respectful of community values than the U.S. or Britain. And many of their health and development outcomes outstrip ours. Some might argue that these are smaller, more homogeneous societies, but so are some of the negative examples of “collectivist values” that Mr. Easterly cites, such as the “Maghribi” network, a 10th-century Cairo-based Jewish trading community. And the world economic meltdown of 2008, with devastating development effects for tens of millions, was the result not of excessively collectivist values but the reverse. Poor development outcomes, in other words, aren’t only a matter of rights, as Mr. Easterly argues. At issue is also the distribution of power—justice as well as liberty.
The book’s argument about the power of freedom and democracy to beget development is made by way of a vast historical tableau. From the 12th-century Italian city-states, the narrative winds past the slave trade, expounds the virtues of migration, explores the ideas of Adam Smith and ruminates on the structure of technological innovation. Supporting anecdotes include a Senegalese religious trading community, the Korean automotive industry and an evolving Manhattan neighborhood.
It is hard to trust an author to command such a welter of detail. And indeed, the result is too often haphazard, self-contradictory or erroneous. For example, while the Maghribi traders are said to demonstrate self-sabotaging collectivist values, the Mourides, a modern Somali religious brotherhood that is organized along nearly the same principles, is cited to illustrate the virtues of migration. The Korean auto industry, depicted as embodying “the amazing potentials of specialization and trade,” emerged under an autocratic government applying protectionist laws.
By my count, finally, about 15% of Mr. Easterly’s text recaps what was just said or announces items from later chapters. Subheadings like “Another Key Moment in This Book” suggest an argument that isn’t tight enough to convince on its own merits. And that’s too bad. Mr. Easterly calls for a profound overhaul of the way powerful nations conceive of and implement aid—and, more important, of the broader foreign-policy decision-making of which aid is a component. That change is needed. It’s just not clear this book is crisp or cogent enough to help advance it.
—Ms. Chayes is a senior associate at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
To buy this book Click Here
Ethiopia is one of the poorest countries in the world and has the second largest population in Africa: Poverty means the health system is weak March 9, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Comparative Advantage, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Human Rights, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“In the early 80′s, Bob Geldof of the band called The Boomtown Rats saw in the news the massive famine engulfing the African country of Ethiopia. He felt guilty because he couldn’t believe that while the Western world was suffering from an abundance of wealth and food, a continent just below them were a people that did not have anything at all. He organized Band Aid, enlisting the help of other stars like Bono, George Michael and Sting, to raise funds for Africa through a song entitled “Do They Know It’s Christmas?” Their counterparts in the United States followed suit, with Michael Jackson and Lionel Richie writing a song called “We are the World.” They then banded together for Live Aid, that added stars like Madonna, Paul McCartney and Elton John in a two-continent concert. Yet, almost three decades after, Africa remains a veritable wasteland. Out of the 20 poorest countries in the world, 17 comes from the continent, including nine out of the top 10. Based on the different countries’ gross domestic product purchasing power parity, here are the 20 poorest countries in the world in 2013.”
‘Ethiopia is one of the poorest countries in the world and has the second largest population in Africa. Poverty means the health system is weak, which means:
The average life expectancy is just 59
Out of every 40 women that go in to labour, one dies
Over a third of children are malnourished
90% of Ethiopians have poor health, a low level of education, and inadequate living conditions
Only 200 doctors are trained per year to serve a country with a population of over 80 million.
Ethiopia has suffered periodic droughts and famines, a long civil conflict in the 20th century, and a border war with Eritrea. This brought millions to the brink of starvation in the 1970s and 1980s.’
http://www.healthpovertyaction.org/where-we-work/africa/ethiopia/
About 29 per cent of the population lives below the national poverty line. Ethiopia ranks 174th out of 187 countries on the United Nations Development Programme’s human development index, and average per capita incomes are less than half the current sub-Saharan average.
Ethiopia has enormous potential for agricultural development. At present only about 25 per cent of its arable land is cultivated, and agriculture is dominated by subsistence rain fed farming, using few inputs and characterized by low productivity. The vast majority of farmers are smallholders. About 12.7 million smallholders produce 95 per cent of agricultural GDP. These farmers are extremely vulnerable to external shocks such as volatile global markets and drought and other natural disasters.
Smallholder farmers form the largest group of poor people in Ethiopia. More than half cultivate plots of 1 hectare or less and struggle to produce enough food to feed their households. A large number of poor households face a prolonged hunger season during the pre-harvest period. Herders, like farmers, are vulnerable to increasingly frequent drought, which can wipe out their livestock and assets and bring on severe poverty.
The persistent lack of rainfall is a major factor in rural poverty. Drought has become more frequent and severe throughout the country over the past decade, and the trend shows signs of worsening. The impact of drought is most severe for vulnerable households living in the pastoral areas of lowlands and the high-density parts of highlands.
In addition to their vulnerability to climatic conditions, poor rural people lack basic social and economic infrastructure such as health and education facilities, veterinary services and access to safe drinking water. Among the more specific causes of rural poverty in Ethiopia are:
• An ineffective and inefficient agricultural marketing system;
• Underdeveloped transport and communications networks;
• Underdeveloped production technologies;
• Limited access of rural households to support services;
• Environmental degradation;
• Lack of participation by rural poor people in decisions that affect their livelihoods.
The intensity of poverty varies at the household level in relation to the land’s size, quality and productivity, climate conditions and production technologies. Households headed by women are particularly vulnerable. Women are much less likely than men to receive an education or health benefits, or to have a voice in decisions affecting their lives. For women, poverty means more infant deaths, undernourished families, lack of education for children and other deprivations.
Ethiopia has an estimated 1.3 million people living with HIV and AIDS. Rural areas have low prevalence rates, but available data suggest that the incidence could increase in these areas. With the support of development partners, the government has embarked on major programmes to combat the spread of HIV and AIDS, and assist poor rural households in coping with the social and economic consequences of living with the disease.- IFAD
http://www.ruralpovertyportal.org/country/home/tags/ethiopia
‘A Unicef report states that in Ethiopia there are at this moment 4.5 million orphans on a population of some 90 million. The 4.5 million means that 5 percent of the total population is an orphan. Orphans are in Ethiopia defined as children under 18 whose both parents died. They died of AIDS, untreated illnesses, hunger, draught and war.’
A Calculation: The ‘Orphan Crisis’ in Ethiopia
Copyright © Oromianeconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer.
Democracy Is On Average Richer, Lets People Speak Their Minds, Shape Their Own And Their Children’s Futures February 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Ancient African Direct Democracy, Corruption, Gadaa System, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Governance System, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: African Studies, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Gadaa System, Gadaa: Ancient Africa (Oromo) democratic system is a form of direct democracy, Governance issues, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Oromia, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
1 comment so far
“Democracies are on average richer than non-democracies, are less likely to go to war and have a better record of fighting corruption. More fundamentally, democracy lets people speak their minds and shape their own and their children’s futures. That so many people in so many different parts of the world are prepared to risk so much for this idea is testimony to its enduring appeal.”
Ethiopia: in 1972 not free, in 1991 partly free and in 2013 not free.

See chart by the Economist through the link and read the analysis@ http://www.economist.com/news/essays/21596796-democracy-was-most-successful-political-idea-20th-century-why-has-it-run-trouble-and-what-can-be-do
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The protesters who have overturned the politics of Ukraine have many aspirations for their country. Their placards called for closer relations with the European Union (EU), an end to Russian intervention in Ukraine’s politics and the establishment of a clean government to replace the kleptocracy of President Viktor Yanukovych. But their fundamental demand is one that has motivated people over many decades to take a stand against corrupt, abusive and autocratic governments. They want a rules-based democracy.
It is easy to understand why. Democracies are on average richer than non-democracies, are less likely to go to war and have a better record of fighting corruption. More fundamentally, democracy lets people speak their minds and shape their own and their children’s futures. That so many people in so many different parts of the world are prepared to risk so much for this idea is testimony to its enduring appeal.
Yet these days the exhilaration generated by events like those in Kiev is mixed with anxiety, for a troubling pattern has repeated itself in capital after capital. The people mass in the main square. Regime-sanctioned thugs try to fight back but lose their nerve in the face of popular intransigence and global news coverage. The world applauds the collapse of the regime and offers to help build a democracy. But turfing out an autocrat turns out to be much easier than setting up a viable democratic government. The new regime stumbles, the economy flounders and the country finds itself in a state at least as bad as it was before. This is what happened in much of the Arab spring, and also in Ukraine’s Orange revolution a decade ago. In 2004 Mr Yanukovych was ousted from office by vast street protests, only to be re-elected to the presidency (with the help of huge amounts of Russian money) in 2010, after the opposition politicians who replaced him turned out to be just as hopeless.
Between 1980 and 2000 democracy experienced a few setbacks, but since 2000 there have been many
Democracy is going through a difficult time. Where autocrats have been driven out of office, their opponents have mostly failed to create viable democratic regimes. Even in established democracies, flaws in the system have become worryingly visible and disillusion with politics is rife. Yet just a few years ago democracy looked as though it would dominate the world.
In the second half of the 20th century, democracies had taken root in the most difficult circumstances possible—in Germany, which had been traumatised by Nazism, in India, which had the world’s largest population of poor people, and, in the 1990s, in South Africa, which had been disfigured by apartheid. Decolonialisation created a host of new democracies in Africa and Asia, and autocratic regimes gave way to democracy in Greece (1974), Spain (1975), Argentina (1983), Brazil (1985) and Chile (1989). The collapse of the Soviet Union created many fledgling democracies in central Europe. By 2000 Freedom House, an American think-tank, classified 120 countries, or 63% of the world total, as democracies.
Representatives of more than 100 countries gathered at the World Forum on Democracy in Warsaw that year to proclaim that “the will of the people” was “the basis of the authority of government”. A report issued by America’s State Department declared that having seen off “failed experiments” with authoritarian and totalitarian forms of government, “it seems that now, at long last, democracy is triumphant.”
Such hubris was surely understandable after such a run of successes. But stand farther back and the triumph of democracy looks rather less inevitable. After the fall of Athens, where it was first developed, the political model had lain dormant until the Enlightenment more than 2,000 years later. In the 18th century only the American revolution produced a sustainable democracy. During the 19th century monarchists fought a prolonged rearguard action against democratic forces. In the first half of the 20th century nascent democracies collapsed in Germany, Spain and Italy. By 1941 there were only 11 democracies left, and Franklin Roosevelt worried that it might not be possible to shield “the great flame of democracy from the blackout of barbarism”. Read further @
http://www.economist.com/news/essays/21596796-democracy-was-most-successful-political-idea-20th-century-why-has-it-run-trouble-and-what-can-be-do
21 Things They Never Tell You About Poverty & Poor Countries February 27, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Theory of Development, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromo people, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
- Poverty-as-rule-not -exception is difficult to bend our minds around because we tend to base our views about the world on direct experience. If people around us seem mostly well-fed and content, then why shouldn’t everybody else be? We still don’t know as much as we should about poverty and we try to ignore poor people. Most people’s experience of the global poor is the waiter at their table or the pool attendant, the ones lucky enough to have jobs. Only by direct experience and immersion in local circumstances is it possible to have a vague inkling of what it might be like to be genuinely destitute. There’s no obligation on holidaymakers to go wandering around in slums, but anybody who claims knowledge about deprivation should experience or observe it first-hand for themselves, ideally for a long time.
- Which undermines my first four points. As Morten Jerven says in his book Poor Numbers: How We Are Misled By African Development Statistics And What To Do About It, “the most basic metric of development, GDP, should not be treated as an objective number but rather as a number that is a product of a process in which a range of arbitrary and controversial assumptions are made.” Jerven finds that the discrepancy between different GDP estimates is up to a half in some cases. This supports my experience from working in the least developed countries, where statistics offices are usually underfunded and don’t have the resources to collect data often or well enough.
- There’s a kind of false scientism: foreign academic economists spend ages refining complicated econometric models despite the raw material being rubbish. In the absence of good numbers, the only immediate alternative is to live in a country, to use good theory and to rely where necessary on case studies and even anecdote.
- A report from Oxfam last month pointed out that 85 people, about as many as would fit on a double-decker bus, own as much wealth as the bottom half of the world’s population.
- The Spirit Level by Kate Pickett and Richard Wilkinson shows that equality is good for everyone. Redistribution reduces poverty and makes life better for the rich in the form of less crime, better education and a more cohesive society. Global inequality is getting worse, not better. If we don’t radically reduce inequality the poor will eat us, so aid isn’t an option, and it’s not about the rich world “saving” the poor. It’s essential for everyone.
- Although things are improving, a huge chunk of the world’s population remain poor. Over a fifth of humans, 1.29 billion, are considered extremely poor . In effect the equivalent of every man, woman and child in Europe, the United States and the Middle East scrape by on 75 British pence a day adjusted for the cost of living in each country. About a third of the world lives on less than $2 a day. The poorest half of the world – 3.5 billion people – own only 0.71% of the world’s wealth between them.
- A billion people live in chronic hunger. Nearly a third of all children are chronically malnourished, which unless addressed before the age of two often leaves them stunted and mentally impaired. A sixth of the world’s adults can’t read or write and many more have only rudimentary literacy. Sub-Saharan Africa has only two doctors for every 10,000 people, which is partly why on average its inhabitants live to an average age of 56.
- Rather than a term like “developing” to describe these people and countries, the travel writer Dervla Murphy’s phrase “majority world” is more accurate.
- “The four basic needs: food, housing, clothes and medicine must be cheap and easy for everybody. That’s civilisation”, says Jon Jandai, a farmer from northeast Thailand. I’d add primary, secondary and tertiary education, too.
- Lower income countries have leapfrogged some technologies. For example many will never install fixed telephone lines because mobile coverage is so good. Vast numbers of people will never touch a PC, doing all their computing on a smartphone or tablet.
- The governments of poor countries should be more adventurous, leapfrogging ideologies too. Some proponents of economic growth argue that environmental sustainability and a focus on happiness will handicap poverty reduction. But it could enable some countries to prioritise the important things in life. Endless growth is impossible and undesirable.
- Beyond a certain point rich inefficiency is the real problem. Why do developing countries ape the development paths and economic structures of the West? We are wage slaves who perform bullshit jobs so that we can service our mortgages. The advance of the car ruined everyone’s quality of life so that a minority can sit in air-conditioned metal boxes in jams. Clever though-leadership in the majority world could lead the way for the rich. Bhutan’s idea of Gross National Happiness is an example.
- There’s plenty of food to go round. World agriculture produces 17% more calories per person today than it did 30 years ago despite a 70% population increase, due to rising yields, higher farming intensity and more use of land. The real problems are the system of distribution and energy use. If the rich world didn’t hog all the food and produce it inefficiently there’d be enough for everyone.
- The amount officially spent on each poor person globally is US$20 a year, according to the World Bank. The amount has doubled in the last decade following a dip in the late 1990s. But several opinion polls show that rich country inhabitants think they’re much more generous than they really are. Americans think that their government spends 28% of the budget on aid when it’s really about 1%. Brits are almost as bad. The result of this widespread overestimation of generosity is that many people in rich countries want to cut aid.
http://emergenteconomics.com/2014/02/24/21-things-they-never-tell-you-about-poor-countries/
Prompted by Bill Gates’s annual letter and the response from the Overseas Development Institute I thought I’d list some of the things that in my experience seem to be less understood about poor countries. (I wanted to list 23 things like Ha-Joon Chang on capitalism but I couldn’t think of another two). I use the word poor on purpose because although the word risks sounding patronising or dismissive, euphemisms like developing and less-developed can be worse. Thoughts are welcome.
1. Poverty is the rule, not the exception.For most people life just isn’t as good as it is for you and I, the comfortable people from a country rich enough to allow us the literacy, time and Internet access to read blogs written by well-meaning left liberals. Poverty-as-rule-not -exception is difficult to bend our minds around because we tend to base our views about the world on direct experience. If…
View original post 3,098 more words
Ethiopia’s Land & Water Grabs Devastate Communities: New Satellite Imagery Shows Extensive Clearance of Land Used By Indigenous People to Make Way for State-Run Sugar Plantations February 25, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Environment, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Hadiya, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Kambata, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Sidama, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Gambella and Omo Valley, Genocide against the Oromo, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Water and Land Grabs in Ormia, World Bank
1 comment so far

‘Ethiopia’s Lower Omo Valley, a UNESCO World Heritage site and home to 200,000 agro-pastoralists, is under development for sugar plantations and processing. The early stages of the development have resulted in the loss of land and livelihoods for thousands of Ethiopia’s most vulnerable citizens. The future of 500,000 agro-pastoralists in Ethiopia and Kenya is at risk.’ – Human Rights Watch
http://www.hrw.org/node/123131
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/lori-pottinger/ethiopia-pushes-river-bas_b_4811584.html
(Nairobi) – New satellite imagery shows extensive clearance of land used by indigenous groups to make way for state-run sugar plantations in Ethiopia’s Lower Omo Valley, Human Rights Watch and International Rivers said today. Virtually all of the traditional lands of the 7,000-member Bodi indigenous group have been cleared in the last 15 months, without adequate consultation or compensation. Human Rights Watch has also documented the forced resettlement of some indigenous people in the area.
The land clearing is part of a broader Ethiopian government development scheme in the Omo Valley, a United National Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Site, including dam construction, sugar plantations, and commercial agriculture. The project will consume the vast majority of the water in the Omo River basin, potentially devastating the livelihoods of the 500,000 indigenous people in Ethiopia and neighboring Kenya who directly or indirectly rely on the Omo’s waters for their livelihoods.
“Ethiopia can develop its land and resources but it shouldn’t run roughshod over the rights of its indigenous communities,” said Leslie Lefkow, deputy Africa director at Human Rights Watch. “The people who rely on the land for their livelihoods have the right to compensation and the right to reject plans that will completely transform their lives.”
A prerequisite to the government’s development plans for the Lower Omo Valley is the relocation of 150,000 indigenous people who live in the vicinity of the sugar plantations into permanent sedentary villages under the government’s deeply unpopular “villagization” program. Under this program, people are to be moved into sedentary villages and provided with schools, clinics, and other infrastructure. As has been seen in other parts of Ethiopia, these movements are not all voluntary.
Satellite images analyzed by Human Rights Watch show devastating changes to the Lower Omo Valley between November 2010 and January 2013, with large areas originally used for grazing cleared of all vegetation and new roads and irrigation canals crisscrossing the valley. Lands critical for the livelihoods of the agro-pastoralist Bodi and Mursi peoples have been cleared for the sugar plantations. These changes are happening without their consent or compensation, local people told Human Rights Watch. Governments have a duty to consult and cooperate with indigenous people to obtain their free and informed consent prior to the approval of any project affecting their lands or territories and other resources.
The imagery also shows the impact of a rudimentary dam built in July 2012 that diverted the waters of the Omo River into the sugar plantations. Water rapidly built up behind the shoddily built mud structure before breaking it twice. The reservoir created behind the dam forced approximately 200 Bodi families to flee to high ground, leaving behind their crops and their homes.
In a 2012 report Human Rights Watchwarned of the risk to livelihoods and potential for increased conflict and food insecurity if the government continued to clear the land. The report also documented how government security forces used violence and intimidation to make communities in the Lower Omo Valley relocate from their traditional lands, threatening their entire way of life with no compensation or choice of alternative livelihoods.
The development in the Lower Omo Valley depends on the construction upstream of a much larger hydropower dam – the Gibe III, which will regulate river flows to support year-round commercial agriculture.
A new film produced by International Rivers, “A Cascade of Development on the Omo River,” reveals how and why the Gibe III will cause hydrological havoc on both sides of the Kenya-Ethiopia border. Most significantly, the changes in river flow caused by the dam and associated irrigated plantations could cause a huge drop in the water levels of Lake Turkana, the world’s largest desert lake and another UNESCO World Heritage site.
Lake Turkana receives 90 percent of its water from the Omo River and is projected to drop by about two meters during the initial filling of the dam, which is estimated to begin around May 2014. If current plans to create new plantations continue to move forward, the lake could drop as much as 16 to 22 meters. The average depth of the lake is just 31 meters.
The river flow past the Gibe III will be almost completely blocked beginning in 2014. According to government documents, it will take up to three years to fill the reservoir, during which the Omo River’s annual flow could drop by as much as 70 percent. After this initial shock, regular dam operations will further devastate ecosystems and local livelihoods. Changes to the river’s flooding regime will harm agricultural yields, prevent the replenishment of important grazing areas, and reduce fish populations, all critical resources for livelihoods of certain indigenous groups.
The government of Ethiopia should halt development of the sugar plantations and the water offtakes until affected indigenous communities have been properly consulted and give their free, prior, and informed consent to the developments, Human Rights Watch and International Rivers said. The impact of all planned developments in the Omo/Turkana basin on indigenous people’s livelihoods should be assessed through a transparent, independent impact assessment process.
“If Ethiopia continues to bulldoze ahead with these developments, it will devastate the livelihoods of half a million people who depend on the Omo River,” said Lori Pottinger, head of International Rivers’ Ethiopia program. “It doesn’t have to be this way – Ethiopia has options for managing this river more sustainably, and pursuing developments that won’t harm the people who call this watershed home.”
Background
Ethiopia’s Lower Omo Valley is one of the most isolated and underdeveloped areas in East Africa. At least eight different groups call the Omo River Valley home and the livelihood of each of these groups is intimately tied to the Omo River and the surrounding lands. Many of the indigenous people that inhabit the valley are agro-pastoralist, growing crops along the Omo River and grazing cattle.
In 2010, Ethiopia announced plans for the construction of Africa’s tallest dam, the 1,870 megawatt Gibe III dam on the Omo River. Controversy has dogged the Gibe III dam ever since. Of all the major funders who considered the dam, only China’s Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) provided financing (the World Bank, African Development Bank, and European Investment Bank all declined to fund it, though the World Bank and African Development Bank have financed related power lines).
The Ethiopian government announced even more ambitious plans for the region in 2011, including the development of at least 245,000 hectares of irrigated state-run sugar plantations. Downstream, the water-intensive sugar plantations, will depend on irrigation canals. Although there have been some independent assessments of the Gibe dam project and its impact on river flow and Lake Turkana, to date the Ethiopian government has not published any environmental or social impact assessments for the sugar plantations and other commercial agricultural developments in the Omo valley.
According to the regional government plan for villagization in Lower Omo, the World Bank-supported Pastoral Community Development Project (PCDP) is funding some of the infrastructure in the new villages. Despite concerns over human rights abuses associated with the villagization program that were communicated to Bank management, in December 2013 the World Bank Board approved funding of the third phase of the PCDP III. PCDP III ostensibly provides much-needed services to pastoral communities throughout Ethiopia, but according to government documents PCDP also pays for infrastructure being used in the sedentary villages that pastoralists are being moved to.
The United States Congress in January included language in the 2014 Appropriations Act that puts conditions on US development assistance in the Lower Omo Valley requiring that there should be consultation with local communities; that the assistance “supports initiatives of local communities to improve their livelihoods”; and that no activities should be supported that directly or indirectly involve forced evictions.
However other donors have not publicly raised concerns about Ethiopia’s Lower Omo development plans. Justine Greening, the British Secretary of State for International Development, in 2012 stated that her Department for International Development (DFID) was not able to “substantiate the human rights concerns” in the Lower Omo Valley despite DFID officials hearing these concerns directly from impacted communities in January 2012.
Ethiopia: Land, Water Grabs Devastate Communities | Human Rights Watch
http://www.hrw.org/news/2014/02/18/ethiopia-land-water-grabs-devastate-communities
The ‘Africa Rising’ Narrative: A Single Optimist Narrative Masks Growing Inequality in the Continent February 24, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Economics, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, International Economics, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, South Sudan, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo culture, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
“Compare that with the mean wealth of a South African at $11,310, Libyan ($11,040) and Namibian ($10,500). While the average Ethiopian has his asset base standing at a mere $260 despite years of economic growth and foreign investment – wealth has not filtered through to the people. With this kind of glaring inequality between and within countries, the “Africa Rising” narrative risks masking the realities of millions of Africans struggling to get by in continent said to be on the move.” http://www.africareview.com//Blogs/Africa-is-rising-but-not-everywhere/-/979192/2219854/-/12at0a8/-/index.html?relative=true
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
“Africa Rising” is now a very popular story – a near-universal belief that the continent is the next investment frontier after more than a decade of sustained high growth rates and increased foreign direct investment.
We even now have memes for this new narrative.
But some people have their doubts about this whole “Afro-optimism” talk – they say Africa isn’t really rising.
They argue that Africa’s low levels of manufacturing and industrialisation discredit the continent’s “growth miracle”. Its share of world trade is remains very small compared to Asia.
Well, Africa cannot be reduced to a single narrative. We have been victims of this before – for hundreds of years the continent has always been seen in a kind of Hobbesian way – where life is poor, nasty, brutish and short.
Now, there is a minority global elite working round the clock trying to turn this long-held view of a continent.
While I do not begrudge them for their PR efforts – we cannot mask the glaring inequality in Africa by developing a new optimist narrative about the continent.
There are many stories about Africa. Not just one.
Genocide
While the sun shines bright in Namibia, not the same can be said of Malawi where the government is bankrupt or the Central African Republic (CAR) where sectarian violence is increasingly becoming genocidal.
Pretty much everyone else in the world seems accustomed to the living hell that is Somalia.
But we have also come to a consensus that Botswana and Ghana are the model countries in Africa.
South Africa is a member of the BRICS. While the petro-dollars are changing the fortunes of Angola – it has grown its wealth per capita by 527 per cent since the end of the civil war in 2002.
Not much can be said of South Sudan. Oil has not done anything despite pronouncements by the liberation leaders that independence holds much promise for the young nation’s prosperity.
The country imploded barely three years into into its independence.
This is the problem of a single narrative – it is indifferent to the growing and glaring inequality in Africa and its various political contexts.
Many Africans still have no access to the basic necessities of life. Millions go to bed without food and die from preventable diseases.
Others live in war-ravaged countries in constant fear for their lives. You can bet the last thing on their mind is not a blanket “rising” narrative about Africa and the promise it holds. That is not their Africa, its someone else’s.
Yes. “Africa Rising” may be real. But only to a small minority.
Wealth distribution
A report by New World Wealth highlights the variations in wealth distribution across the continent’s 19 wealthiest countries.
Africa’s total wealth stood at $2.7 trillion last year down from $3 trillion in 2007 after taking a hit from the global financial crisis.
These 19 countries control 76 per cent while the remaining 35 scrape over $648 billion. And most of this wealth is concentrated in northern and southern Africa.
The western, central and eastern regions have some of the poorest individuals on the continent with the highest per capita wealth from this group – with the exception of Angola – coming from Nigeria at $1,350.
Compare that with the mean wealth of a South African at $11,310, Libyan ($11,040) and Namibian ($10,500).
While the average Ethiopian has his asset base standing at a mere $260 despite years of economic growth and foreign investment – wealth has not filtered through to the people.
With this kind of glaring inequality between and within countries, the “Africa Rising” narrative risks masking the realities of millions of Africans struggling to get by in continent said to be on the move.
The sun may be shining bright in Africa – but only in favoured parts of it.
Read further @:
How to end poverty? February 22, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Poverty, Self determination, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo people, Parliament, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
“Nations fail economically because of extractive institutions. These institutions keep poor countries poor and prevent them from embarking on a path to economic growth. This is true today in Africa, in South America, in Asia, in the Middle East and in some ex-Soviet Union nations. While having very different histories, languages and cultures, poor countries in these regions have similar extractive institutions designed by their elites for enriching themselves and perpetuating their power at the expense of the vast majority of the people on those societies. No meaningful change can be expected in those places until the exclusive extractive institutions, causing the problems in the first place, will become more inclusive.” http://otrazhenie.wordpress.com/2014/02/16/how-to-end-poverty/#
“If we are to build grassroots respect for the institutions and processes that constitute democracy,” Mo Ibrahim writes for Project Syndicate, “the state must treat its citizens as real citizens, rather than as subjects. We cannot expect loyalty to an unjust regime. The state and its elites must be subject, in theory and in practice, to the same laws that its poorest citizens are.” http://www.huffingtonpost.com/dr-mo-ibrahim/africa-needs-rule-of-law_b_4810286.html?utm_hp_ref=tw

I was always wondering about the most effective way to help move billions of people from the rut of poverty to prosperity. More philanthropy from the wealthy nations of the West? As J.W. Smith points it, with the record of corruption within impoverished countries, people will question giving them money as such ‘donations’ rarely ‘reach the target’. Building industries instead? While that approach seems to provide better results (see few examples described by Ray Avery in his book ‘Rabel with a cause‘), it still did not provide a silver bullet solution, as it does not address the roots of poverty and prosperity.

From Christian Bowe
In their book ‘Why nations fail?‘, that examines the origin of poverty and prosperity, Daron Acemoglu and James Robinson conclusively show that it is man-made political and economic institutions that underlie economic success (or the lack of it). Therefore only the development of inclusive…
View original post 844 more words
Economics: The Comparative Advantage & Opportunity Cost February 22, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Comparative Advantage, David Ricardo, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Food Production, International Economics, International Trade, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Specialization, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.Tags: Comparative Advantage, David Ricardo, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Diversity and Trade, Economic and Social Freedom, economics, Opportunity Cost, Oromia, Specialization, Tade, Wealth
1 comment so far
Why States Commit Genocide February 22, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Colonizing Structure, Dictatorship, Ethiopia's Colonizing Structure and the Development Problems of People of Oromia, Afar, Ogaden, Sidama, Southern Ethiopia and the Omo Valley, Ethnic Cleansing, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Sidama, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human rights violations, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
It wasn’t always like this. Before nationalism, empires frequently ruled territory that contained many diverse peoples. The Habsburg family once ruled over the Spanish, Dutch and Austrian nations, along with many of the nations of Latin America. The Romans ruled hundreds of peoples great and small, from Greeks to Gauls to Britons to Iberians to Gallicians to Egyptians to Thracians to Illyrians to Carthaginians to Numidians and on and on. Before nationalism, peoples would rather submit to foreign conquerors than risk the loss of life and limb, and as a result conquerors rarely engaged in genocide except as a means of exacting vengeance on foreign rulers who defied them (as the Mongols and Assyrians were wont to do). Empires often took some of the vanquished as slaves, but rarely did empires kill thousands or millions of defenseless people deliberately and systematically for the sole purpose of decimating another nation. Instead, empires often brought conquered peoples into their trade networks, recruited them into their armies, and, eventually, even granted them citizenship rights. By treating conquered people well, they could in time acquire their loyalty.
Nationalism changed all of that. By placing lexical priority on independence and self-determination, all foreign occupiers become villains regardless of whether they are benign or malevolent in their treatment of the occupied nation. In this day and age, even members of a nation like the Scots, which enjoys spectacularly generous subsidies and full voting rights from the British government in Westminster, desire independence purely on the basis that some Scots are nationalists and believe that nothing less than full self-determination does their nation justice. If good treatment doesn’t buy loyalty, occupiers quickly find that they are without incentives to treat subject peoples well or to attempt to integrate them into their states. Nationalism becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy–if occupiers have nothing to gain by offering fair terms of cooperation, they will not offer them, and the subjugation nationalists fear becomes reality precisely because they fear it and refuse to cooperate with the occupier.
The occupier is left with two choices:
Get Out.
Kill Them All.
Often times, occupiers choose to abandon whatever ambitions they might have had and leave in defeat and disgrace. But this doesn’t always happen–some leaders correctly reason that if they could just replace the existing population with their own people, they could pacify the territory and keep the resources it provides. If those leaders have the stomach for it, they will do the following:
Systematically murder the resisting nation.
Colonize the extinct nation’s territory with their own citizens.
Profit.
If we want to prevent genocide, we need to prevent occupiers from having to choose between defeat and genocide.
Why States Commit Genocide
by Benjamin Studebaker
http://benjaminstudebaker.com/2014/02/21/why-states-commit-genocide/
A Cascade of Development on the Omo River:Lake Turkana at Risk from Dams and Plantations February 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Culture, Development, Economics, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, Land and Water Grabs in Oromia, Land Grabs in Africa, Omo, Omo Valley, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Gambella and Omo Valley, Gibe III Dam, Gibee River, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Lake Turkana, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Omo River, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, State and Development, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
1 comment so far
Omo River, Lake Turkana at Risk from Dams and Plantations
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/lori-pottinger/ethiopia-pushes-river-bas_b_4811584.html
Dams and irrigated plantations being built in Ethiopia will bring major changes to the flow of the Lower Omo River, which in turn will harm ecosystem functions and local livelihoods all the way to the river’s terminus at Lake Turkana in Kenya. More dams are planned for the basin that would compound the damages.
Here we outline some of the basic changes that can be expected as a result of these developments, and include resources on where to get more information.
The Gibe III reservoir is expected to start filling at the beginning of the next Kiremt rainy season (approximately May 2014); filling the reservoir will take up to three years. During this time, the river’s yearly flow will drop as much as 70%.
The Gibe III will provide stable flows year-round that will enable the growth of large commercial agricultural plantations in the Lower Omo. The Kuraz sugar plantation and additional areas identified for cultivation could eventually take almost half of the Omo River inflow to Lake Turkana.
These projects will cause a decrease in river flow and the size, length, and number of floods, which will be disastrous for downstream users. This is the first year in which runoff from the Kiremt season, which is vital for flood-recession agriculture, restoration of grazing areas, and fisheries production, will be almost completely blocked.
Changes to the flooding regime will disrupt fish spawning cues and decrease productive habitat for fish in Lake Turkana and the river. Lake fish catches may decrease.
Because the Omo River contributes almost all of Lake Turkana’s inflows each year, these developments could cause a big drop in lake water levels. Lake Turkana is projected to drop by about two meters during the initial filling of the dam. If current plans to create new plantations move forward, the lake could drop from 16 to 22 meters. The average depth of the lake is just 31 meters.
Climate change could worsen the water situation in the Omo. More extreme droughts and unpredictable precipitation patterns, combined with higher temperatures (which increase evaporation), could cause further stress to a region that already experiences extreme precipitation variability. There is evidence that there will be a drying trend and warmer temperatures.
The Gibe III and associated irrigation projects will limit people’s mobility and ability to practice diverse livelihoods, which are important ways people in the region have adapted to climate variability in the past.
The primary means of livelihood for about 500,000 people will be dismantled by the Gibe III and large-scale commercial agriculture. Conflicts over scarce resources are expected to increase.
http://www.internationalrivers.org/resources/omo-river-lake-turkana-at-risk-from-dams-and-plantations-8199
http://www.internationalrivers.org/blogs/258/human-rights-must-come-first
Africa Must Industrialize: The Time IS Now February 20, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Oromo, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Horn of Africa, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Social Sciences, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
As the current economic growth did not result from value addition and increased manufacturing, but instead from increases in world commodity prices, it makes the region susceptible to commodity price volatility. If commodity prices fall, Africa’s impressive economic growth might grind to a halt — thus, the dire need for diversification through industrialization. Even if commodity prices stay high, natural resources are not infinite and they must be managed with sagacity.
As recommended by the 2013 Africa Progress report, it is advantageous for African governments to fully implement the Accelerated Industrial Development for Africa (AIDA) plan, signed in 2008 in Addis-Ababa. The AIDA is a comprehensive framework for achieving the industrialization of the continent. If Africa can successfully steward its natural resource wealth, investing it wisely and using some to industrialize, then whether the resources run out or not or whether commodity prices fall, Africa would be on a good economic footing.
Moreover, not only will industrialization create the environment for adding value to Africa’s natural resources, but it will also provide much needed employment at various stages of the value adding chain for Africa’s 1.1 billion people — leading to wealth creation.
Industrialization will address many development gaps in sub-Saharan Africa. Some of these gaps, as noted in a UNECA Southern Africa Office Expert Group Meeting Report, include:
Africa’s high dependence on primary products
Low value addition to commodities before exports
High infrastructure deficit
High exposure to commodity price volatility
Limited linkage of the commodities sector to the local economy
Poorly developed private sector, which is highly undercapitalized
Limited commitment to implement industrial policies
Limited investment in R&D, science, innovation and technology
Low intra-Africa trade
Slow progress towards strengthening regional integration
The Time is Now
Is Africa ready? The answer is an emphatic yes. The phenomenal growth is one reason why Africa is ready, but growth on its own is not enough. Other conditions need to be considered: Does the continent have access to enough raw materials for production? What is the proximity of these natural resources to the continent? Is there adequate land, labor, and capital? These are the traditional factors of production or inputs to the production process.
Yes, Africa has access to the raw materials necessary for production. Unlike already industrialized nations who have to import raw materials from Africa and elsewhere over long distances, Africa enjoys close proximity to these resources.
With regards to the factors of production, Africa is the world’s second largest continent and therefore is home to plenty of land — most of which is arable.
Africa is also the world’s second most populous continent. The average age of an African in Africa is under 19 years. This means Africa has enough manpower or labor to industrialize.
Capital refers to man-made products used in the production process such as buildings, machinery and tools. Africa does have a measure of this, but instead needs to do more in this area — hence the need for greater infrastructural and skills development. In fact, African policymakers as well as their counterparts in the developed world should realize that it is high time for a shift in the nature of aid to the continent — from primarily monetary aid to the type of capital aid needed for industrialization.
Finally, when Africa successfully undergoes industrial development, its huge populace will serve as a market for the outputs of its production processes; any excess supply can be exported and swapped for foreign exchange. Africa is ready and the time for it to industrialize is now.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Fair Observer’s editorial policy.
read more@
Dependency Aid is Dysfunctional: Time for Self-sufficiency February 19, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Development, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Food Production, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Aid and Development, Developing country, Development, Development aid, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Land grabbing, Oromia, Social Sciences, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment
Against the dysfunctional dependency foreign assistance, Clare Lockhart in World Affairs argues for cheaper, smarter and stronger aid that creates self-sufficiency.
‘Commerce [and] entrepreneurial capitalism take more people out of poverty than aid . . . . It’s not just aid, it’s trade, investment, social enterprise. It’s working with the citizenry so that they can unlock their own domestic resources so that they can do it for themselves. Think anyone in Africa likes aid? Come on.’
Putting these “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches into effect will require some major shifts. It will involve looking not to how much money was disbursed, or how many schools were built, but to value for money and return on investment. And instead of propping up a vast technical assistance industry of varying and often indifferent quality, a higher priority will be placed on conducting a “skills audit” of key personnel—from doctors and teachers to engineers and agronomists—who can be trained internally rather than importing more costly and less invested technical assistance from abroad.
‘It is also important under this new paradigm to distinguish between “aid” (such as life-saving humanitarian assistance and the financial or material donations it requires) and “development engagement,” which is something quite different. Development engagement can be low-budget, and should be designed to move a needy country toward self-sufficiency—so that the state can collect its own revenues and the people can support their own livelihoods—as soon as possible. Many recipient countries have enormous untapped domestic resources, and with some effort devoted to increasing those revenues and building the systems to spend them, could assume much more of the responsibility of meeting their citizens’ needs.’
But a strategy is only as good as its execution. Implementing development policies and programs correctly will require a clear-eyed look at the way programs are designed and implemented, and a re-examination of the reliance on contractors. There is no substitute in the long term for unleashing a society’s domestic potential of human, institutional, and natural capital through a well governed country.
‘Having judged the development programs of the last decade to be failures, many in the US now call for development budget cuts and wearily espouse isolationism. But it is a classic example of throwing the baby out with the bathwater. Failed methods do not mean that the goal of international development must be abandoned. Development needn’t be an indulgent venture in charity, or risky business, or a road to nowhere paved with good intentions. A more hardheaded approach, one that creates self-sufficiency rather than dependency, is the new beginning that the development world has been waiting for.’ – http://www.worldaffairsjournal.org/article/fixing-us-foreign-assistance-cheaper-smarter-stronger
In 2002, during the early stages of Afghanistan’s reconstruction process, I sat in a remote part of Bamiyan Province with a group of villagers who told me how excited they had been several months before, when a $150 million housing program from a UN agency had been announced on the radio. They felt the program, which promised to bring shelter to their communities, would transform their lives. They were shocked, however, to discover soon after that this program had already come and gone—with very little change to their lives. Indignant, as well as curious, they decided to track the money and find out what had happened to the program that, as far as they were concerned, had never been. Becoming forensic accountants, they went over the files and figures and found that the original amount granted by the UN had first gone through an aid agency in Geneva that took twenty percent off the top before sub-contracting to a Washington-based agency that took another twenty percent. The funds were passed like a parcel from agency to agency, NGO to NGO, until they limped to their final destination—Afghanistan itself. The few remaining funds went to buy wood from Iran, shipped via a trucking cartel at above-market rates. Eventually some wooden beams did reach the village, but they were too heavy for the mud walls used in construction there. All the villagers said they could do was cut up the wood for firewood, sending $150 million literally up in smoke.
With examples like this, it’s really no surprise that a growing chorus of commentators claims that foreign development is expensive, ineffective, and often resented by the intended beneficiaries. In The White Man’s Burden, for instance, William Easterly provides a searing critique of this do-good mentality, which he shows often causes more harm than help. In The Crisis Caravan, Linda Polman documents the unintended consequences of humanitarian assistance. In Dead Aid, Dambisa Moyo argues that aid serves to fuel corruption and lack of accountability among elites.
Critics of US assistance build on this narrative to paint a picture of an America overstretched and in decline, wasting money abroad in a futile effort to serve its uncertain foreign policy objectives, and call for cutbacks and disengagement.
The US has spent $100 billion in nonmilitary funds to rebuild Afghanistan. Yet, after a decade of mind-bending mismanagement and unaccountability, it seems all for naught.
Some of America’s recent engagements abroad have indeed been marked by extraordinary waste and poor design. As Joel Brinkley described in an article in this publication one year ago (“Money Pit,” January/February 2013), American aid to Afghanistan has at times been extravagantly wasteful, as when a contractor overbilled the US government by $500 million. Brinkley also points to the general practice of outsourcing aid projects to contractors with little oversight. Such failures undermine confidence in the very notion of US efforts in confronting poverty and call into question our ability to deal with conflict through “soft power.”
But this criticism misses an important distinction: it is not the principle of engagement, but the way many development projects work that has led to failure. There is, in fact, an alternative way of engaging abroad to promote stability and prosperity with more lasting effect and at a far lower cost than what has become a discredited status quo.
This alternative approach recognizes that there is no shortcut to development that circumvents the citizens and governing institutions of the country. It recognizes the prominent role of entrepreneurial and civic activity. It demonstrates an understanding that institutional change requires years, not months. It has been practiced by a number of farsighted development programs that have reinforced principles of partnership and local ownership of the policy agenda. This “Learn to Fish for a Lifetime” model seeks to build up local institutions that provide security, good governance, and other elements of self-sustaining economic growth. It takes advantage of the things that America knows how to do well: mobilizing investors, firms, universities, and other potent but underused tools that leverage private capital to deliver a kind of development that far outlasts the initial intervention. Many of the activities undertaken with this model actually generate enough revenue to pay back the initial investment, meaning that foreign development projects could someday operate at or close to “net zero” expenditure to the US taxpayer, a particularly appealing prescription in an era of harsh fiscal realities.
Putting “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches into practice, however, requires rejecting the prevailing approach, which makes for a complicated and ultimately self-defeating operation, in favor of one that emphasizes return on investment, both financially and in terms of improved conditions on the ground.
My own wake-up call to the yawning gap between the intentions and impact of major development programs came in that remote part of Afghanistan, soon after the Taliban had fled. Stories similar to the one I heard have been documented by the US special inspectors general for Iraq and Afghanistan reconstruction. But it is not just in combat zones where billions of taxpayers’ funds have created disappointment. After Haiti’s tragic earthquake in January 2010, world powers promised to “build back better” and citizens internationally joined them in committing billions of dollars to that country’s reconstruction. Aid programs in Haiti were notoriously dysfunctional even before the earthquake, but in the scramble to provide help after the catastrophe, funds and opportunities were squandered on an even grander scale. More than three years on, results have fallen far short of the promise. It is what one commentator and Haiti expert, Jonathan Katz, bleakly referred to in the title of his book on the aftermath of the earthquake: The Big Truck That Went By: How the World Came to Save Haiti and Left Behind a Disaster.
Haitian President Michel Martelly has been vocal in his criticisms of the effort, too: “Where has the money given to Haiti after the earthquake gone? . . . Most of the aid was used by nongovernmental organizations for emergency operations, not for the reconstruction of Haiti . . . . Let’s look this square in the eye so we can implement a better system that yields results.”
As Mark Schuller documents in his book Killing with Kindness, foreign donors directed the money to a network of NGOs that bypassed the Haitian government’s policy framework and the implementation capacity of its private sector, and thereby failed to meet the priorities of its citizens. Haitian organizations saw very little of the investment they needed to rebuild their society, but instead were overwhelmed by a vast aid machinery that parachuted down upon them with its own rules and priorities and complex bureaucracy.
Failure, as Haiti showed, does not come from a shortage of money or goodwill. Rather, the aid business has been afflicted by a set of institutional pathologies that almost guarantee failure. Projects designed in national capitals and foreign embassies are often divorced from the realities of the local lives of the people they intend to help, while the long time frames and rigidity of design mean that by the time a project rolls out, it is often irrelevant, even if money actually arrives after the overhead is paid to the food chain of delivery organizations. Multiple contractual layers mean too much of the original project money never even leaves international capital regions—especially Washington.
In Banda Aceh, Indonesia, analysts report how an NGO spent nearly $1 million of European Commission money on a project to construct eleven boatyards intended to stimulate the livelihoods of local fishermen, but in the end only created ten boats, none of them seaworthy.
Somewhere along the way, incentives have become skewed. Project managers and contractors alike are monitored mainly for whether the money in their charge can be tracked, rather than for whether aid activities have any transformational power. For many aid agencies, moreover, running projects has become the goal, rather than seeking to foster institutions and build productive partnerships among governments, firms, and communities. The metrics track whether a project was completed and the money disbursed, not whether sustainable institutions were left after the money had come and gone.
Finally, much of what has become standard procedure in the development business distorts local markets and displaces market activity. Every time a wheat consignment is distributed for free, for instance, local farmers see the market price for their locally grown wheat decrease. In Afghanistan in 2003, after a large-scale World Food Program wheat distribution, farmers threw up their hands and simply let their crops rot because aid had collapsed the market. Nor is it only farmers who are affected by thoughtless charity. Every time solar panels, water pumps, tractors, or cell phones are handed out for free, a local supplier can no longer sell and install his inventory, and a small business that might have long-range prospects for hiring and supporting several people is smothered.
The perversity of incentives operating in the aid and development field is no longer a trade secret. It has caught the attention of even some of the founders of the modern aid movement. “Aid is just a stopgap,” the pop star Bono, one of the forces behind putting charity to Africa on the map through the Live Aid concerts, told an audience at Georgetown University in November 2012. “Commerce [and] entrepreneurial capitalism take more people out of poverty than aid . . . . It’s not just aid, it’s trade, investment, social enterprise. It’s working with the citizenry so that they can unlock their own domestic resources so that they can do it for themselves. Think anyone in Africa likes aid? Come on.”
In an apparent one-eighty from his earlier focus on simply mobilizing aid donations, Bono’s Live Aid partner, Sir Bob Geldof, has followed suit by launching an infrastructure investment firm for Africa, proclaiming, “I want to leave behind me firms, farms, and factories.”
While the stories of what didn’t work in Afghanistan have grabbed the headlines, there have also been several examples of successful development engagement there. The National Solidarity Program in Afghanistan, for example, has directly reached more than thirty-eight thousand villages since 2003. Under its approach, a block grant, ranging from $20,000 to $60,000, goes directly to a bank account held by the village council, or Community Development Council. The village doesn’t have to apply for the funds, but if it wants to, it must follow three simple rules: elect or appoint the council, ensure a quorum of residents attend meetings to choose projects, and post the accounts in a public place. To date, the program has disbursed more than $1.6 billion, and the village councils have completed more than seventy thousand projects—roads to the local markets, water canals, and generators and microhydro systems that electrify the area.
In one case, thirty-seven villages trying to combat the loss of women in childbirth got together and pooled their money to build a maternity hospital. In another case, one hundred and eighty-five villages pooled their money to create a watershed management system, vastly expanding the land they could cultivate. NGOs are involved in these projects as facilitators who support the village through the complex transactions that it must undertake, but unlike in the traditional model of development, they don’t hold the purse strings or oversee the implementation of projects. The US Agency for International Development is now part of an international consortium that contributes to the program costs.
Similar projects exist at even greater scale in Indonesia and Pakistan. In Indonesia, the National Program for Community Empowerment (PNPM) works in more than eighty thousand villages across the nation. The program formed in 1998, in the wake of the Asian financial crisis, with the imperative to benefit communities directly with cash. Neither the government’s social safety nets nor the NGOs could do this alone, and so a partnership between governments and communities was established. Over time, the program has evolved to include micro-finance and other investment facilities, barefoot lawyers programs, and the construction of schools—all managed directly by the villages themselves.
According to official numbers, one of the PNPM programs, PNPM Mandiri Rural, reached four thousand three hundred and seventy-one sub-districts by 2009, and saw the construction or rehabilitation of ten thousand kilometers of road, two thousand and six bridges, two thousand nine hundred and eighty-six health facilities, and three thousand three hundred and seventy-two schools, in addition to the construction of public sanitation facilities and irrigation systems. These projects increased per capita consumption gains by eleven percent and reduced unemployment by one and a half percent. PNPM can accomplish all of this because of an open planning process by which projects are targeted to meet demand as expressed by the community rather than by officials thousands of miles away.
In a similar operation in Pakistan, the Rural Support Programs Network (RSPN) partners with three hundred and twenty thousand community organizations, covering five million households and thirty-three million people. These organizations have led responses to the earthquakes and floods, organized micro-finance and health insurance schemes, and built and operated schools, clinics, roads, and hydropower schemes.
This family of homegrown programs in Afghanistan, Indonesia, and Pakistan, and similar ones in Colombia, Mexico, and India, have proven it is possible to reach communities directly and at scale, cutting out the layers of contractors and NGOs that function as middlemen, while making communities the implementers of their own development in projects that achieve real results.
We really don’t need to look far afield to find approaches that work. There are a number of distinctly American approaches to development that have delivered in the past but have fallen unaccountably into disuse. Take the Economic Cooperation Act of 1948, a framework that for a while worked exceptionally well, but whose practices have been strangely forgotten in recent decades. At its core was the idea of facilitating “the achievement by the countries . . . of a healthy economy independent of extraordinary outside assistance.” The act’s programs, including the tremendously successful Marshall Plan, were geared toward the institutional and economic self-sufficiency of the recipients, with a central premise that the program could be judged a success only if it reduced the need for aid, rather than perpetuating it.
The Marshall Plan worked for the countries it sought to benefit and worked for the donor as well, paying the US back dividends both economically and in security terms far above its costs. This did not happen by chance. One of the participants in this plan, the political scientist Herbert Simon, describes in Administrative Behavior the painstaking organizational design that went into fine-tuning its approach. George Kennan, in a now-declassified memo from 1947, argued that “it is absolutely essential that people in Europe should make the effort to think out their problems and should have forced upon them a sense of direct responsibility for the way the funds are expended. Similarly, it is important that people in this country should feel that a genuine effort has been made to achieve soundness of concept in the way United States funds are to be spent.”
Other lesser-known US development programs similarly brought impressive results with moderate or no cost to the US taxpayer.
In the aftermath of the Korean War, South Korea had one of the lowest GDPs on earth, but between 1966 and 1989, it raised its GDP by an average of eight percent per year. Behind this story lies a dedicated effort to foster local capacity and industrial-led growth, backed by a US partnership. In 1966, President Lyndon Johnson agreed with President Park Chung-hee of South Korea to help establish the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and assembled a team of leading scientists and technical experts to form and plan the institute. KIST aimed to nurture Korea’s own technical and managerial capacity to lay the basis for its economic transformation, rather than remain dependent on foreign management and input for its projects and companies. Korea is now one of a handful of nations that combine GDP per capita in excess of $20,000 with a population of more than fifty million people.
The South Korean government and the US government each contributed $10 million to KIST at its founding, and Washington used a similar model when it helped establish the Saudi Arabian National Center for Science and Technology (SANCST) in 1977. Saudi funds went to the US Treasury, which in turn paid for the technical assistance required for the center and a range of other initiatives.
Many of the best development initiatives are not directed by governments, but by the private sector and its use of market mechanisms. One example is the involvement of the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) in the Afghan telecom sector. In 2002, Afghanistan had sparse telephone coverage, with access only either through a small number of fixed lines or very expensive satellite coverage. The UN proposed that the telecom sector should be addressed through an aid-driven approach, whereby funds would be used to contract with a major cell phone provider to set up services that would provide coverage to key embassies and aid agencies, at an estimated cost in the tens of millions of dollars. But, in line with how cell phone services are organized in any developed country, it was decided instead that rather than being paid by the government or aid agencies, the telephone company would bid for the license to operate a commercial service, with the proviso that services include a certain level of coverage and standard of quality.
The tender process went ahead. Several international companies registered their interest, but many expressed reservations about the level of risk they would be undertaking. This is where OPIC stepped in to draw up a risk guarantee for possible political and security problems. With an expenditure of just $20 million, this agreement provided sufficient confidence in the telecom sector for investment to proceed. By now, several billion dollars have been invested, more than sixteen million phones purchased, significant revenues generated via taxes to the Afghan government—and the $20 million guarantee was never called upon because the risks feared by the private companies never materialized. In this case, a risk instrument was able to pave the way for new market opportunities and to provide an essential service. Contrast that with the typical aid approach, which would have distorted the market, squandered money, and likely produced, at best, ambiguous results.
A similar example came out of the Caribbean. Before 2007, individual insurance companies were reluctant to insure Caribbean islands for hurricane and earthquake damage, the liability being considered commercially too risky. But then the World Bank’s Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility (CCRIF) was created, pooling risk to enable governments in the area to purchase affordable insurance. CCRIF was designed to protect Caribbean countries from the financial fallout of a natural disaster, offering each country timely and flexible payouts. The group can respond more quickly and more efficiently to a member country in need than can the sort of chaos of good intentions that descended on Haiti, as was demonstrated in its response to Hurricane Tomas in 2010. Barbados, St. Lucia, and St. Vincent and the Grenadines received fifty percent of their payouts within days.
In contrast to a top-down, statist aid paradigm, these “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches are all designed to unlock and leverage the value from within the society, state, and market. They all start with the operating principle of co-designing programs with the citizens and leaders from the country concerned. Where there is a market, they do not seek to use grant capital. Once the initial intervention is over, success is judged by whether or not the innovations designed for the crisis are sustainable. This approach is geared toward increasing the self-sufficiency of the country concerned, and in particular boosting its economy and generating its own revenue and tax base.
While the treasuries of most Western countries may be afflicted by the constraints of austerity budgeting, there are vast amounts of private investment capital looking for opportunities. Many of the countries that are seen as the neediest destinations for aid are also considered by emerging market investors as the fastest-growing in the world—Rwanda, Nepal, Indonesia, and India. Infrastructure projects from power to roads and ports can and do attract private capital, and public funds can be used for risk guarantees or as co-investments rather than grant aid for these projects. Rather than seeking to maximize aid, such an approach seeks to maximize the return on investment to the society concerned.
Putting these “Fish for a Lifetime” approaches into effect will require some major shifts. It will involve looking not to how much money was disbursed, or how many schools were built, but to value for money and return on investment. And instead of propping up a vast technical assistance industry of varying and often indifferent quality, a higher priority will be placed on conducting a “skills audit” of key personnel—from doctors and teachers to engineers and agronomists—who can be trained internally rather than importing more costly and less invested technical assistance from abroad.
It is also important under this new paradigm to distinguish between “aid” (such as life-saving humanitarian assistance and the financial or material donations it requires) and “development engagement,” which is something quite different. Development engagement can be low-budget, and should be designed to move a needy country toward self-sufficiency—so that the state can collect its own revenues and the people can support their own livelihoods—as soon as possible. Many recipient countries have enormous untapped domestic resources, and with some effort devoted to increasing those revenues and building the systems to spend them, could assume much more of the responsibility of meeting their citizens’ needs. Getting the toolbox right requires instruments that can best support this approach: the OPIC, enterprise funds, chambers of commerce, public diplomacy, scholarships, international financial institutions, trade measures, and the National Academies, among others.
But a strategy is only as good as its execution. Implementing development policies and programs correctly will require a clear-eyed look at the way programs are designed and implemented, and a re-examination of the reliance on contractors. There is no substitute in the long term for unleashing a society’s domestic potential of human, institutional, and natural capital through a well governed country.
Having judged the development programs of the last decade to be failures, many in the US now call for development budget cuts and wearily espouse isolationism. But it is a classic example of throwing the baby out with the bathwater. Failed methods do not mean that the goal of international development must be abandoned. Development needn’t be an indulgent venture in charity, or risky business, or a road to nowhere paved with good intentions. A more hardheaded approach, one that creates self-sufficiency rather than dependency, is the new beginning that the development world has been waiting for.
Clare Lockhart is the coauthor, with Ashraf Ghani, of Fixing Failed States and the director of the Institute for State Effectiveness, an organization devoted to finding, documenting, and facilitating better approaches to engaging abroad.
Read further at original source:
http://www.worldaffairsjournal.org/article/fixing-us-foreign-assistance-cheaper-smarter-stronger
Afaan Oromo After 100 Years of Disincentives: Toltu Tufa of the Afaan Publications on radio with Jon Faine on the Conversation Hour at ABC Studios Melbourne February 19, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Afaan Publication, Africa, Humanity and Social Civilization, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Language and Development, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Artists, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Social System, Oromummaa, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Self determination, Sirna Gadaa, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Democratic system, The Oromo Governance System, The Oromo Library, Toltu Tufa, Uncategorized.Tags: Afaan Oromo, Afaan Oromo Kushitic Kemetic language, Afaan publication, Africa, African culture, African Studies, Development and Change, Gadaa System, Genocide against the Oromo, Kushitic Languages, Language and Development, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Region, Oromiyaa, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Qubee Afaan Oromo, Toltu Tufa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment
‘EVERY CHILD HAS THE RIGHT TO LEARN THEIR MOTHER TONGUE.’
Related:
http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/toltu-tufa-oprides-oromo-person-2013/
AFAAN Publication: Commemorating UNESCO’s International Mother Language Day on Feb. 21, 2014; Highlighting Past Achievements; and Laying out Plans for 2014
February 21 is UNESCO’s International Mother Language Day. AFAAN Publications’ successful campaign to raise funds to produce children books in Afaan Oromo is the highlight of 2013. The Oromo language, Afaan Oromo, is Africa’s 4th most widelyspoken language, which was banned for 100 years until 1991. AFAAN Publications is based in Melbourne.
AFAAN Publication recounts the 2013 successfulfundraising campaign by recognizing some of the international cities which supported the Melbourne’s drive to create children’s books in Afaan Oromo, and AFAAN Publications was also featured last week on 774 Radio ABC Melbourne.
The communications team is available for comments and interview via telephone. Enquiries can be made via email on connect@afaan.com.au
AFAAN Publication: Commemorating UNESCO’s International Mother Language Day on Feb. 21, 2014; Highlighting Past Achievements; and Laying out Plans for 2014.
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Africa: Agribusiness Feeds the Rich; Small Farmers Feed the Rest February 18, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Africa Rising, African Poor, Agriculture, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Domestic Workers, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Self determination, Slavery, State of Oromia, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Family Farm in Africa, Industrial Agriculture, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Oromo, Oromo people, Small Farm, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, World Bank
add a comment
“Agribusiness feeds the rich; small farmers feed the rest. Yet we have a strong interest in feeding the world and are concerned that food conferences dominated by agribusiness directly threaten our ability to produce affordable, healthy, local food.Solving world hunger is not about industrial agriculture producing more food – our global experience of the green revolution has shown that the drive towards this industrial model has only increased the gap between the rich and the poor. Feeding the world is about increasing access to resources like land and water, so that people have the means to feed themselves, their families and their communities. Small family farms produce the majority of food on the planet – 70% of the world’s food supply! If conferences, like this one, exclude the voice of small farmers, then the debate about feeding the world is dominated by the rich and the solutions proposed will only feed their profits.”
A farming revolution is under way in Africa, pushed by giant corporations and the UK’s aid budget. It will surely be good for the global economy, writes Sophie Morlin-Yron, but will Africa’s small farmers see the benefit?
Many millions of small farmers that were once merely poor, will be propelled into destitution, the chaff of a neoliberal market revolution as pitiless as it is powerful.
World leaders in agriculture and development gathered in London last week at the The Economist’s ‘Feeding the World Summit’ to discuss global solutions to tackling Africa’s food security crisis.
At the event, which cost between £700 and £1,000 to attend, industry leaders spoke of new innovations and initiatives which would help fight poverty, world hunger and malnutrition, and transform the lives of millions of farmers worldwide.
Just one farmer
But there was only one farmer among the speakers, Rose Adongo, with barely a handful more in the audience. A Ugandan beef and honey farmer, Adongo was unimpressed by the technical solutions offered by the corporate speakers.
For her, the main issue was land ownership for farmers – and desperately needed changes in Ugandan law, under which women have no right to land ownership even though 80% of the country’s farmers are women, and they produce 60% of the food.
If only a woman could own land – currently passed down from father to son “she can produce more food”. Besides that she wanted cheaper fertilisers and an end to the desperate toil of hand working in the fields. Much of the land is currently plowed by hand which “can take weeks to do”.
Among the excluded …
But many were excluded from the event – and desperately wanted their voices to be heard. Among them was Jyoti Fernandes, from The Landworkers’ Alliance (member of La Via Campesina), a producer-led organisation representing small-scale agroecological producers in the UK.
“Agribusiness feeds the rich; small farmers feed the rest”, she said. “None of our members could afford to attend the Feeding the World Summit.
“Yet we have a strong interest in feeding the world and are concerned that food conferences dominated by agribusiness directly threaten our ability to produce affordable, healthy, local food.
Solving world hunger, she insisted, “is not about industrial agriculture producing more food – our global experience of the green revolution has shown that the drive towards this industrial model has only increased the gap between the rich and the poor.”
Improving access to land and water
“Feeding the world is about increasing access to resources like land and water, so that people have the means to feed themselves, their families and their communities.
“Small family farms produce the majority of food on the planet – 70% of the world’s food supply! If conferences, like this one, exclude the voice of small farmers, then the debate about feeding the world is dominated by the rich and the solutions proposed will only feed their profits.”
As Graciela Romero of War on Want commented in The Ecologist last week, it is that small farmers are feeding the world – not corporations:
“Millions of small-scale farmers produce 70% of the world’s food. Yet they remain excluded and forgotten from exchanges which affect their livelihoods or concern how to end world hunger.”
Private investment
Among the 27 speakers at the event were Nestlé Head of Agriculture Hans Joehr, Monsanto CEO Hugh Grant, Cargill Vice-Chairman Paul Conway, UN Secretary General for Food Security and Nutrition David Nabarro, and representatives from the World Food Program and World Vision.
And despite the involvement of some NGOs, academics UN officials, the main topic of discussion was private sector investment in agriculture.
Lynne Featherstone, a junior UK minister for International Development, said the way forward is newly developed efficient fertilisers, pest tolerant crops and private sector investment:
“There is substantial room for improvement, and helping farmers increase productivity while consuming fewer inputs is a priority. With partners such as CGIAR we have developed more efficient fertilisers and pest tolerant crop varieties.”
UK spending £280m to support private sector engagement
She also outlined the Government plans to invest £280m from its aid budget funding in businesses and organisations under the Alliance for Food Security and Nutrition (AFNC).
This private sector initiative – which has also involves 14 Governments – ostensibly aims to lift 50 million people in Africa out of poverty by 2022, by attracting more private investment in agriculture. Featherstone explained the rationale:
“Economic growth in these countries is best achieved through agricultural growth, which has the power of raising incomes and getting people out of poverty. And the private sector can catalyse that agricultural growth with sustainable agricultural investment.”
But is it really about land grabs?
But critics fear that is has rather more to do with getting governments on-side so corporations can carry out land grabs – taking the best watered and most fertile land away from African farmers and delivering it up to investors to plant cash crops across the continent, while turning once independent small farmers into a a proletarian underclass of landless plantation workers and rootless urban workers.
Paulus Verschuren, Special Envoy on Food and Nutrition Security, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, The Netherlands attempted to strike a balance:
“We are not going to fix the zero-hunger challenge without involving the private sector, but we need to set the criteria for these transformational partnerships. They need to have a business outcome and a development outcome.”
Corporations keen to help small farmers …
Representatives of major food corporations also insisted that they wanted to work with small farmers and help them to produce their crops efficiently while meeting development objectives.
Nestlé’s Corporate Head of Agriculture, Hans Jöhr, claimed to be willing to work with small farmers as well as large to fulfil development objectives and improving resource efficiency:
“The issue of feeding the world has to been seen in perspective of rural development, and not only technology”, he said. “And it’s definitely not about talking small versus big farmers, I think that was really the yesterday talk. It’s about people, individuals, it’s about farmers.
We cannot go on polluting and destroying
“So in this meeting about farmers, when we are talking about farmers, we are going back to what we have listened to, the restrictions we all face in business is natural resources, natural capital. It’s not only about the land, it’s mainly about water.
“This leads us to looking into production systems and methods and understanding that we cannot continue to go on with polluting destroying and depleting natural resources and with wasting them.
“Farmers who don’t know how to farm waste a tremendous amount of natural resources and agricultural materials because they don’t know how to store, and are not linked to an outlet to markets. That means that we have to help them better understand the production systems.”
Productivity must be raised
Vice Chairman of Cargill, Paul Conway, emphasised the importance of secure land ownership: “The number one thing here isn’t technology, it isn’t finance, it’s security of tenure of the land, which is absolutely critical.”
And Monsanto’s CEO Hugh Grant played down the importance of genetic modification in improving crop yields in Africa, from 20 bushels of grain per hectare to India’s typical level of 100 bushels.
“There is no reason Africa shouldn’t be close to India, it’s all small-holder agriculture. Why is it 20 today and not 90? Now forget biotech, that’s eminently achievable with some sensible husbandry and land reform ownership, the tools are in hand today.”
“We have set goals to double yields in the next 30 years with a third less water, agriculture gets through an enormous amount of water. The first 70 per cent of which goes to agriculture, the next 30 per cent goes to Coke, Pepsi, swimming pools and everything you drink and all of industry, and that isn’t sustainable.
We believe our sole focus on agriculture is vital as the world looks to produce enough nutritious food to feed a growing population while conserving, or even decreasing, the use of precious natural inputs such as land, water and energy.”
Farmers ‘invisible and irrelevant’
But Mariam Mayet, Director of African Safety for Biosafety – which campaigns against genetic engineering, privatisation, industrialisation and private sector control of African agriculture – was not convinced.
To the constellation of famous speakers and corporate representatives, she said, small farmers were a simple obstruction to progress:
“We know that all of African farmers are invisible and irrelevant to those at this summit. These producers are seen as inefficient and backwards, and if they have any role at all, it is to be forced out of agriculture to becoming mere passive consumers of industrial food products.
“Africa is seen as a possible new frontier to make profits, with an eye on land, food and biofuels in particular.
“The recent investment wave must be understood in the context of consolidation of a global food regime dominated by large corporations in input supply such as seed and agrochemicals especially, but also increasingly in processing, storage, trading and distribution.
“Currently African food security rests fundamentally on small-scale and localised production. The majority of the African population continue to rely on agriculture as an important, if not the main, source of income and livelihoods.”
Can the chasm be bridged?
If we take the sentiments expressed by corporate bosses at face value – and why not? – then we do not see any overt determination to destroy Africa’s small farmers. On the contrary, they want to help them to farm better, more productively and efficiently, and more profitably.
And perhaps we should not be surprised. After all that suits their interests, to have a growing and prosperous farming sector in Africa that can both buy their products and produce reliable surpluses for sale on global food markets.
The rather harder question is, what about those farmers who lack the technical or entrepreneurial ability, the education, the desire, the extent of land, the security of land tenure, to join that profitable export-oriented sector? And who simply want to carry on as mainly subsistence farmers, supporting their families, producing only small surpluses for local sale?
The small subsistence farmer has no place
Stop and think about it, and the answer is obvious. They have no place in the new vision of agriculture that is sweeping across the continent, with the generous support of British aid money.
Their role in this process is to be forced off their land – whether expelled by force or by market forces – and deliver it up to their more successful neighbour, the corporation, the urban agricultural entrepreneur, to farm it at profit for the market.
And then, either to leave their village homes and join the displaced masses in Africa’s growing cities, or to stay on as landless workers, serving their new masters.
This all represents ‘economic progress’ and increases in net production. But look behind the warm words – and many millions of small farmers that were once merely poor, will be propelled into destitution, the chaff of a neoliberal market revolution as pitiless as it is powerful.
Is this really how the UK’s aid funds should be invested?
Sophie Morlin-Yron is a freelance journalist.
Oliver Tickell edits The Ecologis
http://www.theecologist.org/News/news_analysis/2287243/africas_farm_revolution_who_will_benefit.html
A landmark G8 initiative to boost agriculture and relieve poverty has been damned as a new form of colonialism after African governments agreed to change seed, land and tax laws to favour private investors over small farmers.
Ten countries made more than 200 policy commitments, including changes to laws and regulations after giant agribusinesses were granted unprecedented access to decision-makers over the past two years.
The pledges will make it easier for companies to do business in Africathrough the easing of export controls and tax laws, and through governments ringfencing huge chunks of land for investment.
The Ethiopian government has said it will “refine” its land law to encourage long-term land leases and strengthen the enforcement of commercial farm contracts. In Malawi, the government has promised to set aside 200,000 hectares of prime land for commercial investors by 2015, and in Ghana, 10,000 hectares will be made available for investment by the end of next year. In Nigeria, promises include the privatisation of power companies.
A Guardian analysis of companies’ plans under the initiative suggests dozens of investments are for non-food crops, including cotton, biofuels and rubber, or for projects explicitly targeting export markets.
Companies were invited to the table through the G8 New Alliance for Food Security and Nutrition initiative that pledges to accelerate agricultural production and lift 50 million people out of poverty by 2022.
But small farmers, who are supposed to be the main beneficiaries of the programme, have been shut out of the negotiations.
Olivier de Schutter, the UN special rapporteur on the right to food, said governments had been making promises to investors “completely behind the screen”, with “no long-term view about the future of smallholder farmers” and without their participation.
He described Africa as the last frontier for large-scale commercialfarming. “There’s a struggle for land, for investment, for seed systems, and first and foremost there’s a struggle for political influence,” he said.
Zitto Kabwe, the chairman of the Tanzanian parliament’s public accountscommittee, said he was “completely against” the commitments his government has made to bolster private investment in seeds.
“By introducing this market, farmers will have to depend on imported seeds. This will definitely affect small farmers. It will also kill innovation at the local level. We have seen this with manufacturing,” he said.
“It will be like colonialism. Farmers will not be able to farm until they import, linking farmers to [the] vulnerability of international prices. Big companies will benefit. We should not allow that.”
Tanzania’s tax commitments would also benefit companies rather than small farmers, he said, adding that the changes proposed would have to go through parliament. “The executive cannot just commit to these changes. These are sensitive issues. There has to be enough debate,” he said.
Million Belay, the head of the Alliance for Food Sovereignty in Africa (AFSA), said the initiative could spell disaster for small farmers in Africa. “It clearly puts seed production and distribution in the hands of companies,” he said.
“The trend is for companies to say they cannot invest in Africa without new laws … Yes, agriculture needs investment, but that shouldn’t be used as an excuse to bring greater control over farmers’ lives.
“More than any other time in history, the African food production system is being challenged. More than any other time in history outside forces are deciding the future of our farming systems.”
AFSA has also denounced the G8 initiative as ushering in a new wave of colonialism on the continent.
http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/feb/18/g8-new-alliance-condemned-new-colonialism
US Congress Takes a Historic Stance Against Land Grabs-Related Forced Evictions in Ethiopia February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo First, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromummaa, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Genocide against the Oromo, Gibe Valley, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Lower Omo, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
See the Omnibus Appropriations Bill (p. 1295-1296) @
http://docs.house.gov/billsthisweek/20140113/CPRT-113-HPRT-RU00-h3547-hamdt2samdt_xml.pdf
Oakland, CA – In a historic move, the US Congress has taken a stance on land grabs-related human rights abuses in Ethiopia. The 2014 Omnibus Appropriations Bill contains provisions that ensure that US development funds are not used to support forced evictions in Ethiopia.
The bill prevents US assistance from being used to support activities that directly or indirectly involve forced displacement in the Lower Omo and Gambella regions. It further requires US assistance in these areas be used to support local community initiatives aimed at improving livelihoods and be subject to prior consultation with affected populations. The bill goes further and even instructs the directors of international financial institutions to oppose financing for any activities that directly or indirectly involve forced evictions in Ethiopia.
According to Anuradha Mittal, Executive Director of the Oakland Institute, “We welcome this move as it aims to address one major flaw of US assistance to Ethiopia. The step taken by the US Congress is very significant, as it signals to both the Ethiopian government and the US administration that turning a blind eye to human rights abuses in the name of development is no longer an option.”
Several reports from the Oakland Institute have raised alarm about the scale, rate, and negative impacts of large-scale land acquisitions in Ethiopia that would result in the forced displacement of over 1.5 million people. This relocation process through the government’s villagization scheme is destroying the livelihoods of small-scale farmers and pastoralist communities. Ethiopian security forces have beaten, arrested, and intimidated individuals who have refused to relocate and free the lands for large-scale agricultural plantations.
Ethiopia’s so-called development programs cannot be carried out without the support of international donors, primarily the US, one of its main donors. Oakland Institute’s on-the-ground research has documented the high toll paid by local people as well as the role of donor countries such as the US in supporting the Ethiopian policy.
This language represents an important first step towards Congress initiating a comprehensive examination of US development practices in Ethiopia. As the oversight authority of the State Department, Congress must now ensure that the law is fully upheld and implemented. This warrants thorough scrutiny of USAID programs to Ethiopia and their contribution to forced resettlements and human rights abuses.
With this bill, USAID, the State Department, as well as the World Bank, will have to reconsider the terms and modalities of the support they provide to the Ethiopian government. According to Frederic Mousseau, Oakland Institute’s Policy Director, “This is a light of hope for the millions of indigenous people in Ethiopia who have sought international support from the international community to recognize their very destruction as communities and people.” Read Further @
USAID’s cover-up of Ethiopia abuses overruled by Congress 12 February 2014
The United States Congress has acted to prevent its aid to Ethiopia being used to fund forced evictions of tribal peoples in the south west of the country.
The provisions in the Omnibus Appropriations Bill for 2014 represent a slap in the face for USAID, which last month said that ‘there are no reports of widespread or systematic human rights abuses’ in the region.
In fact, tribes of the Lower Omo Valley are being violently evicted from their villages by the government to make way for lucrative cotton, palm oil, and sugarcane plantations whose irrigation will be made possible by the controversial Gibe III dam. Transferred to designated resettlement areas, the once self-sufficient tribes will be left with no access to their livestock or lands and, consequently, will be unable to sustain themselves. Intimidation tactics, such as rape and beatings, have reportedly been used against those who resist resettlement.
One Mursi man told Survival International, ‘We are waiting to die. We are crying. When the government collects people into one village there will be no place for crops, and my children will be hungry and have no food.’
The Ethiopian government has not consulted any indigenous communities over its aggressive plantation plans in the Omo Valley, and very few were consulted over the construction of the Gibe III dam.

The region’s top human rights body, the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights, has written to the Ethiopian government asking it to halt the forced resettlement of the Lower Omo tribes while it investigates Survival’s submission regarding human rights violations in the area.
Ethiopia is one of the biggest recipients of American and British aid through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and the UK Department for International Development (DFID).
Although the provisions in the recent spending bill will force USAID to reevaluate the funding given to Ethiopia, it will ultimately be the responsibility of Congress to guarantee that the terms are upheld.
Survival International Director Stephen Corry said today, ‘This bill is a huge step in the right direction, and shows that USAID’s shameful denials of the human rights abuses being committed in the Lower Omo simply haven’t been believed.
‘American taxpayers want to be sure that their money isn’t going toward the destruction of tribal peoples’ lives. Hopefully the historic provisions in this year’s spending bill will ensure that’s the case. It is now high time that British parliamentarians follow suit and ensure that DFID does not use UK taxpayers’ money to fund human rights violations in the Lower Omo.’ http://www.survivalinternational.org/news/9983
Further References on land grabs in Africa
Around 90 percent of the population of 87 million still suffers from numerous deprivations, ranging from insufficient access to education to inadequate health care; average incomes are still well below $1500 a year; and more than 30 million people still face chronic food shortages.
And while there are a number of positive and genuine reasons for the growth spurt – business and legislative reforms, more professional governance, the achievements of a thriving service sector – many critics say that the growth seen in agriculture, which accounts for almost half of Ethiopia’s economic activity and a great deal of its recent success, is actually being driven by an out of control ‘land grab’, as multinational companies and private speculators vie to lease millions of acres of the country’s most fertile territory from the government at bargain basement prices.
At the ministry of agriculture in Addis Ababa, this land-lease programme is often described as a “win-win” because it brings in new technologies and employment and, supposedly, makes it easier to improve health care, education and other services in rural areas.
“Ethiopia needs to develop to fight poverty, increase food supplies and improve livelihoods and is doing so in a sustainable way,” said one official.
But according to a host of NGO’s and policy advocates, including Oxfam, Human Rights Watch and the Oakland Institute, the true consequences of the land grabs are almost all negative. They say that in order to make such huge areas available for foreign investors to grow foodstuffs and bio-fuels for export – and in direct contravention of Ethiopia’s obligations under international law – the authorities are displacing hundreds of thousands of indigenous peoples, abusing their human rights, destroying their traditions, trashing the environment, and making them more dependent on food aid than ever before.
“The benefits for the local populations are very little,” said renowned Ethiopian sociologist Dessalegn Rahmato. “They’ve taken away their land. They’ve taken away their natural resource, because these investors are clearing the land, destroying the forest, cutting down the trees. The government claims that one of the aims of this investment was to enable local areas to benefit by investing in infrastructure, social services … but these benefits are not included in the contract. It’s only left up to the magnanimity of the investor.”
And those investors, he continued, are simply not interested in anything other than serving their own needs: “They can grow any crop they want, when they want it, they can sell in any market they want, whether it’s a global market or a local market. In fact most of them are not interested in the local markets.”
He cited as an example a massive Saudi-owned plantation in the fertile Gambella region of south west Ethiopia, a prime target area for investors: “They have 10,000 hectares and they are producing rice. This rice is going to be exported to the Middle East, to Saudi Arabia and other places. The local people in that area don’t eat rice.”
But the most controversial element of the government’s programme is known as ‘villagisation’ – the displacement of people from land they have occupied for generations and their subsequent resettlement in artificial communities.
In Gambella, where two ethnic groups, the Anuaks and the Nuers, predominate, it has meant tens of thousands of people have been forced to abandon a traditional way of life. One such is Moot, an Anuak farmer who now lives in a government village far from his home.
“When investors showed up, we were told to pack up our things and to go to the village. If we had decided not to go, they would have destroyed our crops, our houses and our belongings. We couldn’t even claim compensation because the government decided that those lands belonged to the investors. We were scared … if you get upset and say that someone stole your land, you are put in prison. If you complain about being arrested, they will kill you. It’s not our land anymore; we have been deprived of our rights.”
Despite growing internal opposition and international criticism, the Ethiopian government shows no sign of scaling the programme back. According to the Oakland Institute, since 2008, an area the size of France has already been handed over to foreign corporations. Over the next few years an area twice that size is thought to be earmarked for leasing to investors.
So what does all this mean for the people on the ground? In Ethiopia – Land for Sale, filmmakers Veronique Mauduy and Romain Pelleray try and find out.
http://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/peopleandpower/2014/01/ethiopia-land-sale-20141289498158575.html
Farming and food in Africa and the battle over land, water and resource rights
Africa is being heralded as the new frontier for commercial farming but, as governments and investors sign deals, a counter movement of family farmers is promoting alternative pathways to development.
The International Year of Family Farming is now underway, and never before have family farmers in Africa been more under threat.
Large land deals between African governments and usually foreign (and sometimes domestic) investors have seen swathes of the countryside leased or conceded, often for as much as 50-99 years. From Senegal in West Africa to Ethiopia in the Horn, and down to Mozambique in the south, land considered idle and available has changed hands, with profound implications for local people and the environment.
Oromia: OSGA Invited to the UN to report on human rights abuses February 13, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Finfinnee, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, Land Grabs in Africa, Nubia, Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Sirna Gadaa, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Oromo Democratic system, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Genocide against the Oromo, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromia Support Group, Oromia Support Group Australia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, State and Development, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


HCH is working in conjunction with the Oromia Support Group of Australia (OSGA), one of our long standing community partners, to raise urgently required funds toward a unique opportunity to
present serious allegations of human rights abuses in Ethiopia, at the highest level; the United Nations Universal Periodic Review (UPR).
Human rights organisations have long been reporting human rights abuses committed by the Ethiopian government, which include rape, torture, arbitrary detention and kidnapping. OSGA is an Australian based organisation that was established in 2008 to report on and raise awareness of these violations.
They have recently been offered a significant opportunity to send a delegate to the 19th session of the UN Human Rights Council’s UPR in April, 2014. There they will present a first-hand account of human rights abuses committed by the Ethiopian government.
This opportunity, to report first-hand accounts of torture, arbitrary imprisonment and rape to senior UN officials, will enable them to forward these concerns to the Ethiopian government during the official UPR process. This process will require the Ethiopian government to answer the accusations.
OSGA is raising urgently needed funds to send a representative from the Ethiopian community in Australia. The estimated total cost is approximately $5,000. If you can help, OSGA can provide a receipt, and will also report on the acquisition of any funds. Any contribution would greatly assist this effort.
If you can contribute, please contact info@osgaustralia
South Sudan: Is Peace Possible? February 11, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Dictatorship, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Human Rights, Humanity and Social Civilization, Kemetic Ancient African Culture, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, South Sudan, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Warlords.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Human Rights and Liberties, Oromo, Oromo people, Parliament, South Sudan, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment

Kiir is accused of creeping authoritarianism, strengthening his control over the security apparatus and threatening to curb non-government organisations and the media. A newspaper reportedly found itself in trouble for daring to publish a photo of the president wiping sweat from his brow. One foreign diplomat commented: “There is a danger that this country that fought so hard for its liberty is going to end up resembling the country it fought against.”
Peter Adwok Nyaba was higher education minister but says he could not get an audience with Kiir from July 2012 until his dismissal in July 2013. “Things were going wrong in the education system but I had a complete year of not being able to meet him,” says Nyaba, who has been under house arrest since Christmas Day. “Many people complained of the same thing. I think being president of the country is too big for him, which is showing itself in him being unable to take charge of the current situation. He’s just a village chief.”
Even the US president was reportedly given short shift. One aid agency official recalls: “Kiir treated Barack Obama like shit. The story goes they were supposed to meet at the UN in New York but Kiir kept him waiting for 20 or 30 minutes. People should have said this guy is not our friend.”
America is feeling buyer’s remorse, the source adds. “The people who were pushing the narrative South Sudan good, Sudan bad, are now calling out the South Sudanese government, but it’s too late. When a crisis like this breaks, the US’s leverage gets less and less.”
Kiir’s increasingly autocratic behaviour sowed division within his governing party, the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement (SPLM), struggling, like so many militant liberation movements before it, to transition to a political party. Last July, his vice-president, Riek Machar, a charismatic and ruthless former warlord once married to a British aid worker, openly defied him, telling the Guardian: “To avoid authoritarianism and dictatorship, it is better to change.” Machar and the rest of the cabinet were sacked three weeks later.
In early December, Machar and other malcontents amplified their dissent at a press conference and planned a public rally. “Growing disenchantment and international criticism created fertile ground for opportunists masquerading as democrats,” noted one insider. On 14 December, Machar and seven others walked out of an SPLM meeting. The following day, with the mood volatile, fighting broke out within the presidential guard. Kiir accused Machar, a rival of old, of attempting to overthrow him in a coup. But many observers pour scorn on this notion. “If it was a coup attempt it was the worst organised, worse conceived and worst executed coup ever,” says a diplomatic source. “There’s a constant battle between chaos and conspiracy in South Sudan. Nine times out of 10, it’s chaos.”
Nevertheless, Machar was content to ride the wave and subsequently accept leadership of a rebellion that quickly took on ugly ethnic dimension. Kiir is a Dinka, the biggest group, while Machar is a Nuer, the second most populous. Some say Kiir used the alleged coup attempt as a pretext to unleash his own private militia and, whether he intended it or not, Nuers were the victims. Machar, linked to a massacre of Dinkas in 1991, stands accused of stoking tribalism and mobilising a Nuer force known as the “white army”.
There is nothing inevitable about this, experts argue, noting that for most of their history Dinkas and Nuers have coexisted peacefully and inter-married. Indeed, five of 11 detainees accused of plotting against Kiir are Dinka, while there are Nuers in his government. Yet in villages across the country, where three in four people are illiterate, each group is feeding a spiral of paranoia about the other. Ivan Simonovic, the UN assistant secretary-general for human rights, warned in Juba last Friday: “There are completely different worldviews and narratives among communities. Truth is becoming ethnicised.”
Nowhere is this more evident than at the UN base in Juba, where more than 20,000 Nuers are crammed into about 45 acres, including young children, who can be seen defecating in the dirt, and heavily pregnant women. Many here believe the Nuer are the target of nothing less than ethnic cleansing and, officials say, some who have dared to venture beyond the gate in search of food and water have been murdered on sight.
Among them are a group of Nuer politicians roughing it inside a tent, lying on mattresses amid suitcases and jerry cans, their suits hanging in zip-up garment bags, one of which has the label, “Shoreditch, London”. One, too fearful to be named, tells me: “Men with guns came to my house and knocked on the door. They started shooting into the house and a bullet just missed my left eye and went into the wall. I ran and told my children to lie down. I felt toothless. It’s what happened in Rwanda exactly: if you were found in your house, you were dead.”
As peace talks in neighbouring Ethiopia go nowhere fast, many are gloomy about the prospects for peace in the short term and democracy in the long term. The conflict appears to be driving Kiir into the arms of Bashir and Uganda’s strongman president Yoweri Museveni, who is providing military support. The Americans are being spurned – described as “heartbreaking” for many senior officials who feel professionally and personally invested in the new nation.
But amid the atrocities on both sides there have been redemptive stories of Dinkas giving hunted Nuer families refuge in their homes and vice versa. No one interviewed by the Guardian believes that South Sudan was a mistake or regrets secession in those idealistic days of 2011. They do, however, blame the political elite. “Independence, with all its challenges, was the best thing that happened to this country,” insists Mading Ngor, a journalist and commentator. “I don’t know anyone who is looking for reunification with Sudan.
“There were a lot of emotional faces on independence day. People teared up when they saw the flag going up for the first time. There were youths running about celebrating the rise of a new nation: Dinka youths, Nuer youths. Now those youths are killing each other. There is a need for a new generation to accomplish what the politicians failed to do, which is to build. My hopes are pinned on the people of South Sudan. The future is always better.”
http://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/jan/20/south-sudan-death-of-a-dream?CMP=twt_gu
On 15 December 2013, South Sudan was rocked by fighting in the capital Juba. The conflict was apparently sparked by a dispute within the presidential guard, pitching Dinka against Nuer in support of, respectively, the President Salva Kiir Mayardit and his previous vice-president Riek Machar. Soon it spread like a wildfire to other parts of the country.
What began as a political power struggle within the political elite soon turned into deadly ethnic conflict taking the life of several thousands. While President Kiir accused his opponents of trying to seize power through a military coup, his opponents led by Riek Machar accused him of trying to use the incident to suppress his opponents. The outbreak of the fighting followed a drawn out political struggle between the two political rivals.
Mr. Machar accused Kiir of incompetence, failure in curbing corruption, ensuring national unity, state building and making progress towards socio-economic development. The president retorted by accusing him of undermining his government. The president also told his opponents to abandon the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement (SPLM) and form their own party.
The opponents however know very well that abandoning the SPLM spells political suicide because it means ending up in the cold. Instead of heeding the admonition of the president they opted to utilize the SPLM in challenging Salva Kiir. Thus, they decided to test their luck within the SPLM and demanded the convening of the SPLM congress.
Instead of convening a congress, however, Kiir decided to cleanse the SPLM and the government from his opponents. Riek Machar was fired as vice-president on 23 July 2013 and Pagan Amun from his post as Secretary General of the SPLM. Then the cabinet was dissolved on 31 July to pave the way for the president to install his loyalists.
After resisting persistent demand to convene the National Liberation Council (legislative organ of the SPLM), the president agreed to call the meeting which took place on 14 December 2013. The NLC however failed to reach an agreement that led to walk out of opponents that sparked the incident of 15 December.
Two interlinked factors of failures could explain the outbreak of the conflict.
The first is the failure of the SPLM government to transform itself from a liberation movement to a democratic political governing party and from bearer of a liberation political culture to civic political culture. Liberation political culture demands loyalty to the leader. Those who harbor political ambition and disloyalty and incline to express rivalry with the leader are thus thrown out in the cold.
In accordance with this political culture the vice-president and the secretary general of SPLM were fired from office because they expressed their intention to run against the president in the coming elections, which was construed by the president as harbouring lack of loyalty to him.
This action of the president threw the ruling party and the government into deep political crisis. Unfortunately democratic institutions of governance and conflict resolution that could mitigate and manage disputes are markedly absent in South Sudan. Therefore the political struggle among the political elite got out of hand plunging the new nation into an unprecedented spree of ethnic massacres.
The second failure concerns the transformation of the, virtually conglomerate, army of militias into an integrated national disciplined army. During the liberation struggle several ethnic based militias emerged and latter were incorporated into the SPLA (Sudan People’s Liberation Army). Following secession no efforts to transform the SPLA was carried out. Rather the SPLA remained divided on ethnic basis.
Militias that fought against the SPLA during the liberation struggle were simply incorporated in the emergent national army following the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) in 2005. The incorporation took place without necessary political education that would lead to integration and cohesion of the national army. Indeed the incorporation remained mechanical. When the political struggle within the political elite exploded the army simply degenerated into its ethnic origins.
This double failure of transformation aggravated the already highly fractured society along ethnic fault-lines. The all-time precarious inter-ethnic relation and fragile state building process was further thrown into disarray. The post-secession nation building and state construction has suffered immensely.
It seems now that whatever efforts of negotiation and reconciliation are attempted between the rivals it will be near to impossibility to bring them to a cordial working relation. There is no way they could work together again. The reconciliation process has come too late and the blood spilled in this conflict will haunt the nation for a long time to come.
Uganda’s meddling has also complicated the mediation and reconciliation efforts. Therefore there is a real possibility that South Sudan could be heading towards prolonged bloody civil war with ethnic accentuation unless friends and neighbours exert real pressure on the leaders. The role of the friendly states, external actors in general, mildly expressed, in the post-secession reconstruction have been paradoxical. It is time that they reassess their role!
Amid this near impossibility of reaching political reconciliation the following measures could be considered to be of critical importance:
- Convening the congress of the SPLM as soon as possible. One of the problems that contribute to the current crisis is the overdue delay of the congress of the SPLM.
- Dissolution of the SPLM. The SPLM has proven itself to be impotent, corrupt and domineering. It has also become divisive and impossible to reform therefore needs to be replaced by other political parties.
- Quickly organise presidential election. This will address the power struggle for the office of the presidency. It will lead to democratic, constitutional and institutionalised transfer of power.
- Undertake serious reconciliation. Throughout the liberation struggle the movement was divided and beset with bloody inter-ethnic civil wars. That history has never been addressed. The current crisis is a reminiscence of that history.
- External actors should exert concerted pressure on the leaders. The leaders on their own are not capable to strike reconciliation. They need all the help they can get.
- Immediate withdrawal of the Ugandan army from South Sudan. The intervention of Ugandan forces in the inter-ethnic conflict not only has complicated the negotiation and national reconciliation; it might also be implicated in the atrocities committed.
Ethiopia: The Declining of the Much Vaunted GDP Growth, the Rise of Youth Unemployment, Extreme Poverty & Social Discrimination February 9, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Ogaden, Oromia, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Youth Unemployment.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Aid, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, Ethiopia, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human Rights Violation Against Ogaden people, Human rights violations, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Sub-Saharan Africa, The Tyranny of Ethiopia, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Youth Unemployment
add a comment

‘The second poorest country in the world according to the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Multidimensional Poverty Index, [2] Ethiopia consistently ranks extremely low upon a variety of socioeconomic, development and human rights indicators. [3] Recently, however, Ethiopia has experienced economic growth – making it amongst ‘Africa’s best performing economies.’ [4] This development reiterates the Ethiopian government’s lofty ambitions to attain ‘middle-income status by 2020.’ [5] The validity, sustainability, and possible ramifications of Ethiopia’s purported and ambitious economic transformation in the near future – which could prove beneficial domestically and regionally – merits closer analysis.’ – http://pambazuka.org/en/category/features/90435
To begin with, it is important that Ethiopia’s economic growth translate into broad scale development. While Ethiopia has reportedly witnessed tangible progress on the UN’s Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), [7] the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has noted that there still remains ‘a pressing need for policies to translate positive growth outcomes into stronger employment gains and further reduction in poverty and set off a dynamic, virtuous cycle of self sustaining and broad-based growth.’ Further challenges include high levels of youth and female unemployment, greater efforts being required to identify and address the needs of those in severe and chronic poverty (approximately 25 million or 27 percent of Ethiopians live in extreme poverty), and pervasive malnutrition. [8]
Ethiopia’s economic growth also arouses questions of equitable growth and redistribution. Handley et al. (2009) outline that, although essential, economic growth is not always wholly sufficient to reduce poverty or inequality. Rather, an assortment of measures must be undertaken to ensure that poorer strata of society are incorporated into national economic growth. [9] Even with Ethiopia’s past reduction of much national inequality, dramatic inequities in education and employment – and broad discrimination – along rural-urban, gender, and ethno-religious lines are starkly apparent. [10]
Another critical issue emanating from Ethiopia’s economic growth and general developmental efforts is the manner in which they have been pursued. For example, a vital component of Ethiopia’s agricultural development strategy is the ‘villagization’ program that entails the relocation of millions of people from locations reserved for industrial plantations. [11] Ethiopia is an agrarian-based society in which more than 80 percent of Ethiopians depend on agriculture and pastoralism for subsistence. Issues arising from the program have led to greater food insecurity, a destruction of livelihoods and the loss of cultural heritage. Additionally, the program, which frequently utilizes forced evictions, has been plagued by a plethora of human rights violations. A variety of human rights groups have documented beatings, killings, rapes, imprisonment, intimidation and political coercion by the government and authorities. [12]
While Ethiopia has suggested that leasing land to foreign investors is necessary to modernize farming, enhance domestic food production and generate employment, [13] it continues to struggle mightily with hunger, under-nutrition and stunting. [14] Further, a UN report has even suggested that such investment deals negatively impact local populations. [15]
Importantly, projections of Ethiopia’s forthcoming evolution into a middle-income country must address the fact that Ethiopia remains overwhelmingly dependent on foreign aid. Long unable to produce enough food for its population, the nation has been dependent on foreign food aid for decades; [16] recent World Food Programme data illustrates that the country remains one of the largest recipients of food aid in the world. [17]
Siyoum, Hilhorst, and Van Uffelen (2012) also note that more than 8 million Ethiopians rely on food aid. Furthermore, the authors find that Ethiopia’s food insecurity stems from government failures in addressing major structural problems including poor soil fertility, environmental degradation, population pressure, fragmented landholdings and a severe lack of income-generating opportunities outside of agriculture. [19]
In addition to its reliance on food aid, Ethiopia is highly dependent on external economic assistance. In 2011, Ethiopia was the world’s fifth largest recipient of official humanitarian aid and received $3.6 billion in total assistance, [20] the latter figure representing between 50-60 percent of its total budget. [21] Additionally, Ethiopia’s 2011 share of total official development assistance – approximately 4 percent – placed it behind only Afghanistan.
According to Finland’s Country Strategy for Development Cooperation in Ethiopia, published by the Finnish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ethiopia’s dependency challenges include the fact that its ‘…humanitarian support programmes are fragmented,’ [22] an outcome likely influenced by the expansive network of foreign development, religious, and charity organizations (2000-4000 in total). [23] The Finnish report also notes that ‘a large proportion of the Ethiopian people have limited coping mechanisms at their disposal.’ Furthermore, the country is faced with ‘an immediate need [to] transition from humanitarian aid to development [and]…without a range of dynamic and comprehensive activities to promote effective private sector development, particularly in agriculture, it will be very difficult to achieve the anticipated growth rates under the [growth and transformation plan].’ [24]
In fact, recent years have seen Ethiopia’s vaunted annual GDP growth rate decrease. [25] Utilizing World Bank data, which reports Ethiopia’s 2012 GNI per capita as $380 (current US$), [26] Ethiopia’s transition to lower middle-income status (between $1,036 – $4,085) [27] would require an annual growth rate of approximately 20 percent. This would appear to be highly unlikely, even if overlooking its recent descending economic trend or the negative effects of inflation.
These issues may be exacerbated by an array of financial risks. According to the IMF, Ethiopia faces growing external debt, [28] even though it was the beneficiary of debt cancellation in 2005 via the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and Multilateral Debt Relief Initiatives (MDRI) programs. [29] Additionally, it is has experienced a worsening of its foreign exchange shortage, and a lack of sufficient financing for its growth and transformation plan. [30]
Beyond the aforementioned developmental challenges, issues of aid dependency and financial risks, domestic governance and external geopolitical factors represent critical concerns for Ethiopia. A multicultural, ethnically-diverse country with a state-structure built along institutionalized ethnic entrenchment in a nominal federal arrangement dominated by a single minority group; rising tensions with a resilient, large and historically repressed Islamic constituency; and troubled ties with neighbours are both challenges and possible impediments to Ethiopia’s projected economic growth unless adequately addressed.
Currently, political oppression, ethnic discrimination, extrajudicial executions, torture and other abuses in detention, [31] in addition to economic factors, have led hundreds of thousands of Ethiopians to flee the country. Many fall prey to human smugglers and traffickers who engage in a variety of the most depraved forms of abuse or exploitation. [32]
Additionally, Ethiopia has been at the forefront of a variety of conflicts. The separatist Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF) continues to wage an insurgency against the central government, [33] while terrorism – largely arising from Ethiopia’s policies and interventions in neighbouring regions – has been a constant threat. According to Global Humanitarian Assistance, in each of the years from 2002-2011 Ethiopia was engaged in some form of active conflict. [34] Prior, the 1998-2000 period saw Ethiopia wage a costly war against Eritrea. Since then, Ethiopia has failed to abide by its obligations as ruled by the international Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission, [35] and instead continues to occupy sovereign Eritrean territories – thus posing an unnecessary problem to both countries and the surrounding region. [36] Ethiopia’s recent tension with Egypt regarding the construction of Ethiopia’s Renaissance Dam is an additional dimension that complicates an already tenuous regional political landscape. [37]
Last, a potential crisis within or outright collapse of the Ethiopian state calls into question any projections of Ethiopia’s impending transition to middle-income status. Since 2006, Ethiopia has experienced a downward trend in the Fund for Peace (FFP) Failed States Index, while for 2013 it received amongst the lowest rankings. [38] This outcome is buttressed by Marshall and Cole’s (2011) State Fragility Index and Matrix which classifies Ethiopia as one of the eight ‘most fragile’ states in the world. State fragility is reported as an aggregate score of an array of governance categories including state effectiveness, legitimacy, security, armed conflict and other socio-economic and political factors. [39] Finally, the National Intelligence Council’s Global Trends 2030: Alternative Worlds (2012) suggests that Ethiopia is among the top 15 ‘high risk’ nations slated for state failure by 2030. [40]
In conclusion, Ethiopia’s recent economic growth and developmental progress are respectable achievements, particularly within a region long plagued by a variety of ailments. However, suggestions of Ethiopia’s socioeconomic transformation may prove fanciful if they fail to consider and address a variety of significant concerns.
-Fikrejesus Amahazion, a PhD candidate focusing on Political Economy, Development and Human Rights.
Read more from original source @:
http://pambazuka.org/en/category/features/90435
Related reference:
The Food Index
The interactive snapshot of 125 countries showing the best and worst places in the world to eat, and the challenges people face getting enough of the right food.
Around the world, one in eight people go to bed hungry every night, even though there is enough food for everyone.
Ethiopia ranks 123 (worst) in over all food availability.
Silence and pain: Ethiopia’s human rights record in the Ogaden February 2, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Aannolee and Calanqo, Africa, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Dictatorship, Ethnic Cleansing, Human Rights, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Ogaden, Omo, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human Rights and Liberties, Human Rights Violation Against Ogaden people, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Ogaden, Oromia, Oromo, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Social Sciences, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
1 comment so far
Repression in the Ogaden is mainly carried out by the notorious Liyu Police; this is a locally recruited force that has been widely condemned for the repressive methods that it uses.
This is how the force is described by Human Rights Watch:[6]
“Ethiopian authorities created the Liyu (“special” in Amharic) police in the Somali region in 2007 when an armed conflict between the insurgent Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF) and the government escalated. By 2008 the Liyu police became a prominent counterinsurgency force recruited and led by the regional security chief at that time, Abdi Mohammed Omar (known as “Abdi Illey”), who is now the president of Somali Regional State.
The Liyu police have been implicated in numerous serious abuses against civilians throughout the Somali region in the context of counterinsurgency operations. The legal status of the force is unclear, but credible sources have informed Human Rights Watch that members have received training, uniforms, arms, and salaries from the Ethiopian government via the regional authorities.”
In January 2013 it was reported that the Liyu police numbered between 10,000 and 14,000. The force was accused of numerous human rights abuses and summary executions.[7] The Guardian newspaper reported that it had seen an internal British government document, from the Department for International Development, indicating that there were plans to spend £13m–15m of aid money on the force as part of a five year “peace-building” programme. The report was denied by the British government, which said all funding would go via United Nations agencies and not through the Ethiopian authorities.[8]
Despite these assurances concern about the behaviour of the Liyu police remains. The testimony below and the reports of atrocities carried out in recent weeks indicate these are well placed.
Testimony of Captain Hassan Mohammed Abdi aka Hassan Afo, a former member of the Liyu Police, who was active with the force in Degehbur Province. June 2012.
“In Balidhuure village (Eastern Degehbur Province) located in between Gurdumi and Koore, a Liyu police unit that left from Aware and commanded by Major Kidinbir rounded up and finally driven away most of the people that lived in the area. Among them was a disabled man who walks with a stick named Ina-Yul-yul or the son of Yul-yul. Not far from the village of Balidhuure, the handicapped man, Ina-Yul-yul could not continue walking. One of the Liyu policemen noticed this and he informed Major Kidinbir by radio. Major Kidinbir said, “He can’t walk? Then kill him where he is at right now.” That’s how Ina-Yulyul was shot and killed. He was killed because of one of his brothers was among the ONLF fighters.”
Reports of human rights atrocities committed in the Ogaden Region over the previous month.
25/12/13: In Guna’gado district of Degahbur province, at least 25 civilians were detained and 25,000 Ethiopian birr was stolen from them
5/1/14: In Gasaangas in Hamara district 5 civilians are unlawfully detained. They were: Hassan Geday, Hassan Nour Moalim Ibrahim, Rukiya Moalim Ibraahin, Anbiya Sheikh Mohammed and Nafis.
5/1/14: In Dhuhun a girl named, Halimo Duulane was detained .
10/1/14: In Eastern Iimay, Fadumo Wacdi Ahmed, Sa’ada Hassan and Gordo Abdi God were detained by the Ethiopian Security Forces.
10/1/14,In Guna’gado, Mohammed Isse Gu’had was tortured, detained and his 11 camels were stolen.
3/1/14: Hamuud-ka, in Fiq Province, the security forces detained Mohammed Ibrahim.
5/1/14: Ya’hob Village in Fiq Province, the security forced killed in a cold-blood Abdullahi Lo’bari in cold blood and injured Ahmed Hassan Awl.
5/1/14: Hamaro in Nogob Province, the security forces detained several people : Mohammed Abdi Rahman Omar, Abdirahman Bade, Ta’kal Yousouf and Ina-Barud.
Annex
Amnesty International on Ethiopia’s Ogaden region[9]
In September, the government and the ONLF briefly entered into peace talks with a view to ending the two-decade long conflict in the Somali region. However, the talks stalled in October. The army, and its proxy militia, the Liyu police, faced repeated allegations of human rights violations, including arbitrary detention, extrajudicial executions, and rape. Torture and other ill-treatment of detainees were widely reported. None of the allegations was investigated and access to the region remained severely restricted. In June, UN employee Abdirahman Sheikh Hassan was found guilty of terrorism offences over alleged links to the ONLF, and sentenced to seven years and eight months’ imprisonment. He was arrested in July 2011 after negotiating with the ONLF over the release of two abducted UN World Food Programme workers.Human Rights Watch on Ethiopia’s Ogaden region
ETHIOPIA: UPR SUBMISSION SEPTEMBER 2013 [10]
http://martinplaut.wordpress.com/2014/01/31/silence-and-pain-ethiopias-human-rights-record-in-the-ogaden/
Related References:
Silence and pain: human rights in the Ogaden
Martin Plaut
Introduction
The Ogaden is Ethiopia’s dark, dirty secret. It is far from prying international eyes, where almost anything can be done to anyone the government does not like.
The Ogaden was conquered and forcibly incorporated into Ethiopia by Emperor Menelik II in the last quarter of the 19th century. Its Somali speaking, almost exclusively Muslim community, never really accepted an Ethiopian identity. In 1977 it was the scene of an international conflict, as Somali President Siad Barre attempted to wrest the region from Ethiopia. The Soviet Union poured arms and Cuban troops into Ethiopia and the invasion was halted. The Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF) has been fighting the Ethiopian government since 1995, and local people have been caught up in the conflict.
 The Ethiopian authorities have sealed off the region to international journalists.
The Ethiopian authorities have sealed off the region to international journalists.
As Human Rights Watch wrote as…
View original post 3,314 more words
African Poors: Poverty, Failed Aid & Extractive Institutions January 28, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, African Poor, Aid to Africa, Climate Change, Dictatorship, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Food Production, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Land Grabs in Africa, Nelson Mandela, Nubia, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African Studies, Amartya Sen, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, poverty, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment

‘Recognising that poor countries are poor because they have extractive institutions helps us understand how best to help them. It also casts a different light on the idea of foreign aid. We do not argue for its reduction. Even if a huge amount of aid is siphoned off by the powerful, the cash can still do a lot of good. It can put roofs on schools, lay roads or build wells. Giving money can feed the hungry, and help the sick — but it does not free people from the institutions that make them hungry and sick in the first place. It doesn’t free them from the system which saps their opportunities and incentives. When aid is given to governments that preside over extractive institutions, it can be at best irrelevant, at worst downright counter-productive. Aid to Angola, for example, is likely to help the president’s daughter rather than the average citizen. Many kleptocratic dictators such as Congo’s Mobutu Sese Seko have been propped up by foreign aid. And it wasn’t foreign aid that helped to undermine the apartheid regime in South Africa and got Nelson Mandela out of prison, but international sanctions. Those sanctions came from pressure on governments — including the British government — that would have preferred not to see them implemented. Today it is no different. Governments don’t like cutting their ties to dictators who open doors for international business, or help their geopolitical agendas. Pressure needs to come from citizens who do care enough about international development to force politicians to overcome the easy temptation of short-run political expediency. Making institutions more inclusive is about changing the politics of a society to empower the poor — the empowerment of those disenfranchised, excluded and often repressed by those monopolising power.’ –Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson, The Spectator magazine, 25th January 2014
Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson in their articles in The Spectator put forward the following interesting analysis regarding what is really at stake and leading issues in Africa’s development problems. They brought to our attentions why aid has failed and proposed how the predicaments can be tackled:-
David Cameron speaks compellingly about international aid. Eradicating poverty, he says, means certain institutional changes: rights for women and minorities, a free media and integrity in government. It means the freedom to participate in society and have a say over how your country is run. We wholeheartedly agree and were flattered to see the Prime Minister tell this magazine that he is ‘obsessed’ by our book on the subject, Why Nations Fail: The Origins of Power, Prosperity, and Poverty. But diagnosing a problem is one thing; fixing it another. And we don’t yet see the political will — in Britain or elsewhere — that could turn this analysis into a practical agenda.
The British government is strikingly generous in foreign aid donations. It spent £8.7 billion on foreign aid in 2012 — which is 0.56 per cent of national income. This is to rise to £11.7 billion, or 0.7 per cent of national income, next year. But if money alone were the solution we would be along the road not just to ameliorating the lives of poor people today but ending poverty for ever.
The idea that large donations can remedy poverty has dominated the theory of economic development — and the thinking in many international aid agencies and governments — since the 1950s. And how have the results been? Not so good, actually. Millions have moved out of abject poverty around the world over the past six decades, but that has had little to do with foreign aid. Rather, it is due to economic growth in countries in Asia which received little aid. The World Bank has calculated that between 1981 and 2010, the number of poor people in the world fell by about 700 million — and that in China over the same period, the number of poor people fell by 627 million.
In the meantime, more than a quarter of the countries in sub-Saharan Africa are poorer now than in 1960 — with no sign that foreign aid, however substantive, will end poverty there. Last year, perhaps the most striking illustration came from Liberia, which has received massive amounts of aid for a decade. In 2011, according to the OECD, official development aid to Liberia totalled $765 million, and made up 73 per cent of its gross national income. The sum was even larger in 2010. But last year every one of the 25,000 students who took the exam to enter the University of Liberia failed. All of the aid is still failing to provide a decent education to Liberians.
One could imagine that many factors have kept sub-Saharan Africa poor — famines, civil wars. But huge aid flows appear to have done little to change the development trajectories of poor countries, particularly in Africa. Why? As we spell out in our book, this is not to do with a vicious circle of poverty, waiting to be broken by foreign money. Poverty is instead created by economic institutions that systematically block the incentives and opportunities of poor people to make things better for themselves, their neighbours and their country.
Let us take for Exhibit A the system of apartheid in South Africa, which Nelson Mandela dedicated himself to abolishing. In essence, apartheid was a set of economic institutions — rules that governed what people could or could not do, their opportunities and their incentives. In 1913, the South African government declared that 93 per cent of South Africa was the ‘white economy’, while 7 per cent was for blacks (who constituted about 70 per cent of the population). Blacks had to have a pass, a sort of internal passport, to travel to the white economy. They could not own property or start a business there. By the 1920s the ‘Colour Bar’ banned blacks from undertaking any skilled or professional occupation. The only jobs blacks could take in the white economy were as unskilled workers on farms, in mines or as servants for white people. Such economic institutions, which we call ‘extractive’, sap the incentives and opportunities of the vast mass of the population and thereby keep a society poor.
The people in poor countries have the same aspirations as those in rich countries — to have the same chances and opportunities, good health care, clean running water in their homes and high-quality schools for their children. The problem is that their aspirations are blocked today — as the aspirations of black people were in apartheid South Africa — by extractive institutions. The poor don’t pull themselves out of poverty, because the basic ability to do so is denied them. You could see this in the protests behind the Arab Spring: those in Cairo’s Tahrir Square spoke in one voice about the corruption of the government, its inability to deliver public services and the lack of equality of opportunity. Poverty in Egypt cannot be eradicated with a bit more aid. As the protestors recognised, the economic impediments they faced stemmed from the way political power was exercised and monopolised by a narrow elite.
This is by no means a phenomenon confined to the Arab world. That the poor people in poor countries themselves understand their predicament is well illustrated by the World Bank’s multi-country project ‘Voices of the Poor’. One message that persistently comes across is that poor people feel powerless — as one person in Jamaica put it, ‘Poverty is like living in jail, living under bondage, waiting to be free.’ Another from Nigeria put it like this: ‘If you want to do something and have no power to do it, it is talauchi [poverty].’ Like black people in South Africa before 1994, poor people are trapped within extractive economic institutions.
But it is not just the poor who are thus trapped. By throwing away a huge amount of potential talent and energy, the entire society condemns itself to poverty.
The key to understanding and solving the problem of world poverty is to recognise not just that poverty is created and sustained by extractive institutions — but to appreciate why the situation arises in he first place. Again, South Africa’s experience is instructive. Apartheid was set up by whites for the benefit of whites. This happened because it was the whites who monopolised political power, just as they did economic opportunities and resources. These monopolies impoverished blacks and created probably the world’s most unequal country — but the system did allow whites to become as prosperous as people in developed countries.
The logic of poverty is similar everywhere. To understand Syria’s enduring poverty, you could do worse than start with the richest man in Syria, Rami Makhlouf. He is the cousin of President Bashar al-Assad and controls a series of government-created monopolies. He is an example of what are known in Syria as ‘abna al-sulta’, ‘sons of power’.
To understand Angola’s endemic poverty, consider its richest woman, Isabel dos Santos, billionaire daughter of the long-serving president. A recent investigation by Forbes magazine into her fortune concluded, ‘As best as we can trace, every major Angolan investment held by dos Santos stems either from taking a chunk of a company that wants to do business in the country or from a stroke of the president’s pen that cut her into the action.’ She does all this while, according to the World Bank, only a quarter of Angolans had access to electricity in 2009 and a third are living on incomes of less than $2 a day.
Recognising that poor countries are poor because they have extractive institutions helps us understand how best to help them. It also casts a different light on the idea of foreign aid. We do not argue for its reduction. Even if a huge amount of aid is siphoned off by the powerful, the cash can still do a lot of good. It can put roofs on schools, lay roads or build wells. Giving money can feed the hungry, and help the sick — but it does not free people from the institutions that make them hungry and sick in the first place. It doesn’t free them from the system which saps their opportunities and incentives. When aid is given to governments that preside over extractive institutions, it can be at best irrelevant, at worst downright counter-productive. Aid to Angola, for example, is likely to help the president’s daughter rather than the average citizen.
Many kleptocratic dictators such as Congo’s Mobutu Sese Seko have been propped up by foreign aid. And it wasn’t foreign aid that helped to undermine the apartheid regime in South Africa and got Nelson Mandela out of prison, but international sanctions. Those sanctions came from pressure on governments — including the British government — that would have preferred not to see them implemented.
Today it is no different. Governments don’t like cutting their ties to dictators who open doors for international business, or help their geopolitical agendas. Pressure needs to come from citizens who do care enough about international development to force politicians to overcome the easy temptation of short-run political expediency.
Making institutions more inclusive is about changing the politics of a society to empower the poor — the empowerment of those disenfranchised, excluded and often repressed by those monopolising power. Aid can help. But it needs to be used in such a way as to help civil society mobilise collectively, find a voice and get involved with decision-making. It needs to help manufacture inclusion.
This brings us back to David Cameron. When answering a question at New York University almost two years ago, he put it perfectly. ‘There is a huge agenda here,’ he said. It is time to ‘stop speaking simply about the quantity of aid’ and ‘start talking about what I call the “golden thread”.’ This, he explained, is his idea that long-term development through aid only happens if there is a ‘golden thread’ of stable government, lack of corruption, human rights, the rule of law and transparent information.
As the Prime Minister says, this is a very different thing to setting an aid spending target. Promoting his golden thread means using not just aid but diplomatic relations to encourage reform in the many parts of the world that remain in the grip of extractive institutions. It means using financial and diplomatic clout (and Britain has plenty of both) to help create room for inclusive institutions to grow. This may be a hard task — far harder than writing a cheque. But it is the surest way to make poverty history.
Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson are the authors of Why Nations Fail, which David Cameron last week declared one of his five favourite books of all time.
Read the full text of this article @:
http://www.spectator.co.uk/features/9121361/why-aid-fails/
This article first appeared in the print edition of The Spectator magazine, dated 25 January 2014
Further references:
Amartya Sen: Poverty and the Tolerance of the Intolerable
http://richmedia.lse.ac.uk/publiclecturesandevents/20130122_1830_povertyToleranceIntolerable.mp3
Copyright © Oromianeconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Oromia Speaks:The Ethiopian Empire State and International Human Rights Laws January 24, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. Africa Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land Grabs in Africa, Nelson Mandela, Nubia, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Culture, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Sirna Gadaa, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Ethiopia, Gadaa System, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment

The Empire States of Ethiopia is a product of colonial conquest. Ethiopia is formed during the 19the century colonial scramble for Africa after the Abyssinian State, the only Black colonial power that took part in the colonial partition of Africa, conquered the Oromos, Sidamas, Ogadenese and other present day Southern Ethiopian peoples. Because of the conquest, the Oromos and other subject peoples were forcefully incorporated into Abyssinia, which was later on renamed Ethiopia.
As an outcome of a colonial conquest, the essence of the Ethiopian Empire State is the deprivation, oppression, subjugation and exploitation of the conquered peoples’ national, political, civic, cultural, social and economic rights. Stated differently, the defining characteristics of the Ethiopian Empire state, since its formation up to present, are the denial of national rights, human rights, and freedoms to the Oromo and other subject peoples. Furthermore, as the old adage goes, “a nation that oppresses others it not itself a free nation,” the successive Ethiopian regimes did not also respect the human rights and freedoms of its citizens, the Abyssinians.
The successive Ethiopian regimes’ stance on ratification of or accession to International Instruments designed for the promotion and protection of human rights corroborates the Ethiopian Empire State’s long-standing anti-human rights policies. It is a fact of history that the Ethiopian regime led by the late Emperor Haile Sillassie was among few states that did not sign/ratify the Universal Declaration of Human Rights of 1948. The Emperor Haile Sillassie regime, which was laboring in consolidation of the colonial conquests and Amharization of the conquered peoples, was engaged in gross violation of human rights, including practice of slavery and servitude failed to sign the Universal Declaration of Human Rights that, among others, abolished slavery and servitude and set standard for human rights protection.
It is instructive to note that, the Emperor Haile Sillassie regime declined from signing the Universal Declaration of Human Rights with, among others, the then minority apartheid regime of South Africa, the other notorious regime for being anti-human rights. The Ethiopian regime led by Emperor Haile Sillassie became Member of the United Nations on 13 November 1945, but it did not become a party to any Intentional Human Rights Conventions.
A military regime, known as Dergue, led by Colonel Mengistu Haile Mariam overthrew Emperor Haile Sillaasie’s regime in 1974. As far as respect for human rights and accession to Intentional Human Rights Conventions is concerned, the Dergue regime continued its predecessor’s anti-human rights policy and practice. The Military regime did not become a party to International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights and International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights that have entered into force in 1976.
However, apparently following its patron the now defunct Soviet Union, the Ethiopian Military regime became a party to International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, 23 June 1976, Convention on the Elimination of All Form of Discrimination against Women, 10 September 1981, and Convention on the Rights of the Child, 14 May 1991.
It is a mockery that the Ethiopian Military regime that failed to be a party to International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights and International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, became a party to International Conventions that prohibit racial discrimination, discrimination against women and the Conventions on the Rights of the Child. Unlike the incumbent Tigrai Peoples Liberation Front, (TPLF) led Ethiopian regime, the two preceding Ethiopian regimes did not pretend to be champions of human rights and stayed out of the International Instruments and Mechanisms made and established for ensuring the protections of Human Rights and freedoms.
As a result of the proposal and strong push made in 1991-92 by Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) group who were then a member of Ethiopian Transitional Government, the current Ethiopian regime of TPLF was forced to depart from the positions held by its predecessors and has acceded to the following international human rights treaties: International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, 11 June 1993, International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, 11 June 1993, and Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment of Punishment, 13 March 1994,
Apparently, accession to International Human Rights Treaties were one of the decisions the TPLF regime made as soon as it came to power as a consequence of two significant factors: (1) the proposal and the push the OLF group made to accept ICCPR and ICESCR and (2) the attempt the TPLF Regime made to please its foreign donors. However, the regime’s gross and appalling human rights violation records in the last fourteen years prove a contrary intention. Stated differently, the TPLF regime’s human rights record proves that the TPLF regime’s position on human rights is not any better, if not worse, than its predecessors that were not parties to the International Human Rights Covenants.
The TPLF regime’s engagement in a gross human rights violation of Oromos and other people is being recognized not only by reputable international non-governmental organizations that monitor states’ compliance with international human rights laws, but also by State Members of the United Nations, including the Untied States of America.
Read more from original source@ http://www.oromoliberationfront.org/Publications/OSvol11Art1003.htm
Oromia Speaks Vol. 11 Issue 1
Further References:
‘Article 2, paragraph 2 of the ICESCR obliges each State Party to guarantee that the rights enunciated in the Covenant are exercised without discrimination as to, inter alia, ethnic origin. In practice, however, the Government of Ethiopia directly and indirectly discriminates against several disadvantaged ethnic groups, including but not limited to the Oromo and the Anuak.’ –http://www2.ohchr.org/english/bodies/cescr/docs/ngos/AHR_Ethiopia_CESCR48.pdf
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4cHBNsqKWnM
http://www.hrw.org/en/reports/2005/05/09/suppressing-dissent
http://www.unpo.org/article/16330
http://oromochurchdc.com/joomla259/index.php/ct-menu-item-9/ct-menu-item-11
http://www.oromo.org/OSG/pr_49.pdf
http://www.hrw.org/world-report/2013/country-chapters/ethiopia
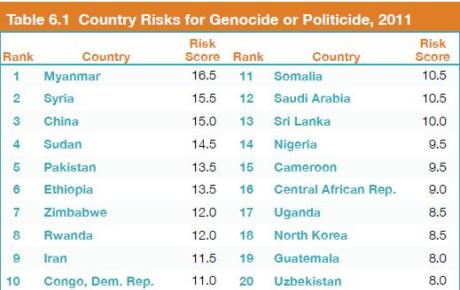
Source: Genocide Watch
http://www.genocidewatch.org/alerts/countriesatrisk2012.html
http://birhanumegersalenjiso.blogspot.co.uk/2014/01/nuding-ethiopian-history-and-naked.html
The Human Right Issues and Violations in the Horn of Africa,Ethiopia-Oromia
The current crisis in the Horn of Africa is, on the one hand, a struggle between oppressed people who are fighting for self-determination and, on the other hand, the regime of the Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF) that is trying to impose its rule by force.
The regime has set loose war, hunger, poverty, and disease to ransack the country. In particular, the regime has been and is systematically violating human rights of the Oromo and other peoples of in the country as well and the neighborings too.
The OLF also believes in peace, democracy and development . As the main organ that is championing the right of self-determination of the Oromo people, it fully realizes the present day global reality. It affirms that the international community does have legitimate concern and interest in political stability and economic development of the Horn of Africa. Moreover, the OLF is cognizant of the fact that the day of carving spheres of influence and promoting clients in superpower rivalry has given way to globalization. Further, the OLF firmly believes in the immediate termination of the vicious cycle of political conflicts, economic backwardness, environmental degradation, natural and man-made disasters that today ravage the peoples of the Horn of Africa.
(http://www.oromoliberationfront.org/PressReleaseArchive/Articles/Liberating.htm)
Human Right Issue in Ethiopia
Allegations of arbitrary detention, torture, and other ill-treatment at the hands of Ethiopianpolice and other security forces are not new. But since the disputed 2005 elections, the Ethiopian government has intensified restrictions on freedom of expression, association,and assembly, deploying a range of measures to clamp down on dissent. These include arresting and detaining political opposition figures, journalists, and other independent voices, and implementing laws that severely restrict independent human rights monitoring and press freedom.
Since 2009 a new law, the Anti-Terrorism Proclamation, has become a particularly potent instrument to restrict free speech. The law’s provision undermine basic legal safeguards against prolonged pre-charge detention and unfair trials. In this context, Maekelawi has become an important site for the detention and investigation of some of the most politically sensitive cases.
Many detainees accused of offenses under the law—including some of Ethiopia’s most prominent political prisoners—have been detained in the Maekelawi facility as their cases were investigated or prepared for trial (Human Rights Watch, 2013). As a result of enforcement of the FDRE Proclamation 621/2009 that has been intended to impose superior regulation of charities, the party leaders decide who should receive and who should not receive the emergency support at grassroots level in the respective community.
Older Oormo people are usually victims of this type of abuse because of their allegiances to the values of the Oromo Gadaa system, that promotes respect and dignity to people in difficult situation. In so doing, technically, the authorities decide who should die from and who should survive the hunger.
http://www.minorityvoices.org/news.php/fr/1381/ethiopiauk-oromo-rally-in-london
Endless focus on Oromos by TPLF, why?
The Oromo people constitute the single largest national groups in the Ethiopia empire and the horn of Africa with the total of over 40 million people. The number of the oromo people and the geographical location of their country Oromia make the oromo country ( Oromia) the heart of Ethiopia. The Ethiopian empire mainly survives on the economic resources of Oromia. Although the Oromo people are one of the most impoverished and terrorized indigenous people .Recognizing that Oromia is the richest and largest populous state, the Tigrayan led Ethiopia government has been using collective violence to dominate, control and exploit Oromia which the key in controlling the Ethiopia government has been using political economy. Understanding the situation in Oromia helps in generalizing what is going through the country (Hassen,2011).
The Oromo people are just arrested and accused of being a member or supporter or sympathiser of the Oromo liberation struggle. To the Ethiopian government authorities, every Oromo appears to be a member of the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF), a political organisation struggling for the socio-economic, cultural and political rights of the Oromo people. One has to prove he/she is not a member or supporter of the OLF in order to live in relative peace. The safest proof is one and only one – to become a member of the EPRDF, the ruling party;failure to proove non-affiliation with OLF or any attempt to remain politically indifferent has come to be dangerous in Ethiopia for every ordinary Oromo. Business persons are systematically eliminated from investment and small scale business if they fail to be members of the ruling party in any case. Every student in college or university is required to secure membership of the ruling party at the campus in order for her/him to get job in public institutions or to run private business after completion of the study. The situation is worse for the rural people whereby farmers are required to be members of and demonstrate allegiance to the EPRDF in order to get agricultural inputs and/or have their children learn in school without assault by the government security.
It always seems impossible until it is done – Nelson Mandela
http://ethiofreespeech.blogspot.no/2014/01/the-human-right-issues-and-violations.html
Ethiopia: land of slavery & brutality – the League of Nations, Geneva 1935
‘
An old Abyssinian was shooting with the sight adjusted at more than a thousand
metres. I said to the Dedjiajmatch [dejazmach] that the bullets might fall on the mountain
and kill someone. He burst out laughing and said, “What does it matter if they
do? There is nobody here but Shangalla [shankilla]”.’
Friends at ER:
The above quote was an extract from a document or a memorandum presented by the Italian Government delineating the reasons for the expulsion of Ethiopia from the League of Nations, the forerunner of today’s United Nations Organisation. The main point of their argument was the condition of slavery and gebbar (a slave-like system) to which Abyssinia/Ethiopia had reduced its subject populations in the southern half of its empire, while pillaging their lands.
The change of political masters in Addis Ababa has so far been a mere case of taking turns at abusing the populations of these same southern provinces of Ethiopia to benefit the gun-toting invaders from the “Habesha highlands” of northern Ethiopia (Tigre-Woyane at the moment).
In this light, you may find the following document of great historical significance. It also provides an insight into the unchanged modus operandi of all Ethiopian regimes before or since.
Here is the complete document….
“Geneva, September 11th , 1935. Official No. C.340.M.171.1935.VII.
(I) CONDITIONAL ADMISSION OF ETHIOPIA TO THE LEAGUE OF NATIONS.
As regards the condition required by Article I of the Covenant [accord]
regarding effective guarantees of a sincere intention to observe international
obligations, the Sub-committee pointed out that, in the past, Ethiopia had not
fully observed her international engagements. During the discussion it was
stressed how difficult it was to reconcile Ethiopia’s demand with the
circumstance that Ethiopia, once admitted to the league, might sit in judgement
on countries under mandate, more civilised than Ethiopia herself and not
stained with the disgrace of slavery…
(II) POLITICAL STRUCTURE AND CONDITIONS OF ETHIOPIA IN RELATION TO ARTICLE I OF
THE COVENANT [of the League of Nations].
(Summary):
Clear distinction between the Abyssinian State and the territories conquered by
it. Difference of religion, language, history, race, and political and social
structure. Negus’s domination over non-Abyssinian populations. The gebbar
system (a form of slavery) applied to subject populations. The Ethiopian
Government’s responsibility for the decimation of the subject populations.
Ethiopia’s incapacity to possess a colony.
ABYSSINIA AND HER “COLONIES”: DISTINCTION BETWEEN THE ABYSSINIAN STATE AND THE
CONQUERED TERRITORIES.
On this subject it is first of all necessary to obtain a fundamental idea of
the position. It is commonly said that Ethiopia is a national State in Africa
which forms a single unit. Nothing could be further from the facts. The
Ethiopian State, in its present form, is composed of two regions which are
clearly distinct both geographically and politically.
(i) The old Abyssinian State, consisting of the regions inhabited mainly by
Abyssinian populations speaking kindred languages derived from Southern Arabic.
But the old Abyssinian State itself could not be called a national State,
because even in those regions there are considerable non-Abyssinian minorities,
such as the Agau in the Tsana and Nile regions, the Falasha of Semien,
professing the Jewish religion …and others. Nevertheless, their common
allegiance to the dynasty of the House of Solomon, and the fact that for ages
they [peoples of the northern half of Ethiopia] had belonged to the same group
of States, have to a certain extent welded all these regions into a political
unit which, though rough and shapeless in structure, might have a position of
its own in the composition of present-day Ethiopia.
This Abyssinian State has well-defined and exact historical, geographical and ethnical boundaries. On the west, towards the Nile basin, and on the east, towards Danakil, the frontier of
the Abyssinian State coincided with the edge of the plateau. The Abyssinians, a
mountain people, are clearly distinguished by race, language and religion from
the populations which inhabit the torrid Danakil plain and the valleys sloping
down towards the Sudan.
To the south, the boundary of the Abyssinian State was marked by the course of
the Blue Nile as far as its confluence with the Adabai, by the watershed
between the Blue Nile and the Awash, and by the course of the river Awash as
far as its entry into the Danakil plain. The territories beyond these
boundaries, in the south, are inhabited by non-Abyssinian populations which,
throughout the centuries of their history, have been traditional enemies of the
Abyssinian State.
(ii) The non-Abyssinian areas recently conquered by the arms of the Negus
Menelik.-Beyond the confines of this nucleus of the Abyssinian State there
were, until forty years ago, other native States, some of which have a long
historical tradition of independence. Among the principal may be mentioned the
Emirate of Harrar, which comprised the regions between the river Awash, the
Webi Shebeli, and the south-eastern edge of the plateau, having the inhabitants
of Ogaden as tributaries.
The Emirate of Harrar is a Moslem State which was
ruled for centuries by the dynasty of its Emirs, and was the cultural and
religious centre of Islam in South-East Africa. The continuous relations
maintained by the Emirate with the Arab countries of the Levant had brought
that state up to a level of civilisation far superior to that of Abyssinia. We
need only mention the fact that, even to-day, Harrar is the only town in the
territory of the present Ethiopian State which is built of masonry and is not
composed of huts hovels made of branches, apart from few buildings in Addis
Ababa.
In the south-west, the kingdom of kafa was founded by the western Sidama
peoples. The political and social constitution of this kingdom and its history
(which comprises at least 600 years of independence, from the fourteenth
century to the Abyssinian conquest) form the subject of various well-known
works published only recently; and, not to quote Italian writers, we need only
refer to the voluminous work of the Austrian traveller Franz Bieber.
In the south, there is the kingdom of Wollamo, founded by the Sidama
populations of the Omo. How this peaceful little agricultural State was
devastated and destroyed by the Abyssinians is described in a work by a
Frenchman, M Vanderheym, which is nothing les than an indictment of the
Abyssinian State.
In the west, there is the Sultanate of Jimma, a Moslem State that became a
centre in Westrn Ethiopia towards which Moslem currents flowed from Harrar and
Egypt. Under the patriarchal administration of its sultans of the local
dynasty, Jimma had reached a high degree of economic prosperity, which it
retained, being the only Moslem State remaining independent of the Abyssinians
until the Negus annexed it to Ethiopia a few months ago.
The Abyssinian State is completely different in every respect from these vast
“colonies” which it has recently acquired:
(a) In religion, because the Abyssinians are Monophysite Christians, whereas
the Somali, Harrari, [deleted] [Oromo], Sidama are largely Moslem, and in part
still pagan;
(b) In language, because the Abyssinians speak Amharic and Tigrai (Semitic
languages), whereas in the conquered regions the languages spoken are totally
different from the Abyssinian languages, but are interrelated among
themselves-e.g.-Galla [Oromo], Somali, Kafi, Wolamo, etc.;
(c) In political and social structure, because the Abyssinian State is based on
the feudal system, whereas the Emirate of Harrar was organised on the model of
the States of the Arabian peninsula, and the Sidama States have a highly
centralised organisation of their own;
(d) In race, because the Abyssinians are Semiticised people, whereas the [deleted],
Sidama, Somali, Tishana, Yambo and the rest are Cushitic and Nilotic peoples;
(e) In history, because the Emirate of Harrar, for instance, has for centuries
waged relentless warfare against the Abyssinian State. Indeed, this warfare
might be said to constitute the whole history of Abyssinia itself; records of
it existed from at least the fourteenth century onwards. The Abyssinian
domination constitutes, in fact, the subjugation of a conquered people by its
age-long enemy.
DOMINATION OF THE NEGUS OVER NON-ABYSSINIAN POPULATIONS.
The Abyssinian domination in the conquered countries takes concrete form in the
slave trade and the so-called gebbar system. The slave trade will be considered
below. It should be pointed out here, however, that the slave trade is due not
only to a desire for gain, but also to the idea, deep-rooted in the
Abyssinians’ mind, that their victories have left them absolute masters of
populations which, in their eyes, are no more than human cattle.
This conception of the Abyssinians is confirmed b a typical incident narrated by Sir
Arnold Hodson in his work Where the Lion Reigns (page 41): ‘An old Abyssinian
was shooting with the sight adjusted at more than a thousand metres. I said to
the Dedjiajmatch [dejazmach] that the bullets might fall on the mountain and kill someone.
He burst out laughing and said, “What does it matter if they do? There is
nobody here but Shangalla [shankilla]”‘ (Shangalla is the name given by the Abyssinians to
the Nilotic peoples).
The gebbar system is a form of slavery, and is regarded as such by European
writers and travellers. In each of the countries conquered and annexed by
Abyssinia, a body of Abyssinian troops is stationed, comprising the soldiers
themselves and their families. The inhabitants of the conquered country are
registered in families by the Abyssinian chiefs, and to every family of
Abyssinians settled in the country there is assigned one or more families of
the conquered as gebbar. The gebbar family is obliged to support the Abyssinian
family; it gives that family its own lands, builds and maintains the huts in
which it lives, cultivate the fields, grazes the cattle, and carries out every
kind of work and performs all possible services for the Abyssinian family. All
this is done without any remuneration, merely in token of the perpetual
servitude resulting from the defeat sustained thirty years ago. It amounts to
what Anglo-Indians are accustomed to call “the law of the jungle”.
The gebbar can never obtain freedom from their chains, even by ransom. They must not leave
the land assigned for their work, and, if they run away, they themselves are
subject to the terrible punishment which are inflicted in Ethiopia, and to
which we shall refer shortly, while their village is bound to supply the
Abyssinians with another family to be reduced to the condition of gebbar, in
place of the fugitive family.
As to the effects of slavery and the gebbar system, all who know the facts are
agreed: the non-Abyssinian regions of Ethiopia are becoming a vast desert.
Every Abyssinian chief sent to those parts finds it necessary on his arrival to
provide himself with slaves and his soldiers’ families with gebbar. And when he
leaves the conquered countries to be transferred elsewhere, he takes away with
him, and allow his soldiers to take away with them, the greatest possible
number of slaves and gebbar to be employed at his new residence. This constant
draining of the population of the subject territories is particularly terrible,
because the slaves and gabbar are decimated, during the long journeys, by
hunger, thirst and ill-treatment from their Abyssinian masters. We quote
evidence from non-Italian sources.
Sir Arnold Hodson (Seven Years in Southern Abyssinia, London, 1927, page 146)
writes of Kafa: ‘There has recently been a change of Governors in Kafa, and, as
usual, the outgoing official was taking away as much as he could in goods and
slaves’. … Thus the population of Kafa, which Cardinal Gugliemo Massaja
estimated at a million and a half before the Abyssinian conquest, is now
reduced to 20,000. Again, whereas Vittorio Bottego estimated the population of
the Burji in 1895 at 200,000, there are now no more than 15,000 people in the
region. And Sir Arnold Hodson, who was Consul at Gardulla, not far from Burji,
writes as follows (Seven Years in Southern Abyssinia, page 102): ‘Burji had
been sadly devastated quite recently, and very few natives were left there. The
responsibility for this rests with a former Governor of Sidamo, named Ato
Finkabo, who appears to have carried on a very flourishing business in slaves
from these parts. In fact, he became so enterprising that most of the natives
who were left fled to Conso and Boran to escape falling into his clutches’.
George Montandon calculates (Au pays des Ghimirra, page 223) that the
population of Ghimirra has declined in a few years from 110,000 to 10,000.
The responsibility of the Addis Ababa Government for this incredible state of
affairs in the non-Abyssinian areas of the south is particularly great, because
it has compelled some of the more warlike non-Abyssinian peoples to arm
themselves in defence of their lives and liberty; and theses foreign peoples,
having acquired arms and ammunition, have in their turn become slave-raiders,
preying upon the unarmed neighbouring tribes, and so have increased the
destruction and the scourge of slavery.
In conclusion we need only quote …Major M Darley, who has had a very long
experience of Ethiopian affairs, and who wrote in 1926, three years after
Abyssinia’s entry into the League (Slaves and Ivory, page 34): ‘Abyssinia
should be the heart of North-East Africa, but all the veins or roads, which
should supply the rest of the starving body with nourishment, are blocked by
the Abyssinian policy, abysmal and suicidal, of depopulation, retrogression and
racial extermination’.
It will thus be seen that the Ethiopian State, administratively and politically
disorganised as It is, carries the dire effects of its domination (slavery and
gebbar) into vast regions of East Africa which were conquered by the arms of
the Negus only a few years ago. It is surely in the interests of civilisation
that the Harrari, [deleted] [Oromo], Somali, Sidama, and other peoples which have
for centuries formed separate national entities, should be removed from
Abyssinian oppression. To effect an immediate settlement of this grave problem
is, indeed, to act in conformity with the spirit of the covenant, which
requires that colonisation should be carried out only by advanced States which
are in a position to ensure the development and welfare of the native
peoples…
The documents show:
(a) That Ethiopia recognises slavery as a legal condition;
(b) That raids for the capture of individuals for purposes of slavery are
continuing on a large scale, especially in the southern and western regions of
Ethiopia;
(c) That the slave trade is still practiced;
(d) that the Ethiopian Government participates directly in the slave trade by
accepting slaves in payment of taxes and allowing detachments of regular troops
to capture new slaves;
(e) That, in addition to slavery proper, there exists the institution known as
“gebbar”, to which the population of non-Ethiopian [sic] regions are subject,
and which is a form of servitude akin to slavery;
(f) That the Ethiopian Government has taken no account of the recommendations
made to it by the committee of Experts on slavery, more particularly as regards
the abolition o the legal status of slave, as appears further from the report
submitted to the League of Nations in May 1935…
By her conduct, Ethiopia has openly placed herself outside the covenant of the
League and has rendered herself unworthy of the trust placed in her when she
was admitted to membership. Italy, rising up against such an intolerable
situation, is defending her security, her rights and her dignity. She is also
defending the prestige and good name of the League of Nations.”
http://www.ethiopianewsforum.com/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=60396
http://www.huffingtonpost.co.uk/eleanor-ross/ethiopia-human-rights_b_4649953.html?utm_hp_ref=tw
Copyright © OromianEconomist 2014 & Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Repression of the Oromo and the State of Freedom in Ethiopia: Freedom House’s Annual 2013 Survey January 23, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Development, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Economics, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Land Grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Slavery, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, economics, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo people, Oromummaa, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment

Ethiopia’s 2013 SCORES
STATUS:
FREEDOM RATING : 6.0
CIVIL LIBERTIES: 6.0
POLITICAL RIGHTS: 6.0
“The government tends to favor Tigrayan ethnic interests in economic and political matters, and the EPRDF is dominated by the Tigrayan People’s Liberation Front. Repression of the Oromo and ethnic Somalis, and government attempts to co-opt their parties into subsidiaries of the EPRDF, have fueled nationalism in both the Oromia and Ogaden regions.” -Freedom House
Ethiopia is not an electoral democracy. Parliament is made up of a 108-seat upper house, the House of Federation, and a 547-seat lower house, the House of People’s Representatives. The lower house is filled through popular elections, while the upper chamber is selected by the state legislatures, with both serving five-year terms. The lower house selects the prime minister, who holds most executive power, and the president, a largely ceremonial figure who serves up to two six-year terms. All of these institutions are dominated by the EPRDF, which tightly controlled the 2010 elections and the succession process following the death of Prime Minister Meles Zenawi in 2012. While the 1995 constitution grants the right of secession to ethnically-based states, the government acquired powers in 2003 to intervene in states’ affairs on issues of public security.
Corruption is a significant problem in Ethiopia. EPRDF officials reportedly receive preferential access to credit, land leases, and jobs. Petty corruption extends to lower level officials, who allegedly solicit bribes in return for processing documents. In a survey of 1,000 people conducted by Transparency International (TI) in 2011, 64 percent of respondents reported having had to pay a bribe to customs officials, and 55 percent to a member of the judiciary. Ethiopia was ranked 113 out of 176 countries surveyed in TI’s 2012 Corruption Perceptions Index.
The media are dominated by state-owned broadcasters and government-oriented newspapers. One of the few independent papers in the capital, Addis Neger, closed in 2009, claiming harassment by the authorities. Privately-owned papers tend to steer clear of political issues and have low circulations. A 2008 media law criminalizes defamation and allows prosecutors to seize material before publication in the name of national security.
Journalists reporting on opposition activities face serious harassment and the threat of prosecution under the country’s sweeping 2009 Antiterrorism Proclamation. In July 2012, six journalists were convicted of terrorism. While five were convicted in absentia, the sixth, Eskinder Nega, received 18 years in prison. The judge said that he had consorted with the political group, Ginbot 7, a designated terrorist entity in Ethiopia. The United States, European Union and the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights expressed dismay at the verdicts. In other cases, the courts reduced sentences handed out to journalists convicted of terrorism. In August, a columnist with the Feteh weekly newspaper had her 14-year sentence reduced to 5 years; while in September, two Swedish journalists who had received 11-year sentences in 2011 for assisting the ONLF were pardoned.
Due to the risks of operating inside Ethiopia, many of the country’s journalists work in exile. The Committee to Protect Journalists says that Ethiopia has driven 79 journalists into exile in the past decade, more than any other nation. The authorities use high-tech jamming equipment to filter and block news websites seen as pro-opposition. Legislation adopted in May criminalizes the use of telecommunications devices to transmit any “terrorizing message.” Critics said the vaguely worded law also effectively banned the use of Skype and other voice-over-internet protocol services that cannot be closely monitored by the government.
The constitution guarantees religious freedom, but the government has increasingly harassed the Muslim community, which has grown to rival the Ethiopian Orthodox Church as the country’s largest religious group. Muslim groups accuse the government of trying to impose the beliefs of an obscure Islamic sect, al-Ahbash, at the expense of the dominant Sufi-influenced strain of Islam. Before his death, Meles said the Muslim community was a source of extremism, claiming it had links to Al-Qaeda.
Academic freedom is restricted. The government has accused universities of being pro-opposition and prohibits political activities on campuses. There have been reports of students being pressured into joining the EPRDF in order to secure places at universities.
The presence of the EPRDF at all levels of society inhibits free private discussion. Many people are wary of speaking against the government for fear of being overheard by party officials. The EPRDF maintains a network of paid informants, and opposition politicians have accused the government of tapping their telephones.
Freedoms of assembly and association are guaranteed by the constitution but limited in practice. Organizers of large public meetings must request permission from the authorities 48 hours in advance. Applications by opposition groups are routinely denied. Peaceful demonstrations were held outside mosques in July 2012, but the security forces responded violently, detaining protestors, including several prominent Muslim leaders. A total of 29 Muslims were eventually charged with offences under the antiterrorism law. They were awaiting trial at year’s end.
The 2009 Charities and Societies Proclamation restricts the activities of foreign NGOs by prohibiting work on political and human rights issues. Foreign NGOs are defined as groups receiving more than 10 percent of their funding from abroad, a classification that captures most domestic organizations as well. NGOs have struggled to maintain operations as a result of the law, which also requires them to reregister with the authorities. According to Justice Ministry figures, there were 3,522 registered NGOs before the law was passed and 1,655 afterward. In 2010, the Human Rights Council (HRCO) and the Ethiopian Women Lawyers’ Association had their bank accounts frozen for violating the rules on receiving foreign funds. An appeal against the ruling by the HRCO was rejected by the Supreme Court in October 2012.
Trade union rights are tightly restricted. All unions must be registered, and the government retains the authority to cancel registration. Two-thirds of union members belong to organizations affiliated with the Confederation of Ethiopian Trade Unions, which is under government influence. Independent unions face harassment. There has not been a legal strike since 1993.
The judiciary is officially independent, but its judgments rarely deviate from government policy. The Antiterrorism Proclamation gives great discretion to the security forces, allowing the detention of suspects for up to four months without charge. It was used in 2011 to detain more than 100 members of opposition parties; terrorist suspects were denied legal assistance while they awaited trial. A total of 31 people have been convicted under the law, 12 of them journalists. Conditions in Ethiopia’s prisons are harsh, and detainees frequently report abuse.
The government tends to favor Tigrayan ethnic interests in economic and political matters, and the EPRDF is dominated by the Tigrayan People’s Liberation Front. Repression of the Oromo and ethnic Somalis, and government attempts to co-opt their parties into subsidiaries of the EPRDF, have fueled nationalism in both the Oromia and Ogaden regions. Persistent claims that war crimes have been committed by government troops in the Ogaden are difficult to verify, as independent media are barred from the region. However, Human Rights Watch accused government paramilitaries of executing 10 men during an operation in the Gashaamo district in March 2012.
Private business opportunities are limited by rigid state control of economic life and the prevalence of state-owned enterprises. All land must be leased from the state. The government has evicted indigenous groups from various areas to make way for projects such as hydroelectric dams. It has also leased large tracts of land to foreign governments and investors for agricultural development in opaque deals. Up to 70,000 people have been forced to move from the western Gambella region, although the government denies the resettlement plans are connected to land investments. Journalists and international organizations have persistently alleged that the government has withheld development assistance from villages perceived as being unfriendly to the ruling party.
Women are relatively well represented in Parliament, having won 152 seats in the lower house in the 2010 elections. Legislation protects women’s rights, but they are routinely violated in practice. Enforcement of the law against rape and domestic abuse is patchy, with cases routinely stalling in the courts. Forced child labor is a significant problem, particularly in the agricultural sector. Same-sex sexual activity is prohibited by law and punishable with imprisonment.
The state of freedom declined for the eighth consecutive year in 2013, according to the latest edition of Freedom House’s annual survey, ‘Freedom in the World.’
Read Further @:
Report Link: http://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2013/ethiopia#.UuFm1tLFLf8
http://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/freedom-world-2014
High quality version of the map: http://www.freedomhouse.org/sites/default/files/MapofFreedom2014.pdf
Country ratings: http://freedomhouse.org/sites/default/files/FIW%202014%20Scores%20-%20Countries%20and%20Territories.pdf
Copyright © Oromianeconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Ethiopia: Human Rights Watch World Report 2014 January 22, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Human Rights, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Nubia, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Warlords.Tags: Africa, African culture, African Studies, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic growth, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromummaa, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, World Bank
add a comment


The following is Human Rights Watch World Report 2014 on Ethiopia:
Hopes that Ethiopia’s new leadership would pursue human rights reforms following Prime Minister Meles Zenawi’s death in August 2012 have been shattered; there was no tangible change of policy in 2013. Instead, the Ethiopian authorities continue to severely restrict the rights to freedom of expression, association, and peaceful assembly, using repressive laws to constrain civil society and independent media, and target individuals with politically motivated prosecutions.
Muslim protests against perceived government interference in their religious affairs were met by security forces with arbitrary arrests and detentions, beatings, and other mistreatment throughout the year. The trial of 29 protest leaders who were arrested in July 2012 has been closed to the public, media, and family members since January. Others convicted under the country’s deeply flawed antiterrorism law—including opposition leaders and four journalists—remain in prison.
Ethiopia’s ambitious development schemes, funded from domestic revenue sources and foreign assistance, sometimes displace indigenous communities without appropriate consultation or any compensation. Security forces have also used violence, threats, and intimidation to force some groups to relocate, such as in the Lower Omo Valley where indigenous people continue to be displaced from their traditional lands, which are earmarked for state-run irrigated sugar plantations.
Freedom of Peaceful Assembly
Since early 2012, members of Ethiopia’s Muslim community—which constitutes at least 30 percent of the country’s population—have organized regular public protests. Demonstrations were triggered by perceived government interference in the Supreme Council of Islamic Affairs and the Awalia mosque in Addis Ababa.
The government has clamped down heavily on the protests, arbitrarily detaining and beating protesters, including 29 prominent activists and leaders who were arrested in July 2012 and charged in October 2012 under the Anti-Terrorism Proclamation. In January, the High Court closed those hearings to the public, including media, diplomats, and family members. Some defendants have alleged mistreatment in detention and the trials raise a number of due process concerns, including lack of access to legal counsel for some defendants for almost two months, and erratic access to relatives.
The government has also undermined the defendants’ presumption of innocence by broadcasting inflammatory material and accusations against them on state television. In February, the state-run Ethiopian Television (ETV) broadcast a program called “Jihadawi Harakat” (“Jihad War”) that included footage of at least five of the defendants filmed in pretrial detention. The program equated the Muslim protest movement with Islamist extremist groups, casting the protest leaders as terrorists.
Despite the arrests, protests continued throughout 2013. In early August, protests were organized in the capital, Addis Ababa, as well as in other cities to commemorate Eid al Fitr, the end of Ramadan. Witnesses described a heavy police presence in Addis Ababa, and credible sources said that police used excessive force to disperse the demonstrators and detained hundreds, at least temporarily.
The Semayawi Party (“Blue Party”), a newcomer to Ethiopia’s political scene, held a peaceful protest in June—the first large-scale protest organized by a political opposition party in eight years. A planned protest in August was cancelled when the Blue Party offices were raided by security forces, resulting in the arrest of dozens of people and the confiscation of equipment. The Blue Party had earlier been denied a permit by government to hold the protest.
Arbitrary Detention and Ill-Treatment
Arbitrary detention and ill-treatment in detention continues to be a major problem. Students, members of opposition groups, journalists, peaceful protesters, and others seeking to express their rights to freedom of assembly, expression, or association are frequently detained arbitrarily.
Ill-treatment is often reported by people detained for political reasons, particularly in Addis Ababa’s Federal Police Crime Investigation Center, known as Maekelawi, where most individuals are held during pre-charge or pretrial detention. Abuse and coercion that in some cases amount to torture and other ill-treatment are used to extract information, confessions, and statements from detainees.
Individuals are often denied access to legal counsel, particularly during pre-charge detention. Mistreated detainees have little recourse in the courts and there is no regular access to prisons and detention centers by independent investigators. Although the government-affiliated Ethiopian Human Rights Commission has visited some detainees and detention centers, there is no regular monitoring by any independent human rights or other organizations.
In July, a delegation from the European Parliament was denied access to Kaliti prison in Addis Ababa by Ethiopian authorities, despite having received prior authorization.
Freedom of Expression and Association
Since 2009, when the Anti-Terrorism Proclamation and the Charities and Societies Proclamation (CSO Law) were passed, freedoms of expression and association have been severely restricted in Ethiopia. The CSO law is one of the most draconian laws regulating nongovernmental activity in the world. It bars work on human rights, good governance, conflict resolution, and advocacy on the rights of women, children, and people with disabilities if organizations receive more than 10 percent of their funds from foreign sources.
Ethiopia’s most reputable human rights groups have either dramatically scaled down their operations or removed human rights from their mandates. Several of the country’s most prominent human rights activists have fled the country due to threats.
Ethiopian media remains under a tight government stranglehold, and many journalists practice self-censorship. Webpages and blogs critical of the government are regularly blocked, and foreign radio and TV stations are routinely jammed. Journalists working for independent domestic newspapers continue to face regular harassment and threats.
The Anti-Terrorism Proclamation has been used to target political opponents, stifle dissent, and silence journalists. In May, the Supreme Court upheld the 18-year sentence of journalist and blogger Eskinder Nega Fenta, who was convicted in July 2012 for conspiracy to commit terrorist acts and participation in a terrorist organization. Eskinder received the PEN Freedom to Write award in 2012. Reeyot Alemu Gobebo, a journalist for Feteh, was convicted on three counts under the terrorism law for her writings. Her sentence was reduced from 14 to 5 years on appeal, but her appeal of the remaining five-year sentence was dismissed in January. Reeyot was awarded the prestigious 2013 UNESCO/Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize.
Journalists covering the Muslim protests were threatened and arbitrarily detained. Solomon Kebede, chief editor of the now-defunct Yemuslimoch Guday (“Muslim Affairs”), was arrested in January and charged under the Anti-Terrorism Proclamation. Yusuf Getachew, his predecessor, was charged under the same law in 2012. Several other journalists fled Ethiopia in 2013, making it one of the top three countries in the world in terms of the number of journalists in exile.
Forced Displacement Associated with Development Programs
Both the government of Ethiopia and the donor community have failed to adequately investigate allegations of abuses associated with Ethiopia’s “villagization program.” Under this program, 1.5 million rural people are being relocated, ostensibly to improve their access to basic services. However, some of the relocations in the first year of the program in Gambella region were accompanied by violence, including beatings and arbitrary arrests, and insufficient consultation and compensation.
On July 12, the World Bank’s board of executive directors approved the recommendation of the Inspection Panel, the institution’s independent accountability mechanism, to investigate a complaint from ethnic Anuak refugees alleging that the bank violated its own safeguards in Gambella. The investigation was ongoing at time of writing.
Ethiopia is proceeding with development of a sugar plantation in the Lower Omo Valley, clearing 245,000 hectares of land that is home to 200,000 indigenous peoples. Displaced from their ancestral lands, these agro-pastoralists are being moved to permanent villages under the villagization program.
Key International Actors
Ethiopia enjoys warm relations with foreign donors and most of its regional neighbors. Ethiopia has forged strong ties based on its role as the seat of the African Union (AU), its contribution to United Nations peacekeeping, security partnerships with Western nations, and its progress on some of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). These strong relationships have contributed to the international community’s silence on Ethiopia’s dismal human rights record.
The year 2013 saw Ethiopia continue to play a mediation role between Sudan and South Sudan, while its troops maintained an uneasy calm in the disputed Abyei region. Ethiopia continues to deploy its troops inside Somalia, but outside the AU mission.
Ethiopia also continues to receive significant amounts of donor assistance—almost US$4 billion in 2013. As partners in Ethiopia’s development, donor nations remain muted in their criticism of Ethiopia’s appalling human rights record and are taking little meaningful action to investigate allegations of abuses associated with development programs.
Relations with Egypt worsened in 2013 due to Egyptian concerns that Ethiopia’s Grand Renaissance Dam will divert valuable water from the Nile River. An estimated 85 percent of the Nile’s waters originate in the Ethiopian highlands and Egypt is completely dependent on the Nile for all its water needs. At 6,000 megawatts of electricity, the dam will be Africa’s largest hydroelectric project. Construction started in 2012 and the dam is scheduled to be completed in 2018.
In addition to Western donors, China, India, and Brazil are increasingly financing a variety of large-scale development initiatives. Foreign private investment into Ethiopia is increasing with agro-business, hydroelectric, mining, and oil exploration all gaining prominence in 2013. Agro-business investment is coming mainly from India, the Gulf, and the Ethiopian diaspora, attracted to very low land prices and labor costs. As seen in several of Ethiopia’s other large-scale development projects, there is a serious risk of forced displacement of people from their land when some of these programs are implemented. The full text of the report is available@:
The genocidal Ethiopia and Its Janjaweed Style Liyu Police: The Killings of 59 Oromo Men, Women and Children, The Wounding of 42 Others, the Confiscation of Property and the Forcible Removal of People from Their Ancestral Land in Eastern Oromia January 19, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Colonizing Structure, Corruption, Dictatorship, Domestic Workers, Environment, Ethnic Cleansing, Food Production, Human Rights, Human Traffickings, ICC, Janjaweed Style Liyu Police of Ethiopia, Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure., Knowledge and the Colonizing Structure. African Heritage. The Genocide Against Oromo Nation, Land Grabs in Africa, Nelson Mandela, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Identity, Oromo Nation, Oromo Social System, Oromo the Largest Nation of Africa. Human Rights violations and Genocide against the Oromo people in Ethiopia, Oromummaa, Self determination, Slavery, South Sudan, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Tyranny, Uncategorized, Warlords.Tags: African culture, African Studies, Aid, Developing country, Development, Development and Change, Economic and Social Freedom, economics, Ethiopia, Ethnic Cleansing, Gadaa System, Genocide, Genocide against the Oromo, Governance issues, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, ICC, Janjaweed in Darfur Liyu Police in Oromia, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, Mass killings, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo culture, Oromo people, Oromo Studies Association, Oromummaa, Politics of Ethiopia, poverty, Social Sciences, State and Development, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tyranny, United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
5 comments


Oromo Studies Association’s (OSA’s) Letter to U.S. Secretary of State on the Killings of 59 and Wounding of 42 Oromos in Eastern Oromia by Ethiopian-Trained “Liyu Police”:
January 17, 2014
The Honorable John F. Kerry
Secretary of State
U.S. Department of State
2201 C Street N.W.
Washington, DC20520
Subject: The killings of 59 Oromo men, women and children, the wounding of 42 others, the confiscation of property and the forcible removal of people from their ancestral land in eastern Ethiopia
Dear Mr. Secretary,
I am writing this letter on behalf of the Oromo Studies Association, an independent scholarly, multi-disciplinary, non-profit organization based in North American. My purpose is to bring to your attention and to protest on behalf of the members of OSA a crime committed against the Oromo in Eastern Ethiopia, that is, the killings of 59 Oromo men, women and children, the wounding of 42 others and the confiscation/destruction of property with an estimated value of Eth$14,726,000 in the eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia. These acts of extreme and unprovoked violence, killings, violent wounding, burning of houses and confiscation of cattle and other property of the Oromo citizens in eastern Oromia zone, were committed by Ethiopian government-trained special Somali militia forces known as “Liyu Police” (translation: Special Police Force). The Ethiopian regime arms Somali in that region while disarming Oromo farmers. These actions of deliberately arming one people while equally deliberately disarming the other and, thus, by creating conflict between formerly closely related people – groups who have lived peacefully as neighbors for centuries – goes beyond abdicating governmental responsibility. It is a heinous crime that this government commits against peoples within its jurisdictional borders. The world regards these victims as citizens of Ethiopia, but they are being seriously mistreated with no proper defense available.
In the past several months, there has been a new wave of killing of Oromo nationals in particular who reside in the eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia. Targeted Oromo victims suffer also the confiscation of their property and removal by the thousand of residents from their ancestral lands. This is a miserable new policy which constitutes nothing less than a strategy for creating a blood feud between the two culturally related people, namely, the Oromo and Somali in eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia. In the sacred land of their birth, Oromo children, women and unarmed men are killed systematically by Ethiopian government Special Police forces. Once the slaughter is completed, these government-equipped forces then callously deny their victims even decent burial, which, in itself, is a crime against humanity.
The Ethiopian government is responsible for inflicting a great deal of harm and damage on defenseless Oromo peasants through this practice of arming Somali against disarmed Oromo farmers by building special police force comprised of Somalis. This appears to be a continuation of the callously inhuman policy of the Ethiopian regime that led to the removal of Oromo peasants from seven major ancestral regions covering extensive territories in the eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia. Most OSA members are Oromo Americans, who closely follow events in the region and whose findings are confirmed by the reports of pain and suffering of their families – mothers, fathers, sisters, brothers, relatives and friends – who were killed, wounded and displaced, and whose livelihood was destroyed by Ethiopian government Special Police forces made up of Somali armed by the regime.
The Oromo Studies Association, OSA, was established 26 years ago by international scholars from around the globe to promote studies related and relevant to the Oromo and other peoples in the Horn of Africa. In its attempt to create academic forums where ideas and research findings about the Oromo and other people of Ethiopia and the Horn of Africa are freely discussed, OSA has established a peer-reviewed Journal of Oromo Studies, other periodic publications, as well as organizing regular mid-year and annual conferences. OSA has been involved in building a knowledge base for creating a democratic future for the peoples of Ethiopia and the Horn of Africa. In our scholarly organization Somali and Oromo scholars work together. The Journal of Oromo Studies publishes research papers on Somali studies. Our goal is to strengthen historical relations between the two related peoples.
You may be surprised to learn that Oromia, the Oromo regional state in Ethiopia, is the largest, the richest and the most densely populated regional state in Ethiopia. Because the Oromo constitute the single largest national group in Ethiopia – and in the entire region – they are regarded as the greatest threat to the ruling minority group, dominated by members historically affiliated with the Tigrayan Liberation Front (TPLF). The current government is dominated by Tigrayans persons whose ethnicity represents less than seven percent of the population of Ethiopia. Current Ethiopian government policies, which target populations on the basis of ethnicity, are best understood in light of a history of ethnic politics and ethnic discrimination. Arming Somalis to destroy Oromo in order to confiscate their lands and other resources continues ethnic politics in its most brutal form.
Oromo do not have powerful friends in the western world who bring the injustices that they suffer to the attention of international community. The Oromo Studies Association requests that you respond to our voice as a voice of conscience uttered to the international community. We urge that you immediately put pressure on the Ethiopian regime to desist from driving Oromo out their ancestral land in eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia. We request that the State Department under your able leadership look into this critical matter take effective action while there is time to reverse a criminal policy and save the lives and livelihood of vulnerable populations in Eastern Ethiopia.
In the light of the issue raised which is only the most recent of an ongoing series of violent attacks on Oromo farmers in eastern Oromia zone during 2013, the Oromo Studies Association (OSA) urgently requests that the State Department utilize its good offices to seek justice by putting pressure on the Ethiopian government to:
• Stop immediately the Liyu Police attacks on Oromo farmers in the eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia.
• Return, without delay, those who were forcibly driven from their ancestral lands in eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia.
• Bring to speedy trial those who ordered the Liyu Police force to attack, killing 59 defenseless Oromo children, men and women and wounding 42 others while confiscating or destroying property estimated at Eth$14,726,000.
• Pay compensation for the lives lost and the property confiscated from those defenseless Oromo farmers in eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia.
• Urge the Ethiopian government officials to stop the forcible removal of thousands of Oromo farmers from their ancestral lands in eastern Oromia zone of Ethiopia and make sure that such measures will never be repeated in Oromia or other parts of Ethiopia.
• Advise the leaders of the Ethiopian government to abandon the cruel and crude policy of disarming Oromo while unleashing the special police force on defenseless children, men and women.
• Strongly urge the leaders of the Ethiopian government to respect and implement the provisions in their own Constitution, which officially guarantees respect for human rights and democratic governance.
The Oromo Studies Association requests that the State Department, under your leadership, set an example by taking the above measures in a timely fashion.
You have an extraordinary opportunity to make a difference in the lives of millions of Oromo and other people in Ethiopia. Our scholarly association appreciates your good efforts in this regard.
Sincerely,
Ibrahim Elemo, President
Oromo Studies Association
P.O.Box: 6541
Minneapolis, MN 55406-0541
E-mail: ielemo@weisshospital.com
CC:
Ambassador Girma Birru
Embassy of FDRE, Washington, D.C
3506 International Drive, N.W.
Washington, D.C. 20008
Mr. Ban Ki-moon, Secretary-General
Office of the Secretary General of United Nations
885 Second Avenue
New York, NY 10017, USA
Mr. David Cameron, Prime Minister of UK
10 Downing Street, London, UK
The Hon. Tony Abbott, MP
Prime Minister
Parliament House
CANBERRA ACT 2600
Liyu Police is Ethiopia’s (TPLF’s) style of Janjaweed to conduct genocide against the Oromo people.
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/1003597/Janjaweed
Copyright © Oromianeconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Rivalry: Japan, China & the Scramble for Africa January 14, 2014
Posted by OromianEconomist in Africa, Aid to Africa, Colonizing Structure, Economics: Development Theory and Policy applications, Land Grabs in Africa, Oromia, Oromiyaa, Oromo, Oromo Nation, The Colonizing Structure & The Development Problems of Oromia, Theory of Development, Tyranny, Uncategorized.Tags: Abebe Bikila, Africa, African culture, African Studies, Aid, China, Developing country, Development, Economic and Social Freedom, Economic development, Economic growth, Horn of Africa, Human rights, Human Rights and Liberties, Human rights violations, Japan, Japan and Africa, Land grabbing, Land grabs in Africa, National Self Determination, Oromia, Oromo, Oromo Athlets, Oromo people, Sub-Saharan Africa, Tade, Tikki Galana, Tyranny, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
add a comment




Abe (Japanese PM) recalls Abe (the legend Oromo Olympian, Abebe Bikila)
Japanese premier, Mr. Abe, received a gift from the son of the late Oromo barefoot marathon legend Abebe Bikila, winner of the Tokyo Olympic marathon 50 years ago.
Japan’s rivalry with China is going global. After years of jousting over obscure islands in the East China Sea and competing for Asian influence, the two countries are now battling for power in a new arena: Africa.
It’s a region that Tokyo has long ceded to the Chinese, allowing Beijing to pile up massive economic and political capital across Africa. But on Friday, in a major shift in strategy, Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe arrived in Ivory Coast to begin his first tour of sub-Saharan Africa – and the first by any Japanese prime minister in eight years.
As he has finished a three-nation tour of Africa on Monday in which he offered aid and development projects potentially worth billions of dollars to help his nation catch up with China’s enormous footprint on the continent, the prime minister, Shinzo Abe, has said he wants to expand Japan’s presence in Africa, and tap a region that can serve as both a source of minerals and energy for Japan’s industrial economy and a new market for Japanese goods.
Mr. Abe has made Africa one of the centerpieces of a diplomatic push to complement his domestic growth policies, known as Abenomics, which aim to end Japan’s long economic decline.
By placing more emphasis on Africa, Mr. Abe is throwing Japan into a scramble for resources there that also involves companies from China, the United States and other Western countries. Japan is particularly keen to find new sources of so-called rare earths and metals, raw material used in electronics and cellphones that it currently imports mostly from China.
But Japan also finds itself lagging far behind its rival China, which has been investing heavily in Africa for a decade. As if to underscore that great rivalry, at the same time that Mr. Abe was in Africa, China’s foreign minister, Wang Yi, was on a four-nation visit to the region. Japan will find it difficult to catch up to China’s political influence here. China’s leaders are frequent visitors to the continent. Chinese President Xi Jinping visited Africa last year on his first overseas trip as President. Beijing has cultivated close relationships with Africa’s ruling parties, routinely inviting their officials on junkets to China.
China’s state media were quick to portray Mr. Abe’s visit as an attempt to challenge Beijing in the African arena. Quoting several Japanese sources, state-owned China Daily said the Japanese leader is seeking to “contain” China’s influence in Africa.
Another Chinese newspaper, Global Times, quoted Japan analyst Geng Xin as saying that Tokyo was “cozying up” to Africa to try to dispel Japan’s image as an “economic giant and political dwarf.” He said Japan is wooing the votes of African countries for its bid to become a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council.
A spokeswoman for the Chinese Foreign Ministry, Hua Chunying, issued a veiled warning to Japan. “If there is any country out there that attempts to make use of Africa for rivalry, the country is making a wrong decision, which is doomed to fail,” she told a press conference this week.
Japanese officials have said that while they cannot match the $75 billion indevelopment aid that China has poured into Africa since 2000, they hope to close the gap in other ways. One is to use Japanese aid to train African engineers and technicians, in order to differentiate Japanese efforts from Chinese projects that have been criticized for employing mainly Chinese workers while offering few jobs to Africans. Japan, he said, prefers to “aid the human capital of Africa.”
The visit also brought an unusual amount of showmanship to Japan’s often drab style of diplomacy. On Friday, Mr. Abe traded jokes and even exchanged soccer jerseys with the president of Ivory Coast, Alassane Ouattara. The next day, Mr. Abe attended a tournament of the Japanese sport of judo in Abidjan.
Japan criticizes Beijing for its tendency to build lavish headquarters and office towers as donations for African politicians – including, most famously, the new $200-million headquarters of the African Union in Finfinnee (Addis Ababa), where Mr. Abe is scheduled to give a policy speech next week.
“Countries like Japan … cannot provide African leaders with beautiful houses or beautiful ministerial buildings,” Mr. Abe’s spokesman, Tomohiko Taniguchi, told the BBC.
But while the two countries take verbal shots at each other, the reality is that China has adopted a far more aggressive strategy in Africa, and has been enormously successful so far. China’s investment in Africa was reported to be about seven times that of Japan in 2011, and its exports to Africa were about five times greater.
China has become the top trading partner, or second-biggest trading partner, of about half of Africa’s countries. It is a major investor in Africa’s resources sector, and the biggest buyer of oil and minerals from many African countries. Its construction companies are building roads, highways, railway lines, sports stadiums, transit systems and hospitals across Africa.
Japan has lagged far behind in this race. Most of its engagement with Africa is as an aid donor. Last year it promised up to $32-billion in public and private assistance to Africa over the next five years, but this only confirmed its reputation as a donor, rather than a business partner.
Only a handful of Japanese investors are active in Ivory Coast, Ethiopia and Mozambique According to a fact sheet by the Japanese government, there are only two Japanese companies in Ivory Coast and only one in Ethiopia.
http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2014/01/14/national/abe-recalls-abebe-meets-ethiopias-running-heroes/#.UtcsptJdXbh
http://www.globalpost.com/dispatch/news/regions/africa/south-africa/140110/japan-china-lord-voldemort-africa
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/01/14/world/asia/japans-leader-pledges-aid-on-africa-tour.html?ref=world
















You must be logged in to post a comment.